- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章java数据结构基础:单,双向链表由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
单向链表比顺序结构的线性表最大的好处就是不用保证存放的位置,它只需要用指针去指向下一个元素就能搞定.
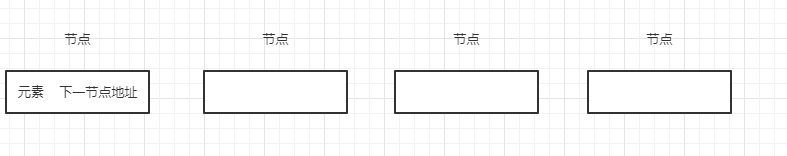
图画的比较粗糙,简单的讲解一下:
上面四个长方形,每个长方形都是一个节点。在长方形中,一种包含两个东西,一个是当前节点的元素,一个是指向下一节点的地址。这个下一个节点的地址指向了下一个节点中的元素。以此类推.
在最左边的叫做头节点,同样,最后面的叫尾节点.
所以,我们所有的操作都是根据节点来进行操作.
这些代码都有很详细的注释,我就不做过多的解释了,你直接复制代码到本地idea运行一遍就全部知道了.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
|
package
com.zxy.lianbiao;
/**
* @Author Zxy
* @Date 2021/2/3 21:25
* @Version 1.0
*/
/**
* 基于单向链表实现元素的存取
*
* @param <E>
*/
public
class
MySinglyLinkedList<E>
implements
MyList<E> {
/**
* 定义单向链表中的节点对象
*/
class
Node<E> {
private
E item;
// 存储元素
private
Node next;
// 存储下一个节点对象
public
Node(E item, Node next) {
this
.item = item;
this
.next = next;
}
}
private
Node head;
// 存放链表中的头节点
private
int
size;
// 记录元素的个数
/**
* 向链表中添加元素
*
* @param element
*/
@Override
public
void
add(E element) {
// 创建节点
Node<E> node =
new
Node<>(element,
null
);
// 找到尾节点
Node tail = getTail();
// 节点的挂接
if
(tail ==
null
) {
// 如果没有尾节点,那意思就是头节点都不存在
// 没有头节点,那么就把创建的节点给头节点
this
.head = node;
}
else
{
tail.next = node;
}
// 记录元素的个数
this
.size++;
}
/**
* 找尾节点
*/
private
Node getTail() {
// 判断头节点是否存在
if
(
this
.head ==
null
) {
return
null
;
}
// 查找尾节点
Node node =
this
.head;
while
(
true
) {
if
(node.next ==
null
) {
break
;
}
node = node.next;
// 移动指针指向下一个
}
return
node;
}
/**
* 根据元素的位置获取元素
*
* @param index
* @return
*/
@Override
public
E get(
int
index) {
// 校验index的合法性
this
.checkIndex(index);
// 根据位置获取指定节点
Node<E> node =
this
.getNode(index);
// 将该节点中的元素返回
return
node.item;
}
/**
* 对index进行校验
*/
private
void
checkIndex(
int
index) {
// 0<=index<size
if
(!(index >=
0
&& index <
this
.size)) {
throw
new
IndexOutOfBoundsException(
"Index: "
+ index +
" this.size: "
+
this
.size);
}
}
/**
* 根据位置获取节点
*/
private
Node<E> getNode(
int
index) {
Node<E> node =
this
.head;
for
(
int
i =
0
; i < index; i++) {
node = node.next;
}
return
node;
}
/**
* 获取元素的个数
*
* @return
*/
@Override
public
int
size() {
return
this
.size;
}
/**
* 根据元素位置删除元素
*
* @param index
* @return
*/
@Override
public
E remove(
int
index) {
// 校验index合法性
this
.checkIndex(index);
// 根据位置找到节点对象
Node<E> node = getNode(index);
// 获取该节点对象中的元素
E item = node.item;
// 将该节点对象从单向链表中移除
// 判断当前删除的节点是否为头节点
if
(
this
.head == node) {
this
.head = node.next;
}
else
{
Node<E> temp =
this
.head;
for
(
int
i =
0
; i < index -
1
; i++) {
temp = temp.next;
// 此时的temp就是要删除的那个节点的前一个节点
}
temp.next = node.next;
// 将当前节点的前一个节点指向当前节点的后一个节点
}
// 然后将当前节点的下一个节点指向null
node.next =
null
;
// 记录元素个数
this
.size--;
// 将该元素返回
return
item;
}
/**
* 插入节点思路:如果当前共有三个节点分别是1,2,3,在1和2的中间插入4,原本的指向是1->2 现改变成1->4 4->2 先获取到指定位置的node,再获取到前一个位置的node和下一个位置的node
*/
public
void
insert(
int
index, E element) {
// 先根据要插入的位置拿到这个位置的节点对象
Node<E> item = getNode(index);
// 根据插入的元素新建一个节点
Node<E> eNode =
new
Node<>(element,
null
);
// 如果是头节点,那么就找不到前一个,直接把这个赋值给head
if
(index ==
0
){
// index==0代表是替换掉头节点
this
.head = eNode;
eNode.next = item;
this
.size++;
}
else
{
// 根据当前的节点对象去找到前一个节点对象和后一个节点对象
Node<E> before =
this
.head;
// 根据头节点去找
for
(
int
i =
0
; i < index -
1
; i++) {
before = before.next;
// 此时的before就是当前节点的前一个节点
}
before.next = eNode;
eNode.next = item;
this
.size++;
}
}
public
static
void
main(String[] args) {
MySinglyLinkedList<String> list =
new
MySinglyLinkedList<>();
System.out.println(
"添加节点开始------------------------"
);
list.add((String)
"a"
);
list.add((String)
"b"
);
list.add((String)
"c"
);
list.add((String)
"d"
);
System.out.println(
"添加节点完成-------------------------\n"
);
System.out.println(
"插入指定的元素"
);
list.insert(
0
,
"f"
);
for
(
int
i =
0
; i < list.size; i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
}
}
|
昨天写完单向链表和栈结构之后,看了看程杰大大的书中有介绍双向链表的部分。虽然是c语言写的,但是我还是用Java给翻译出来了.
思路如下:
首先,双向链表和单向链表的最大区别就是,双向链表比单链表多了个指向前一节点的指针。代码量其实并不比单链表多很多,只是思路的转变需要克服一下.
其次就是在插入元素的时候,我们可以在链表的头部插入,也可以在链表的尾部插入(因为有两个指针嘛) 。
代码其实和单链表差不多,如果感兴趣的话可以去看看我之前写的单链表的文章。虽然文笔很烂,但是代码货真价实.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
|
package
com.zxy.lianbiao;
/**
* @Author Zxy
* @Date 2021/2/4 20:11
* @Version 1.0
*/
/**
* 基于双向链表实现元素存取的容器
*
* @param <E>
*/
public
class
MyDoublyLinkedList<E>
implements
MyList<E> {
/**
* 定义双向链表节点对象
*/
class
Node<E> {
E item;
// 记录元素
Node<E> prev;
// 记录前一个节点对象
Node<E> next;
// 记录下一个节点对象
public
Node(Node<E> prev, E item, Node<E> next) {
this
.item = item;
this
.prev = prev;
this
.next = next;
}
}
private
Node head;
// 记录头节点
private
Node tail;
// 记录尾节点
private
int
size;
// 记录元素个数
/**
* 向双向链表中添加元素的方法
*
* @param element
*/
@Override
public
void
add(E element) {
linkLast(element);
}
/**
* 将节点对象添加到双向链表的尾部
*/
private
void
linkLast(E element) {
Node t =
this
.tail;
// 获取尾节点
Node<E> node =
new
Node<>(t, element,
null
);
// 创建节点对象
this
.tail = node;
// 将新节点定义为尾节点 因为原来的尾节点被这个新节点替代了
if
(t ==
null
) {
// 说明一个节点都没有,这个还得是头节点
this
.head = node;
}
else
{
t.next = node;
}
this
.size++;
}
/**
* 根据指定位置获取元素
*
* @param index
* @return
*/
@Override
public
E get(
int
index) {
this
.checkIndex(index);
// 根据位置查找节点对象
Node<E> node =
this
.getNode(index);
return
node.item;
}
/**
* 对index的合法性校验
*/
private
void
checkIndex(
int
index) {
if
(!(index >=
0
&& index <
this
.size)) {
throw
new
IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
}
/**
* 根据位置获取指定节点对象
*/
private
Node getNode(
int
index) {
// 判断当前位置距离头或者尾哪个节点更近 使用二分法
if
(index < (
this
.size >>
1
)) {
Node node =
this
.head;
for
(
int
i =
0
; i < index; i++) {
node = node.next;
}
return
node;
}
else
{
Node node =
this
.tail;
for
(
int
i =
this
.size -
1
; i > index; i--) {
node = node.prev;
}
return
node;
}
}
/**
* 返回元素的个数
*
* @return
*/
@Override
public
int
size() {
return
this
.size;
}
/**
* 删除元素
*
* @param index
* @return
*/
@Override
public
E remove(
int
index) {
// 对index进行合法性校验
this
.checkIndex(index);
Node node =
this
.getNode(index);
// 根据位置获取到节点对象
// 获取节点对象的元素
E item = (E) node.item;
// 判断当前节点是否为头节点
if
(node.prev ==
null
) {
this
.head = node.next;
}
else
{
node.prev.next = node.next;
}
// 判断当前节点是否为尾节点
if
(node.next ==
null
) {
// node.prev.next = null;
this
.tail = node.prev;
}
else
{
node.next.prev = node.prev;
}
// 当前节点断掉与他后继节点的连接
node.next =
null
;
// 当前节点断掉与直接前驱节点的连接
node.prev =
null
;
node.item =
null
;
this
.size--;
return
item;
}
/**
* 在双向链表的头添加元素
*/
public
void
addFirst(E element) {
this
.linkFirst(element);
}
/**
* 在链表的头添加元素
*
* @param element
*/
public
void
linkFirst(E element) {
// 获取头节点对象
Node head =
this
.head;
Node<E> eNode =
new
Node<>(
null
, element, head);
// 将新节点定义为头节点
this
.head = eNode;
if
(head ==
null
) {
// 如果为空,说明该链表中一个节点都没有 也就是该头节点也是尾节点
this
.tail = eNode;
}
else
{
head.prev = eNode;
}
this
.size++;
}
/**
* 在链表的尾部添加元素
*
* @param element
*/
public
void
addLast(E element) {
this
.linkLast(element);
}
public
static
void
main(String[] args) {
MyDoublyLinkedList<String> list =
new
MyDoublyLinkedList<>();
list.add(
"a"
);
list.add(
"b"
);
list.add(
"c"
);
list.add(
"d"
);
list.add(
"e"
);
System.out.println(list.remove(
2
));
System.out.println(list.size);
for
(
int
i =
0
; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
}
}
|
本篇文章就到这里了,希望能给你带来帮助,也希望您能够多多关注我的更多内容! 。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43581288/article/details/113660067 。
最后此篇关于java数据结构基础:单,双向链表的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于java数据结构基础:单,双向链表的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我有 2 个类:User 和 UserPicture,它们具有 1:1 关系。 public class User { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy=G
使用ssh转发时,我无法针对远程服务器使用cvs和ftp进行提交。是否可以让服务器对我的机器发起请求-我希望服务器上的Web应用程序调用我的机器上的REST方法。 谢谢。 尼古拉·G。 最佳答案 是的
我正在 Python 2.7.12 中实现双向 A* 算法,并在 Russell 和 Norvig 第 3 章的罗马尼亚 map 上进行测试。边具有权重,目的是找到两个节点之间的最短路径。 这是测试图
您能否建议一种映射或类似的数据结构,让我们可以轻松地相互获取值和键。也就是说,每个都可以用来寻找另一个。 最佳答案 Java 在其标准库中没有双向映射。 例如使用 BiMap 来自Google Gua
我想同步两个数据库运行时 服务器 A:安装了公共(public) IP 和 mysql 的 Amazon ec2。服务器B:这是局域网中带有mysql的私有(private)机器。 (IP是私有(pr
保存双向@OneToOne 映射时,hibernate 是否应该在两个表上都记录? 我有一个包含 applicant_id 列的表 interview,它引用了包含字段 interview_id 的
我喜欢新的 SwipeRefreshLayout!它看起来很棒,而且非常容易使用。但我想在两个方向上使用它。我有一个消息屏幕,我想通过从上到下滑动来加载旧消息,我想通过从下到上滑动来加载新消息。 这个
使用 ICS 4.0.1(愿意升级到 4.0.3)(不会 root 和重写 android 操作系统) 在接收到 android beam 后,是否可以将 NDEF 消息发送回 android 手机
我想知道处理这种 git 场景的最佳方法: Git 仓库:CoreProduct Git repo b: SpecificCustomerProduct 是从 a fork 出来的 到目前为止,我们一
这个问题在这里已经有了答案: How to implement an efficient bidirectional hash table? (8 个回答) 关闭2年前。 我在 python 中做这个
您能否推荐一种 map 或类似的数据结构,我们可以在其中轻松地从彼此获取值和键。也就是说,每个都可以用来寻找另一个。 最佳答案 Java 在其标准库中没有双向映射。 例如使用 BiMap 来自 Goo
Java中是否有类似双面列表的东西?也许第三方实现? 这里有一个小例子来证明我的想法。 原始状态: 答:0-1-2-3 | | | | 乙:0-1-2-3 删除 B 中的元素 1 后: 空值 | 答:
我有两个实体通过这样的双向 OneToOne 关联连接: @Entity class Parent { @NotNull String businessKey; @OneToO
我已将 Vagrant 配置为使用 Rsync 共享文件夹而不是(非常慢)vboxsf VirtualBox 默认提供的文件系统: Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
@keyframes mgm { from { max-height: 250px; } to { max-height: 0px; } } .mgm {
我想了解有关使用双向 LSTM 进行序列分类时合并模式的更多详细信息,尤其是对于我还不清楚的“Concat”合并模式。 根据我对这个方案的理解: 在将前向和后向层的合并结果传递到 sigmoid 函数
我有兴趣将本地 git 存储库设置为远程存储库的镜像。我已经阅读了一些可能相关的帖子,但主要区别在于我需要对两个存储库进行读写访问。 大多数时候,用户会针对 Repo A 工作,但是有时他们会针对 R
我已经仔细阅读了文档 https://firebase.google.com/docs/database/web/read-and-write以及网上很多例子。但这里有一个脱节:在将对象添加到数据库时
这个问题已经有答案了: Hibernate bidirectional @ManyToOne, updating the not owning side not working (3 个回答) 已关闭
我知道有很多关于它的问题,但我找不到针对我的问题的好的答案。 我使用 Jboss 作为 7,Spring 和 Hibernate (4) 作为 JPA 2.0 提供程序,因此我有简单的 @OneToM

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!