- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章详解Java实现缓存(LRU,FIFO)由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
现在软件或者网页的并发量越来越大了,大量请求直接操作数据库会对数据库造成很大的压力,处理大量连接和请求就会需要很长时间,但是实际中百分之80的数据是很少更改的,这样就可以引入缓存来进行读取,减少数据库的压力.
常用的缓存有redis和memcached,但是有时候一些小场景就可以直接使用java实现缓存,就可以满足这部分服务的需求.
缓存主要有lru和fifo,lru是least recently used的缩写,即最近最久未使用,fifo就是先进先出,下面就使用java来实现这两种缓存.
lru 。
lru缓存的思想 。
按照如上思想,可以使用linkedhashmap来实现lru缓存.
这是linkedhashmap的一个构造函数,传入的第三个参数accessorder为true的时候,就按访问顺序对linkedhashmap排序,为false的时候就按插入顺序,默认是为false的.
当把accessorder设置为true后,就可以将最近访问的元素置于最前面,这样就可以满足上述的第二点.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
/**
* constructs an empty <tt>linkedhashmap</tt> instance with the
* specified initial capacity, load factor and ordering mode.
*
* @param initialcapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadfactor the load factor
* @param accessorder the ordering mode - <tt>true</tt> for
* access-order, <tt>false</tt> for insertion-order
* @throws illegalargumentexception if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public
linkedhashmap(
int
initialcapacity,
float
loadfactor,
boolean
accessorder) {
super
(initialcapacity, loadfactor);
this
.accessorder = accessorder;
}
|
这是linkedhashmap中另外一个方法,当返回true的时候,就会remove其中最久的元素,可以通过重写这个方法来控制缓存元素的删除,当缓存满了后,就可以通过返回true删除最久未被使用的元素,达到lru的要求。这样就可以满足上述第三点要求.
|
1
2
3
|
protected
boolean
removeeldestentry(map.entry<k,v> eldest) {
return
false
;
}
|
由于linkedhashmap是为自动扩容的,当table数组中元素大于capacity * loadfactor的时候,就会自动进行两倍扩容。但是为了使缓存大小固定,就需要在初始化的时候传入容量大小和负载因子.
为了使得到达设置缓存大小不会进行自动扩容,需要将初始化的大小进行计算再传入,可以将初始化大小设置为(缓存大小 / loadfactor) + 1,这样就可以在元素数目达到缓存大小时,也不会进行扩容了。这样就解决了上述第一点问题.
通过上面分析,实现下面的代码 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
|
import
java.util.linkedhashmap;
import
java.util.map;
import
java.util.set;
public
class
lru1<k, v> {
private
final
int
max_cache_size;
private
final
float
default_load_factory =
0
.75f;
linkedhashmap<k, v> map;
public
lru1(
int
cachesize) {
max_cache_size = cachesize;
int
capacity = (
int
)math.ceil(max_cache_size / default_load_factory) +
1
;
/*
* 第三个参数设置为true,代表linkedlist按访问顺序排序,可作为lru缓存
* 第三个参数设置为false,代表按插入顺序排序,可作为fifo缓存
*/
map =
new
linkedhashmap<k, v>(capacity, default_load_factory,
true
) {
@override
protected
boolean
removeeldestentry(map.entry<k, v> eldest) {
return
size() > max_cache_size;
}
};
}
public
synchronized
void
put(k key, v value) {
map.put(key, value);
}
public
synchronized
v get(k key) {
return
map.get(key);
}
public
synchronized
void
remove(k key) {
map.remove(key);
}
public
synchronized
set<map.entry<k, v>> getall() {
return
map.entryset();
}
@override
public
string tostring() {
stringbuilder stringbuilder =
new
stringbuilder();
for
(map.entry<k, v> entry : map.entryset()) {
stringbuilder.append(string.format(
"%s: %s "
, entry.getkey(), entry.getvalue()));
}
return
stringbuilder.tostring();
}
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
lru1<integer, integer> lru1 =
new
lru1<>(
5
);
lru1.put(
1
,
1
);
lru1.put(
2
,
2
);
lru1.put(
3
,
3
);
system.out.println(lru1);
lru1.get(
1
);
system.out.println(lru1);
lru1.put(
4
,
4
);
lru1.put(
5
,
5
);
lru1.put(
6
,
6
);
system.out.println(lru1);
}
}
|
运行结果:
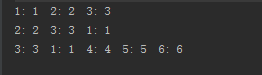
从运行结果中可以看出,实现了lru缓存的思想.
接着使用hashmap和链表来实现lru缓存.
主要的思想和上述基本一致,每次添加元素或者读取元素就将元素放置在链表的头,当缓存满了之后,就可以将尾结点元素删除,这样就实现了lru缓存.
这种方法中是通过自己编写代码移动结点和删除结点,为了防止缓存大小超过限制,每次进行put的时候都会进行检查,若缓存满了则删除尾部元素.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
|
import
java.util.hashmap;
/**
* 使用cache和链表实现缓存
*/
public
class
lru2<k, v> {
private
final
int
max_cache_size;
private
entry<k, v> head;
private
entry<k, v> tail;
private
hashmap<k, entry<k, v>> cache;
public
lru2(
int
cachesize) {
max_cache_size = cachesize;
cache =
new
hashmap<>();
}
public
void
put(k key, v value) {
entry<k, v> entry = getentry(key);
if
(entry ==
null
) {
if
(cache.size() >= max_cache_size) {
cache.remove(tail.key);
removetail();
}
}
entry =
new
entry<>();
entry.key = key;
entry.value = value;
movetohead(entry);
cache.put(key, entry);
}
public
v get(k key) {
entry<k, v> entry = getentry(key);
if
(entry ==
null
) {
return
null
;
}
movetohead(entry);
return
entry.value;
}
public
void
remove(k key) {
entry<k, v> entry = getentry(key);
if
(entry !=
null
) {
if
(entry == head) {
entry<k, v> next = head.next;
head.next =
null
;
head = next;
head.pre =
null
;
}
else
if
(entry == tail) {
entry<k, v> prev = tail.pre;
tail.pre =
null
;
tail = prev;
tail.next =
null
;
}
else
{
entry.pre.next = entry.next;
entry.next.pre = entry.pre;
}
cache.remove(key);
}
}
private
void
removetail() {
if
(tail !=
null
) {
entry<k, v> prev = tail.pre;
if
(prev ==
null
) {
head =
null
;
tail =
null
;
}
else
{
tail.pre =
null
;
tail = prev;
tail.next =
null
;
}
}
}
private
void
movetohead(entry<k, v> entry) {
if
(entry == head) {
return
;
}
if
(entry.pre !=
null
) {
entry.pre.next = entry.next;
}
if
(entry.next !=
null
) {
entry.next.pre = entry.pre;
}
if
(entry == tail) {
entry<k, v> prev = entry.pre;
if
(prev !=
null
) {
tail.pre =
null
;
tail = prev;
tail.next =
null
;
}
}
if
(head ==
null
|| tail ==
null
) {
head = tail = entry;
return
;
}
entry.next = head;
head.pre = entry;
entry.pre =
null
;
head = entry;
}
private
entry<k, v> getentry(k key) {
return
cache.get(key);
}
private
static
class
entry<k, v> {
entry<k, v> pre;
entry<k, v> next;
k key;
v value;
}
@override
public
string tostring() {
stringbuilder stringbuilder =
new
stringbuilder();
entry<k, v> entry = head;
while
(entry !=
null
) {
stringbuilder.append(string.format(
"%s:%s "
, entry.key, entry.value));
entry = entry.next;
}
return
stringbuilder.tostring();
}
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
lru2<integer, integer> lru2 =
new
lru2<>(
5
);
lru2.put(
1
,
1
);
system.out.println(lru2);
lru2.put(
2
,
2
);
system.out.println(lru2);
lru2.put(
3
,
3
);
system.out.println(lru2);
lru2.get(
1
);
system.out.println(lru2);
lru2.put(
4
,
4
);
lru2.put(
5
,
5
);
lru2.put(
6
,
6
);
system.out.println(lru2);
}
}
|
运行结果:
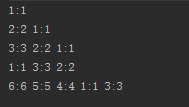
fifo 。
fifo就是先进先出,可以使用linkedhashmap进行实现.
当第三个参数传入为false或者是默认的时候,就可以实现按插入顺序排序,就可以实现fifo缓存了.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
/**
* constructs an empty <tt>linkedhashmap</tt> instance with the
* specified initial capacity, load factor and ordering mode.
*
* @param initialcapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadfactor the load factor
* @param accessorder the ordering mode - <tt>true</tt> for
* access-order, <tt>false</tt> for insertion-order
* @throws illegalargumentexception if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public
linkedhashmap(
int
initialcapacity,
float
loadfactor,
boolean
accessorder) {
super
(initialcapacity, loadfactor);
this
.accessorder = accessorder;
}
|
实现代码跟上述使用linkedhashmap实现lru的代码基本一致,主要就是构造函数的传值有些不同.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
|
import
java.util.linkedhashmap;
import
java.util.map;
import
java.util.set;
public
class
lru1<k, v> {
private
final
int
max_cache_size;
private
final
float
default_load_factory =
0
.75f;
linkedhashmap<k, v> map;
public
lru1(
int
cachesize) {
max_cache_size = cachesize;
int
capacity = (
int
)math.ceil(max_cache_size / default_load_factory) +
1
;
/*
* 第三个参数设置为true,代表linkedlist按访问顺序排序,可作为lru缓存
* 第三个参数设置为false,代表按插入顺序排序,可作为fifo缓存
*/
map =
new
linkedhashmap<k, v>(capacity, default_load_factory,
false
) {
@override
protected
boolean
removeeldestentry(map.entry<k, v> eldest) {
return
size() > max_cache_size;
}
};
}
public
synchronized
void
put(k key, v value) {
map.put(key, value);
}
public
synchronized
v get(k key) {
return
map.get(key);
}
public
synchronized
void
remove(k key) {
map.remove(key);
}
public
synchronized
set<map.entry<k, v>> getall() {
return
map.entryset();
}
@override
public
string tostring() {
stringbuilder stringbuilder =
new
stringbuilder();
for
(map.entry<k, v> entry : map.entryset()) {
stringbuilder.append(string.format(
"%s: %s "
, entry.getkey(), entry.getvalue()));
}
return
stringbuilder.tostring();
}
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
lru1<integer, integer> lru1 =
new
lru1<>(
5
);
lru1.put(
1
,
1
);
lru1.put(
2
,
2
);
lru1.put(
3
,
3
);
system.out.println(lru1);
lru1.get(
1
);
system.out.println(lru1);
lru1.put(
4
,
4
);
lru1.put(
5
,
5
);
lru1.put(
6
,
6
);
system.out.println(lru1);
}
}
|
运行结果:

以上就是使用java实现这两种缓存的方式,从中可以看出,linkedhashmap实现缓存较为容易,因为底层函数对此已经有了支持,自己编写链表实现lru缓存也是借鉴了linkedhashmap中实现的思想。在java中不只是这两种数据结构可以实现缓存,比如concurrenthashmap、weakhashmap在某些场景下也是可以作为缓存的,到底用哪一种数据结构主要是看场景再进行选择,但是很多思想都是可以通用的.
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/liuyang0/p/6664586.html 。
最后此篇关于详解Java实现缓存(LRU,FIFO)的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于详解Java实现缓存(LRU,FIFO)的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我阅读了有关 JSR 107 缓存 (JCache) 的内容。 我很困惑:据我所知,每个 CPU 都管理其缓存内存(无需操作系统的任何帮助)。 那么,为什么我们需要 Java 缓存处理程序? (如果C
好吧,我是 jQuery 的新手。我一直在这里和那里搞乱一点点并习惯它。我终于明白了(它并不像某些人想象的那么难)。因此,鉴于此链接:http://jqueryui.com/sortable/#dis
我正在使用 Struts 2 和 Hibernate。我有一个简单的表,其中包含一个日期字段,用于存储有关何时发生特定操作的信息。这个日期值显示在我的 jsp 中。 我遇到的问题是hibernate更
我有点不确定这里发生了什么,但是我试图解释正在发生的事情,也许一旦我弄清楚我到底在问什么,就可能写一个更好的问题。 我刚刚安装了Varnish,对于我的请求时间来说似乎很棒。这是一个Magneto 2
解决 Project Euler 的问题后,我在论坛中发现了以下 Haskell 代码: fillRow115 minLength = cache where cache = ((map fill
我正试图找到一种方法来为我网络上的每台计算机缓存或存储某些 python 包。我看过以下解决方案: pypicache但它不再被积极开发,作者推荐 devpi,请参见此处:https://bitbuc
我想到的一个问题是可以从一开始就缓存网络套接字吗?在我的拓扑中,我在通过双 ISP 连接连接到互联网的 HAProxy 服务器后面有 2 个 Apache 服务器(带有 Google PageSpee
我很难说出不同缓存区域 (OS) 之间的区别。我想简要解释一下磁盘\缓冲区\交换\页面缓存。他们住在哪里?它们之间的主要区别是什么? 据我了解,页面缓存是主内存的一部分,用于存储从 I/O 设备获取的
1.题目 请你为最不经常使用(LFU)缓存算法设计并实现数据结构。 实现 LFUCache 类: LFUCache(int capacity) - 用数据结构的容量 capacity 初始化对象 in
1.题目 请你设计并实现一个满足 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存 约束的数据结构。 实现 LRUCache 类: ① LRUCache(int capacity) 以正整数作为容量 capacity
我想在访问该 View 时关闭某些页面的缓存。它适用于简单查询模型对象的页面。 好像什么时候 'django.middleware.cache.FetchFromCacheMiddleware', 启
documents为 ExePackage element state Cache属性的目的是 Whether to cache the package. The default is "yes".
我知道 docker 用图层存储每个图像。如果我在一台开发服务器上有多个用户,并且每个人都在运行相同的 Dockerfile,但将镜像存储为 user1_myapp . user2 将其存储为 use
在 Codeigniter 中没有出现缓存问题几年后,我发现了一个问题。我在其他地方看到过该问题,但没有适合我的解决方案。 例如,如果我在 View 中更改一些纯 html 文本并上传新文件并按 F5
我在 Janusgraph 文档中阅读了有关 Janusgraph Cache 的内容。关于事务缓存,我几乎没有怀疑。我在我的应用程序中使用嵌入式 janusgrah 服务器。 如果我只对例如进行读取
我想知道是否有来自终端的任何命令可以用来匹配 Android Studio 中执行文件>使缓存无效/重新启动的使用。 谢谢! 最佳答案 According to a JetBrains employe
我想制作一个 python 装饰器来内存函数。例如,如果 @memoization_decorator def add(a, b, negative=False): print "Com
我经常在 jQuery 事件处理程序中使用 $(this) 并且从不缓存它。如果我愿意的话 var $this = $(this); 并且将使用变量而不是构造函数,我的代码会获得任何显着的额外性能吗?
是的,我要说实话,我不知道varnish vcl,我可以解决一些基本问题,但是我不太清楚,这就是为什么我遇到问题了。 我正在尝试通过http请求设置缓存禁止,但是该请求不能通过DNS而是通过 Varn
在 WP 站点上加载约 4000 个并发用户时遇到此问题。 这是我的配置: F5 负载均衡器 ---> Varnish 4,8 核,32 Gb RAM ---> 9 个后端,4 个核,每个 16 RA

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!