- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章JavaWeb Spring开发入门深入学习由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
1 Spring基本特征 。

Spring是一个非常活跃的开源框架;它是一个基于Core来构架多层JavaEE系统的框架,它的主要目地是简化企业开发. Spring以一种非侵入式的方式来管理你的代码,Spring提倡”最少侵入”,这也就意味着你可以适当的时候安装或卸载Spring,Spring让java亮了。 (开放–闭合原理),这里是闭原则.
2 开发spring所需要的工具 。
(这里先将spring2.5 ,后面3.0) 。
2.1 Spring的jar包 。
到http://www.springsource.org/download下载spring,然后进行解压缩,在解压目录中找到下面jar文件,拷贝到类路径下 。
—spring的核心类库 在spring文档的dist下 dist\spring.jar 。
—引入的第三方类库 都spring文档的lib下,lib\jakarta-commons\commons-logging.jar 。
—如果使用了切面编程(AOP),还需要下列jar文件 lib/aspectj/aspectjweaver.jar和aspectjrt.jarlib/cglib/cglib-nodep-2.1_3.jar 。
—如果使用了JSR-250中的注解,如@Resource/@PostConstruct/@PreDestroy,还需要下列jar文件lib\j2ee\common-annotations.jar 。
注:JSR(Java 规范请求)是指向JCP(Java Community Process)提出新增一个标准化技术规范的正式请求。任何人都可以提交JSR(Java 规范请求),以向Java平台增添新的API和服务。JSR已成为Java界的一个重要标准 。
2.2 Spring配置文件 。
默认情况下是applicationContext.xml文件。可以建立很多xml文件,工程中一般都是这样配置的。(src目录下建) 。
3 Spring基本功能详解 。
3.1 SpringIOC 。
Spring的控制反转:把对象的创建、初始化、销毁等工作交给spring容器来做。由spring容器控制对象的生命周期.
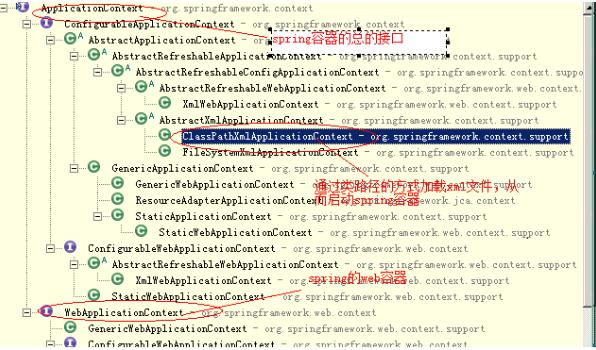
步骤: •A. 启动spring容器 1、 在类路径下寻找配置文件来实例化容器 。
。
。
可以在整个类路径中寻找xml文件 * 通过这种方式加载。需要将spring的配置文件放到当前项目的classpath路径下 * classpath路径指的是当前项目的src目录,该目录是java源文件的存放位置.
2、 在文件系统路径下寻找配置文件来实例化容器 。
Spring的配置文件可以指定多个,可以通过String数组传入。 注:经常用第一种方法启动容器 •B. 从spring容器中提取对象 。
spring 容器结构:
3.2 别名 。
|
1
2
3
4
|
<beans>
<alias name=
"person"
alias=
"p"
/>
//alias这里是别名,可以通过p,得到person这个bean.
<bean name=
"person"
class
=
"cn.itcast.aliasspring.Person"
/>
</beans>
|
通过这样的配置,可以达到在一个地方命名,在多个地方使用不同的名字的效果.
3.3 Spring容器内部对象 。
1 创建对象的方式 。
1.1 无参构造函数 。
<bean id="helloWorld" class="com.itheima10.spring.createobject.HelloWorld"></bean> 。
1.2 静态工厂方法 。
<bean id="helloWorld2" class="com.itheima10.spring.createobject.method.HelloWorldFactory" factory-method="getInstance"></bean> 。
1.3 实例工厂方法 。
<bean id="helloWorldFactory" class="com.itheima10.spring.createobject.method.HelloWorldFactory2"></bean> <bean id="helloWorld3" factory-bean="helloWorldFactory" factory-method="getInstance"></bean> 。
记住概念即可,用的最多的是第一种方法,但是和别的工具集成时,用的是实例工厂模式.
实例: 配置applicationContext.xml 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
<?
xml
version
=
"1.0"
encoding
=
"UTF-8"
?>
<
beans
xmlns
=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi
=
"http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd">
<!--
把一个类放入到spring容器中,该类就称为一个bean
-->
<!--
bean描述了一个类
id 唯一的标示
class 类的全名
-->
<
bean
id
=
"helloWorld"
class
=
"com.itheima10.spring.createobject.HelloWorld"
></
bean
>
<!-----------------------别名-------------------------------------->
<!--
name的属性和bean的id匹配
alias 别名
-->
<
alias
name
=
"helloWorld"
alias
=
"狗蛋"
/>
<
alias
name
=
"helloWorld"
alias
=
"习近平"
/>
<!-----------------------静态工厂方法-------------------------------------->
<!--
把helloWorldFactory放入到spring容器中
factory-method 工厂方法
-->
<
bean
id
=
"helloWorld2"
factory-method
=
"getInstance"
class
=
"com.itheima10.spring.createobject.method.HelloWorldFactory"
></
bean
>
<!-----------------------实例工厂方法-------------------------------------->
<!--
把helloWorldFactory2放入到spring容器中
factory-bean 指明了工厂bean
factory-method 指明了该工厂bean中的方法
-->
<
bean
id
=
"helloWorldFactory"
class
=
"com.itheima10.spring.createobject.method.HelloWorldFactory2"
></
bean
>
<
bean
id
=
"helloWorld3"
factory-bean
=
"helloWorldFactory"
factory-method
=
"getInstance"
></
bean
>
</
beans
>
|
建立实体类HelloWorld 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
package
com.itheima10.spring.createobject;
public
class
HelloWorld {
public
void
hello(){
System.out.println(
"hello"
);
}
}
|
建立静态工厂HelloWorldFactory 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
package
com.itheima10.spring.createobject.method;
public
class
HelloWorldFactory {
public
static
HelloWorld getInstance(){
System.out.println(
"static method"
);
return
new
HelloWorld();
}
}
|
建立实体工厂HelloWorldFactory2 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
package
com.itheima10.spring.createobject.method;
public
class
HelloWorldFactory2 {
/**
* 必须先创建工厂对象,才能调用该方法
* @return
*/
public
HelloWorld getInstance(){
return
new
HelloWorld();
}
}
|
编写测试方法CreateObjectMethodTest 。
。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
package
com.itheima10.spring.createobject.method;
import
org.junit.Test;
import
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import
org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* 第二种和第三种产生方式能看明白就OK了
* @author zd
*
*/
public
class
CreateObjectMethodTest {
/**
* 在默认情况下,spring容器调用的是一个类的默认的构造函数创建对象
*/
@Test
public
void
testCreateObject_Default(){
ApplicationContext context =
new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"applicationContext.xml"
);
HelloWorld helloWorld = (HelloWorld)context.getBean(
"helloWorld"
);
helloWorld.hello();
}
/**
* 利用静态工厂创建对象
* <bean id="helloWorld2"
factory-method="getInstance"
class="com.itheima10.spring.createobject.method.HelloWorldFactory"></bean>
spring容器做的事情:
利用HelloWorldFactory类调用了getInstance方法
*/
@Test
public
void
testCreateObject_StaticFactory(){
ApplicationContext context =
new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"applicationContext.xml"
);
HelloWorld helloWorld = (HelloWorld)context.getBean(
"helloWorld2"
);
helloWorld.hello();
}
/**
* 实例工厂方法创建对象
* <bean id="helloWorldFactory"
* class="com.itheima10.spring.createobject.method.HelloWorldFactory2"></bean>
* <bean id="helloWorld3"
factory-bean="helloWorldFactory"
factory-method="getInstance"></bean>
spring容器内部做的事情:
1、创建一个helloWorldFactory对象
2、由该对象调用getInstance产生helloWorld对象
*/
@Test
public
void
testCreateObject_InstanceFactory(){
ApplicationContext context =
new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"applicationContext.xml"
);
HelloWorld helloWorld = (HelloWorld)context.getBean(
"helloWorld3"
);
helloWorld.hello();
}
}
|
2 对象的scope 。
对象的scope有两个属性:singleton 与prototype。singleton表示单例 2.1 singleton(默认值) 。
在每个Spring IoC容器中一个bean定义只有一个对象实例(共享).
2.2 prototype 允许bean可以被多次实例化(使用一次就创建一个实例) . Spring不能对一个prototype bean的整个生命周期负责.这就意味着清楚prototype作用域的对象并释放任何prototype bean所持有的昂贵资源都是客户端的责任.
<bean id="helloWorld" class="com.itheima10.spring.scope.HelloWorld" scope="singleton"></bean> <bean id="helloWorld" class="com.itheima10.spring.scope.HelloWorld" scope="prototype"></bean> 。
建立HelloWorld类 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public
class
HelloWorld {
public
List<String> lists =
new
ArrayList<String>();
public
HelloWorld(){
System.out.println(
"new instance"
);
}
public
void
hello(){
System.out.println(
"hello"
);
}
}
|
建立测试类ScopeTest 。
。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
package
com.itheima10.spring.scope;
import
org.junit.Test;
import
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import
org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public
class
ScopeTest {
/**
* 把一个bean放入到spring容器中,默认的是单例
* 如果一个类放入到spring容易中,而这个类是单例的,那么该类中的属性将会成为共享的
*/
@Test
public
void
testCreateObject_Scope_Default(){
ApplicationContext context =
new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"applicationContext.xml"
);
HelloWorld hello1 = (HelloWorld)context.getBean(
"helloWorld"
);
hello1.lists.add(
"aaaa"
);
hello2= (HelloWorld)context.getBean(
"helloWorld"
);
hello2.lists.add(
"bbbb"
);
System.out.println(helloWorld.lists.size());
//2,并且只输出一次new instance
}
/**
* 如果spring的配置文件如下:
* <bean id="helloWorld"
class="com.itheima10.spring.scope.HelloWorld"
scope="prototype"></bean>
那么spring容器会为创建多个对象
*/
@Test
public
void
testCreateObject_Scope_Prototype(){
ApplicationContext context =
new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"applicationContext.xml"
);
HelloWorld hello1 = (HelloWorld)context.getBean(
"helloWorld"
);
hello1.lists.add(
"aaaa"
);
hello2= (HelloWorld)context.getBean(
"helloWorld"
);
hello2.lists.add(
"bbbb"
);
System.out.println(helloWorld.lists.size());
//1,并且只输出两次new instance
}
}
|
3 初始化bean时机 。
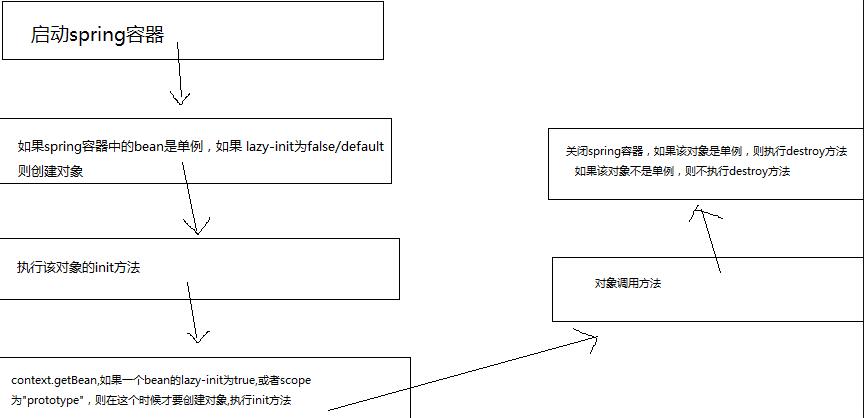
懒加载——默认情况下会在容器启动时初始化bean,但我们可以指定Bean节点的lazy-init=“true”来延迟初始化bean,这时候,只有第一次获取bean会才初始化bean。如:
<bean id="xxx" class="cn.itcast.OrderServiceBean" lazy-init="true"/> 。
如果想对所有bean都应用延迟初始化,可以在根节点beans设置default-lazy-init=“true“,如下:
<beans default-lazy-init="true“ ...> 。
Spring默认在启动时将所有singleton bean提前进行实例化。提前实例化意味着作为初始化的一部分,ApplicationContext会自动创建并配置所有的singleton bean.通常情况下这是件好事。因为这样在配置中有任何错误能立即发现.
Lazy-init 为false,spring容器将在启动的时候报错(比较好的一种方式) Lazy-init 为true,spring容器将在调用该类的时候出错.
配置applicationContext.xml 。
|
1
2
3
4
|
<
bean
id
=
"helloWorld"
class
=
"com.itheima10.spring.createobject.when.HelloWorld"
scope
=
"prototype"
></
bean
>
</
beans
>
|
建立测试类CreateObjectWhenTest 。
。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
package
com.itheima10.spring.createobject.when;
import
org.junit.Test;
import
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import
org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public
class
CreateObjectWhenTest {
/**
* 默认情况下的顺序
* 1、启动spring容器
* 2、创建HelloWorld对象
* 3、对象调用方法
*
* <bean id="helloWorld" class="com.itheima10.spring.createobject.when.HelloWorld"></bean>
<bean id="helloWorld2" class="com.itheima10.spring.createobject.when.HelloWorld"></bean>
因为在spring容器中声明了两个bean,所以spring容器要创建两个对象
说明:
如果struts2,hibernate,spring容器整合,如果spring的配置文件中出现错误
当 tomcat容器启动的时候,就会报错,错误会特别早的显示出来
如果一个bean存放了大量的数据,这种方式不好,有可能会把数据过早的停留在内存中
如果一个bean不是单例,那么不管怎么样配置,都在是context.getBean时才要创建对象
*/
@Test
public
void
testCreateObject_When_Default(){
ApplicationContext context =
new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"applicationContext.xml"
);
context.getBean(
"helloWorld"
);
}
/**
* <bean id="helloWorld"
class="com.itheima10.spring.createobject.when.HelloWorld"
lazy-init="true"></bean>
* 顺序
* 1、启动spring容器
* 2、context.getBean
* 3、调用构造器函数创建对象
* 说明:
如果struts2,hibernate,spring容器整合,如果spring的配置文件中出现错误
只有当用到该bean的时候才会报错。
如果一个bean存放了大量的数据,需要的时候才要加载数据
*/
@Test
public
void
testCreateObject_When_Lazy(){
ApplicationContext context =
new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"applicationContext.xml"
);
context.getBean(
"helloWorld"
);
}
}
|
4 init、destroy方法 。
Spring初始化bean或销毁bean时,有时需要作一些处理工作,因此spring可以在创建和拆卸bean的时候调用bean的两个生命周期方法。可以指定方法进行操作.
<bean id=“foo” class=“...Foo” init-method=“setup” destory-method=“teardown”/> 。
当foo被载入到Spring容器中时调用init-method方法。当foo从容器中删除时调用destory-method(scope = singleton有效) 。
编写HelloWorld 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
public
class
HelloWorld {
public
HelloWorld(){
System.out.println(
"new instance"
);
}
public
void
init(){
System.out.println(
"init"
);
}
public
void
destroy(){
System.out.println(
"destroy"
);
}
public
void
hello(){
System.out.println(
"hello"
);
}
}
|
编写测试类InitDestroyTest 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
package
com.itheima10.spring.ioc.initdestroy;
import
org.junit.Test;
import
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import
org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public
class
InitDestroyTest {
/**
* init-method="init"
* 执行顺序:
* 1、启动spring容器
* 2、创建helloWorld对象
* 3、执行init方法
* spring容器内部自动执行的
* 4、对象调用方法
* 5、只有当spring容器关闭掉的情况下才能执行destroy方法 前提条件:bean是单例的
* 该方法也是由spring容器内部调用的
* 说明:
* 如果一个bean不是单例的,则spring容器不负责对象的销毁。
* 在spring容器中,只有一个bean是单例的情况下,spring容器才要负责对象的创建、初始化、销毁工作
* 如果一个bean不是单例,spring容器只负责创建、初始化
*/
@Test
public
void
testInitDestroy(){
ApplicationContext context =
new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"applicationContext.xml"
);
HelloWorld helloWorld = (HelloWorld)context.getBean(
"helloWorld"
);
helloWorld.hello();
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = (ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)context;
applicationContext.close();
}
}
|
执行顺序图:
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我.
原文链接:http://blog.csdn.net/i10630226/article/details/50502167 。
最后此篇关于JavaWeb Spring开发入门深入学习的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于JavaWeb Spring开发入门深入学习的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
Hive —— 入门 Hive介绍 Apache Hive是一款建立在Hadoop之上的开源数据仓库系统,可以将存储在Hadoop文件中的结构化、半结构化数据文件映射为一张数据库表,基于表提供了一
HBase —— 入门 HBase介绍 HBase是一个分布式的、面向列的开源数据库,该技术来源于 Fay Chang 所撰写的Google论文“Bigtable:一个结构化数据的分布式存储系统”
零:前端目前形势 前端的发展史 HTML(5)、CSS(3)、JavaScript(ES5、ES6):编写一个个的页面 -> 给后端(PHP、Python、Go、Java) ->
在本教程中,您将了解在计算机上运行 JavaScript 的不同方法。 JavaScript 是一种流行的编程语言,具有广泛的应用程序。 JavaScript 以前主要用于使网页具有交
我曾经是一个对编程一窍不通的小白,但因为对互联网世界的好奇心和求知欲的驱使,我踏入了编程的殿堂。在学习的过程中,我发现了一门神奇的编程语言——Python。Python有着简洁、易读的语法,让初学者能
嗨,亲爱的读者们! 今天我要给大家分享一些关于Python爬虫的小案例。你是否曾为了获取特定网页上的数据而烦恼过?或者是否好奇如何从网页中提取信息以供自己使用?那么,这篇文章将会给你一些启示和灵感。
关闭。这个问题是opinion-based 。目前不接受答案。 想要改进这个问题吗?更新问题,以便 editing this post 可以用事实和引文来回答它。 . 已关闭 8 年前。 Improv
我想创建一个像https://apprtc.appspot.com/?r=04188292这样的应用程序。我对 webrtc 了解一点,但无法掌握 google app-engine。如何为 java
我刚刚开始使用 Python 并编写了一个简单的周边程序。但是,每当我在终端中键入 python perimeter.py 时,都会收到以下错误,我不知道如何解决。 >>> python perime
Redis有5个基本数据结构,string、list、hash、set和zset。它们是日常开发中使用频率非常高应用最为广泛的数据结构,把这5个数据结构都吃透了,你就掌握了Redis应用知识的一半了
创建发布web项目 具体步骤: 1.在开发工具中创建一个dynamic web project helloword 2.在webContent中创建index.html文件 3.发布web应用到
如果你在 Ubuntu 上使用终端的时间很长,你可能会希望调整终端的字体和大小以获取一种良好的体验。 更改字体是一种最简单但最直观的 Linux 的终端自定义 的方法。让我
1. 前言 ADODB 是 Active Data Objects Data Base 的简称,它是一种 PHP 存取数据库的函式组件。现在 SFS3 系统 (校园自由软件交流网学务系统) 计划的
我对 neo4j 完全陌生,我很抱歉提出这样一个基本问题。我已经安装了neo4j,我正在使用shell“localhost:7474/webadmin/#/console/” 我正在寻找一个很好的例子
我正在阅读 ios 4 的核心音频,目的是构建一个小测试应用程序。 在这一点上,我对所有 api 的研究感到非常困惑。理想情况下,我想知道如何从两个 mp3 中提取一些样本到数组中。 然后在回调循环中
关闭。这个问题不符合Stack Overflow guidelines .它目前不接受答案。 要求我们推荐或查找工具、库或最喜欢的场外资源的问题对于 Stack Overflow 来说是无关紧要的,因
我下载了 GNUStep并安装了它,但是我不确定在哪里可以找到 IDE。有谁知道什么程序可以用作 GNUStep IDE/从哪里获取它们?否则,有没有人知道有关如何创建和编译基本 GNUStep 程序
我正在尝试开始使用 Apache Solr,但有些事情我不清楚。通读tutorial ,我已经设置了一个正在运行的 Solr 实例。我感到困惑的是 Solr 的所有配置(架构等)都是 XML 格式的。
请问有没有关于如何开始使用 BruTile 的文档? 我目前正在使用 SharpMap,我需要预缓存切片以加快进程 最佳答案 我今天正在研究这个:)Mapsui项目site严重依赖 SharpMap
尽我所能,我无法让 CEDET 做任何事情。 Emacs 24.3。我下载了最新的 CEDET 快照。我从他的底部(不是这样)Gentle Introduction 中获取了 Alex Ott 的设置

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!