- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章Python实现简单遗传算法(SGA)由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
本文用Python3完整实现了简单遗传算法(SGA) 。
Simple Genetic Alogrithm是模拟生物进化过程而提出的一种优化算法。SGA采用随机导向搜索全局最优解或者说近似全局最优解。传统的爬山算法(例如梯度下降,牛顿法)一次只优化一个解,并且对于多峰的目标函数很容易陷入局部最优解,而SGA算法一次优化一个种群(即一次优化多个解),SGA比传统的爬山算法更容易收敛到全局最优解或者近似全局最优解。 SGA基本流程如下
1、对问题的解进行二进制编码。编码涉及精度的问题,在本例中精度delta=0.0001,根据决策变量的上下界确定对应此决策变量的染色体基因的长度(m)。假设一个决策变量x0上界为upper,下界为lower,则精度delta = (upper-lower)/2^m-1。如果已知决策变量边界和编码精度,那么可以用下面的公式确定编码决策变量x0所对应的染色体长度:
2^(length-1)<(upper-lower)/delta<=2^length-1 。
2、对染色体解码得到表现形
解码后得到10进制的值;decoded = lower + binary2demical(chromosome)*delta。其中binary2demical为二进制转10进制的函数,在代码中有实现,chromosome是编码后的染色体.
3、确定初始种群,初始种群随机生成 。
4、根据解码函数得到初始种群的10进制表现型的值 。
5、确定适应度函数,对于求最大值最小值问题,一般适应度函数就是目标函数。根据适应度函数确定每个个体的适应度值Fi=FitnessFunction(individual);然后确定每个个体被选择的概率Pi=Fi/sum(Fi),sum(Fi)代表所有个体适应度之和.
6、根据轮盘赌选择算子,选取适应度较大的个体。一次选取一个个体,选取n次,得到新的种群population 。
7、确定交叉概率Pc,对上一步得到的种群进行单点交叉。每次交叉点的位置随机.
8、确定变异概率Pm,假设种群大小为10,每个个体染色体编码长度为33,则一共有330个基因位,则变异的基因位数是330*Pm。接下来,要确定是那个染色体中哪个位置的基因发生了变异。将330按照10进制序号进行编码即从0,1,2,.......229。随机从330个数中选择330*Pm个数,假设其中一个数时154,chromosomeIndex = 154/33 =4, geneIndex = 154%33 = 22。由此确定了第154号位置的基因位于第4个染色体的第22个位置上,将此位置的基因值置反完成基本位变异操作.
9、以上步骤完成了一次迭代的所有操作。接下就是评估的过程。对变异后得到的最终的种群进行解码,利用解码值求得每个个体的适应度值,将最大的适应度值保存下来,对应的解码后的决策变量的值也保存下来.
10、根据迭代次数,假设是500次,重复执行1-9的步骤,最终得到是一个500个数值的最优适应度取值的数组以及一个500*n的决策变量取值数组(假设有n个决策变量)。从500个值中找到最优的一个(最大或者最小,根据定义的适应度函数来选择)以及对应的决策变量的取值。 对于以上流程不是很清楚的地方,在代码中有详细的注释。也可以自行查找资料补充理论。本文重点是实现 本代码实现的问题是: maxf(x1,x2) = 21.5+x1*sin(4*pi*x1)+x2*sin(20*pi*x2) s.t. -3.0<=x1<=12.1 4.1<=x2<=5.8 。
初始种群的编码结果如下图所示

初始种群的解码结果如下图所示
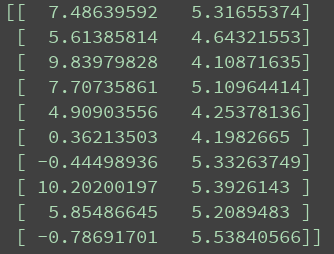
适应度值如图所示
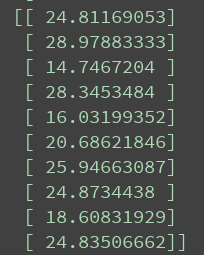
轮盘赌选择后的种群如图所示; 。

单点交叉后的种群如图所示

基本位变异后的种群如图所示; 。

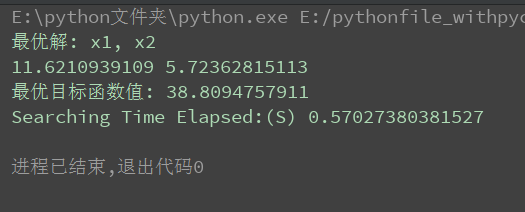
最终结果如下图所示; 。
源代码如下; 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
|
# !/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author: wsw
# 简单实现SGA算法
import
numpy as np
from
scipy.optimize
import
fsolve, basinhopping
import
random
import
timeit
# 根据解的精度确定染色体(chromosome)的长度
# 需要根据决策变量的上下边界来确定
def
getEncodedLength(delta
=
0.0001
, boundarylist
=
[]):
# 每个变量的编码长度
lengths
=
[]
for
i
in
boundarylist:
lower
=
i[
0
]
upper
=
i[
1
]
# lamnda 代表匿名函数f(x)=0,50代表搜索的初始解
res
=
fsolve(
lambda
x: ((upper
-
lower)
*
1
/
delta)
-
2
*
*
x
-
1
,
50
)
length
=
int
(np.floor(res[
0
]))
lengths.append(length)
return
lengths
pass
# 随机生成初始编码种群
def
getIntialPopulation(encodelength, populationSize):
# 随机化初始种群为0
chromosomes
=
np.zeros((populationSize,
sum
(encodelength)), dtype
=
np.uint8)
for
i
in
range
(populationSize):
chromosomes[i, :]
=
np.random.randint(
0
,
2
,
sum
(encodelength))
# print('chromosomes shape:', chromosomes.shape)
return
chromosomes
# 染色体解码得到表现型的解
def
decodedChromosome(encodelength, chromosomes, boundarylist, delta
=
0.0001
):
populations
=
chromosomes.shape[
0
]
variables
=
len
(encodelength)
decodedvalues
=
np.zeros((populations, variables))
for
k, chromosome
in
enumerate
(chromosomes):
chromosome
=
chromosome.tolist()
start
=
0
for
index, length
in
enumerate
(encodelength):
# 将一个染色体进行拆分,得到染色体片段
power
=
length
-
1
# 解码得到的10进制数字
demical
=
0
for
i
in
range
(start, length
+
start):
demical
+
=
chromosome[i]
*
(
2
*
*
power)
power
-
=
1
lower
=
boundarylist[index][
0
]
upper
=
boundarylist[index][
1
]
decodedvalue
=
lower
+
demical
*
(upper
-
lower)
/
(
2
*
*
length
-
1
)
decodedvalues[k, index]
=
decodedvalue
# 开始去下一段染色体的编码
start
=
length
return
decodedvalues
# 得到个体的适应度值及每个个体被选择的累积概率
def
getFitnessValue(func, chromosomesdecoded):
# 得到种群规模和决策变量的个数
population, nums
=
chromosomesdecoded.shape
# 初始化种群的适应度值为0
fitnessvalues
=
np.zeros((population,
1
))
# 计算适应度值
for
i
in
range
(population):
fitnessvalues[i,
0
]
=
func(chromosomesdecoded[i, :])
# 计算每个染色体被选择的概率
probability
=
fitnessvalues
/
np.
sum
(fitnessvalues)
# 得到每个染色体被选中的累积概率
cum_probability
=
np.cumsum(probability)
return
fitnessvalues, cum_probability
# 新种群选择
def
selectNewPopulation(chromosomes, cum_probability):
m, n
=
chromosomes.shape
newpopulation
=
np.zeros((m, n), dtype
=
np.uint8)
# 随机产生M个概率值
randoms
=
np.random.rand(m)
for
i, randoma
in
enumerate
(randoms):
logical
=
cum_probability >
=
randoma
index
=
np.where(logical
=
=
1
)
# index是tuple,tuple中元素是ndarray
newpopulation[i, :]
=
chromosomes[index[
0
][
0
], :]
return
newpopulation
pass
# 新种群交叉
def
crossover(population, Pc
=
0.8
):
"""
:param population: 新种群
:param Pc: 交叉概率默认是0.8
:return: 交叉后得到的新种群
"""
# 根据交叉概率计算需要进行交叉的个体个数
m, n
=
population.shape
numbers
=
np.uint8(m
*
Pc)
# 确保进行交叉的染色体个数是偶数个
if
numbers
%
2
!
=
0
:
numbers
+
=
1
# 交叉后得到的新种群
updatepopulation
=
np.zeros((m, n), dtype
=
np.uint8)
# 产生随机索引
index
=
random.sample(
range
(m), numbers)
# 不进行交叉的染色体进行复制
for
i
in
range
(m):
if
not
index.__contains__(i):
updatepopulation[i, :]
=
population[i, :]
# crossover
while
len
(index) >
0
:
a
=
index.pop()
b
=
index.pop()
# 随机产生一个交叉点
crossoverPoint
=
random.sample(
range
(
1
, n),
1
)
crossoverPoint
=
crossoverPoint[
0
]
# one-single-point crossover
updatepopulation[a,
0
:crossoverPoint]
=
population[a,
0
:crossoverPoint]
updatepopulation[a, crossoverPoint:]
=
population[b, crossoverPoint:]
updatepopulation[b,
0
:crossoverPoint]
=
population[b,
0
:crossoverPoint]
updatepopulation[b, crossoverPoint:]
=
population[a, crossoverPoint:]
return
updatepopulation
pass
# 染色体变异
def
mutation(population, Pm
=
0.01
):
"""
:param population: 经交叉后得到的种群
:param Pm: 变异概率默认是0.01
:return: 经变异操作后的新种群
"""
updatepopulation
=
np.copy(population)
m, n
=
population.shape
# 计算需要变异的基因个数
gene_num
=
np.uint8(m
*
n
*
Pm)
# 将所有的基因按照序号进行10进制编码,则共有m*n个基因
# 随机抽取gene_num个基因进行基本位变异
mutationGeneIndex
=
random.sample(
range
(
0
, m
*
n), gene_num)
# 确定每个将要变异的基因在整个染色体中的基因座(即基因的具体位置)
for
gene
in
mutationGeneIndex:
# 确定变异基因位于第几个染色体
chromosomeIndex
=
gene
/
/
n
# 确定变异基因位于当前染色体的第几个基因位
geneIndex
=
gene
%
n
# mutation
if
updatepopulation[chromosomeIndex, geneIndex]
=
=
0
:
updatepopulation[chromosomeIndex, geneIndex]
=
1
else
:
updatepopulation[chromosomeIndex, geneIndex]
=
0
return
updatepopulation
pass
# 定义适应度函数
def
fitnessFunction():
return
lambda
x:
21.5
+
x[
0
]
*
np.sin(
4
*
np.pi
*
x[
0
])
+
x[
1
]
*
np.sin(
20
*
np.pi
*
x[
1
])
pass
def
main(max_iter
=
500
):
# 每次迭代得到的最优解
optimalSolutions
=
[]
optimalValues
=
[]
# 决策变量的取值范围
decisionVariables
=
[[
-
3.0
,
12.1
], [
4.1
,
5.8
]]
# 得到染色体编码长度
lengthEncode
=
getEncodedLength(boundarylist
=
decisionVariables)
for
iteration
in
range
(max_iter):
# 得到初始种群编码
chromosomesEncoded
=
getIntialPopulation(lengthEncode,
10
)
# 种群解码
decoded
=
decodedChromosome(lengthEncode, chromosomesEncoded, decisionVariables)
# 得到个体适应度值和个体的累积概率
evalvalues, cum_proba
=
getFitnessValue(fitnessFunction(), decoded)
# 选择新的种群
newpopulations
=
selectNewPopulation(chromosomesEncoded, cum_proba)
# 进行交叉操作
crossoverpopulation
=
crossover(newpopulations)
# mutation
mutationpopulation
=
mutation(crossoverpopulation)
# 将变异后的种群解码,得到每轮迭代最终的种群
final_decoded
=
decodedChromosome(lengthEncode, mutationpopulation, decisionVariables)
# 适应度评价
fitnessvalues, cum_individual_proba
=
getFitnessValue(fitnessFunction(), final_decoded)
# 搜索每次迭代的最优解,以及最优解对应的目标函数的取值
optimalValues.append(np.
max
(
list
(fitnessvalues)))
index
=
np.where(fitnessvalues
=
=
max
(
list
(fitnessvalues)))
optimalSolutions.append(final_decoded[index[
0
][
0
], :])
# 搜索最优解
optimalValue
=
np.
max
(optimalValues)
optimalIndex
=
np.where(optimalValues
=
=
optimalValue)
optimalSolution
=
optimalSolutions[optimalIndex[
0
][
0
]]
return
optimalSolution, optimalValue
solution, value
=
main()
print
(
'最优解: x1, x2'
)
print
(solution[
0
], solution[
1
])
print
(
'最优目标函数值:'
, value)
# 测量运行时间
elapsedtime
=
timeit.timeit(stmt
=
main, number
=
1
)
print
(
'Searching Time Elapsed:(S)'
, elapsedtime)
|
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我.
原文链接:http://blog.csdn.net/qq_30666517/article/details/78637255 。
最后此篇关于Python实现简单遗传算法(SGA)的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于Python实现简单遗传算法(SGA)的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
如何将 solr 与 heritrix 集成? 我想使用 heritrix 归档一个站点,然后使用 solr 在本地索引和搜索该文件。 谢谢 最佳答案 使用 Solr 进行索引的问题在于它是一个纯文本
我的任务: 创建一个程序来仅使用基元(如三角形或其他东西)复制图片(作为输入给出)。该程序应使用进化算法来创建输出图片。 我的问题: 我需要发明一种算法来创建种群并检查它们(它们与输入图片的匹配程度
我看过几篇文章和文章,建议使用模拟退火等方法来避免局部最小值/最大值问题。 我不明白为什么如果您从足够大的随机人口开始,这将是必要的。 这只是确保初始人口实际上足够大和随机的另一项检查吗?或者这些技术

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!