CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章举例详解iOS开发过程中的沙盒机制与文件由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
ios沙盒机制 ios应用程序只能在为该改程序创建的文件系统中读取文件,不可以去其它地方访问,此区域被成为沙盒,所以所有的非代码文件都要保存在此,例如图像,图标,声音,映像,属性列表,文本文件等.
- 每个应用程序都有自己的存储空间
- 应用程序不能翻过自己的围墙去访问别的存储空间的内容
打开模拟器沙盒目录 方法1、可以设置显示隐藏文件,然后在finder下直接打开。设置查看隐藏文件的方法如下:打开终端,输入命名 <p class="p1">显示mac隐藏文件的命令:
。
复制代码 代码如下:
defaults write com.apple.finder appleshowallfiles -bool true</p><p class="p1">
隐藏mac隐藏文件的命令:
复制代码 代码如下:
defaults write com.apple.finder appleshowallfiles -bool false</p>
现在能看到资源库文件夹了。 打开资源库后找到/application support/iphone simulator/文件夹。这里面就是模拟器的各个程序的沙盒目录了。 方法2、这种方法更方便,在finder上点->前往 然后按住"option"键,就会出现"资源库",其他同上 。
。
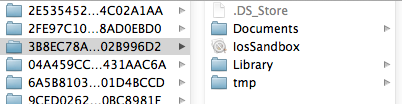
目录结构 默认情况下,每个沙盒含有3个文件夹:documents, library 和 tmp。因为应用的沙盒机制,应用只能在几个目录下读写文件 documents:苹果建议将程序中建立的或在程序中浏览到的文件数据保存在该目录下,itunes备份和恢复的时候会包括此目录 library:存储程序的默认设置或其它状态信息; library/caches:存放缓存文件,itunes不会备份此目录,此目录下文件不会在应用退出删除 tmp:提供一个即时创建临时文件的地方.
itunes在与iphone同步时,备份所有的documents和library文件。 iphone在重启时,会丢弃所有的tmp文件。 这是上面提到的三个目录 :documents、library、 tmp 。
几个常用的代码示例: 1、获取程序的home目录 。
复制代码 代码如下:
nsstring *homedirectory = nshomedirectory();
nslog(@"path:%@", homedirectory);
2、获取document目录 。
复制代码 代码如下:
nsarray *paths = nssearchpathfordirectoriesindomains(nsdocumentdirectory, nsuserdomainmask, yes);
nsstring *path = [paths objectatindex:0];
nslog(@"path:%@", path);
3、获取cache目录 。
复制代码 代码如下:
nsarray *paths = nssearchpathfordirectoriesindomains(nscachesdirectory, nsuserdomainmask, yes);
nsstring *path = [paths objectatindex:0];
nslog(@"%@", path);
4、获取library目录 。
复制代码 代码如下:
nsarray *paths = nssearchpathfordirectoriesindomains(nslibrarydirectory, nsuserdomainmask, yes);
nsstring *path = [paths objectatindex:0];
nslog(@"%@", path);
5、获取tmp目录 。
复制代码 代码如下:
nsstring *tmpdir = nstemporarydirectory();
nslog(@"%@", tmpdir);
6、写入文件 。
复制代码 代码如下:
nsarray *paths = nssearchpathfordirectoriesindomains(nsdocumentdirectory, nsuserdomainmask, yes);
nsstring *docdir = [paths objectatindex:0];
if (!docdir) {
nslog(@"documents 目录未找到");
}
nsarray *array = [[nsarray alloc] initwithobjects:@"内容",@"content",nil];
nsstring *filepath = [docdir stringbyappendingpathcomponent:@"testfile.txt"];
[array writetofile:filepath atomically:yes];
7、写入文件 。
复制代码 代码如下:
nsarray *paths = nssearchpathfordirectoriesindomains(nsdocumentdirectory, nsuserdomainmask, yes);
nsstring *docdir = [paths objectatindex:0];
nsstring *filepath = [docdir stringbyappendingpathcomponent:@"testfile.txt"];
nsarray *array = [[nsarray alloc]initwithcontentsoffile:filepath];
nslog(@"%@", array);
。
8、判断一个文件是否存在,传入全路径(fileexistsatpath) 。
复制代码 代码如下:
// 创建文件管理器
nsfilemanager * filemanager = [nsfilemanager defaultmanager];
nsstring * documents = [nssearchpathfordirectoriesindomains(nsdocumentdirectory, nsuserdomainmask, yes)lastobject];
nsstring * filepath = [documents stringbyappendingpathcomponent:@"test"];
// 判断一个文件是否存在,传入全路径
if ([filemanager fileexistsatpath:filepath]) {
nslog(@"it is exit");
}
。
9、在documents里创建目录 。
复制代码 代码如下:
nsarray *paths = nssearchpathfordirectoriesindomains(nsdocumentdirectory, nsuserdomainmask, yes);
nsstring *documentsdirectory = [paths objectatindex:0];
nslog(@"documentsdirectory%@",documentsdirectory);
nsfilemanager *filemanager = [nsfilemanager defaultmanager];
nsstring *testdirectory = [documentsdirectory stringbyappendingpathcomponent:@"test"];
// 创建目录
[filemanager createdirectoryatpath:testdirectory withintermediatedirectories:yes attributes:nil error:nil];
。
10、在目录下创建文件 。
复制代码 代码如下:
nsstring *testpath = [testdirectory stringbyappendingpathcomponent:@"test00.txt"];
nsstring *testpath2 = [testdirectory stringbyappendingpathcomponent:@"test22.txt"];
nsstring *testpath3 = [testdirectory stringbyappendingpathcomponent:@"test33.txt"];
nsstring *string = @"写入内容,write string";
[filemanager createfileatpath:testpath contents:[string datausingencoding:nsutf8stringencoding] attributes:nil];
[filemanager createfileatpath:testpath2 contents:[string datausingencoding:nsutf8stringencoding] attributes:nil];
[filemanager createfileatpath:testpath3 contents:[string datausingencoding:nsutf8stringencoding] attributes:nil];
。
11、获取目录列里所有文件名 两种方法获取:subpathsofdirectoryatpath 和subpathsatpath 。
复制代码 代码如下:
nsarray *paths = nssearchpathfordirectoriesindomains(nsdocumentdirectory, nsuserdomainmask, yes);
nsstring *documentsdirectory = [paths objectatindex:0];
nslog(@"documentsdirectory%@",documentsdirectory);
nsfilemanager *filemanage = [nsfilemanager defaultmanager];
nsstring *mydirectory = [documentsdirectory stringbyappendingpathcomponent:@"test"];
nsarray *file = [filemanage subpathsofdirectoryatpath: mydirectory error:nil];
nslog(@"%@",file);
nsarray *files = [filemanage subpathsatpath: mydirectory ];
nslog(@"%@",files);
。
12、filemanager使用操作当前目录 。
复制代码 代码如下:
//创建文件管理器
nsfilemanager *filemanager = [nsfilemanager defaultmanager];
nsarray *paths = nssearchpathfordirectoriesindomains(nsdocumentdirectory, nsuserdomainmask, yes);
nsstring *documentsdirectory = [paths objectatindex:0];
//更改到待操作的目录下
[filemanager changecurrentdirectorypath:[documentsdirectory stringbyexpandingtildeinpath]];
//创建文件filename文件名称,contents文件的内容,如果开始没有内容可以设置为nil,attributes文件的属性,初始为nil
nsstring * filename = @"testfilensfilemanager.txt";
nsarray *array = [[nsarray alloc] initwithobjects:@"hello world",@"hello world1", @"hello world2",nil];
[filemanager createfileatpath:filename contents:array attributes:nil];
13、删除文件 。
复制代码 代码如下:
[filemanager removeitematpath:filename error:nil];
最后此篇关于举例详解iOS开发过程中的沙盒机制与文件的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于举例详解iOS开发过程中的沙盒机制与文件的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。


我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!