- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章使用Python下的XSLT API进行web开发的简单教程由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
Kafka 样式的 soap 端点 。
Christopher Dix 所开发的“Kafka — XSL SOAP 工具箱”(请参阅 参考资料)是一种用于构造 SOAP 端点的 XSLT 框架。它只涵盖了 SOAP 1.1,但 Kafka 端点演示了传递 UserLand SOAP 验证器(UserLand SOAP Validator)的能力,并且根据 SOAP 1.2 对它进行更新似乎并不太困难。 清单 1展示了一个样本 Kafka 端点:求两数之和的 SOAP 服务器(一个典型而简单的 SOAP 样本).
清单 1. 求两数之和的 Kafka SOAP 端点 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
<?xml version
=
"1.0"
encoding
=
"UTF-8"
?>
<xsl:stylesheet version
=
"1.0"
xmlns:method
=
"http://www.topxml.com/"
xmlns:xsl
=
"http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
>
<!
-
-
add.xsl : Kafka SOAP Endpoint Example, with modifications
-
-
>
<!
-
-
Import soap.xsl to use the framework
-
-
>
<xsl:
import
href
=
"kafka/soap.xsl"
/
>
<xsl:output method
=
"xml"
encoding
=
"utf-8"
omit
-
xml
-
declaration
=
"yes"
/
>
<!
-
-
Define the
global
variables
for
the framework
-
-
>
<xsl:variable name
=
"Method"
>Add<
/
xsl:variable>
<xsl:variable name
=
"MethodNS"
>http:
/
/
www.topxml.com
/
<
/
xsl:variable>
<!
-
-
Add : Add two numbers
and
return
the
sum
-
-
>
<!
-
-
Function Add( A as Double, B as Double ) as Double
-
-
>
<xsl:template name
=
"ProcessPayload"
>
<xsl:param name
=
"Payload"
/
>
<xsl:
for
-
each select
=
"$Payload"
>
<!
-
-
This
is
how to retrieve parameters
from
the
input
-
-
>
<xsl:variable name
=
"A"
select
=
"number(A|method:A)"
/
>
<xsl:variable name
=
"B"
select
=
"number(B|method:B)"
/
>
<!
-
-
The WriteParameter template takes the qualified name
for
a response parameter as well as its value
and
a QName specifying the tpe (
for
the xsi:
type
attribute)
-
-
>
<xsl:call
-
template name
=
"WriteParameter"
>
<xsl:with
-
param name
=
"p"
select
=
"'Result'"
/
>
<xsl:with
-
param name
=
"v"
select
=
"$A + $B"
/
>
<xsl:with
-
param name
=
"t"
select
=
"'xsd:double'"
/
>
<
/
xsl:call
-
template>
<
/
xsl:
for
-
each>
<
/
xsl:template>
<
/
xsl:stylesheet>
|
XSLT 端点导入 SOAP 框架(文件 kafka/soap.xsl),然后设置该框架将要使用的参数,并设置它在处理构成 SOAP 消息的整个 XML 文档的过程中将要分派的模板。全局变量 Method 和 MethodNS 声明了组成消息的 XML 元素。在处理完 SOAP 信封之后,该框架调用 ProcessPayload 模板,该模板传入了 XML 主体的有效负载。 xsl:for-each 是将上下文切换成想要的节点的标准技巧。参数 A 和 B 是使用简单 XPaths 从这个元素读取的,而框架被再次调用以帮助写出响应参数。 WriteParameter 模板让您指定元素名称、数据类型和每个输出参数的值。本示例中的响应值是将两个输入参数相加所得的结果.
将这个端点部署为服务器相当于设置一个 HTTP 侦听器。Python 的 BaseHTTPServer 模块向您提供了所需的机制,能够轻而易举地处理该协议的 HTTP 部分。请参阅 清单 2.
清单 2. 用于清单 1 中所实现的 Kafka SOAP 端点的 Python HTTP 框架 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
|
#HTTP Listener code for SOAP server
import
BaseHTTPServer
#The processor class is the core of the XSLT API
from
Ft.Xml.Xslt
import
Processor
#4XSLT uses an InputSource system for reading XML
from
Ft.Xml
import
InputSource
SOAP_IMPL_FILE
=
"add.xsl"
class
KafkaSoapHandler(BaseHTTPServer.BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
def
init(
cls
):
from
Ft.Lib
import
Uri
#Set up a processor instance to use
KafkaSoapHandler.processor
=
Processor.Processor()
#Load it with add.xsl
add_uri
=
Uri.OsPathToUri(SOAP_IMPL_FILE, attemptAbsolute
=
1
)
transform
=
InputSource.DefaultFactory.fromUri(add_uri)
KafkaSoapHandler.processor.appendStylesheet(transform)
#Now the processor is prepped with a transform and can be used
#over and over for the same transform
return
#Make init() a static method of the class
init
=
classmethod
(init)
def
do_POST(
self
):
clen
=
self
.headers.getheader(
'content-length'
)
if
clen:
clen
=
int
(clen)
else
:
print
'POST ERROR: missing content-length'
return
if
self
.path !
=
'/add'
:
self
.send_error(
404
)
input_body
=
self
.rfile.read(clen)
#input_body is the request SOAP envelope and contents
response_body
=
self
._run_through_kafka(input_body)
#response_body is the response SOAP envelope and contents
self
._send_response(
200
,
'OK'
, response_body)
return
def
_run_through_kafka(
self
, body):
#In 4Suite all InputSources have base URIs in case they refer to
#other URIs in some way and resolution is required.
#The SOAP messages will not have any such URI references,
#So use a dummy base URI
source
=
InputSource.DefaultFactory.fromString(body,
"urn:dummy"
)
response
=
self
.processor.run(source)
return
response
def
_send_response(
self
, code, msg, body):
#Prepare a normal response
self
.send_response(
200
,
'OK'
)
#Send standard HTP headers
self
.send_header(
'Content-type'
,
'text/html; charset=utf-8'
)
self
.send_header(
"Connection"
,
"close"
)
self
.send_header(
"Accept-Ranges"
,
"bytes"
)
self
.send_header(
'Content-length'
,
len
(body)
-
1
)
self
.end_headers()
#Send the response prepared by the SOAP end point
self
.wfile.write(body)
return
listen_on_port
=
8888
#Set up to run on local machine
server_address
=
(
'127.0.0.1'
, listen_on_port)
KafkaSoapHandler.init()
httpd
=
BaseHTTPServer.HTTPServer(server_address, KafkaSoapHandler)
print
"Listening on port"
, listen_on_port
#Go into a the main event loop
httpd.serve_forever()
|
我们详细地注释了该清单,因此它应该是易于理解的。请注意,这段代码非常简单,这是因为它仅需处理该协议的 HTTP 部分,而将 XML 和 SOAP 部分的工作交由 Kafka 框架完成。该服务器专用于一个端点,因此它只须对 XSLT 转换进行一次解析和设置,然后它就可以简单地反复为每次新的请求运行该转换。这就是将处理器设置迁移到特殊的类方法中的原因,处理程序一注册到服务器就立即调用该方法。 classmethod 内置方法是 Python 2.2 中的新功能,实际上该版本是本例和后面的示例所必需的版本。它提供了隐式类对象 (cls) ,您可以将静态数据(如已准备好的处理器实例)附加到该对象上,然后通常可以通过普通方法上的 self 实例引用来使用该数据.
我们使用 SOAPpy 0.10.1 的最新发行版(请参阅 参考资料)测试了该端点,该发行版具有许多很棒的新功能,稍后我们将在本专栏中进行讨论。 清单 3是使用该端点的 SOAPpy 客户机。打开一个命令 shell 并为服务器运行 python listing2.py。然后打开另一个 shell 并运行 python listing3.py,该命令将报告正确的响应,形如 Add result: 7.0.
清单 3: 用于求两数之和的 SOAPpy 客户机 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
import
SOAPpy
ENDPOINT
=
"http://localhost:8888/add"
ADD_NS
=
"http://www.topxml.com/"
remote
=
SOAPpy.SOAPProxy(ENDPOINT, namespace
=
ADD_NS)
print
"Add result:"
, remote.Add(A
=
3
, B
=
4
)
|
使用描述 。
正如我们先前所说的,不仅 XML 中的有效负载是有用的 Web 服务特性,描述也是有用的特性。 清单 4是一个用于添加服务的 WSDL 文件,它是根据 Christopher Dix 的原始文件修改而得到的。它是 WSDL 1.1 版本的.
清单 4. 用于添加服务的 WSDL 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
<?xml version
=
"1.0"
encoding
=
"UTF-8"
?>
<definitions name
=
"adder"
targetNamespace
=
"http://www.topxml.com/"
xmlns:tns
=
"http://www.topxml.com/"
xmlns:xsd
=
"http://www.w3.org/1999/XMLSchema"
xmlns
=
"http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/"
>
<message name
=
"Add"
>
<part name
=
"A"
type
=
"xsd:double"
/
>
<part name
=
"B"
type
=
"xsd:double"
/
>
<
/
message>
<message name
=
"AddResponse"
>
<part name
=
"param"
type
=
"xsd:double"
/
>
<
/
message>
<portType name
=
"adder-port-type"
>
<operation name
=
"Add"
>
<
input
message
=
"tns:Add"
/
>
<output message
=
"tns:AddResponse"
/
>
<
/
operation>
<
/
portType>
<binding name
=
"adder-soap-binding"
type
=
"tns:adder-port-type"
xmlns:soap
=
"http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/soap/"
>
<soap:binding transport
=
"http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/http"
style
=
"rpc"
/
>
<operation name
=
"Add"
>
<soap:operation soapAction
=
"http://tempuri.org/"
/
>
<
input
>
<soap:body use
=
"encoded"
namespace
=
"http://www.topxml.com/"
encodingStyle
=
"http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/"
/
>
<
/
input
>
<output>
<soap:body use
=
"encoded"
namespace
=
"http://www.topxml.com/"
encodingStyle
=
"http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/"
/
>
<
/
output>
<
/
operation>
<
/
binding>
<service name
=
"adder-service"
>
<port name
=
"adder-port"
binding
=
"tns:adder-soap-binding"
>
<soap:address location
=
"http://127.0.0.1:8888/add"
xmlns:soap
=
"http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/soap/"
/
>
<
/
port>
<
/
service>
<
/
definitions>
|
清单 5提供了一个为端点用户呈现有用信息的 XSLT 脚本。它是从先前的 developerWorks 文章“WSDL processing with XSLT”(请参阅 参考资料)中所开发的一个转换改编而来的。它使用了许多自由方式(liberty)和快捷方式(尤其是在它处理 WSDL 上下文中的限定名时),但它也许可用于目前使用的大多数 WSDL 1.1 文件.
清单 5. XSLT 脚本 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
|
<?xml version
=
"1.0"
encoding
=
"utf-8"
?>
<xsl:stylesheet version
=
'1.0'
xmlns:xsl
=
"http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:wsdl
=
"http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/"
xmlns:soap
=
"http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/soap/"
>
<xsl:output method
=
'html'
/
>
<!
-
-
Lookup tables
for
messages, portTypes, bindings
and
services
-
-
>
<xsl:key name
=
'message'
match
=
"wsdl:definitions/wsdl:message"
use
=
'@name'
/
>
<xsl:key name
=
'port-type'
match
=
"wsdl:definitions/wsdl:portType"
use
=
'@name'
/
>
<xsl:key name
=
'binding'
match
=
"wsdl:definitions/wsdl:binding"
use
=
'@name'
/
>
<xsl:key name
=
'service'
match
=
"wsdl:definitions/wsdl:service"
use
=
'@name'
/
>
<xsl:template match
=
'/'
>
<html>
<head>
<title>
Service summary: <xsl:value
-
of select
=
'wsdl:definitions/@name'
/
>
<
/
title>
<meta http
-
equiv
=
"content-type"
content
=
"text/html"
charset
=
"UTF-8"
/
>
<
/
head>
<body>
<h1>
Service summary: <xsl:value
-
of select
=
'wsdl:definitions/@name'
/
>
<
/
h1>
<p><xsl:value
-
of select
=
'wsdl:definitions/@documentation'
/
><
/
p>
<xsl:
apply
-
templates select
=
"wsdl:definitions/wsdl:service"
/
>
<
/
body>
<
/
html>
<
/
xsl:template>
<xsl:template match
=
'wsdl:service'
>
<div style
=
"background: #ccffff"
>
Service
"<xsl:value-of select='@name'/>"
hosted at
<code>
<xsl:value
-
of select
=
'wsdl:port/soap:address/@location'
/
>
<
/
code>
<xsl:variable name
=
"binding"
select
=
"key(
'binding'
,
substring
-
after(wsdl:port
/
@binding,
':'
))"
/
>
<xsl:variable name
=
"port-type"
select
=
"key(
'port-type'
,
substring
-
after($binding
/
@
type
,
':'
))"
/
>
<xsl:
apply
-
templates select
=
"$port-type/wsdl:operation"
/
>
<
/
div>
<
/
xsl:template>
<xsl:template match
=
'wsdl:operation'
>
<p>Operation
"<b><xsl:value-of select='@name'/></b>"
message details:<
/
p>
<!
-
-
Yes, should sue CSS, but keep this example simple
-
-
>
<table border
=
"1"
width
=
"50%"
>
<tbody>
<xsl:
if
test
=
"wsdl:input"
>
<xsl:call
-
template name
=
'message-role'
>
<xsl:with
-
param name
=
"role-node"
select
=
"wsdl:input"
/
>
<
/
xsl:call
-
template>
<
/
xsl:
if
>
<xsl:
if
test
=
"wsdl:output"
>
<xsl:call
-
template name
=
'message-role'
>
<xsl:with
-
param name
=
"role-node"
select
=
"wsdl:output"
/
>
<
/
xsl:call
-
template>
<
/
xsl:
if
>
<xsl:
if
test
=
"wsdl:fault"
>
<xsl:call
-
template name
=
'message-role'
>
<xsl:with
-
param name
=
"role-node"
select
=
"wsdl:fault"
/
>
<
/
xsl:call
-
template>
<
/
xsl:
if
>
<
/
tbody>
<
/
table>
<
/
xsl:template>
<xsl:template name
=
'message-role'
>
<xsl:param name
=
"role-node"
/
>
<xsl:variable name
=
"role-name"
select
=
"local-name($role-node)"
/
>
<xsl:variable name
=
"message"
select
=
"key(
'message'
,
substring
-
after($role
-
node
/
@message,
':'
))"
/
>
<tr>
<td><xsl:value
-
of select
=
'$role-name'
/
><
/
td>
<td>
<table width
=
"100%"
>
<xsl:
apply
-
templates select
=
"$message/wsdl:part"
/
>
<
/
table>
<
/
td>
<
/
tr>
<
/
xsl:template>
<xsl:template match
=
'wsdl:part'
>
<tr>
<td width
=
"50%"
><b><xsl:value
-
of select
=
'@name'
/
><
/
b><
/
td>
<td><xsl:value
-
of select
=
'@type'
/
><
/
td>
<
/
tr>
<
/
xsl:template>
<
/
xsl:stylesheet>
|
通常在 Web 服务本身所在的主机上提供该服务人性化的 WSDL 描述是很方便的。 清单 6是 清单 2的变体,它也完成这一任务。它实际上提供三种功能:
清单 6. 清单 2 的变体 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
|
#HTTP Listener code for SOAP server
import
BaseHTTPServer
#The processor class is the core of the XSLT API
from
Ft.Xml.Xslt
import
Processor
#4XSLT uses an InputSource system for reading XML
from
Ft.Xml
import
InputSource
SOAP_IMPL_FILE
=
"add.xsl"
WSDL_FILE
=
"listing4.xml"
HTML_VIEW_TRANSFORM
=
"listing5.xslt"
class
KafkaSoapHandler(BaseHTTPServer.BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
def
init(
cls
):
from
Ft.Lib
import
Uri
#Set up a processor instance to use
cls
.processor
=
Processor.Processor()
#Load it with add.xsl
add_uri
=
Uri.OsPathToUri(SOAP_IMPL_FILE, attemptAbsolute
=
1
)
transform
=
InputSource.DefaultFactory.fromUri(add_uri)
cls
.processor.appendStylesheet(transform)
#Now the processor is prepped with a transform and can be used
#over and over for the same transform
#Prep for WSDL requests
cls
.wsdl
=
open
(WSDL_FILE).read()
return
#Make init() a static method of the class
init
=
classmethod
(init)
def
do_POST(
self
):
clen
=
self
.headers.getheader(
'content-length'
)
if
clen:
clen
=
int
(clen)
else
:
print
'POST ERROR: missing content-length'
return
if
self
.path !
=
'/add'
:
self
.send_error(
404
)
input_body
=
self
.rfile.read(clen)
#input_body is the request SOAP envelope and contents
response_body
=
self
._run_through_kafka(input_body)
#response_body is the response SOAP envelope and contents
_send_response(
self
,
200
,
'OK'
, response_body)
return
def
do_GET(
self
):
#response_body is the WSDL file
_send_response(
self
,
200
,
'OK'
,
self
.wsdl)
return
def
_run_through_kafka(
self
, body):
#In 4Suite all InputSources have base URIs in case they refer to
#other URIs in some way and resolution is required.
#The SOAP messages will not have any such URI references,
#So use a dummy base URI
source
=
InputSource.DefaultFactory.fromString(body,
"urn:dummy"
)
response
=
self
.processor.run(source)
return
response
class
HtmlHandler(BaseHTTPServer.BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
def
init(
cls
):
from
Ft.Lib
import
Uri
#Perform the transform once and store the result
processor
=
Processor.Processor()
html_desc_uri
=
Uri.OsPathToUri(HTML_VIEW_TRANSFORM,
attemptAbsolute
=
1
)
transform
=
InputSource.DefaultFactory.fromUri(html_desc_uri)
processor.appendStylesheet(transform)
wsdl_uri
=
Uri.OsPathToUri(WSDL_FILE, attemptAbsolute
=
1
)
source
=
InputSource.DefaultFactory.fromUri(wsdl_uri)
cls
.html_desc
=
processor.run(source)
return
#Make init() a static class method
init
=
classmethod
(init)
def
do_GET(
self
):
#response_body is the WSDL file
_send_response(
self
,
200
,
'OK'
,
self
.html_desc)
return
#Turn _send_response into a global function
#for sharing between the classes
def
_send_response(handler, code, msg, body):
#Prepare a normal response
handler.send_response(
200
,
'OK'
)
#Send standard HTP headers
handler.send_header(
'Content-type'
,
'text/html; charset=utf-8'
)
handler.send_header(
"Connection"
,
"close"
)
handler.send_header(
"Accept-Ranges"
,
"bytes"
)
handler.send_header(
'Content-length'
,
len
(body)
-
1
)
handler.end_headers()
#Send the response prepared by the SOAP end point
handler.wfile.write(body)
return
def
soap_listener_function():
listen_on_port
=
8888
#Set up to run on local machine
server_address
=
(
'127.0.0.1'
, listen_on_port)
KafkaSoapHandler.init()
httpd
=
BaseHTTPServer.HTTPServer(server_address, KafkaSoapHandler)
print
"Listening for GET and POST on port"
, listen_on_port
#Go into a the main event loop
httpd.serve_forever()
def
html_listener_function():
listen_on_port
=
9000
#Set up to run on local machine
server_address
=
(
'127.0.0.1'
, listen_on_port)
HtmlHandler.init()
httpd
=
BaseHTTPServer.HTTPServer(server_address, HtmlHandler)
print
"Listening for GET on port"
, listen_on_port
#Go into a the main event loop
httpd.serve_forever()
return
import
time
from
threading
import
Thread
soap_thread
=
Thread(
None
, soap_listener_function)
html_thread
=
Thread(
None
, html_listener_function)
soap_thread.start()
#Pause before spawning the next thread
time.sleep(
1
)
html_thread.start()
|
通过在服务器上定义 do_GET 和 do_POST ,您可以在单个服务器实例上处理 GET 和 POST 请求,但是因为所使用的简单事件循环的性质,您可以使用线程技术在不同端口上进行侦听。这让您同时运行两个服务器实例。线程技术是方法之一,而使用异步事件处理程序是另一种方法。Python 2.2 为更轻松地支持后一种技术而引入了 asyncore 模块,我们在本专栏的上一篇文章中介绍了这种方法(请参阅 参考资料)。这一次我们将举例说明线程技术的用法。关于使用线程技术还是使用异步技术的问题,Python 2.2 文档提出了很好的建议.
仅当您的程序很大程度上受 I/O 限制时,[异步方法才是] 真正实用的。如果您的程序受处理器限制,那么抢先式调度的线程可能是您所真正需要的。但是,网络服务器很少受处理器限制.
图 1显示了易于理解的 Web 服务描述的浏览器视图.
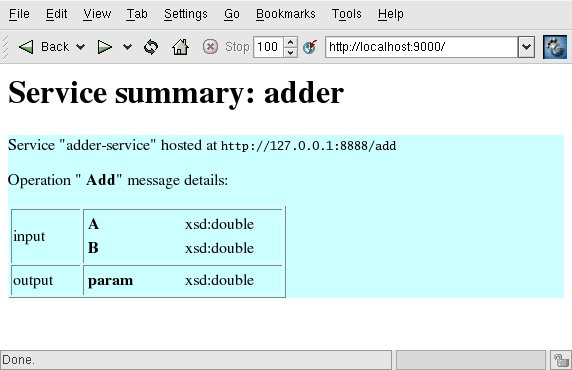
结束语 。
请将这一切都看作实验素材。Kafka 已经相当落伍了 — 它似乎从 2001 年以来就没有得到过维护,并且它使用了相当差劲的 XSLT 样式(其作者坦率地承认自己是个 XSLT 菜鸟)。但其思想是非常有用的,并且很有价值。只需要作很小的努力就可以将它更新到 SOAP 1.2 并扩展其能力。我们所提供的 WSDL 表示转换也只是一个起点。也可以将它更新到 WSDL 1.2 并可扩展它以显示关于 Web 服务的更多信息。还应该更新它以利用名称空间轴和其它 XSLT 功能以便进行更为正确的处理.
XSLT 是一个沙箱,使用各种语言和环境的开发人员都可以在其中施展身手。Kafka 是由一位坚定的 .NET 开发人员开发的,但我们也可以很快地学会它和利用它。这就是拥有一种既可以处理 XML 也可处理 Web 服务的通用语言(lingua franca)的威力。我们预计可以使用用于 Web 服务的 XSLT 模块的领域将继续扩展。如果是这样,本文所提供的基本技术可能会促使 Python 程序员们马上使用这些有用的技术.
最后此篇关于使用Python下的XSLT API进行web开发的简单教程的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于使用Python下的XSLT API进行web开发的简单教程的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我正在处理一组标记为 160 个组的 173k 点。我想通过合并最接近的(到 9 或 10 个组)来减少组/集群的数量。我搜索过 sklearn 或类似的库,但没有成功。 我猜它只是通过 knn 聚类
我有一个扁平数字列表,这些数字逻辑上以 3 为一组,其中每个三元组是 (number, __ignored, flag[0 or 1]),例如: [7,56,1, 8,0,0, 2,0,0, 6,1,
我正在使用 pipenv 来管理我的包。我想编写一个 python 脚本来调用另一个使用不同虚拟环境(VE)的 python 脚本。 如何运行使用 VE1 的 python 脚本 1 并调用另一个 p
假设我有一个文件 script.py 位于 path = "foo/bar/script.py"。我正在寻找一种在 Python 中通过函数 execute_script() 从我的主要 Python
这听起来像是谜语或笑话,但实际上我还没有找到这个问题的答案。 问题到底是什么? 我想运行 2 个脚本。在第一个脚本中,我调用另一个脚本,但我希望它们继续并行,而不是在两个单独的线程中。主要是我不希望第
我有一个带有 python 2.5.5 的软件。我想发送一个命令,该命令将在 python 2.7.5 中启动一个脚本,然后继续执行该脚本。 我试过用 #!python2.7.5 和http://re
我在 python 命令行(使用 python 2.7)中,并尝试运行 Python 脚本。我的操作系统是 Windows 7。我已将我的目录设置为包含我所有脚本的文件夹,使用: os.chdir("
剧透:部分解决(见最后)。 以下是使用 Python 嵌入的代码示例: #include int main(int argc, char** argv) { Py_SetPythonHome
假设我有以下列表,对应于及时的股票价格: prices = [1, 3, 7, 10, 9, 8, 5, 3, 6, 8, 12, 9, 6, 10, 13, 8, 4, 11] 我想确定以下总体上最
所以我试图在选择某个单选按钮时更改此框架的背景。 我的框架位于一个类中,并且单选按钮的功能位于该类之外。 (这样我就可以在所有其他框架上调用它们。) 问题是每当我选择单选按钮时都会出现以下错误: co
我正在尝试将字符串与 python 中的正则表达式进行比较,如下所示, #!/usr/bin/env python3 import re str1 = "Expecting property name
考虑以下原型(prototype) Boost.Python 模块,该模块从单独的 C++ 头文件中引入类“D”。 /* file: a/b.cpp */ BOOST_PYTHON_MODULE(c)
如何编写一个程序来“识别函数调用的行号?” python 检查模块提供了定位行号的选项,但是, def di(): return inspect.currentframe().f_back.f_l
我已经使用 macports 安装了 Python 2.7,并且由于我的 $PATH 变量,这就是我输入 $ python 时得到的变量。然而,virtualenv 默认使用 Python 2.6,除
我只想问如何加快 python 上的 re.search 速度。 我有一个很长的字符串行,长度为 176861(即带有一些符号的字母数字字符),我使用此函数测试了该行以进行研究: def getExe
list1= [u'%app%%General%%Council%', u'%people%', u'%people%%Regional%%Council%%Mandate%', u'%ppp%%Ge
这个问题在这里已经有了答案: Is it Pythonic to use list comprehensions for just side effects? (7 个答案) 关闭 4 个月前。 告
我想用 Python 将两个列表组合成一个列表,方法如下: a = [1,1,1,2,2,2,3,3,3,3] b= ["Sun", "is", "bright", "June","and" ,"Ju
我正在运行带有最新 Boost 发行版 (1.55.0) 的 Mac OS X 10.8.4 (Darwin 12.4.0)。我正在按照说明 here构建包含在我的发行版中的教程 Boost-Pyth
学习 Python,我正在尝试制作一个没有任何第 3 方库的网络抓取工具,这样过程对我来说并没有简化,而且我知道我在做什么。我浏览了一些在线资源,但所有这些都让我对某些事情感到困惑。 html 看起来

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!