- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章解析Java中的定时器及使用定时器制作弹弹球游戏的示例由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
在我们编程过程中如果需要执行一些简单的定时任务,无须做复杂的控制,我们可以考虑使用JDK中的Timer定时任务来实现。下面LZ就其原理、实例以及Timer缺陷三个方面来解析java Timer定时器.
1、简介 在java中一个完整定时任务需要由Timer、TimerTask两个类来配合完成。 API中是这样定义他们的,Timer:一种工具,线程用其安排以后在后台线程中执行的任务。可安排任务执行一次,或者定期重复执行。由TimerTask:Timer 安排为一次执行或重复执行的任务。我们可以这样理解Timer是一种定时器工具,用来在一个后台线程计划执行指定任务,而TimerTask一个抽象类,它的子类代表一个可以被Timer计划的任务。 Timer类 在工具类Timer中,提供了四个构造方法,每个构造方法都启动了计时器线程,同时Timer类可以保证多个线程可以共享单个Timer对象而无需进行外部同步,所以Timer类是线程安全的。但是由于每一个Timer对象对应的是单个后台线程,用于顺序执行所有的计时器任务,一般情况下我们的线程任务执行所消耗的时间应该非常短,但是由于特殊情况导致某个定时器任务执行的时间太长,那么他就会“独占”计时器的任务执行线程,其后的所有线程都必须等待它执行完,这就会延迟后续任务的执行,使这些任务堆积在一起,具体情况我们后面分析。 当程序初始化完成Timer后,定时任务就会按照我们设定的时间去执行,Timer提供了schedule方法,该方法有多中重载方式来适应不同的情况,如下: schedule(TimerTask task, Date time):安排在指定的时间执行指定的任务。 schedule(TimerTask task, Date firstTime, long period) :安排指定的任务在指定的时间开始进行重复的固定延迟执行。 schedule(TimerTask task, long delay) :安排在指定延迟后执行指定的任务。 schedule(TimerTask task, long delay, long period) :安排指定的任务从指定的延迟后开始进行重复的固定延迟执行。 同时也重载了scheduleAtFixedRate方法,scheduleAtFixedRate方法与schedule相同,只不过他们的侧重点不同,区别后面分析。 scheduleAtFixedRate(TimerTask task, Date firstTime, long period):安排指定的任务在指定的时间开始进行重复的固定速率执行。 scheduleAtFixedRate(TimerTask task, long delay, long period):安排指定的任务在指定的延迟后开始进行重复的固定速率执行。 TimerTask TimerTask类是一个抽象类,由Timer 安排为一次执行或重复执行的任务。它有一个抽象方法run()方法,该方法用于执行相应计时器任务要执行的操作。因此每一个具体的任务类都必须继承TimerTask,然后重写run()方法。 另外它还有两个非抽象的方法: boolean cancel():取消此计时器任务。 long scheduledExecutionTime():返回此任务最近实际执行的安排执行时间.
2、实例 2.1、指定延迟时间执行定时任务 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
public
class
TimerTest01 {
Timer timer;
public
TimerTest01(
int
time){
timer =
new
Timer();
timer.schedule(
new
TimerTaskTest01(), time *
1000
);
}
public
static
void
main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(
"timer begin...."
);
new
TimerTest01(
3
);
}
}
public
class
TimerTaskTest01
extends
TimerTask{
public
void
run() {
System.out.println(
"Time's up!!!!"
);
}
}
|
运行结果:
首先打印:
|
1
|
timer begin....
|
3秒后打印:
|
1
|
Time's up!!!!
|
2.2、在指定时间执行定时任务 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
public
class
TimerTest02 {
Timer timer;
public
TimerTest02(){
Date time = getTime();
System.out.println(
"指定时间time="
+ time);
timer =
new
Timer();
timer.schedule(
new
TimerTaskTest02(), time);
}
public
Date getTime(){
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.set(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY,
11
);
calendar.set(Calendar.MINUTE,
39
);
calendar.set(Calendar.SECOND,
00
);
Date time = calendar.getTime();
return
time;
}
public
static
void
main(String[] args) {
new
TimerTest02();
}
}
public
class
TimerTaskTest02
extends
TimerTask{
@Override
public
void
run() {
System.out.println(
"指定时间执行线程任务..."
);
}
}
|
当时间到达11:39:00时就会执行该线程任务,当然大于该时间也会执行!!执行结果为:
|
1
2
|
指定时间time=Tue Jun 10 11:39:00 CST 2014
指定时间执行线程任务...
|
2.3、在延迟指定时间后以指定的间隔时间循环执行定时任务 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
public
class
TimerTest03 {
Timer timer;
public
TimerTest03(){
timer =
new
Timer();
timer.schedule(
new
TimerTaskTest03(),
1000
,
2000
);
}
public
static
void
main(String[] args) {
new
TimerTest03();
}
}
public
class
TimerTaskTest03
extends
TimerTask{
@Override
public
void
run() {
Date date =
new
Date(
this
.scheduledExecutionTime());
System.out.println(
"本次执行该线程的时间为:"
+ date);
}
}
|
运行结果
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
本次执行该线程的时间为:Tue Jun 10 21:19:47 CST 2014
本次执行该线程的时间为:Tue Jun 10 21:19:49 CST 2014
本次执行该线程的时间为:Tue Jun 10 21:19:51 CST 2014
本次执行该线程的时间为:Tue Jun 10 21:19:53 CST 2014
本次执行该线程的时间为:Tue Jun 10 21:19:55 CST 2014
本次执行该线程的时间为:Tue Jun 10 21:19:57 CST 2014
.................
|
对于这个线程任务,如果我们不将该任务停止,他会一直运行下去。 对于上面三个实例,LZ只是简单的演示了一下,同时也没有讲解scheduleAtFixedRate方法的例子,其实该方法与schedule方法一样! 2.4、分析schedule和scheduleAtFixedRate (1)schedule(TimerTask task, Date time)、schedule(TimerTask task, long delay) 对于这两个方法而言,如果指定的计划执行时间scheduledExecutionTime<= systemCurrentTime,则task会被立即执行。scheduledExecutionTime不会因为某一个task的过度执行而改变。 (2)schedule(TimerTask task, Date firstTime, long period)、schedule(TimerTask task, long delay, long period) 这两个方法与上面两个就有点儿不同的,前面提过Timer的计时器任务会因为前一个任务执行时间较长而延时。在这两个方法中,每一次执行的task的计划时间会随着前一个task的实际时间而发生改变,也就是scheduledExecutionTime(n+1)=realExecutionTime(n)+periodTime。也就是说如果第n个task由于某种情况导致这次的执行时间过程,最后导致systemCurrentTime>= scheduledExecutionTime(n+1),这是第n+1个task并不会因为到时了而执行,他会等待第n个task执行完之后再执行,那么这样势必会导致n+2个的执行实现scheduledExecutionTime放生改变即scheduledExecutionTime(n+2) = realExecutionTime(n+1)+periodTime。所以这两个方法更加注重保存间隔时间的稳定。 (3)scheduleAtFixedRate(TimerTask task, Date firstTime, long period)、scheduleAtFixedRate(TimerTask task, long delay, long period) 在前面也提过scheduleAtFixedRate与schedule方法的侧重点不同,schedule方法侧重保存间隔时间的稳定,而scheduleAtFixedRate方法更加侧重于保持执行频率的稳定。为什么这么说,原因如下。在schedule方法中会因为前一个任务的延迟而导致其后面的定时任务延时,而scheduleAtFixedRate方法则不会,如果第n个task执行时间过长导致systemCurrentTime>= scheduledExecutionTime(n+1),则不会做任何等待他会立即执行第n+1个task,所以scheduleAtFixedRate方法执行时间的计算方法不同于schedule,而是scheduledExecutionTime(n)=firstExecuteTime +n*periodTime,该计算方法永远保持不变。所以scheduleAtFixedRate更加侧重于保持执行频率的稳定.
3、Timer的缺陷 3.1、Timer的缺陷 Timer计时器可以定时(指定时间执行任务)、延迟(延迟5秒执行任务)、周期性地执行任务(每隔个1秒执行任务),但是,Timer存在一些缺陷。首先Timer对调度的支持是基于绝对时间的,而不是相对时间,所以它对系统时间的改变非常敏感。其次Timer线程是不会捕获异常的,如果TimerTask抛出的了未检查异常则会导致Timer线程终止,同时Timer也不会重新恢复线程的执行,他会错误的认为整个Timer线程都会取消。同时,已经被安排单尚未执行的TimerTask也不会再执行了,新的任务也不能被调度。故如果TimerTask抛出未检查的异常,Timer将会产生无法预料的行为。 (1)Timer管理时间延迟缺陷 前面Timer在执行定时任务时只会创建一个线程任务,如果存在多个线程,若其中某个线程因为某种原因而导致线程任务执行时间过长,超过了两个任务的间隔时间,会发生一些缺陷:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
public
class
TimerTest04 {
private
Timer timer;
public
long
start;
public
TimerTest04(){
this
.timer =
new
Timer();
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public
void
timerOne(){
timer.schedule(
new
TimerTask() {
public
void
run() {
System.out.println(
"timerOne invoked ,the time:"
+ (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
try
{
Thread.sleep(
4000
);
//线程休眠3000
}
catch
(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},
1000
);
}
public
void
timerTwo(){
timer.schedule(
new
TimerTask() {
public
void
run() {
System.out.println(
"timerOne invoked ,the time:"
+ (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
}
},
3000
);
}
public
static
void
main(String[] args)
throws
Exception {
TimerTest04 test =
new
TimerTest04();
test.timerOne();
test.timerTwo();
}
}
|
按照我们正常思路,timerTwo应该是在3s后执行,其结果应该是:
|
1
2
|
timerOne invoked ,the time:1001
timerOne invoked ,the time:3001
|
但是事与愿违,timerOne由于sleep(4000),休眠了4S,同时Timer内部是一个线程,导致timeOne所需的时间超过了间隔时间,结果:
|
1
2
|
timerOne invoked ,the time:1000
timerOne invoked ,the time:5000
|
(2)Timer抛出异常缺陷 如果TimerTask抛出RuntimeException,Timer会终止所有任务的运行。如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
public
class
TimerTest04 {
private
Timer timer;
public
TimerTest04(){
this
.timer =
new
Timer();
}
public
void
timerOne(){
timer.schedule(
new
TimerTask() {
public
void
run() {
throw
new
RuntimeException();
}
},
1000
);
}
public
void
timerTwo(){
timer.schedule(
new
TimerTask() {
public
void
run() {
System.out.println(
"我会不会执行呢??"
);
}
},
1000
);
}
public
static
void
main(String[] args) {
TimerTest04 test =
new
TimerTest04();
test.timerOne();
test.timerTwo();
}
}
|
运行结果:timerOne抛出异常,导致timerTwo任务终止.
|
1
2
3
4
|
Exception in thread "Timer-0" java.lang.RuntimeException
at com.chenssy.timer.TimerTest04$1.run(TimerTest04.java:25)
at java.util.TimerThread.mainLoop(Timer.java:555)
at java.util.TimerThread.run(Timer.java:505)
|
对于Timer的缺陷,我们可以考虑 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 来替代。Timer是基于绝对时间的,对系统时间比较敏感,而ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 则是基于相对时间;Timer是内部是单一线程,而ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor内部是个线程池,所以可以支持多个任务并发执行。 3.2、用ScheduledExecutorService替代Timer (1)解决问题一:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
public
class
ScheduledExecutorTest {
private
ScheduledExecutorService scheduExec;
public
long
start;
ScheduledExecutorTest(){
this
.scheduExec = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(
2
);
this
.start = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public
void
timerOne(){
scheduExec.schedule(
new
Runnable() {
public
void
run() {
System.out.println(
"timerOne,the time:"
+ (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
try
{
Thread.sleep(
4000
);
}
catch
(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},
1000
,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
public
void
timerTwo(){
scheduExec.schedule(
new
Runnable() {
public
void
run() {
System.out.println(
"timerTwo,the time:"
+ (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
}
},
2000
,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
public
static
void
main(String[] args) {
ScheduledExecutorTest test =
new
ScheduledExecutorTest();
test.timerOne();
test.timerTwo();
}
}
|
运行结果:
|
1
2
|
timerOne,the time:1003
timerTwo,the time:2005
|
(2)解决问题二 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
public
class
ScheduledExecutorTest {
private
ScheduledExecutorService scheduExec;
public
long
start;
ScheduledExecutorTest(){
this
.scheduExec = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(
2
);
this
.start = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public
void
timerOne(){
scheduExec.schedule(
new
Runnable() {
public
void
run() {
throw
new
RuntimeException();
}
},
1000
,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
public
void
timerTwo(){
scheduExec.scheduleAtFixedRate(
new
Runnable() {
public
void
run() {
System.out.println(
"timerTwo invoked ....."
);
}
},
2000
,
500
,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
public
static
void
main(String[] args) {
ScheduledExecutorTest test =
new
ScheduledExecutorTest();
test.timerOne();
test.timerTwo();
}
}
|
运行结果:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
timerTwo invoked .....
timerTwo invoked .....
timerTwo invoked .....
timerTwo invoked .....
timerTwo invoked .....
timerTwo invoked .....
timerTwo invoked .....
timerTwo invoked .....
timerTwo invoked .....
........................
|
4、使用定时器实现弹弹球 模拟书上的一个例题做了一个弹弹球,是在画布上的指定位置画多个圆,经过一段的延时后,在附近位置重新画。使球看起来是动,通过JSpinner组件调节延时,来控制弹弹球的移动速度. BallsCanvas.java 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
|
public
class
BallsCanvas
extends
Canvas
implements
ActionListener,
FocusListener {
private
Ball balls[];
// 多个球
private
Timer timer;
private
static
class
Ball {
int
x, y;
// 坐标
Color color;
// 颜色
boolean
up, left;
// 运动方向
Ball(
int
x,
int
y, Color color) {
this
.x = x;
this
.y = y;
this
.color = color;
up = left =
false
;
}
}
public
BallsCanvas(Color colors[],
int
delay) {
// 初始化颜色、延时
this
.balls =
new
Ball[colors.length];
for
(
int
i =
0
, x =
40
; i < colors.length; i++, x +=
40
) {
balls[i] =
new
Ball(x, x, colors[i]);
}
this
.addFocusListener(
this
);
timer =
new
Timer(delay,
this
);
// 创建定时器对象,delay指定延时
timer.start();
}
// 设置延时
public
void
setDelay(
int
delay) {
timer.setDelay(delay);
}
// 在canvas上面作画
public
void
paint(Graphics g) {
for
(
int
i =
0
; i < balls.length; i++) {
g.setColor(balls[i].color);
// 设置颜色
balls[i].x = balls[i].left ? balls[i].x -
10
: balls[i].x +
10
;
if
(balls[i].x <
0
|| balls[i].x >=
this
.getWidth()) {
// 到水平方向更改方向
balls[i].left = !balls[i].left;
}
balls[i].y = balls[i].up ? balls[i].y -
10
: balls[i].y +
10
;
if
(balls[i].y <
0
|| balls[i].y >=
this
.getHeight()) {
// 到垂直方向更改方向
balls[i].up = !balls[i].up;
}
g.fillOval(balls[i].x, balls[i].y,
20
,
20
);
// 画指定直径的圆
}
}
// 定时器定时执行事件
@Override
public
void
actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
repaint();
// 重画
}
// 获得焦点
@Override
public
void
focusGained(FocusEvent e) {
timer.stop();
// 定时器停止
}
// 失去焦点
@Override
public
void
focusLost(FocusEvent e) {
timer.restart();
// 定时器重启动
}
}
|
BallsJFrame.java 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
class
BallsJFrame
extends
JFrame
implements
ChangeListener {
private
BallsCanvas ball;
private
JSpinner spinner;
public
BallsJFrame() {
super
(
"弹弹球"
);
this
.setBounds(
300
,
200
,
480
,
360
);
this
.setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
Color colors[] = { Color.red, Color.green, Color.blue,
Color.magenta, Color.cyan };
ball =
new
BallsCanvas(colors,
100
);
this
.getContentPane().add(ball);
JPanel panel =
new
JPanel();
this
.getContentPane().add(panel,
"South"
);
panel.add(
new
JLabel(
"Delay"
));
spinner =
new
JSpinner();
spinner.setValue(
100
);
panel.add(spinner);
spinner.addChangeListener(
this
);
this
.setVisible(
true
);
}
@Override
public
void
stateChanged(ChangeEvent e) {
// 修改JSpinner值时,单击JSpinner的Up或者down按钮时,或者在JSpinner中按Enter键
ball.setDelay(Integer.parseInt(
""
+ spinner.getValue()));
}
public
static
void
main(String[] args) {
new
BallsJFrame();
}
}
|
效果如下:
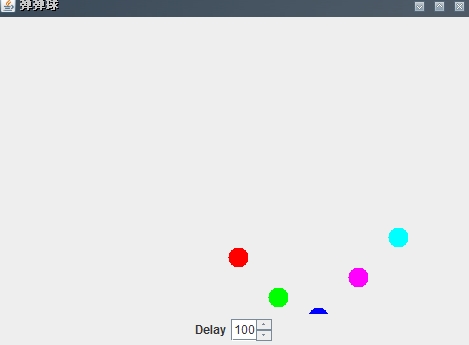
最后此篇关于解析Java中的定时器及使用定时器制作弹弹球游戏的示例的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于解析Java中的定时器及使用定时器制作弹弹球游戏的示例的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我在网上搜索但没有找到任何合适的文章解释如何使用 javascript 使用 WCF 服务,尤其是 WebScriptEndpoint。 任何人都可以对此给出任何指导吗? 谢谢 最佳答案 这是一篇关于
我正在编写一个将运行 Linux 命令的 C 程序,例如: cat/etc/passwd | grep 列表 |剪切-c 1-5 我没有任何结果 *这里 parent 等待第一个 child (chi
所以我正在尝试处理文件上传,然后将该文件作为二进制文件存储到数据库中。在我存储它之后,我尝试在给定的 URL 上提供文件。我似乎找不到适合这里的方法。我需要使用数据库,因为我使用 Google 应用引
我正在尝试制作一个宏,将下面的公式添加到单元格中,然后将其拖到整个列中并在 H 列中复制相同的公式 我想在 F 和 H 列中输入公式的数据 Range("F1").formula = "=IF(ISE
问题类似于this one ,但我想使用 OperatorPrecedenceParser 解析带有函数应用程序的表达式在 FParsec . 这是我的 AST: type Expression =
我想通过使用 sequelize 和 node.js 将这个查询更改为代码取决于在哪里 select COUNT(gender) as genderCount from customers where
我正在使用GNU bash,版本5.0.3(1)-发行版(x86_64-pc-linux-gnu),我想知道为什么简单的赋值语句会出现语法错误: #/bin/bash var1=/tmp
这里,为什么我的代码在 IE 中不起作用。我的代码适用于所有浏览器。没有问题。但是当我在 IE 上运行我的项目时,它发现错误。 而且我的 jquery 类和 insertadjacentHTMl 也不
我正在尝试更改标签的innerHTML。我无权访问该表单,因此无法编辑 HTML。标签具有的唯一标识符是“for”属性。 这是输入和标签的结构:
我有一个页面,我可以在其中返回用户帖子,可以使用一些 jquery 代码对这些帖子进行即时评论,在发布新评论后,我在帖子下插入新评论以及删除 按钮。问题是 Delete 按钮在新插入的元素上不起作用,
我有一个大约有 20 列的“管道分隔”文件。我只想使用 sha1sum 散列第一列,它是一个数字,如帐号,并按原样返回其余列。 使用 awk 或 sed 执行此操作的最佳方法是什么? Accounti
我需要将以下内容插入到我的表中...我的用户表有五列 id、用户名、密码、名称、条目。 (我还没有提交任何东西到条目中,我稍后会使用 php 来做)但由于某种原因我不断收到这个错误:#1054 - U
所以我试图有一个输入字段,我可以在其中输入任何字符,但然后将输入的值小写,删除任何非字母数字字符,留下“。”而不是空格。 例如,如果我输入: 地球的 70% 是水,-!*#$^^ & 30% 土地 输
我正在尝试做一些我认为非常简单的事情,但出于某种原因我没有得到想要的结果?我是 javascript 的新手,但对 java 有经验,所以我相信我没有使用某种正确的规则。 这是一个获取输入值、检查选择
我想使用 angularjs 从 mysql 数据库加载数据。 这就是应用程序的工作原理;用户登录,他们的用户名存储在 cookie 中。该用户名显示在主页上 我想获取这个值并通过 angularjs
我正在使用 autoLayout,我想在 UITableViewCell 上放置一个 UIlabel,它应该始终位于单元格的右侧和右侧的中心。 这就是我想要实现的目标 所以在这里你可以看到我正在谈论的
我需要与 MySql 等效的 elasticsearch 查询。我的 sql 查询: SELECT DISTINCT t.product_id AS id FROM tbl_sup_price t
我正在实现代码以使用 JSON。 func setup() { if let flickrURL = NSURL(string: "https://api.flickr.com/
我尝试使用for循环声明变量,然后测试cols和rols是否相同。如果是,它将运行递归函数。但是,我在 javascript 中执行 do 时遇到问题。有人可以帮忙吗? 现在,在比较 col.1 和
我举了一个我正在处理的问题的简短示例。 HTML代码: 1 2 3 CSS 代码: .BB a:hover{ color: #000; } .BB > li:after {

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!