- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章spring-session简介及实现原理源码分析由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
一:spring-session介绍 。
1.简介 。
session一直都是我们做集群时需要解决的一个难题,过去我们可以从serlvet容器上解决,比如开源servlet容器-tomcat提供的tomcat-redis-session-manager、memcached-session-manager.
或者通过nginx之类的负载均衡做ip_hash,路由到特定的服务器上.. 。
但是这两种办法都存在弊端.
|
1
|
spring-session是spring旗下的一个项目,把servlet容器实现的httpSession替换为spring-session,专注于解决 session管理问题。可简单快速且无缝的集成到我们的应用中。
|
2.支持功能 。
1)轻易把session存储到第三方存储容器,框架提供了redis、jvm的map、mongo、gemfire、hazelcast、jdbc等多种存储session的容器的方式.
2)同一个浏览器同一个网站,支持多个session问题.
3)RestfulAPI,不依赖于cookie。可通过header来传递jessionID 。
4)WebSocket和spring-session结合,同步生命周期管理.
3.集成方式 。
集成方式非常简单,直接看官网的samplesandguide。http://docs.spring.io/spring-session/docs/1.3.0.RELEASE/reference/html5/ 。
主要分为以下几个集成步骤:
1)引入依赖jar包 。
2)注解方式或者xml方式配置特定存储容器的存储方式,如redis的xml配置方式 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<
context:annotation-config
/>
/** 初始化一切spring-session准备,且把springSessionFilter放入IOC **/
<
beanclass
=
"org.springframework.session.data.redis.config.annotation.web.http.RedisHttpSessionConfiguration"
/>
/** 这是存储容器的链接池 **/
<
beanclass
=
"org.springframework.data.redis.connection.lettuce.LettuceConnectionFactory"
/>
|
3)xml方式配置 web.xml ,配置 springSessionFilter到 filter chain中 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
<
filter
>
<
filter-name
>springSessionRepositoryFilter</
filter-name
>
<
filter-class
>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</
filter-class
>
</
filter
>
<
filter-mapping
>
<
filter-name
>springSessionRepositoryFilter</
filter-name
>
<
url-pattern
>/*</
url-pattern
>
<
dispatcher
>REQUEST</
dispatcher
><
dispatcher
>ERROR</
dispatcher
>
</
filter-mapping
>
|
二:spring-session框架内部剖析 。
1.框架高层抽象结构图 。
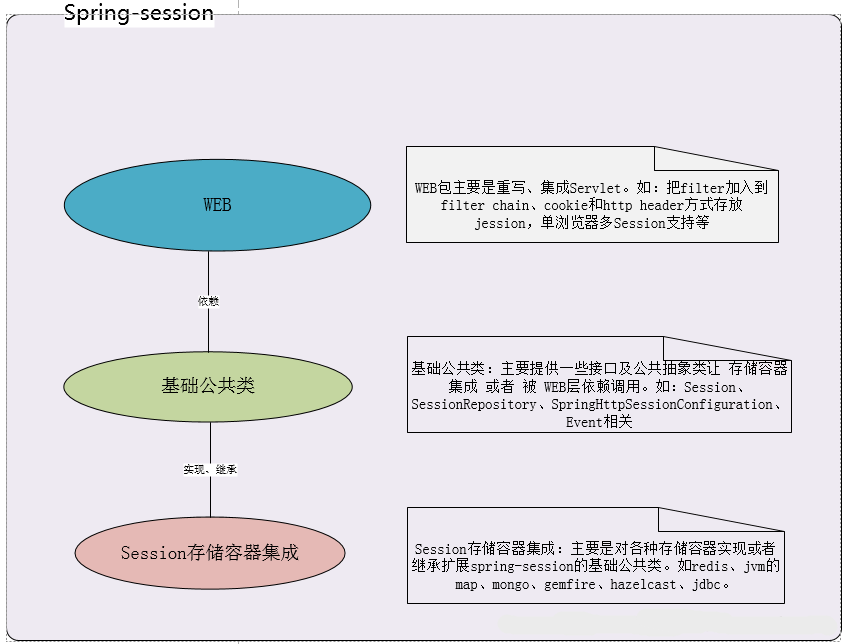
2.spring-session重写servlet request 及 redis实现存储相关问题 。
spring-session无缝替换应用服务器的request大概原理是: 1.自定义个Filter,实现doFilter方法 2.继承 HttpServletRequestWrapper 、HttpServletResponseWrapper 类,重写getSession等相关方法(在这些方法里调用相关的 session存储容器操作类)。 3.在 第一步的doFilter中,new 第二步 自定义的request和response的类。并把它们分别传递 到 过滤器链 4.把该filter配置到 过滤器链的第一个位置上 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
|
/** 这个类是spring-session的1.30源码,也是实现上面第一到第三步的关键类 **/
public
class
SessionRepositoryFilter<S
extends
ExpiringSession>
extends
OncePerRequestFilter {
/** session存储容器接口,redis、mongoDB、genfire等数据库都是实现该接口 **/
private
final
SessionRepository<S> sessionRepository;
private
ServletContext servletContext;
/**
sessionID的传递方式接口。目前spring-session自带两个实现类
1.cookie方式 :CookieHttpSessionStrategy
2.http header 方式:HeaderHttpSessionStrategy
当然,我们也可以自定义其他方式。
**/
private
MultiHttpSessionStrategy httpSessionStrategy =
new
CookieHttpSessionStrategy();
public
SessionRepositoryFilter(SessionRepository<S> sessionRepository) {
if
(sessionRepository ==
null
) {
throw
new
IllegalArgumentException(
"sessionRepository cannot be null"
);
}
this
.sessionRepository = sessionRepository;
}
public
void
setHttpSessionStrategy(HttpSessionStrategy httpSessionStrategy) {
if
(httpSessionStrategy ==
null
) {
throw
new
IllegalArgumentException(
"httpSessionStrategy cannot be null"
);
}
/**
通过前面的spring-session功能介绍,我们知道spring-session可以支持单浏览器多
session, 就是通过MultiHttpSessionStrategyAdapter来实现的。
每个浏览器拥有一个sessionID,但是这个sessionID拥有多个别名(根据浏览器的tab)。如:
别名1 sessionID
别名2 sessionID
...
而这个别名通过url来传递,这就是单浏览器多session原理了
**/
this
.httpSessionStrategy =
new
MultiHttpSessionStrategyAdapter(
httpSessionStrategy);
}
public
void
setHttpSessionStrategy(MultiHttpSessionStrategy httpSessionStrategy) {
if
(httpSessionStrategy ==
null
) {
throw
new
IllegalArgumentException(
"httpSessionStrategy cannot be null"
);
}
this
.httpSessionStrategy = httpSessionStrategy;
}
/**
该方法相当于重写了doFilter,只是spring-session又做了多一层封装。
在这个方法里创建自定义的 request和response,然后传递到过滤器链filterChain
**/
@Override
protected
void
doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws
ServletException, IOException {
request.setAttribute(SESSION_REPOSITORY_ATTR,
this
.sessionRepository);
/**
spring-session重写的ServletRequest。这个类继承了HttpServletRequestWrapper
**/
SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper wrappedRequest =
new
SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper(
request, response,
this
.servletContext);
SessionRepositoryResponseWrapper wrappedResponse =
new
SessionRepositoryResponseWrapper(
wrappedRequest, response);
HttpServletRequest strategyRequest =
this
.httpSessionStrategy
.wrapRequest(wrappedRequest, wrappedResponse);
HttpServletResponse strategyResponse =
this
.httpSessionStrategy
.wrapResponse(wrappedRequest, wrappedResponse);
try
{
/**
传递自定义 request和response到链中,想象下如果
该spring-sessionFilter位于过滤器链的第一个,那么后续的Filter,
以及到达最后的控制层所获取的 request和response,是不是就是我们自定义的了?
**/
filterChain.doFilter(strategyRequest, strategyResponse);
}
finally
{
wrappedRequest.commitSession();
}
}
public
void
setServletContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
this
.servletContext = servletContext;
}
/**
这个就是Servlet response的重写类了
*/
private
final
class
SessionRepositoryResponseWrapper
extends
OnCommittedResponseWrapper {
private
final
SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper request;
SessionRepositoryResponseWrapper(SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
super
(response);
if
(request ==
null
) {
throw
new
IllegalArgumentException(
"request cannot be null"
);
}
this
.request = request;
}
/**
这步是持久化session到存储容器,我们可能会在一个控制层里多次调用session的操作方法
如果我们每次对session的操作都持久化到存储容器,必定会带来性能的影响。比如redis
所以我们可以在整个控制层执行完毕了,response返回信息到浏览器时,才持久化session
**/
@Override
protected
void
onResponseCommitted() {
this
.request.commitSession();
}
}
/**
spring-session 的request重写类,这几乎是最重要的一个重写类。里面重写了获取getSession,Session等方法以及类
*/
private
final
class
SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper
extends
HttpServletRequestWrapper {
private
Boolean requestedSessionIdValid;
private
boolean
requestedSessionInvalidated;
private
final
HttpServletResponse response;
private
final
ServletContext servletContext;
private
SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, ServletContext servletContext) {
super
(request);
this
.response = response;
this
.servletContext = servletContext;
}
/**
* Uses the HttpSessionStrategy to write the session id to the response and
* persist the Session.
*/
private
void
commitSession() {
HttpSessionWrapper wrappedSession = getCurrentSession();
if
(wrappedSession ==
null
) {
// session失效,删除cookie或者header
if
(isInvalidateClientSession()) {
SessionRepositoryFilter.
this
.httpSessionStrategy
.onInvalidateSession(
this
,
this
.response);
}
}
else
{
S session = wrappedSession.getSession();
SessionRepositoryFilter.
this
.sessionRepository.save(session);
if
(!isRequestedSessionIdValid()
|| !session.getId().equals(getRequestedSessionId())) {
// 把cookie或者header写回给浏览器保存
SessionRepositoryFilter.
this
.httpSessionStrategy.onNewSession(session,
this
,
this
.response);
}
}
}
@SuppressWarnings
(
"unchecked"
)
private
HttpSessionWrapper getCurrentSession() {
return
(HttpSessionWrapper) getAttribute(CURRENT_SESSION_ATTR);
}
private
void
setCurrentSession(HttpSessionWrapper currentSession) {
if
(currentSession ==
null
) {
removeAttribute(CURRENT_SESSION_ATTR);
}
else
{
setAttribute(CURRENT_SESSION_ATTR, currentSession);
}
}
@SuppressWarnings
(
"unused"
)
public
String changeSessionId() {
HttpSession session = getSession(
false
);
if
(session ==
null
) {
throw
new
IllegalStateException(
"Cannot change session ID. There is no session associated with this request."
);
}
// eagerly get session attributes in case implementation lazily loads them
Map<String, Object> attrs =
new
HashMap<String, Object>();
Enumeration<String> iAttrNames = session.getAttributeNames();
while
(iAttrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = iAttrNames.nextElement();
Object value = session.getAttribute(attrName);
attrs.put(attrName, value);
}
SessionRepositoryFilter.
this
.sessionRepository.delete(session.getId());
HttpSessionWrapper original = getCurrentSession();
setCurrentSession(
null
);
HttpSessionWrapper newSession = getSession();
original.setSession(newSession.getSession());
newSession.setMaxInactiveInterval(session.getMaxInactiveInterval());
for
(Map.Entry<String, Object> attr : attrs.entrySet()) {
String attrName = attr.getKey();
Object attrValue = attr.getValue();
newSession.setAttribute(attrName, attrValue);
}
return
newSession.getId();
}
// 判断session是否有效
@Override
public
boolean
isRequestedSessionIdValid() {
if
(
this
.requestedSessionIdValid ==
null
) {
String sessionId = getRequestedSessionId();
S session = sessionId ==
null
?
null
: getSession(sessionId);
return
isRequestedSessionIdValid(session);
}
return
this
.requestedSessionIdValid;
}
private
boolean
isRequestedSessionIdValid(S session) {
if
(
this
.requestedSessionIdValid ==
null
) {
this
.requestedSessionIdValid = session !=
null
;
}
return
this
.requestedSessionIdValid;
}
private
boolean
isInvalidateClientSession() {
return
getCurrentSession() ==
null
&&
this
.requestedSessionInvalidated;
}
private
S getSession(String sessionId) {
// 从session存储容器中根据sessionID获取session
S session = SessionRepositoryFilter.
this
.sessionRepository
.getSession(sessionId);
if
(session ==
null
) {
return
null
;
}
// 设置sesison的最后访问时间,以防过期
session.setLastAccessedTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
return
session;
}
/**
这个方法是不是很熟悉,下面还有个getSession()才更加熟悉。没错,就是在这里重新获取session方法
**/
@Override
public
HttpSessionWrapper getSession(
boolean
create) {
//快速获取session,可以理解为一级缓存、二级缓存这种关系
HttpSessionWrapper currentSession = getCurrentSession();
if
(currentSession !=
null
) {
return
currentSession;
}
//从httpSessionStratge里面根据cookie或者header获取sessionID
String requestedSessionId = getRequestedSessionId();
if
(requestedSessionId !=
null
&& getAttribute(INVALID_SESSION_ID_ATTR) ==
null
) {
//从存储容器获取session以及设置当次初始化属性
S session = getSession(requestedSessionId);
if
(session !=
null
) {
this
.requestedSessionIdValid =
true
;
currentSession =
new
HttpSessionWrapper(session, getServletContext());
currentSession.setNew(
false
);
setCurrentSession(currentSession);
return
currentSession;
}
else
{
if
(SESSION_LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
SESSION_LOGGER.debug(
"No session found by id: Caching result for getSession(false) for this HttpServletRequest."
);
}
setAttribute(INVALID_SESSION_ID_ATTR,
"true"
);
}
}
if
(!create) {
return
null
;
}
if
(SESSION_LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
SESSION_LOGGER.debug(
"A new session was created. To help you troubleshoot where the session was created we provided a StackTrace (this is not an error). You can prevent this from appearing by disabling DEBUG logging for "
+ SESSION_LOGGER_NAME,
new
RuntimeException(
"For debugging purposes only (not an error)"
));
}
// 如果该浏览器或者其他http访问者是初次访问服务器,则为他创建个新的session
S session = SessionRepositoryFilter.
this
.sessionRepository.createSession();
session.setLastAccessedTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
currentSession =
new
HttpSessionWrapper(session, getServletContext());
setCurrentSession(currentSession);
return
currentSession;
}
@Override
public
ServletContext getServletContext() {
if
(
this
.servletContext !=
null
) {
return
this
.servletContext;
}
// Servlet 3.0+
return
super
.getServletContext();
}
@Override
public
HttpSessionWrapper getSession() {
return
getSession(
true
);
}
@Override
public
String getRequestedSessionId() {
return
SessionRepositoryFilter.
this
.httpSessionStrategy
.getRequestedSessionId(
this
);
}
/**
HttpSession的重写类
*/
private
final
class
HttpSessionWrapper
extends
ExpiringSessionHttpSession<S> {
HttpSessionWrapper(S session, ServletContext servletContext) {
super
(session, servletContext);
}
@Override
public
void
invalidate() {
super
.invalidate();
SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper.
this
.requestedSessionInvalidated =
true
;
setCurrentSession(
null
);
SessionRepositoryFilter.
this
.sessionRepository.delete(getId());
}
}
}
}
|
总结 。
以上就是本文关于spring-session简介及实现原理源码分析的全部内容,希望对大家有所帮助。感兴趣的朋友可以继续参阅本站其他相关专题,如有不足之处,欢迎留言指出! 。
原文链接:http://blog.csdn.net/wojiaolinaaa/article/details/62424642 。
最后此篇关于spring-session简介及实现原理源码分析的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于spring-session简介及实现原理源码分析的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
是否为每个 Shiny session 分配了 session ID/ session key (如果部署在 Shiny 服务器上)?如果是,我如何访问该信息?我已阅读文档here然而上网查了一下,并
我正在使用 this koajs session 模块。 我检查了源代码,但我真的无法理解。 我想知道它保存 session 数据的位置,因为我没有看到创建的文件,并且当服务器重新启动时, sessi
实现高可扩展性的一种方法是使用网络负载平衡在多个服务器之间分配处理负载。 这种方法提出的一个挑战是服务器是否具有状态意识 - 将用户状态存储在“ session ”中。 此问题的一个解决方案是“粘性
在负载平衡服务器的上下文中, session 亲和性和粘性 session 之间有什么区别? 最佳答案 我见过这些术语可以互换使用,但有不同的实现方式: 在第一个响应中发送 cookie,然后在后续响
我希望其他人向我解释哪种方法更好:使用 session 或设计无 session 。我们正在开始开发一个新的 Web 应用程序,但尚未决定要遵循什么路径。 无 session 设计在我看来更可取: 优
现在用户在他的权限中有很多角色,我将允许他点击 href 并在新窗口中扮演另一个角色。每个角色都有自己的 session 。 既然浏览器打开窗口不能用新 session 打开,我必须在服务器端想办法。
我正在尝试为express.js Node 应用程序实现 session 存储我的问题是: 如何删除具有浏览器 session 生命周期的 cookie(根据连接文档标记有 expires = fal
在开始在 golang 中使用 session 之前,我需要回答一些问题 session 示例 import "github.com/gorilla/sessions" var store = ses
我读过 Namespaced Attributes . 我尝试使用此功能: #src/Controller/CartController.php public function addProduct(
我正在努力完成以下工作: 根据用户的类型更改用户的 session cookie 到期日期。 我有一个 CakePHP Web 应用程序,其中我使用 CakePHP session 创建了我的身份验证
这是我在这里的第一个问题,我希望我做对了。 我需要处理一个 Java EE 项目,所以在开始之前,我会尝试做一些简单的事情,看看我是否能做到。 我坚持使用有状态 session Bean。 这是问题:
ColdFusion session 与 J2EE session 相比有什么优势吗? ColdFusion session documentation提到了 J2EE session 的优点,但没有
在执行任何任务之前,我需要准确地在创建 session 时创建一个 session 范围变量(因为我的所有任务都需要一个初始 session 范围变量才能运行)。因为,创建 session 时,gra
我们当前的应用使用 HTTP session ,我们希望将其替换为 JWT。 该设置仅允许每个用户进行一次 session 。这意味着: 用户在设备 1 上登录 用户已在设备 1 上登录(已创建新 s
很难说出这里问的是什么。这个问题是含糊的、模糊的、不完整的、过于宽泛的或修辞性的,无法以目前的形式得到合理的回答。如需帮助澄清此问题以便重新打开它,visit the help center 。 已关
假设我在两个或更多设备上打开了两个或更多用户 session (同一用户没有管理员权限)。 在当前 session 中,如果我注销,是否意味着所有其他 session 也会关闭?如果没有,有没有办法通
我正在评估在 tomcat 中使用带有 session 复制的粘性 session 的情况。根据我的初步评估,我认为如果我们启用 session 复制,那么在一个 tomcat 节点中启动的 sess
我开始使用 golang 和 Angular2 构建一个常规的网络应用程序,最重要的是我试图在 auth0.com 的帮助下保护我的登录.我从 here 下载快速入门代码并尝试运行代码,它运行了一段时
我在 Spring Controller 中有一个方法,它接受两个相同类型的参数其中一个来自 session ,另一个来自表单提交(UI)。 问题是在 Controller 方法中我的非 sessio
在我登录之前,我可以点击我的安全约束目录之外的任何内容。如果我尝试转到安全约束目录内的某个位置,它会将我重定向到表单登录页面。如您所料。 登录后,我可以继续我的业务,并访问我的安全约束内外的资源。

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!