- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章探究ASP.NET Core Middleware实现方法由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
概念 。
ASP.NET Core Middleware是在应用程序处理管道pipeline中用于处理请求和操作响应的组件.
每个组件:
特性和行为 。
ASP.NET Core处理管道由一系列请求委托组成,一环接一环的被调用, 下面给出自己绘制的Middleware pipeline流程图:

从上图可以看出,请求自进入处理管道,经历了四个中间件,每个中间件都包含后续紧邻中间件 执行委托(next)的引用,同时每个中间件在交棒之前和交棒之后可以自行决定参与一些Http请求和响应的逻辑处理.
每个中间件还可以决定不将请求转发给下一个委托,这称为请求管道的短路(短路是有必要的,某些专有中间件比如 StaticFileMiddleware 可以在完成功能之后,避免请求被转发到其他动态处理过程).
源码实现 。
观察一个标准的中间件代码的写法和用法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Alyio.AspNetCore.ApiMessages;
using Gridsum.WebDissector.Common;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
namespace Gridsum.WebDissector
{
sealed
class
AuthorizationMiddleware
{
private
readonly RequestDelegate _next;
// 下一个中间件执行委托的引用
public
AuthorizationMiddleware(RequestDelegate next)
{
_next = next;
}
public
Task Invoke(HttpContext context)
// 贯穿始终的HttpContext对象
{
if
(context.Request.Path.Value.StartsWith(
"/api/"
))
{
return
_next(context);
}
if
(context.User.Identity.IsAuthenticated && context.User().DisallowBrowseWebsite)
{
throw
new
ForbiddenMessage(
"You are not allow to browse the website."
);
}
return
_next(context);
}
}
}
public
static
IApplicationBuilder UserAuthorization(
this
IApplicationBuilder app)
{
return
app.UseMiddleware<AuthorizationMiddleware>();
}
// 启用该中间件,也就是注册该中间件
app.UserAuthorization();
|
标准的中间件使用方式是如此简单明了,带着几个问题探究一下源码实现 。
(1).中间件传参是怎样完成的: app.UseMiddleware<Authorization>(AuthOption); 我们传参的时候,为什么能自动注入中间件构造函数非第1个参数 。
(2).编写中间件的时候,为什么必须要定义特定的 Invoke/InvokeAsync 函数?
(3).设定中间件的顺序很重要,中间件的嵌套顺序是怎么确定的 ?
思考以上标准中间件的行为: 输入下一个中间件的执行委托Next, 定义当前中间件的执行委托Invoke/InvokeAsync; 。
每个中间件完成了 Func<RequestDelegate,RequestDelegate>这样的行为; 。
通过参数next与下一个中间件的执行委托Invoke/InvokeAsync 建立"链式"关系.
|
1
|
public
delegate Task RequestDelegate(HttpContext context);
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
|
//-----------------节选自 Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder.UseMiddlewareExtensions------------------
/// <summary>
/// Adds a middleware type to the application's request pipeline.
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="TMiddleware">The middleware type.</typeparam>
/// <param name="app">The <see cref="IApplicationBuilder"/> instance.</param>
/// <param name="args">The arguments to pass to the middleware type instance's constructor.</param>
/// <returns>The <see cref="IApplicationBuilder"/> instance.</returns>
public
static
IApplicationBuilder UseMiddleware<TMiddleware>(
this
IApplicationBuilder app, params object[] args)
{
return
app.UseMiddleware(typeof(TMiddleware), args);
}
/// <summary>
/// Adds a middleware type to the application's request pipeline.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="app">The <see cref="IApplicationBuilder"/> instance.</param>
/// <param name="middleware">The middleware type.</param>
/// <param name="args">The arguments to pass to the middleware type instance's constructor.</param>
/// <returns>The <see cref="IApplicationBuilder"/> instance.</returns>
public
static
IApplicationBuilder UseMiddleware(
this
IApplicationBuilder app, Type middleware, params object[] args)
{
if
(typeof(IMiddleware).GetTypeInfo().IsAssignableFrom(middleware.GetTypeInfo()))
{
// IMiddleware doesn't support passing args directly since it's
// activated from the container
if
(args.Length >
0
)
{
throw
new
NotSupportedException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareExplicitArgumentsNotSupported(typeof(IMiddleware)));
}
return
UseMiddlewareInterface(app, middleware);
}
var applicationServices = app.ApplicationServices;
return
app.Use(next =>
{
var methods = middleware.GetMethods(BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.Public);
// 执行委托名称被限制为Invoke/InvokeAsync
var invokeMethods = methods.Where(m =>
string.Equals(m.Name, InvokeMethodName, StringComparison.Ordinal)
|| string.Equals(m.Name, InvokeAsyncMethodName, StringComparison.Ordinal)
).ToArray();
if
(invokeMethods.Length >
1
)
{
throw
new
InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddleMutlipleInvokes(InvokeMethodName, InvokeAsyncMethodName));
}
if
(invokeMethods.Length ==
0
)
{
throw
new
InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareNoInvokeMethod(InvokeMethodName, InvokeAsyncMethodName, middleware));
}
var methodInfo = invokeMethods[
0
];
if
(!typeof(Task).IsAssignableFrom(methodInfo.ReturnType))
{
throw
new
InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareNonTaskReturnType(InvokeMethodName, InvokeAsyncMethodName, nameof(Task)));
}
var parameters = methodInfo.GetParameters();
if
(parameters.Length ==
0
|| parameters[
0
].ParameterType != typeof(HttpContext))
{
throw
new
InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareNoParameters(InvokeMethodName, InvokeAsyncMethodName, nameof(HttpContext)));
}
var ctorArgs =
new
object[args.Length +
1
];
ctorArgs[
0
] = next;
Array.Copy(args,
0
, ctorArgs,
1
, args.Length);
// 通过反射形成中间件实例的时候,构造函数第一个参数被指定为 下一个中间件的执行委托
var instance = ActivatorUtilities.CreateInstance(app.ApplicationServices, middleware, ctorArgs);
if
(parameters.Length ==
1
)
{
return
(RequestDelegate)methodInfo.CreateDelegate(typeof(RequestDelegate), instance);
}
// 当前执行委托除了可指定HttpContext参数以外, 还可以注入更多的依赖参数
var factory = Compile<object>(methodInfo, parameters);
return
context =>
{
var serviceProvider = context.RequestServices ?? applicationServices;
if
(serviceProvider ==
null
)
{
throw
new
InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareIServiceProviderNotAvailable(nameof(IServiceProvider)));
}
return
factory(instance, context, serviceProvider);
};
});
}
//-------------------节选自 Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder.Internal.ApplicationBuilder-------------------
private
readonly IList<Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>> _components =
new
List<Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>>();
publicIApplicationBuilder Use(Func<RequestDelegate,RequestDelegate> middleware)
{
this
._components.Add(middleware);
return
this
;
}
public
RequestDelegate Build()
{
RequestDelegate app = context =>
{
context.Response.StatusCode =
404
;
return
Task.CompletedTask;
};
foreach (var component in _components.Reverse())
{
app = component(app);
}
return
app;
}
|
通过以上代码我们可以看出:

分析源码:回答上面的问题:
附:非标准中间件的用法 。
短路中间件、 分叉中间件、条件中间件 。
整个处理管道的形成,存在一些管道分叉或者临时插入中间件的行为,一些重要方法可供使用 。
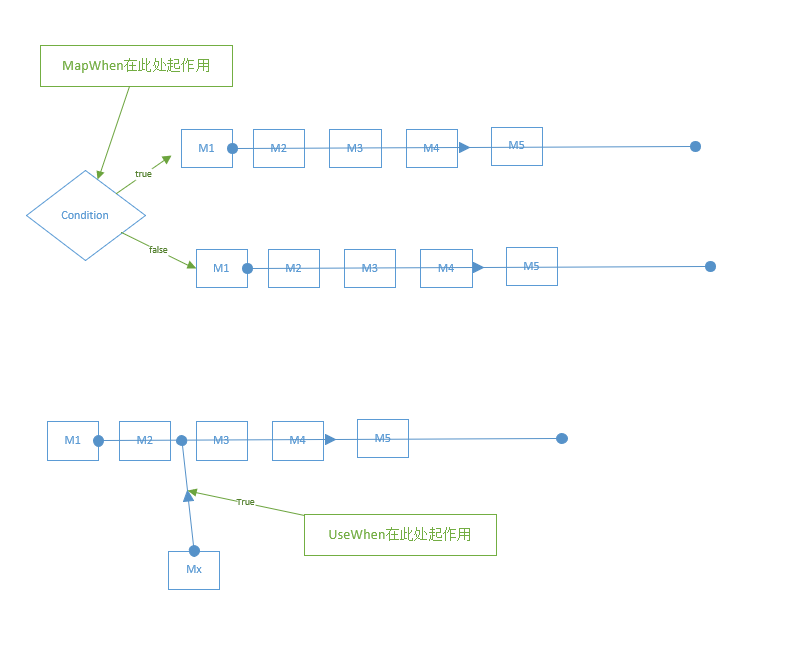
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我.
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/mi12205599/p/10334472.html 。
最后此篇关于探究ASP.NET Core Middleware实现方法的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于探究ASP.NET Core Middleware实现方法的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我想了解 Ruby 方法 methods() 是如何工作的。 我尝试使用“ruby 方法”在 Google 上搜索,但这不是我需要的。 我也看过 ruby-doc.org,但我没有找到这种方法。
Test 方法 对指定的字符串执行一个正则表达式搜索,并返回一个 Boolean 值指示是否找到匹配的模式。 object.Test(string) 参数 object 必选项。总是一个
Replace 方法 替换在正则表达式查找中找到的文本。 object.Replace(string1, string2) 参数 object 必选项。总是一个 RegExp 对象的名称。
Raise 方法 生成运行时错误 object.Raise(number, source, description, helpfile, helpcontext) 参数 object 应为
Execute 方法 对指定的字符串执行正则表达式搜索。 object.Execute(string) 参数 object 必选项。总是一个 RegExp 对象的名称。 string
Clear 方法 清除 Err 对象的所有属性设置。 object.Clear object 应为 Err 对象的名称。 说明 在错误处理后,使用 Clear 显式地清除 Err 对象。此
CopyFile 方法 将一个或多个文件从某位置复制到另一位置。 object.CopyFile source, destination[, overwrite] 参数 object 必选
Copy 方法 将指定的文件或文件夹从某位置复制到另一位置。 object.Copy destination[, overwrite] 参数 object 必选项。应为 File 或 F
Close 方法 关闭打开的 TextStream 文件。 object.Close object 应为 TextStream 对象的名称。 说明 下面例子举例说明如何使用 Close 方
BuildPath 方法 向现有路径后添加名称。 object.BuildPath(path, name) 参数 object 必选项。应为 FileSystemObject 对象的名称
GetFolder 方法 返回与指定的路径中某文件夹相应的 Folder 对象。 object.GetFolder(folderspec) 参数 object 必选项。应为 FileSy
GetFileName 方法 返回指定路径(不是指定驱动器路径部分)的最后一个文件或文件夹。 object.GetFileName(pathspec) 参数 object 必选项。应为
GetFile 方法 返回与指定路径中某文件相应的 File 对象。 object.GetFile(filespec) 参数 object 必选项。应为 FileSystemObject
GetExtensionName 方法 返回字符串,该字符串包含路径最后一个组成部分的扩展名。 object.GetExtensionName(path) 参数 object 必选项。应
GetDriveName 方法 返回包含指定路径中驱动器名的字符串。 object.GetDriveName(path) 参数 object 必选项。应为 FileSystemObjec
GetDrive 方法 返回与指定的路径中驱动器相对应的 Drive 对象。 object.GetDrive drivespec 参数 object 必选项。应为 FileSystemO
GetBaseName 方法 返回字符串,其中包含文件的基本名 (不带扩展名), 或者提供的路径说明中的文件夹。 object.GetBaseName(path) 参数 object 必
GetAbsolutePathName 方法 从提供的指定路径中返回完整且含义明确的路径。 object.GetAbsolutePathName(pathspec) 参数 object
FolderExists 方法 如果指定的文件夹存在,则返回 True;否则返回 False。 object.FolderExists(folderspec) 参数 object 必选项
FileExists 方法 如果指定的文件存在返回 True;否则返回 False。 object.FileExists(filespec) 参数 object 必选项。应为 FileS

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!