- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章Spring依赖注入的两种方式(根据实例详解)由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
1,Set注入 2,构造注入 。
Set方法注入:
原理:通过类的setter方法完成依赖关系的设置 。
name属性的取值依setter方法名而定,要求这个类里面这个对应的属性必须有setter方法.
Set方法注入时spring中配置文件:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
<?
xml
version
=
"1.0"
encoding
=
"UTF-8"
?>
<
beans
xmlns
=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi
=
"http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p
=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<
bean
id
=
"car"
class
=
"org.spring01.Car"
>
<
constructor-arg
value
=
"奔驰"
></
constructor-arg
>
<
constructor-arg
type
=
"java.lang.String"
>
<
value
>土豪金</
value
>
</
constructor-arg
>
<
constructor-arg
value
=
"高级轿车"
></
constructor-arg
>
</
bean
>
<
bean
id
=
"person"
class
=
"org.spring01.Person"
>
<
property
name
=
"name"
value
=
"张三"
></
property
>
<
property
name
=
"age"
value
=
"11"
></
property
>
<
property
name
=
"car"
ref
=
"car"
></
property
>
</
bean
>
</
beans
>
|
定义Car类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
package
org.spring01;
public
class
Car {
private
String name;
//车名
private
String color;
//颜色
private
String clas;
//等级
public
String getName() {
return
name;
}
public
void
setName(String name) {
this
.name = name;
}
public
String getColor() {
return
color;
}
public
void
setColor(String color) {
this
.color = color;
}
public
String getClas() {
return
clas;
}
public
void
setClas(String clas) {
this
.clas = clas;
}
public
Car(String name, String color, String clas) {
super
();
this
.name = name;
this
.color = color;
this
.clas = clas;
}
public
Car() {
super
();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
@Override
public
String toString() {
return
"Car [name="
+ name +
", color="
+ color +
", clas="
+ clas
+
"]"
;
}
}
|
定义Person类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
package
org.spring01;
public
class
Person {
private
String name;
//名字
private
int
age;
//年龄
private
Car car;
//他的车
public
String getName() {
return
name;
}
public
void
setName(String name) {
this
.name = name;
}
public
int
getAge() {
return
age;
}
public
void
setAge(
int
age) {
this
.age = age;
}
public
Car getCar() {
return
car;
}
public
void
setCar(Car car) {
this
.car = car;
}
public
Person(String name,
int
age, Car car) {
super
();
this
.name = name;
this
.age = age;
this
.car = car;
}
public
Person() {
super
();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
@Override
public
String toString() {
return
"Person [name="
+ name +
", age="
+ age +
", car="
+ car +
"]"
;
}
}
|
测试类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
package
org.spring01;
import
org.junit.Test;
import
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import
org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public
class
SpringTest{
@Test
public
void
toGetPerson(){
ApplicationContext context =
new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"applicationContext.xml"
);
Person person = (Person) context.getBean(
"person"
);
System.out.println(person);
}
@Test
public
void
toGetCar(){
ApplicationContext context =
new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"applicationContext.xml"
);
Car car = (Car) context.getBean(
"car"
);
System.out.println(car);
}
}
|
使用单元测试(JUnit)测试toGetPerson()方法,结果为:
|
1
|
Person [name=张三, age=11, car=Car [name=奔驰, color=土豪金, clas=高级轿车]]
|
构造方法注入:
原理:通过构造函数完成依赖关系的设定 。
构造注入指的是在接受注入的类中,定义一个构造方法,并在构造方法的参数中定义需要注入的元素,其中,index表示构造方法中的参数索引(第一个参数索引为0).
构造方法注入时spring中配置文件:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
<?
xml
version
=
"1.0"
encoding
=
"UTF-8"
?>
<
beans
xmlns
=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi
=
"http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p
=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<
bean
id
=
"car"
class
=
"org.spring02.Car"
>
<
constructor-arg
value
=
"大众"
></
constructor-arg
>
<
constructor-arg
type
=
"java.lang.String"
>
<
value
>白色</
value
>
</
constructor-arg
>
<
constructor-arg
value
=
"中级轿车"
></
constructor-arg
>
</
bean
>
<
bean
id
=
"person"
class
=
"org.spring02.Person"
>
<
constructor-arg
index
=
"0"
value
=
"李四"
></
constructor-arg
>
<
constructor-arg
index
=
"1"
value
=
"23"
></
constructor-arg
>
<
constructor-arg
index
=
"2"
ref
=
"car"
></
constructor-arg
>
</
bean
>
</
beans
>
|
定义Car类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
package
org.spring02;
public
class
Car {
private
String name;
//车名
private
String color;
//颜色
private
String clas;
//等级
public
Car(String name, String color, String clas) {
super
();
this
.name = name;
this
.color = color;
this
.clas = clas;
}
public
Car() {
super
();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
@Override
public
String toString() {
return
"Car [name="
+ name +
", color="
+ color +
", clas="
+ clas
+
"]"
;
}
}
|
定义Person类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
package
org.spring02;
public
class
Person {
private
String name;
//名字
private
int
age;
//年龄
private
Car car;
//他的车
public
Person(String name,
int
age, Car car) {
super
();
this
.name = name;
this
.age = age;
this
.car = car;
}
public
Person() {
super
();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
@Override
public
String toString() {
return
"Person [name="
+ name +
", age="
+ age +
", car="
+ car +
"]"
;
}
}
|
测试类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
package
org.spring02;
import
org.junit.Test;
import
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import
org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public
class
SpringTest{
@Test
public
void
toGetPerson(){
ApplicationContext context =
new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"applicationContext01.xml"
);
Person person = (Person) context.getBean(
"person"
);
System.out.println(person);
}
@Test
public
void
toGetCar(){
ApplicationContext context =
new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"applicationContext01.xml"
);
Car car = (Car) context.getBean(
"car"
);
System.out.println(car);
}
}
|
使用单元测试(JUnit)测试toGetPerson()方法,结果为:
|
1
|
Person [name=李四, age=23, car=Car [name=大众, color=白色, clas=中级轿车]]
|
上面的例子都采用了单元测试的方法检测运行结果,需要导库: JUnit 。
Demo的大体结构:
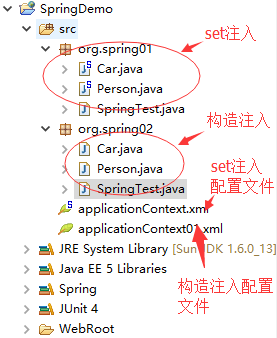
我们可以看到,set方法和构造方法都可以设值成功, 实际开发中最常用到的是set方法设值。但这两种依赖注入的方式并没有绝对的好坏,只是使用的场合不同.
使用构造注入可以在构建对象的同时完成依赖关系到的建立,所以如果要建立的对象的关系很多,使用构造注入会在构造方法上留下很多参数,可读性极差,所以当对象的关系比较多的时候采用set方法注入.
使用set方法注入是通过类的setter方法完成依赖关系的设置的,所以不能保证相关的数据在执行时不被更改设定。所以如果想使一些数据变为只读或者私有,就要采用构造注入了.
建议采用以set注入为主,构造注入为辅的注入策略。对于依赖关系无须变化的注入,尽量采用构造注入;而其他的依赖关系的注入,则考虑采用set注入.
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我.
原文链接:http://blog.csdn.net/weixin_36380516/article/details/72301260?utm_source=tuicool&utm_medium=referral 。
最后此篇关于Spring依赖注入的两种方式(根据实例详解)的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于Spring依赖注入的两种方式(根据实例详解)的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
全称“Java Virtual Machine statistics monitoring tool”(statistics 统计;monitoring 监控;tool 工具) 用于监控虚拟机的各种运
主要是讲下Mongodb的索引的查看、创建、删除、类型说明,还有就是Explain执行计划的解释说明。 可以转载,但请注明出处。
1>单线程或者单进程 相当于短链接,当accept之后,就开始数据的接收和数据的发送,不接受新的连接,即一个server,一个client 不存在并发。 2>循环服务器和并发服务器
详解 linux中的关机和重启命令 一 shutdown命令 shutdown [选项] 时间 选项: ?
首先,将json串转为一个JObject对象: ? 1
matplotlib官网 matplotlib库默认英文字体 添加黑体(‘SimHei')为绘图字体 代码: plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei'
在并发编程中,synchronized关键字是常出现的角色。之前我们都称呼synchronized关键字为重量锁,但是在jdk1.6中对synchronized进行了优化,引入了偏向锁、轻量锁。本篇
一般我们的项目中会使用1到2个数据库连接配置,同程艺龙的数据库连接配置被收拢到统一的配置中心,由DBA统一配置和维护,业务方通过某个字符串配置拿到的是Connection对象。
实例如下: ? 1
1. MemoryCahe NetCore中的缓存和System.Runtime.Caching很相似,但是在功能上做了增强,缓存的key支持object类型;提供了泛型支持;可以读缓存和单个缓存
argument是javascript中函数的一个特殊参数,例如下文,利用argument访问函数参数,判断函数是否执行 复制代码 代码如下: <script
一不小心装了一个Redis服务,开了一个全网的默认端口,一开始以为这台服务器没有公网ip,结果发现之后悔之莫及啊 某天发现cpu load高的出奇,发现一个minerd进程 占了大量cpu,googl
今天写这个是为了 提醒自己 编程过程 不仅要有逻辑 思想 还有要规范 代码 这样可读性 1、PHP 编程规范与编码习惯最主要的有以下几点: 1 文件说明 2 funct
摘要:虚拟机安装时一般都采用最小化安装,默认没有lspci工具。一台测试虚拟网卡性能的虚拟机,需要lspci工具来查看网卡的类型。本文描述了在一个虚拟机中安装lspci工具的具体步骤。 由于要测试
1、修改用户进程可打开文件数限制 在Linux平台上,无论编写客户端程序还是服务端程序,在进行高并发TCP连接处理时,最高的并发数量都要受到系统对用户单一进程同时可打开文件数量的限制(这是因为系统
目录 算术运算符 基本四则运算符 增量赋值运算符 自增/自减运算符 关系运算符 逻
如下所示: ? 1
MapperScannerConfigurer之sqlSessionFactory注入方式讲解 首先,Mybatis中的有一段配置非常方便,省去我们去写DaoImpl(Dao层实现类)的时间,这个
Linux的网络虚拟化是LXC项目中的一个子项目,LXC包括文件系统虚拟化,进程空间虚拟化,用户虚拟化,网络虚拟化,等等,这里使用LXC的网络虚拟化来模拟多个网络环境。 本文从基本的网络设备讲
? 1

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!