- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章利用Python绘制数据的瀑布图的教程由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
介绍 。
对于绘制某些类型的数据来说,瀑布图是一种十分有用的工具。不足为奇的是,我们可以使用Pandas和matplotlib创建一个可重复的瀑布图.
在往下进行之前,我想先告诉大家我指代的是哪种类型的图表。我将建立一个维基百科文章中描述的2D瀑布图.
这种图表的一个典型的用处是显示开始值和结束值之间起“桥梁”作用的+和-的值。因为这个原因,财务人员有时会将其称为一个桥梁。跟我之前所采用的其他例子相似,这种类型的绘图在Excel中不容易生成,当然肯定有生成它的方法,但是不容易记住.
关于瀑布图需要记住的关键点是:它本质上是一个堆叠在一起的条形图,不过特殊的一点是,它有一个空白底栏,所以顶部栏会“悬浮”在空中。那么,让我们开始吧。 创建图表 。
首先,执行标准的输入,并确保IPython能显示matplot图。 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
import
numpy as np
import
pandas as pd
import
matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%
matplotlib inline
|
设置我们想画出瀑布图的数据,并将其加载到数据帧(DataFrame)中.
数据需要以你的起始值开始,但是你需要给出最终的总数。我们将在下面计算它。 。
|
1
2
3
|
index
=
[
'sales'
,
'returns'
,
'credit fees'
,
'rebates'
,
'late charges'
,
'shipping'
]
data
=
{
'amount'
: [
350000
,
-
30000
,
-
7500
,
-
25000
,
95000
,
-
7000
]}
trans
=
pd.DataFrame(data
=
data,index
=
index)
|
我使用了IPython中便捷的display函数来更简单地控制我要显示的内容。 。
|
1
2
|
from
IPython.display
import
display
display(trans)
|
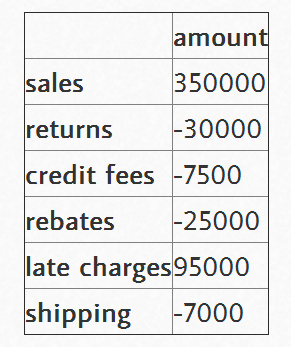
瀑布图的最大技巧是计算出底部堆叠条形图的内容。有关这一点,我从stackoverflow上的讨论中学到很多.
首先,我们得到累积和。 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
display(trans.amount.cumsum())
sales
350000
returns
320000
credit fees
312500
rebates
287500
late charges
382500
shipping
375500
Name: amount, dtype: int64
|
这看起来不错,但我们需要将一个地方的数据转移到右边。 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
blank
=
trans.amount.cumsum().shift(
1
).fillna(
0
)
display(blank)
sales
0
returns
350000
credit fees
320000
rebates
312500
late charges
287500
shipping
382500
Name: amount, dtype: float64
|
我们需要向trans和blank数据帧中添加一个净总量。 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
total
=
trans.
sum
().amount
trans.loc[
"net"
]
=
total
blank.loc[
"net"
]
=
total
display(trans)
display(blank)
|
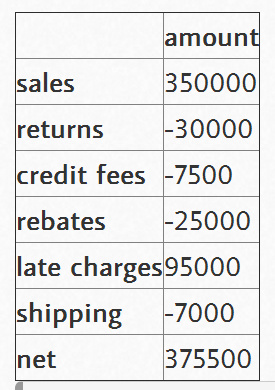
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
sales
0
returns
350000
credit fees
320000
rebates
312500
late charges
287500
shipping
382500
net
375500
Name: amount, dtype: float64
|
创建我们用来显示变化的步骤。 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
step
=
blank.reset_index(drop
=
True
).repeat(
3
).shift(
-
1
)
step[
1
::
3
]
=
np.nan
display(step)
0
0
0
NaN
0
350000
1
350000
1
NaN
1
320000
2
320000
2
NaN
2
312500
3
312500
3
NaN
3
287500
4
287500
4
NaN
4
382500
5
382500
5
NaN
5
375500
6
375500
6
NaN
6
NaN
Name: amount, dtype: float64
|
对于“net”行,为了不使堆叠加倍,我们需要确保blank值为0。 。
|
1
|
blank.loc[
"net"
]
=
0
|
然后,将其画图,看一下什么样子。 。
|
1
2
|
my_plot
=
trans.plot(kind
=
'bar'
, stacked
=
True
, bottom
=
blank,legend
=
None
, title
=
"2014 Sales Waterfall"
)
my_plot.plot(step.index, step.values,
'k'
)
|
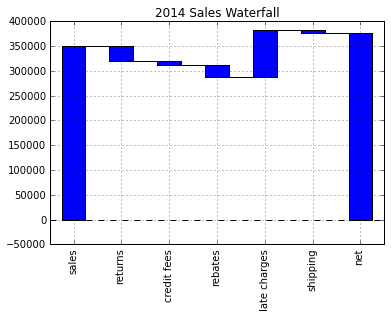
看起来相当不错,但是让我们试着格式化Y轴,以使其更具有可读性。为此,我们使用FuncFormatter和一些Python2.7+的语法来截断小数并向格式中添加一个逗号。 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
def
money(x, pos):
'The two args are the value and tick position'
return
"${:,.0f}"
.
format
(x)
from
matplotlib.ticker
import
FuncFormatter
formatter
=
FuncFormatter(money)
|
然后,将其组合在一起。 。
|
1
2
3
4
|
my_plot
=
trans.plot(kind
=
'bar'
, stacked
=
True
, bottom
=
blank,legend
=
None
, title
=
"2014 Sales Waterfall"
)
my_plot.plot(step.index, step.values,
'k'
)
my_plot.set_xlabel(
"Transaction Types"
)
my_plot.yaxis.set_major_formatter(formatter)
|
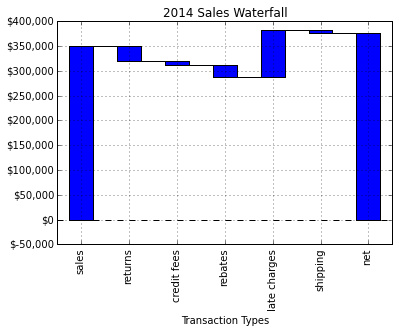
完整脚本 。
基本图形能够正常工作,但是我想添加一些标签,并做一些小的格式修改。下面是我最终的脚本: 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
|
import
numpy as np
import
pandas as pd
import
matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from
matplotlib.ticker
import
FuncFormatter
#Use python 2.7+ syntax to format currency
def
money(x, pos):
'The two args are the value and tick position'
return
"${:,.0f}"
.
format
(x)
formatter
=
FuncFormatter(money)
#Data to plot. Do not include a total, it will be calculated
index
=
[
'sales'
,
'returns'
,
'credit fees'
,
'rebates'
,
'late charges'
,
'shipping'
]
data
=
{
'amount'
: [
350000
,
-
30000
,
-
7500
,
-
25000
,
95000
,
-
7000
]}
#Store data and create a blank series to use for the waterfall
trans
=
pd.DataFrame(data
=
data,index
=
index)
blank
=
trans.amount.cumsum().shift(
1
).fillna(
0
)
#Get the net total number for the final element in the waterfall
total
=
trans.
sum
().amount
trans.loc[
"net"
]
=
total
blank.loc[
"net"
]
=
total
#The steps graphically show the levels as well as used for label placement
step
=
blank.reset_index(drop
=
True
).repeat(
3
).shift(
-
1
)
step[
1
::
3
]
=
np.nan
#When plotting the last element, we want to show the full bar,
#Set the blank to 0
blank.loc[
"net"
]
=
0
#Plot and label
my_plot
=
trans.plot(kind
=
'bar'
, stacked
=
True
, bottom
=
blank,legend
=
None
, figsize
=
(
10
,
5
), title
=
"2014 Sales Waterfall"
)
my_plot.plot(step.index, step.values,
'k'
)
my_plot.set_xlabel(
"Transaction Types"
)
#Format the axis for dollars
my_plot.yaxis.set_major_formatter(formatter)
#Get the y-axis position for the labels
y_height
=
trans.amount.cumsum().shift(
1
).fillna(
0
)
#Get an offset so labels don't sit right on top of the bar
max
=
trans.
max
()
neg_offset
=
max
/
25
pos_offset
=
max
/
50
plot_offset
=
int
(
max
/
15
)
#Start label loop
loop
=
0
for
index, row
in
trans.iterrows():
# For the last item in the list, we don't want to double count
if
row[
'amount'
]
=
=
total:
y
=
y_height[loop]
else
:
y
=
y_height[loop]
+
row[
'amount'
]
# Determine if we want a neg or pos offset
if
row[
'amount'
] >
0
:
y
+
=
pos_offset
else
:
y
-
=
neg_offset
my_plot.annotate(
"{:,.0f}"
.
format
(row[
'amount'
]),(loop,y),ha
=
"center"
)
loop
+
=
1
#Scale up the y axis so there is room for the labels
my_plot.set_ylim(
0
,blank.
max
()
+
int
(plot_offset))
#Rotate the labels
my_plot.set_xticklabels(trans.index,rotation
=
0
)
my_plot.get_figure().savefig(
"waterfall.png"
,dpi
=
200
,bbox_inches
=
'tight'
)
|
运行该脚本将生成下面这个漂亮的图表:
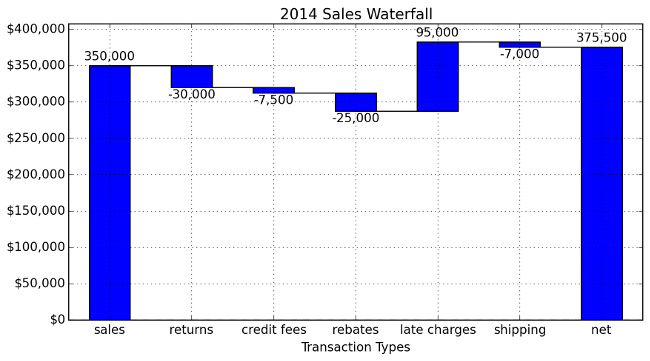
最后的想法 。
如果你之前不熟悉瀑布图,希望这个示例能够向你展示它到底是多么有用。我想,可能一些人会觉得对于一个图表来说需要这么多的脚本代码有点糟糕。在某些方面,我同意这种想法。如果你仅仅只是做一个瀑布图,而以后不会再碰它,那么你还是继续用Excel中的方法吧.
然而,如果瀑布图真的很有用,并且你需要将它复制给100个客户,将会怎么样呢?接下来你将要怎么做呢?此时使用Excel将会是一个挑战,而使用本文中的脚本来创建100个不同的表格将相当容易。再次说明,这一程序的真正价值在于,当你需要扩展这个解决方案时,它能够便于你创建一个易于复制的程序.
我真的很喜欢学习更多Pandas、matplotlib和IPothon的知识。我很高兴这种方法能够帮到你,并希望其他人也可以从中学习到一些知识,并将这一课所学应用到他们的日常工作中.
最后此篇关于利用Python绘制数据的瀑布图的教程的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于利用Python绘制数据的瀑布图的教程的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我正在处理一组标记为 160 个组的 173k 点。我想通过合并最接近的(到 9 或 10 个组)来减少组/集群的数量。我搜索过 sklearn 或类似的库,但没有成功。 我猜它只是通过 knn 聚类
我有一个扁平数字列表,这些数字逻辑上以 3 为一组,其中每个三元组是 (number, __ignored, flag[0 or 1]),例如: [7,56,1, 8,0,0, 2,0,0, 6,1,
我正在使用 pipenv 来管理我的包。我想编写一个 python 脚本来调用另一个使用不同虚拟环境(VE)的 python 脚本。 如何运行使用 VE1 的 python 脚本 1 并调用另一个 p
假设我有一个文件 script.py 位于 path = "foo/bar/script.py"。我正在寻找一种在 Python 中通过函数 execute_script() 从我的主要 Python
这听起来像是谜语或笑话,但实际上我还没有找到这个问题的答案。 问题到底是什么? 我想运行 2 个脚本。在第一个脚本中,我调用另一个脚本,但我希望它们继续并行,而不是在两个单独的线程中。主要是我不希望第
我有一个带有 python 2.5.5 的软件。我想发送一个命令,该命令将在 python 2.7.5 中启动一个脚本,然后继续执行该脚本。 我试过用 #!python2.7.5 和http://re
我在 python 命令行(使用 python 2.7)中,并尝试运行 Python 脚本。我的操作系统是 Windows 7。我已将我的目录设置为包含我所有脚本的文件夹,使用: os.chdir("
剧透:部分解决(见最后)。 以下是使用 Python 嵌入的代码示例: #include int main(int argc, char** argv) { Py_SetPythonHome
假设我有以下列表,对应于及时的股票价格: prices = [1, 3, 7, 10, 9, 8, 5, 3, 6, 8, 12, 9, 6, 10, 13, 8, 4, 11] 我想确定以下总体上最
所以我试图在选择某个单选按钮时更改此框架的背景。 我的框架位于一个类中,并且单选按钮的功能位于该类之外。 (这样我就可以在所有其他框架上调用它们。) 问题是每当我选择单选按钮时都会出现以下错误: co
我正在尝试将字符串与 python 中的正则表达式进行比较,如下所示, #!/usr/bin/env python3 import re str1 = "Expecting property name
考虑以下原型(prototype) Boost.Python 模块,该模块从单独的 C++ 头文件中引入类“D”。 /* file: a/b.cpp */ BOOST_PYTHON_MODULE(c)
如何编写一个程序来“识别函数调用的行号?” python 检查模块提供了定位行号的选项,但是, def di(): return inspect.currentframe().f_back.f_l
我已经使用 macports 安装了 Python 2.7,并且由于我的 $PATH 变量,这就是我输入 $ python 时得到的变量。然而,virtualenv 默认使用 Python 2.6,除
我只想问如何加快 python 上的 re.search 速度。 我有一个很长的字符串行,长度为 176861(即带有一些符号的字母数字字符),我使用此函数测试了该行以进行研究: def getExe
list1= [u'%app%%General%%Council%', u'%people%', u'%people%%Regional%%Council%%Mandate%', u'%ppp%%Ge
这个问题在这里已经有了答案: Is it Pythonic to use list comprehensions for just side effects? (7 个答案) 关闭 4 个月前。 告
我想用 Python 将两个列表组合成一个列表,方法如下: a = [1,1,1,2,2,2,3,3,3,3] b= ["Sun", "is", "bright", "June","and" ,"Ju
我正在运行带有最新 Boost 发行版 (1.55.0) 的 Mac OS X 10.8.4 (Darwin 12.4.0)。我正在按照说明 here构建包含在我的发行版中的教程 Boost-Pyth
学习 Python,我正在尝试制作一个没有任何第 3 方库的网络抓取工具,这样过程对我来说并没有简化,而且我知道我在做什么。我浏览了一些在线资源,但所有这些都让我对某些事情感到困惑。 html 看起来

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!