- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章如何用 Python 子进程关闭 Excel 自动化中的弹窗由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
利用Python进行Excel自动化操作的过程中,尤其是涉及VBA时,可能遇到消息框/弹窗(MsgBox)。此时需要人为响应,否则代码卡死直至超时 [^1] [^2]。根本的解决方法是VBA代码中不要出现类似弹窗,但有时我们无权修改被操作的Excel文件,例如这是我们进行自动化测试的对象。所以本文记录从代码角度解决此类问题的方法.
使用xlwings(或者其他自动化库)打开Excel文件test.xlsm,读取Sheet1!A1单元格内容。很简单的一个操作:
import xlwings as xwwb = xw.Book("test.xlsm")msg = wb.sheets("Sheet1").range("A1").valueprint(msg)wb.close()
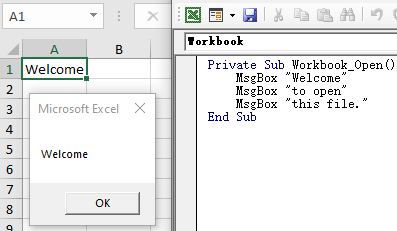
然而不幸的是,打开工作簿时进行了热情的欢迎仪式:
Private Sub Workbook_Open() MsgBox "Welcome" MsgBox "to open" MsgBox "this file."End Sub
第一个弹窗Welcome就卡住了Excel,Python代码相应卡死在第一行.
主程序中不可能直接处理或者绕过此类问题,也不能奢望有人随时蹲守点击下一步――那就开启一个子线程来护航吧。因此,解决方案是利用子线程监听并随时关闭弹窗,直到主程序圆满结束。 解决这个问题,需要以下两个知识点(基础知识请课外学习):
pywinauto顾名思义是Windows界面自动化库,模拟鼠标和键盘操作窗体和控件 [^3]。不同于先获取句柄再获取属性的传统方式,pywinauto的API更加友好和pythonic。例如,两行代码搞定窗口捕捉和点击:
from pywinauto.application import Applicationwin = Application(backend="win32").connect(title="Microsoft Excel")win.Dialog.Button.click()
本文采用自定义线程类的方式,启动线程后自动执行run()函数来完成上述操作。具体代码如下,注意构造函数中的两个参数:
# listener.pyimport timefrom threading import Thread, Eventfrom pywinauto.application import Applicationclass MsgBoxListener(Thread): def __init__(self, title:str, interval:int): Thread.__init__(self) self._title = title self._interval = interval self._stop_event = Event() def stop(self): self._stop_event.set() @property def is_running(self): return not self._stop_event.is_set() def run(self): while self.is_running: try: time.sleep(self._interval) self._close_msgbox() except Exception as e: print(e, flush=True) def _close_msgbox(self): """Close the default Excel MsgBox with title "Microsoft Excel".""" win = Application(backend="win32").connect(title=self._title) win.Dialog.Button.click()if __name__=="__main__": t = MsgBoxListener("Microsoft Excel", 3) t.start() time.sleep(10) t.stop()
于是,整个过程分为三步:
import xlwings as xwfrom listener import MsgBoxListener# start listen threadlistener = MsgBoxListener("Microsoft Excel", 3)listener.start()# main process as beforewb = xw.Book("test.xlsm")msg = wb.sheets("Sheet1").range("A1").valueprint(msg)wb.close()# stop listener threadlistener.stop()
到此问题基本解决,本地运行效果完全达到预期。但我的真实需求是以系统服务方式在服务器上进行Excel文件自动化测试,后续发现,当以系统服务方式运行时,pywinauto竟然捕捉不到弹窗!这或许是pywinauto一个潜在的问题 [^4].
那就只好转向相对底层的win32gui,所幸完美解决了上述问题。 win32gui是pywin32库的一部分,所以实际安装命令是:
pip install pywin32
整个方案和前文描述完全一致,只是替换MsgBoxListener类中关闭弹窗的方法:
import win32gui, win32condef _close_msgbox(self): # find the top window by title hwnd = win32gui.FindWindow(None, self._title) if not hwnd: return # find child button h_btn = win32gui.FindWindowEx(hwnd, None,"Button", None) if not h_btn: return # show text text = win32gui.GetWindowText(h_btn) print(text) # click button win32gui.PostMessage(h_btn, win32con.WM_LBUTTONDOWN, None, None) time.sleep(0.2) win32gui.PostMessage(h_btn, win32con.WM_LBUTTONUP, None, None) time.sleep(0.2)
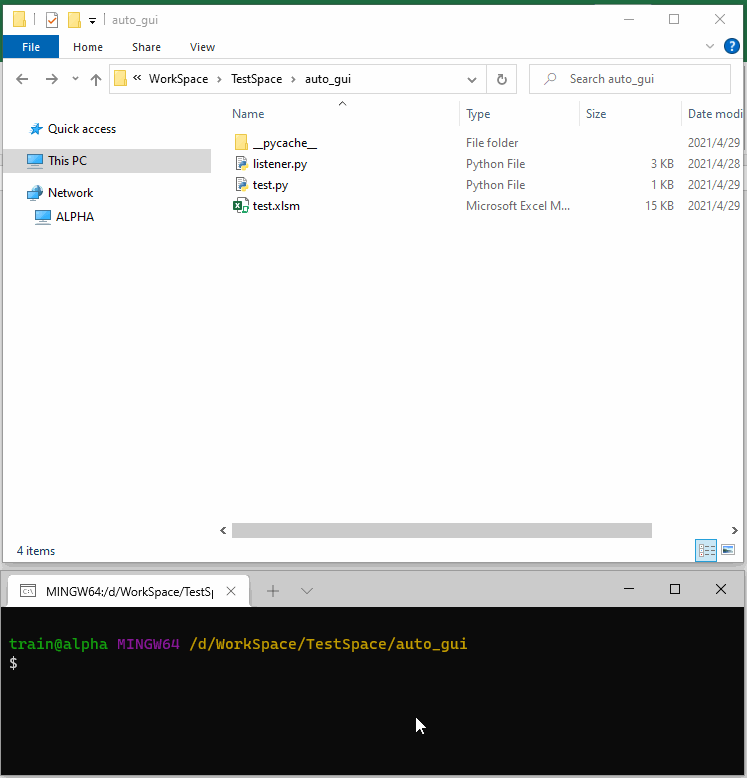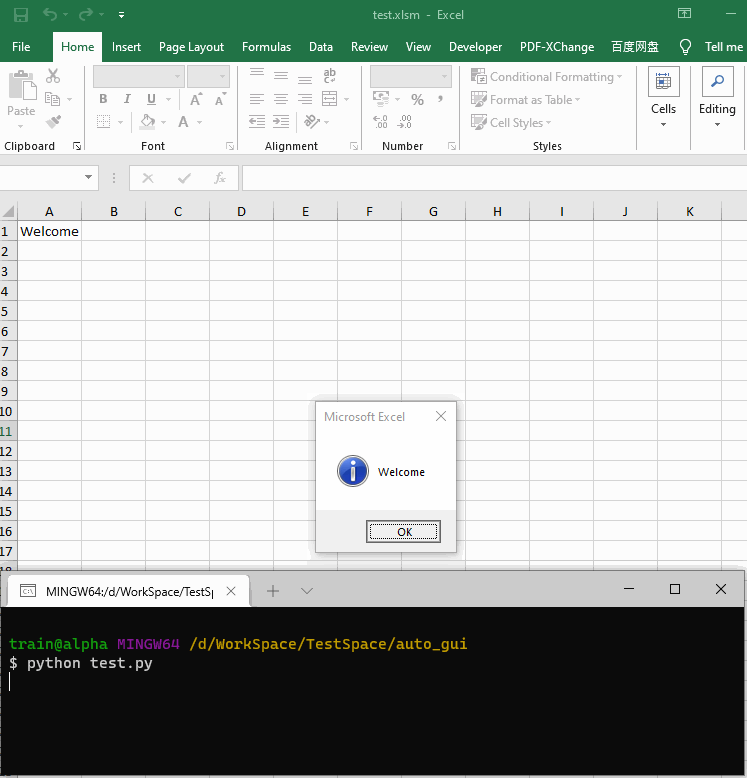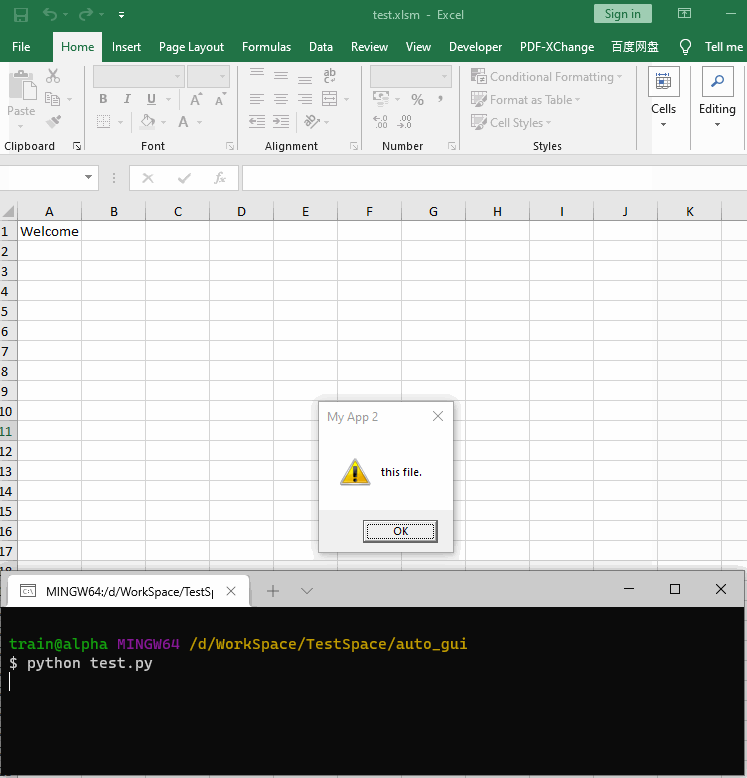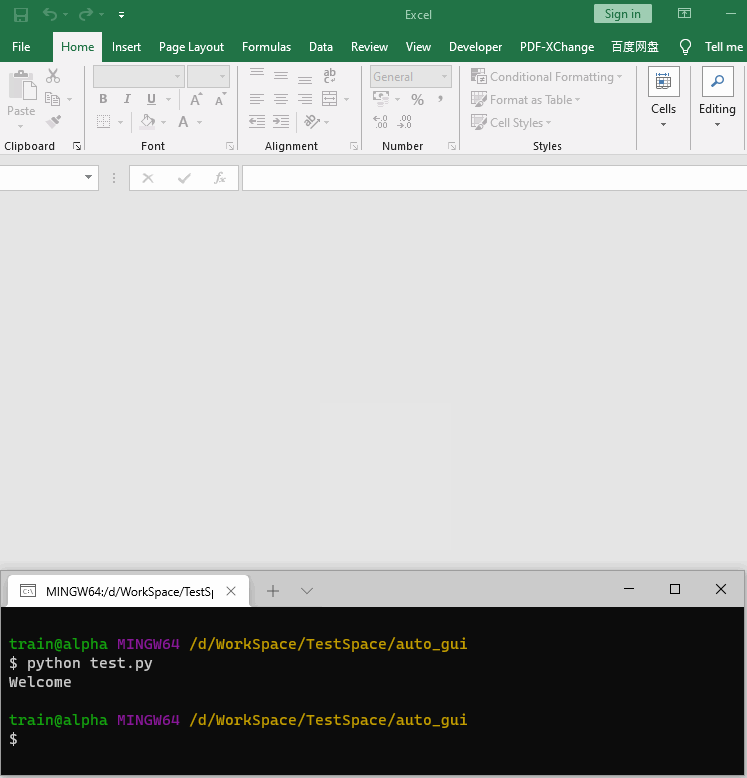
更一般地,当同时存在默认标题和自定义标题的弹窗时,就不便于采用标题方式进行捕捉了。例如 。
MsgBox "Message with default title.", vbInformation, MsgBox "Message with title My App 1", vbInformation, "My App 1"MsgBox "Message with title My App 2", vbInformation, "My App 2"
那就扩大搜索范围,依次点击所有包含确定性描述的按钮(例如OK,Yes,Confirm)来关闭弹窗。同理替换MsgBoxListener类的_close_msgbox()方法(同时构造函数中不再需要title参数):
def _close_msgbox(self): """Click any button ("OK", "Yes" or "Confirm") to close message box.""" # get handles of all top windows h_windows = [] win32gui.EnumWindows(lambda hWnd, param: param.append(hWnd), h_windows) # check each window for h_window in h_windows: # get child button with text OK, Yes or Confirm of given window h_btn = win32gui.FindWindowEx(h_window, None,"Button", None) if not h_btn: continue # check button text text = win32gui.GetWindowText(h_btn) if not text.lower() in ("ok", "yes", "confirm"): continue # click button win32gui.PostMessage(h_btn, win32con.WM_LBUTTONDOWN, None, None) time.sleep(0.2) win32gui.PostMessage(h_btn, win32con.WM_LBUTTONUP, None, None) time.sleep(0.2)
最后,实例演示结束全文,以后再也不用担心意外弹窗了.
以上就是如何用 Python 子进程关闭 Excel 自动化中的弹窗的详细内容,更多关于Python 子进程关闭 Excel 弹窗的资料请关注我其它相关文章! 。
原文链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/t36llQH-edcP3ShTT4Q5tQ 。
最后此篇关于如何用 Python 子进程关闭 Excel 自动化中的弹窗的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于如何用 Python 子进程关闭 Excel 自动化中的弹窗的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我想做的是让 JTextPane 在 JPanel 中占用尽可能多的空间。对于我使用的 UpdateInfoPanel: public class UpdateInfoPanel extends JP
我在 JPanel 中有一个 JTextArea,我想将其与 JScrollPane 一起使用。我正在使用 GridBagLayout。当我运行它时,框架似乎为 JScrollPane 腾出了空间,但
我想在 xcode 中实现以下功能。 我有一个 View Controller 。在这个 UIViewController 中,我有一个 UITabBar。它们下面是一个 UIView。将 UITab
有谁知道Firebird 2.5有没有类似于SQL中“STUFF”函数的功能? 我有一个包含父用户记录的表,另一个表包含与父相关的子用户记录。我希望能够提取用户拥有的“ROLES”的逗号分隔字符串,而
我想使用 JSON 作为 mirth channel 的输入和输出,例如详细信息保存在数据库中或创建 HL7 消息。 简而言之,输入为 JSON 解析它并输出为任何格式。 最佳答案 var objec
通常我会使用 R 并执行 merge.by,但这个文件似乎太大了,部门中的任何一台计算机都无法处理它! (任何从事遗传学工作的人的附加信息)本质上,插补似乎删除了 snp ID 的 rs 数字,我只剩
我有一个以前可能被问过的问题,但我很难找到正确的描述。我希望有人能帮助我。 在下面的代码中,我设置了varprice,我想添加javascript变量accu_id以通过rails在我的数据库中查找记
我有一个简单的 SVG 文件,在 Firefox 中可以正常查看 - 它的一些包装文本使用 foreignObject 包含一些 HTML - 文本包装在 div 中:
所以我正在为学校编写一个 Ruby 程序,如果某个值是 1 或 3,则将 bool 值更改为 true,如果是 0 或 2,则更改为 false。由于我有 Java 背景,所以我认为这段代码应该有效:
我做了什么: 我在这些账户之间创建了 VPC 对等连接 互联网网关也连接到每个 VPC 还配置了路由表(以允许来自双方的流量) 情况1: 当这两个 VPC 在同一个账户中时,我成功测试了从另一个 La
我有一个名为 contacts 的表: user_id contact_id 10294 10295 10294 10293 10293 10294 102
我正在使用 Magento 中的新模板。为避免重复代码,我想为每个产品预览使用相同的子模板。 特别是我做了这样一个展示: $products = Mage::getModel('catalog/pro
“for”是否总是检查协议(protocol)中定义的每个函数中第一个参数的类型? 编辑(改写): 当协议(protocol)方法只有一个参数时,根据该单个参数的类型(直接或任意)找到实现。当协议(p
我想从我的 PHP 代码中调用 JavaScript 函数。我通过使用以下方法实现了这一点: echo ' drawChart($id); '; 这工作正常,但我想从我的 PHP 代码中获取数据,我使
这个问题已经有答案了: Event binding on dynamically created elements? (23 个回答) 已关闭 5 年前。 我有一个动态表单,我想在其中附加一些其他 h
我正在尝试找到一种解决方案,以在 componentDidMount 中的映射项上使用 setState。 我正在使用 GraphQL连同 Gatsby返回许多 data 项目,但要求在特定的 pat
我在 ScrollView 中有一个 View 。只要用户按住该 View ,我想每 80 毫秒调用一次方法。这是我已经实现的: final Runnable vibrate = new Runnab
我用 jni 开发了一个 android 应用程序。我在 GetStringUTFChars 的 dvmDecodeIndirectRef 中得到了一个 dvmabort。我只中止了一次。 为什么会这
当我到达我的 Activity 时,我调用 FragmentPagerAdapter 来处理我的不同选项卡。在我的一个选项卡中,我想显示一个 RecyclerView,但他从未出现过,有了断点,我看到
当我按下 Activity 中的按钮时,会弹出一个 DialogFragment。在对话框 fragment 中,有一个看起来像普通 ListView 的 RecyclerView。 我想要的行为是当

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!