- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章面向新手解析python Beautiful Soup基本用法由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
Beautiful Soup就是Python的一个HTML或XML的解析库,可以用它来方便地从网页中提取数据。它有如下三个特点:
首先,我们要安装它:pip install bs4,然后安装 pip install beautifulsoup4. 。
Beautiful Soup支持的解析器 。
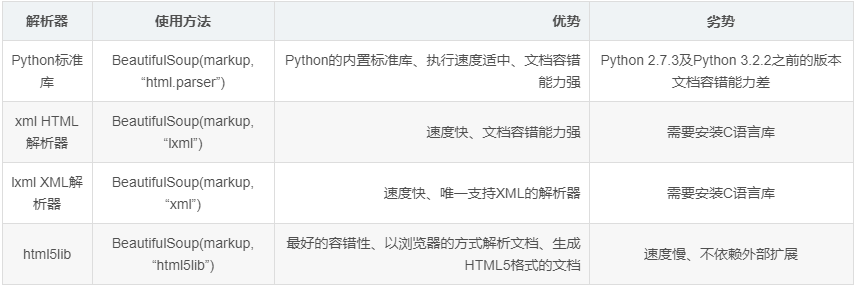
下面我们以lxml解析器为例:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup('<p>Hello</p>', 'lxml') print(soup.p.string) 。
结果:
Hello 。
beautiful soup美化的效果实例:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
html
=
"""
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
from
bs4
import
BeautifulSoup
soup
=
BeautifulSoup(html,
'lxml'
)
#调用prettify()方法。这个方法可以把要解析的字符串以标准的缩进格式输出
print
(soup.prettify())
print
(soup.title.string)
|
结果:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
<html>
<head>
<title>
The Dormouse's story
</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse">
<b>
The Dormouse's story
</b>
</p>
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" id="link1">
<!-- Elsie -->
</a>
,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" id="link2">
Lacie
</a>
and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" id="link3">
Tillie
</a>
;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">
...
</p>
</body>
</html>
The Dormouse's story
|
下面举例说明选择元素、属性、名称的方法 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
html
=
"""
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
from
bs4
import
BeautifulSoup
soup
=
BeautifulSoup(html,
'lxml'
)
print
(
'输出结果为title节点加里面的文字内容:\n'
,soup.title)
print
(
'输出它的类型:\n'
,
type
(soup.title))
print
(
'输出节点的文本内容:\n'
,soup.title.string)
print
(
'结果是节点加其内部的所有内容:\n'
,soup.head)
print
(
'结果是第一个p节点的内容:\n'
,soup.p)
print
(
'利用name属性获取节点的名称:\n'
,soup.title.name)
#这里需要注意的是,有的返回结果是字符串,有的返回结果是字符串组成的列表。
# 比如,name属性的值是唯一的,返回的结果就是单个字符串。
# 而对于class,一个节点元素可能有多个class,所以返回的是列表。
print
(
'每个节点可能有多个属性,比如id和class等:\n'
,soup.p.attrs)
print
(
'选择这个节点元素后,可以调用attrs获取所有属性:\n'
,soup.p.attrs[
'name'
])
print
(
'获取p标签的name属性值:\n'
,soup.p[
'name'
])
print
(
'获取p标签的class属性值:\n'
,soup.p[
'class'
])
print
(
'获取第一个p节点的文本:\n'
,soup.p.string)
|
结果:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
输出结果为title节点加里面的文字内容:
<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
输出它的类型:
<class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
输出节点的文本内容:
The Dormouse's story
结果是节点加其内部的所有内容:
<head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
结果是第一个p节点的内容:
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
利用name属性获取节点的名称:
title
每个节点可能有多个属性,比如id和class等:
{'class': ['title'], 'name': 'dromouse'}
选择这个节点元素后,可以调用attrs获取所有属性:
dromouse
获取p标签的name属性值:
dromouse
获取p标签的class属性值:
['title']
获取第一个p节点的文本:
The Dormouse's story
|
在上面的例子中,我们知道每一个返回结果都是bs4.element.Tag类型,它同样可以继续调用节点进行下一步的选择.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
html = """
<
html
><
head
><
title
>The Dormouse's story</
title
></
head
>
<
body
>
"""
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print('获取了head节点元素,继续调用head来选取其内部的head节点元素:\n',soup.head.title)
print('继续调用输出类型:\n',type(soup.head.title))
print('继续调用输出内容:\n',soup.head.title.string)
|
结果:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
获取了head节点元素,继续调用head来选取其内部的head节点元素:
<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
继续调用输出类型:
<class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
继续调用输出内容:
The Dormouse's story
|
(1)find_all() 。
find_all,顾名思义,就是查询所有符合条件的元素。给它传入一些属性或文本,就可以得到符合条件的元素,它的功能十分强大.
find_all(name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs) 。
他的用法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
html='''
<
div
class
=
"panel"
>
<
div
class
=
"panel-heading"
>
<
h4
>Hello</
h4
>
</
div
>
<
div
class
=
"panel-body"
>
<
ul
class
=
"list"
id
=
"list-1"
>
<
li
class
=
"element"
>Foo</
li
>
<
li
class
=
"element"
>Bar</
li
>
<
li
class
=
"element"
>Jay</
li
>
</
ul
>
<
ul
class
=
"list list-small"
id
=
"list-2"
>
<
li
class
=
"element"
>Foo</
li
>
<
li
class
=
"element"
>Bar</
li
>
</
ul
>
</
div
>
</
div
>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print('查询所有ul节点,返回结果是列表类型,长度为2:\n',soup.find_all(name='ul'))
print('每个元素依然都是bs4.element.Tag类型:\n',type(soup.find_all(name='ul')[0]))
#将以上步骤换一种方式,遍历出来
for ul in soup.find_all(name='ul'):
print('输出每个u1:',ul.find_all(name='li'))
#遍历两层
for ul in soup.find_all(name='ul'):
print('输出每个u1:',ul.find_all(name='li'))
for li in ul.find_all(name='li'):
print('输出每个元素:',li.string)
|
结果:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
查询所有ul节点,返回结果是列表类型,长度为2:
[<ul class="list" id="list-1">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>, <ul class="list list-small" id="list-2">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
</ul>]
每个元素依然都是bs4.element.Tag类型:
<class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
输出每个u1: [<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>, <li class="element">Jay</li>]
输出每个u1: [<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>]
输出每个u1: [<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>, <li class="element">Jay</li>]
输出每个元素: Foo
输出每个元素: Bar
输出每个元素: Jay
输出每个u1: [<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>]
输出每个元素: Foo
输出每个元素: Bar
|
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我.
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiao02fang/p/13269984.html 。
最后此篇关于面向新手解析python Beautiful Soup基本用法的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于面向新手解析python Beautiful Soup基本用法的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
关闭。这个问题不符合Stack Overflow guidelines .它目前不接受答案。 想改进这个问题?将问题更新为 on-topic对于堆栈溢出。 6年前关闭。 Improve this qu
我有实体: @Entity @Table(name = "CARDS") public class Card { @ManyToOne @JoinColumn(name = "PERSON_I
我正在尝试计算二维多边形的表面法线。我正在使用 OpenGL wiki 中的 Newell 方法来计算表面法线。 https://www.opengl.org/wiki/Calculating_a_S
关闭。这个问题不符合Stack Overflow guidelines .它目前不接受答案。 这个问题似乎与 help center 中定义的范围内的编程无关。 . 关闭 7 年前。 Improve
关闭。这个问题是off-topic .它目前不接受答案。 想改进这个问题吗? Update the question所以它是on-topic用于堆栈溢出。 关闭 9 年前。 Improve this
我这里有以下 XML: Visa, Mastercard, , , , 0, Discover, American Express siteonly, Buyer Pay
即将发生的 Google 政策变更迫使我们实现一个对话框,以通知欧盟用户有关 Cookie/设备标识符用于广告和分析的情况。我只想向欧盟用户显示此对话框。我不想使用额外的权限(例如 android.p
本文分享自华为云社区《华为大咖说 | 企业应用AI大模型的“道、法、术” ——道:认知篇》,作者:华为云PaaS服务小智。 本期核心观点 上车:AGI是未来5~10年内,每个人都无法回避的技
我有一个与酒精相关的网站,需要先验证年龄,然后才能让他们进入该网站。我使用 HttpModule 来执行此操作,该模块检查 cookie,如果未设置,我会将它们重定向到验证页面。我验证他们的年龄并存储
在欧盟,我们有一项法律,要求网页请求存储 cookie 的许可。我们大多数人都了解 cookie 并同意它们,但仍然被迫在任何地方明确接受它们。所以我计划编写这个附加组件(ff & chrome),它
以下在 C 和/或 C++ 中是否合法? void fn(); inline void fn() { /*Do something here*/ } 让我担心的是,第一个声明看起来暗示函数将被定义

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!