- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章Java使用设计模式中迭代器模式构建项目的代码结构示例由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
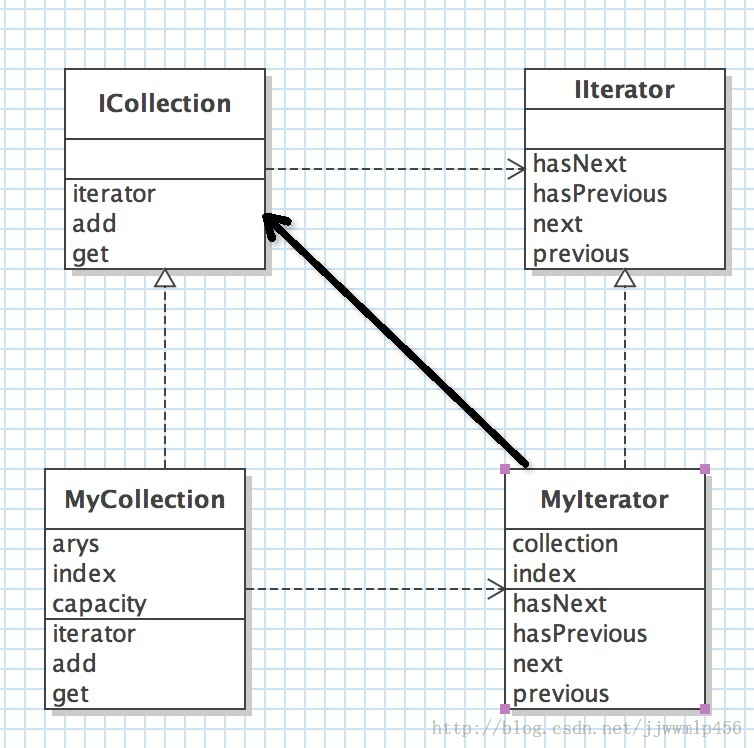
迭代器(Iterator)模式,又叫做游标(Cursor)模式。GOF给出的定义为:提供一种方法访问一个容器(container)对象中各个元素,而又不需暴露该对象的内部细节。 迭代器模式由以下角色组成: 迭代器角色(Iterator):迭代器角色负责定义访问和遍历元素的接口。 具体迭代器角色(Concrete Iterator):具体迭代器角色要实现迭代器接口,并要记录遍历中的当前位置。 容器角色(Container):容器角色负责提供创建具体迭代器角色的接口。 具体容器角色(Concrete Container):具体容器角色实现创建具体迭代器角色的接口。这个具体迭代器角色与该容器的结构相关.
Java实现示例 类图:
代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
/**
* 自定义集合接口, 类似java.util.Collection
* 用于数据存储
* @author stone
*
*/
public
interface
ICollection<T> {
IIterator<T> iterator();
//返回迭代器
void
add(T t);
T get(
int
index);
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
/**
* 自定义迭代器接口 类似于java.util.Iterator
* 用于遍历集合类ICollection的数据
* @author stone
*
*/
public
interface
IIterator<T> {
boolean
hasNext();
boolean
hasPrevious();
T next();
T previous();
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
/**
* 集合类, 依赖于MyIterator
* @author stone
*/
public
class
MyCollection<T>
implements
ICollection<T> {
private
T[] arys;
private
int
index = -
1
;
private
int
capacity =
5
;
public
MyCollection() {
this
.arys = (T[])
new
Object[capacity];
}
@Override
public
IIterator<T> iterator() {
return
new
MyIterator<T>(
this
);
}
@Override
public
void
add(T t) {
index++;
if
(index == capacity) {
capacity *=
2
;
this
.arys = Arrays.copyOf(arys, capacity);
}
this
.arys[index] = t;
}
@Override
public
T get(
int
index) {
return
this
.arys[index];
}
}
|
。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
/*
* 若有新的存储结构,可new 一个ICollection, 对应的 new 一个IIterator来实现它的遍历
*/
@SuppressWarnings
({
"rawtypes"
,
"unchecked"
})
public
class
Test {
public
static
void
main(String[] args) {
ICollection<Integer> collection =
new
MyCollection<Integer>();
add(collection,
3
,
5
,
8
,
12
,
3
,
3
,
5
);
for
(IIterator<Integer> iterator = collection.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
System.out.println(
"-------------"
);
ICollection collection2 =
new
MyCollection();
add(collection2,
"a"
,
"b"
,
"c"
,
3
,
8
,
12
,
3
,
5
);
for
(IIterator iterator = collection2.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
static
<T>
void
add(ICollection<T> c, T ...a) {
for
(T i : a) {
c.add(i);
}
}
}
|
打印:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
3
5
8
12
3
3
5
-------------
a
b
c
3
8
12
3
5
|
。
最后此篇关于Java使用设计模式中迭代器模式构建项目的代码结构示例的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于Java使用设计模式中迭代器模式构建项目的代码结构示例的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我正在使用 NetBeans 开发 Java 中的 WebService,并使用 gradle 作为依赖管理。 我找到了this article关于使用 gradle 开发 Web 项目。它使用 Gr
我正在将旧项目从 ant 迁移到 gradle(以使用其依赖项管理和构建功能),并且在生成 时遇到问题>eclipse 项目。今天的大问题是因为该项目有一些子项目被拆分成 war 和 jar 包部署到
我已经为这个错误苦苦挣扎了很长时间。如果有帮助的话,我会提供一些问题的快照。请指导我该怎么办????在我看来,它看起来一团糟。 *** glibc detected *** /home/shivam/
我在 Ubuntu 12.10 上运行 NetBeans 7.3。我正在学习 Java Web 开发类(class),因此我有一个名为 jsage8 的项目,其中包含我为该类(class)所做的工作。
我想知道 Codeplex、GitHub 等中是否有任何突出的项目是 C# 和 ASP.NET,甚至只是 C# API 与功能测试 (NUnit) 和模拟(RhinoMocks、NMock 等)。 重
我创建了一个 Maven 项目,包装类型为“jar”,名为“Y”我已经完成了“Maven 安装”,并且可以在我的本地存储库中找到它.. 然后,我创建了另一个项目,包装类型为“war”,称为“X”。在这
我一直在关注the instructions用于将 facebook SDK 集成到我的应用程序中。除了“helloFacebookSample”之外,我已经成功地编译并运行了所有给定的示例应用程序。
我想知道,为什么我们(Java 社区)需要 Apache Harmony 项目,而已经有了 OpenJDK 项目。两者不是都是在开源许可下发布的吗? 最佳答案 事实恰恰相反。 Harmony 的成立是
我正在尝试使用 Jsoup HTML Parser 从网站获取缩略图 URL我需要提取所有以 60x60.jpg(或 png)结尾的 URL(所有缩略图 URL 都以此 URL 结尾) 问题是我让它在
我无法构建 gradle 项目,即使我编辑 gradle 属性,我也会收到以下错误: Error:(22, 1) A problem occurred evaluating root project
我有这个代码: var NToDel:NSArray = [] var addInNToDelArray = "Test1 \ Test2" 如何在 NToDel:NSArray 中添加 addInN
如何在单击显示更多(按钮)后将主题列表限制为 5 个(项目)。 还有 3(项目),依此类推到列表末尾,然后它会显示显示更少(按钮)。 例如:在 Udemy 过滤器选项中,当您点击查看更多按钮时,它仅显
如何将现有的 Flutter 项目导入为 gradle 项目? “导入项目”向导要求 Gradle 主路径。 我有 gradle,安装在我的系统中。但是这里需要设置什么(哪条路径)。 这是我正在尝试的
我有一个关于 Bitbucket 的项目。只有源被提交。为了将项目检索到新机器上,我在 IntelliJ 中使用了 Version Control > Checkout from Ve
所以,我想更改我公司的一个项目,以使用一些与 IDE 无关的设置。我在使用 Tomcat 设置 Java 应用程序方面有非常少的经验(我几乎不记得它是如何工作的)。 因此,为了帮助制作独立于 IDE
我有 2 个独立的项目,一个在 Cocos2dx v3.6 中,一个在 Swift 中。我想从 Swift 项目开始游戏。我该怎么做? 我已经将整个 cocos2dx 项目复制到我的 Swift 项目
Cordova 绝对是新手。这些是我完成的步骤: checkout 现有项目 运行cordova build ios 以上生成此构建错误: (node:10242) UnhandledPromiseR
我正在使用 JQuery 隐藏/显示 li。我的要求是,当我点击任何 li 时,它应该显示但隐藏所有其他 li 项目。当我将鼠标悬停在文本上时 'show all list item but don
我想将我所有的java 项目(223 个项目)迁移到gradle 项目。我正在使用由 SpringSource STS 团队开发的 Gradle Eclipse 插件。 目前,我所有的 java 项目
我下载this Eclipse Luna ,对于 Java EE 开发人员,如描述中所见,它支持 Web 应用程序。我找不到 file -> new -> other -> web projects

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!