- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章Android图片处理实例介绍(图)由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
1.图片处理 。
1.圆角图片 。
复制代码 代码如下
/** * 转换成圆角 * * @param bmp * @param roundpx * @return */ public static bitmap converttoroundedcorner(bitmap bmp, float roundpx) { 。
。
bitmap newbmp = bitmap.createbitmap(bmp.getwidth(), bmp.getheight(), config.argb_8888); // 得到画布 canvas canvas = new canvas(newbmp),
final int color = 0xff424242; final paint paint = new paint(); final rect rect = new rect(0, 0, bmp.getwidth(), bmp.getheight()); final rectf rectf = new rectf(rect),
paint.setantialias(true); canvas.drawargb(0, 0, 0, 0); paint.setcolor(color); // 第二个和第三个参数一样则画的是正圆的一角,否则是椭圆的一角 canvas.drawroundrect(rectf, roundpx, roundpx, paint),
paint.setxfermode(new porterduffxfermode(mode.src_in)); canvas.drawbitmap(bmp, rect, rect, paint),
return newbmp; } 。
。
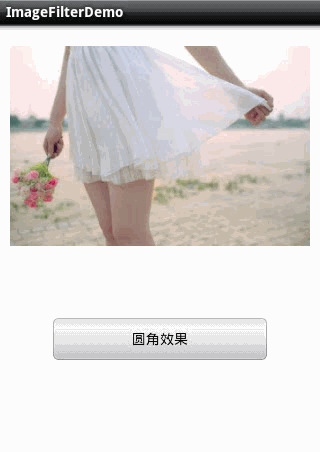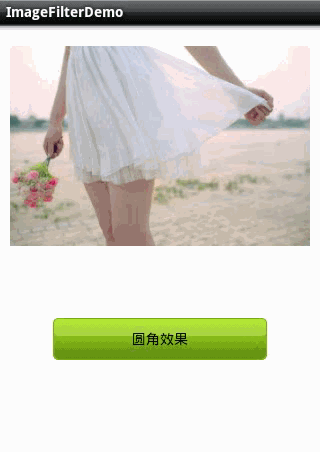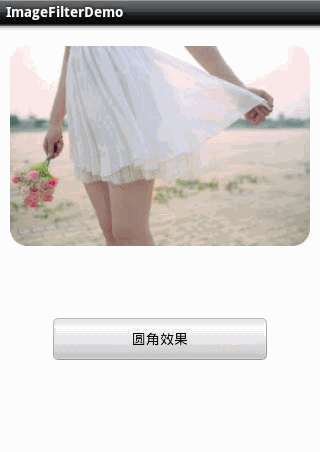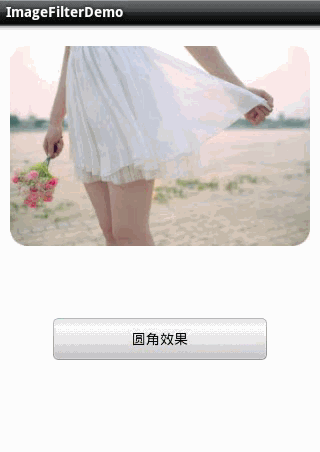
2.滤镜效果 。
1.黑白效果 。
。
复制代码 代码如下
/** * 将彩色图转换为黑白图 * * @param 位图 * @return 返回转换好的位图 */ public static bitmap converttoblackwhite(bitmap bmp) { int width = bmp.getwidth(); // 获取位图的宽 int height = bmp.getheight(); // 获取位图的高 。
。
int[] pixels = new int[width * height]; // 通过位图的大小创建像素点数组 。
bmp.getpixels(pixels, 0, width, 0, 0, width, height); int alpha = 0xff << 24; for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < width; j++) { int grey = pixels[width * i + j],
int red = ((grey & 0x00ff0000) >> 16); int green = ((grey & 0x0000ff00) >> 8); int blue = (grey & 0x000000ff),
grey = (int) (red * 0.3 + green * 0.59 + blue * 0.11); grey = alpha | (grey << 16) | (grey << 8) | grey; pixels[width * i + j] = grey; } } bitmap newbmp = bitmap.createbitmap(width, height, config.rgb_565); newbmp.setpixels(pixels, 0, width, 0, 0, width, height); return newbmp; } 。
。

。
2.高斯模糊 。
复制代码 代码如下
/** * 高斯模糊 * * @param bmp * @return */ public static bitmap converttoblur(bitmap bmp) { // 高斯矩阵 int[] gauss = new int[] { 1, 2, 1, 2, 4, 2, 1, 2, 1 },
。
int width = bmp.getwidth(); int height = bmp.getheight(); bitmap newbmp = bitmap.createbitmap(width, height, bitmap.config.rgb_565),
int pixr = 0; int pixg = 0; int pixb = 0,
int pixcolor = 0,
int newr = 0; int newg = 0; int newb = 0,
int delta = 16; // 值越小图片会越亮,越大则越暗 。
int idx = 0; int[] pixels = new int[width * height]; bmp.getpixels(pixels, 0, width, 0, 0, width, height); for (int i = 1, length = height - 1; i < length; i++) { for (int k = 1, len = width - 1; k < len; k++) { idx = 0; for (int m = -1; m <= 1; m++) { for (int n = -1; n <= 1; n++) { pixcolor = pixels[(i + m) * width + k + n]; pixr = color.red(pixcolor); pixg = color.green(pixcolor); pixb = color.blue(pixcolor),
newr = newr + pixr * gauss[idx]; newg = newg + pixg * gauss[idx]; newb = newb + pixb * gauss[idx]; idx++; } } 。
newr /= delta; newg /= delta; newb /= delta,
newr = math.min(255, math.max(0, newr)); newg = math.min(255, math.max(0, newg)); newb = math.min(255, math.max(0, newb)),
pixels[i * width + k] = color.argb(255, newr, newg, newb),
newr = 0; newg = 0; newb = 0; } } 。
newbmp.setpixels(pixels, 0, width, 0, 0, width, height),
return newbmp; } 。
3.素描效果 。
复制代码 代码如下
/** * 素描效果 * * @param bmp * @return */ public static bitmap converttosketch(bitmap bmp) { int pos, row, col, clr; int width = bmp.getwidth(); int height = bmp.getheight(); int[] pixsrc = new int[width * height]; int[] pixnvt = new int[width * height]; // 先对图象的像素处理成灰度颜色后再取反 bmp.getpixels(pixsrc, 0, width, 0, 0, width, height),
。
for (row = 0; row < height; row++) { for (col = 0; col < width; col++) { pos = row * width + col; pixsrc[pos] = (color.red(pixsrc[pos]) + color.green(pixsrc[pos]) + color.blue(pixsrc[pos])) / 3; pixnvt[pos] = 255 - pixsrc[pos]; } } 。
// 对取反的像素进行高斯模糊, 强度可以设置,暂定为5.0 gaussgray(pixnvt, 5.0, 5.0, width, height),
// 灰度颜色和模糊后像素进行差值运算 for (row = 0; row < height; row++) { for (col = 0; col < width; col++) { pos = row * width + col,
clr = pixsrc[pos] << 8; clr /= 256 - pixnvt[pos]; clr = math.min(clr, 255),
pixsrc[pos] = color.rgb(clr, clr, clr); } } bmp.setpixels(pixsrc, 0, width, 0, 0, width, height),
return bmp,
} 。
private static int gaussgray(int[] psrc, double horz, double vert, int width, int height) { int[] dst, src; double[] n_p, n_m, d_p, d_m, bd_p, bd_m; double[] val_p, val_m; int i, j, t, k, row, col, terms; int[] initial_p, initial_m; double std_dev; int row_stride = width; int max_len = math.max(width, height); int sp_p_idx, sp_m_idx, vp_idx, vm_idx,
val_p = new double[max_len]; val_m = new double[max_len],
n_p = new double[5]; n_m = new double[5]; d_p = new double[5]; d_m = new double[5]; bd_p = new double[5]; bd_m = new double[5],
src = new int[max_len]; dst = new int[max_len],
initial_p = new int[4]; initial_m = new int[4],
// 垂直方向 if (vert > 0.0) { vert = math.abs(vert) + 1.0; std_dev = math.sqrt(-(vert * vert) / (2 * math.log(1.0 / 255.0))),
// 初试化常量 findconstants(n_p, n_m, d_p, d_m, bd_p, bd_m, std_dev),
for (col = 0; col < width; col++) { for (k = 0; k < max_len; k++) { val_m[k] = val_p[k] = 0; } 。
for (t = 0; t < height; t++) { src[t] = psrc[t * row_stride + col]; } 。
sp_p_idx = 0; sp_m_idx = height - 1; vp_idx = 0; vm_idx = height - 1,
initial_p[0] = src[0]; initial_m[0] = src[height - 1],
for (row = 0; row < height; row++) { terms = (row < 4) ? row : 4,
for (i = 0; i <= terms; i++) { val_p[vp_idx] += n_p[i] * src[sp_p_idx - i] - d_p[i] * val_p[vp_idx - i]; val_m[vm_idx] += n_m[i] * src[sp_m_idx + i] - d_m[i] * val_m[vm_idx + i]; } for (j = i; j <= 4; j++) { val_p[vp_idx] += (n_p[j] - bd_p[j]) * initial_p[0]; val_m[vm_idx] += (n_m[j] - bd_m[j]) * initial_m[0]; } 。
sp_p_idx++; sp_m_idx--; vp_idx++; vm_idx--; } 。
transfergausspixels(val_p, val_m, dst, 1, height),
for (t = 0; t < height; t++) { psrc[t * row_stride + col] = dst[t]; } } } 。
// 水平方向 if (horz > 0.0) { horz = math.abs(horz) + 1.0,
if (horz != vert) { std_dev = math.sqrt(-(horz * horz) / (2 * math.log(1.0 / 255.0))),
// 初试化常量 findconstants(n_p, n_m, d_p, d_m, bd_p, bd_m, std_dev); } 。
for (row = 0; row < height; row++) { for (k = 0; k < max_len; k++) { val_m[k] = val_p[k] = 0; } 。
for (t = 0; t < width; t++) { src[t] = psrc[row * row_stride + t]; } 。
sp_p_idx = 0; sp_m_idx = width - 1; vp_idx = 0; vm_idx = width - 1,
initial_p[0] = src[0]; initial_m[0] = src[width - 1],
for (col = 0; col < width; col++) { terms = (col < 4) ? col : 4,
for (i = 0; i <= terms; i++) { val_p[vp_idx] += n_p[i] * src[sp_p_idx - i] - d_p[i] * val_p[vp_idx - i]; val_m[vm_idx] += n_m[i] * src[sp_m_idx + i] - d_m[i] * val_m[vm_idx + i]; } for (j = i; j <= 4; j++) { val_p[vp_idx] += (n_p[j] - bd_p[j]) * initial_p[0]; val_m[vm_idx] += (n_m[j] - bd_m[j]) * initial_m[0]; } 。
sp_p_idx++; sp_m_idx--; vp_idx++; vm_idx--; } 。
transfergausspixels(val_p, val_m, dst, 1, width),
for (t = 0; t < width; t++) { psrc[row * row_stride + t] = dst[t]; } } } 。
return 0; } 。
private static void transfergausspixels(double[] src1, double[] src2, int[] dest, int bytes, int width) { int i, j, k, b; int bend = bytes * width; double sum,
i = j = k = 0; for (b = 0; b < bend; b++) { sum = src1[i++] + src2[j++],
if (sum > 255) sum = 255; else if (sum < 0) sum = 0,
dest[k++] = (int) sum; } } 。
private static void findconstants(double[] n_p, double[] n_m, double[] d_p, double[] d_m, double[] bd_p, double[] bd_m, double std_dev) { double div = math.sqrt(2 * 3.141593) * std_dev; double x0 = -1.783 / std_dev; double x1 = -1.723 / std_dev; double x2 = 0.6318 / std_dev; double x3 = 1.997 / std_dev; double x4 = 1.6803 / div; double x5 = 3.735 / div; double x6 = -0.6803 / div; double x7 = -0.2598 / div; int i,
n_p[0] = x4 + x6; n_p[1] = (math.exp(x1) * (x7 * math.sin(x3) - (x6 + 2 * x4) * math.cos(x3)) + math .exp(x0) * (x5 * math.sin(x2) - (2 * x6 + x4) * math.cos(x2))); n_p[2] = (2 * math.exp(x0 + x1) * ((x4 + x6) * math.cos(x3) * math.cos(x2) - x5 * math.cos(x3) * math.sin(x2) - x7 * math.cos(x2) * math.sin(x3)) + x6 * math.exp(2 * x0) + x4 * math.exp(2 * x1)); n_p[3] = (math.exp(x1 + 2 * x0) * (x7 * math.sin(x3) - x6 * math.cos(x3)) + math.exp(x0 + 2 * x1) * (x5 * math.sin(x2) - x4 * math.cos(x2))); n_p[4] = 0.0,
d_p[0] = 0.0; d_p[1] = -2 * math.exp(x1) * math.cos(x3) - 2 * math.exp(x0) * math.cos(x2); d_p[2] = 4 * math.cos(x3) * math.cos(x2) * math.exp(x0 + x1) + math.exp(2 * x1) + math.exp(2 * x0); d_p[3] = -2 * math.cos(x2) * math.exp(x0 + 2 * x1) - 2 * math.cos(x3) * math.exp(x1 + 2 * x0); d_p[4] = math.exp(2 * x0 + 2 * x1),
for (i = 0; i <= 4; i++) { d_m[i] = d_p[i]; } 。
n_m[0] = 0.0; for (i = 1; i <= 4; i++) { n_m[i] = n_p[i] - d_p[i] * n_p[0]; } 。
double sum_n_p, sum_n_m, sum_d; double a, b,
sum_n_p = 0.0; sum_n_m = 0.0; sum_d = 0.0,
for (i = 0; i <= 4; i++) { sum_n_p += n_p[i]; sum_n_m += n_m[i]; sum_d += d_p[i]; } 。
a = sum_n_p / (1.0 + sum_d); b = sum_n_m / (1.0 + sum_d),
for (i = 0; i <= 4; i++) { bd_p[i] = d_p[i] * a; bd_m[i] = d_m[i] * b; } } 。
。
。
。
4.锐化 。
复制代码 代码如下
/** * 图片锐化(拉普拉斯变换) * * @param bmp * @return */ public static bitmap sharpenimageameliorate(bitmap bmp) { 。
。
// 拉普拉斯矩阵 int[] laplacian = new int[] { -1, -1, -1, -1, 9, -1, -1, -1, -1 },
int width = bmp.getwidth(); int height = bmp.getheight(); bitmap bitmap = bitmap.createbitmap(width, height, bitmap.config.rgb_565),
int pixr = 0; int pixg = 0; int pixb = 0,
int pixcolor = 0,
int newr = 0; int newg = 0; int newb = 0,
int idx = 0; float alpha = 0.3f; int[] pixels = new int[width * height]; bmp.getpixels(pixels, 0, width, 0, 0, width, height); for (int i = 1, length = height - 1; i < length; i++) { for (int k = 1, len = width - 1; k < len; k++) { idx = 0; for (int m = -1; m <= 1; m++) { for (int n = -1; n <= 1; n++) { pixcolor = pixels[(i + n) * width + k + m]; pixr = color.red(pixcolor); pixg = color.green(pixcolor); pixb = color.blue(pixcolor),
newr = newr + (int) (pixr * laplacian[idx] * alpha); newg = newg + (int) (pixg * laplacian[idx] * alpha); newb = newb + (int) (pixb * laplacian[idx] * alpha); idx++; } } 。
newr = math.min(255, math.max(0, newr)); newg = math.min(255, math.max(0, newg)); newb = math.min(255, math.max(0, newb)),
pixels[i * width + k] = color.argb(255, newr, newg, newb); newr = 0; newg = 0; newb = 0; } } 。
bitmap.setpixels(pixels, 0, width, 0, 0, width, height); return bitmap; } 。
。
5.浮雕 。

最后此篇关于Android图片处理实例介绍(图)的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于Android图片处理实例介绍(图)的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我想填充 3D 等高线图 (contour3(X,Y,Z)),就像 2D 等高线填充图 (contourf(X,Y,Z))。但我无法弄清楚如何实现这一目标。 contour3 和 surf 的组合不是
我有一个 c3.js 折线图,表示 2 个值的演变。我需要折线图的工具提示是饼图(工具提示 = 另一个 c3.js 图形)。 这是我成功的: http://jsfiddle.net/owhxgaqm/
我有具有结构的 Pandas 数据框: A B 0 1 1 1 2 1 2 3 4 3 3 7 4 6 8 如何生成 Seaborn Violin 图,每列作为其自己的单独
我正在使用 D3DXSPRITE 方法将我的 map 图 block 绘制到屏幕上,我刚刚添加了一个缩放功能,当您按住向上箭头时会放大,但注意到您现在可以看到图 block 之间的间隙,这是一些屏幕截
今天我们开始学习目前学习到的最难最复杂的数据结构图。 简单回顾一下之前学习的数据结构,数组、单链表、队列等线性表中数据元素是一对一关系,而树结构中数据元素是一对多关系,而图结构中数据元素则是多对
1、系统环境如下图: 2、为该系统添加一块新的虚拟硬盘,添加后需重启虚拟机,否则系统不识别;如下图,/dev/sdc 是新添加的硬盘; 3、fdisk /dev/sdc为新硬盘创建分区:
1、nagios简介 nagios是一款开源的电脑系统和网络监视工具,能有效监控windows、linux和unix的主机状态,交换机路由器等网络设置,打印机等。在系统或服务状态异常时发
越来越多人开始习惯用手机上网,浏览网页、查看邮件···移动化已经成为互联网发展必然趋势,包括facebook在内的很多互联网公司都将移动广告作为下一个淘金地
1.图片处理 1.圆角图片 复制代码 代码如下: /** * 转换成圆角 * &n
Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio是SQL SERVER的客户端工具,相信大家都知道。我不知道大伙使用导入数据的情况怎么样,反正我最近是遇到过。主要是因为没
debian6系统: 首先先安装mysql吧: 打开终端(root)用户登入 apt-get purge mysql-server-5.5 安装完成后: 默认情况下Mysql只允许本地登录
fedora16英文环境下支持中文输入法的方法 fedora16英文环境下支持FCITX的中文输入法: $ im-chooser 就会出现选择界面,选择第二个就行了。
Net预编译命令 C:\WINDOWS\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v2.0.50727\aspnet_compiler.exe -? 显示说明 我们需要选择的命令为&n
有的时候电脑出现一些故障有的时候通过将其修改bios设置的方法来解决故障,那么在bios上设置能不能将电脑恢复出厂设置呢?其实也是可以的。方法也很简单的,只要会进入电脑的bios懂的上面英文的意思就
笔者曾介绍过Deepin 将对龙芯进行全面支持,打造最优美龙芯电脑桌面。现在Deepin团队移植工作取得了突破性的成果,Deepin桌面已经在龙芯3A和龙芯3B电脑上成功运行起来了。 以下为龙芯3
在安装一些软件之后,我们的电脑总是会发生一点小变化,不是桌面上多了几个网址图标,就是IE浏览器的默认主页被篡改成乱七八糟的网址。最可气的是,在IE设置中将默认主页改回来后,下次启动Win7后又变了回
“注册表编辑器怎么打开”虽说不是很难的问题,但是对于对电脑常识不是很擅长的网民来说,当电脑出现问题或需要更改设置时,着实还是件头疼的问题。因为需要打开注册表进行操作解决。那么如何打开注册表编辑器呢?
这篇文章重点介绍10个重要的WordPress安全插件和技巧,用来保护WordPress网站或者博客。 1. WP Security 人工帮助你修复被黑客入侵的网站,只要按照他们网站上的联系电话
其实运用object和javascript调用外部文件,也能实现不同栏目调用不同友情链接,即相当于调用不同栏目友情链接文件, {dede:field.typeid/}来获取当前栏目的ID。
我有一个复值矩阵。 如果我发出命令: plot(myMatrix) 然后它在图形设备上显示一种散点图,X 轴标记为 Re(myMatrix),Y 轴标记为 Im(myMatrix)。这显示了我正在寻找

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!