- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章C/C++中多重继承详解及其作用介绍由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
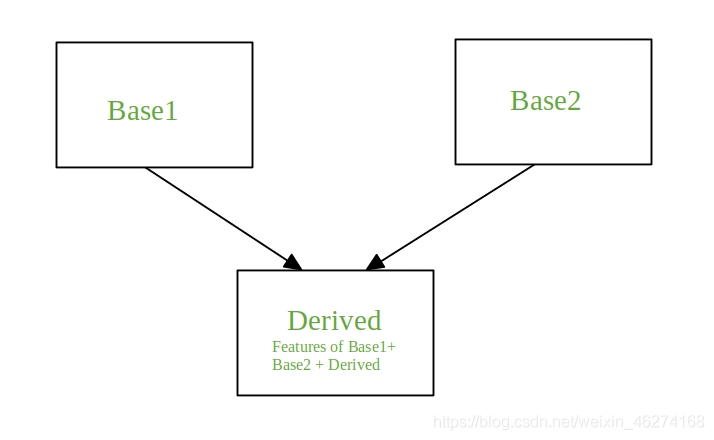
多重继承 (multiple inheritance): 一个派生类有两个或多个基类, 派生类从两个或多个基类中继承所需的属性. C++ 为了适应这种情况, 允许一个派生类同时继承多个基类. 这种行为称为多重继承. 。
。
。
多重继承的格式
派生类构造函数名(总形式参数表列): 基类1构造函数(实际参数表列), 基类2构造函数(实际参数表列), 基类3构造函数(实际参数表列){ 派生类中新增数成员据成员初始化语句}
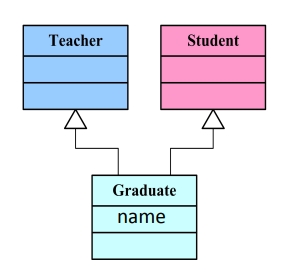
Teacher 类
#ifndef PROJECT5_TEACHER_H#define PROJECT5_TEACHER_H#include <string>using namespace std;class Teacher {protected: string name; int age; string title;public: Teacher(string n, int a, string t); void display_teacher();};#endif //PROJECT5_TEACHER_H
Teacher.cpp
#include <iostream>#include "Teacher.h"using namespace std;Teacher::Teacher(string n, int a, string t) : name(n), age(a), title(t) {}void Teacher::display_teacher() { cout << "Teacher name: " << name << endl; cout << "age: " << age << endl; cout << "title: " << title << endl;}
Student 类
#ifndef PROJECT5_STUDENT_H#define PROJECT5_STUDENT_H#include <string>using namespace std;class Student {protected: string name; char gender; double score;public: Student(string n, char g, double s); void display_student();};#endif //PROJECT5_STUDENT_H
Student.cpp
#include <iostream>#include "Student.h"using namespace std;Student::Student(string n, char g, double s) : name(n), gender(g), score(s) {}void Student::display_student() { cout << "Student name: " << name << endl; cout << "gender: " << gender << endl; cout << "score: " << score << endl;}
Graduate 类:
#ifndef PROJECT5_GRADUATE_H#define PROJECT5_GRADUATE_H#include "Teacher.h"#include "Student.h"#include <string>using namespace std;class Graduate : public Teacher, public Student{private: double wage;public: Graduate(string t_n, int t_a, string t_t, string s_n, char s_g, double s_s); void display_graduate();};#endif //PROJECT5_GRADUATE_H
Graduate.cpp
#include "Graduate.h"Graduate::Graduate(string t_n, int t_a, string t_t, string s_n, char s_g, double s_s) : Teacher(t_n, t_a, t_t), Student(s_n, s_g, s_s) {}void Graduate::display_graduate() { display_teacher(); display_student();}
main
#include <iostream>#include "Graduate.h"using namespace std;int main() { Graduate graduate1("王叔叔", 18, "隔壁老王", "我是小白呀", 'f', 99); graduate1.display_graduate(); return 0;}
输出结果:
Teacher name: 王叔叔age: 18title: 隔壁老王Student name: 我是小白呀gender: fscore: 99
。
二义性 (Ambiguity) 指在多重继承中, 两个基类中的数据成员名相同. 。
二义性在派生类中的解决方法
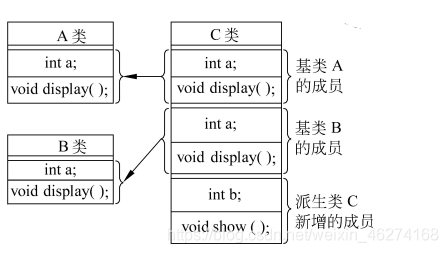
A 类
#ifndef PROJECT5_A_H#define PROJECT5_A_H#include <iostream>using namespace std;class A {public: int num; void display() {cout << "A's num:" << num << endl;};};#endif //PROJECT5_A_H
B 类
#ifndef PROJECT5_B_H#define PROJECT5_B_H#include <iostream>using namespace std;class B {public: int num; void display() {cout << "B's num:" << num << endl;};};#endif //PROJECT5_B_H
C 类
#ifndef PROJECT5_C_H#define PROJECT5_C_H#include <iostream>#include "A.h"#include "B.h"using namespace std;class C: public A, public B{public: int c; void display() {cout << c << endl;};};#endif //PROJECT5_C_H
main
#include <iostream>#include "C.h"using namespace std;int main() { C c1; c1.A::num = 1; // 用基类名限定 c1.B::num = 2; // 用基类名限定 c1.A::display(); c1.B::display(); return 0;}
输出结果
A's num:1B's num:2
错误的写法 。
#include <iostream>#include "C.h"using namespace std;int main() { C c1; c1.num = 1; c1.display(); return 0;}
A 类
class A {public: int num; void display() {cout << "A's num:" << num << endl;};};
B 类
class B {public: int num; void display() {cout << "B's num:" << num << endl;};};
C 类
class C: public A, public B{public: int num; void display() {cout << "C's num:" << num << endl;};};
main
int main() { C c1; c1.num = 3; c1.A::num = 1; c1.B::num = 2; c1.display(); c1.A::display(); c1.B::display(); return 0;}
输出结果
C's num:3A's num:1B's num:2
同名覆盖
N 类
class N {public: int a; void display(){ cout << "A::a=" << a <<endl; }};
A 类
class A : public N {public: int a1;};
B 类
class B : public N {public: int a2;};
C 类
class C: public A, public B{public: int a3; void display() {cout << "a3=" << a3 << endl;};};
main
int main() { C c1; // 合法访问 c1.A::a = 3; c1.A::display(); return 0;}
输出结果
A::a=3
到此这篇关于C/C++中多重继承详解及其作用介绍的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C++多重继承内容请搜索我以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我! 。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46274168/article/details/116729769 。
最后此篇关于C/C++中多重继承详解及其作用介绍的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于C/C++中多重继承详解及其作用介绍的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我需要将文本放在 中在一个 Div 中,在另一个 Div 中,在另一个 Div 中。所以这是它的样子: #document Change PIN
奇怪的事情发生了。 我有一个基本的 html 代码。 html,头部, body 。(因为我收到了一些反对票,这里是完整的代码) 这是我的CSS: html { backgroun
我正在尝试将 Assets 中的一组图像加载到 UICollectionview 中存在的 ImageView 中,但每当我运行应用程序时它都会显示错误。而且也没有显示图像。 我在ViewDidLoa
我需要根据带参数的 perl 脚本的输出更改一些环境变量。在 tcsh 中,我可以使用别名命令来评估 perl 脚本的输出。 tcsh: alias setsdk 'eval `/localhome/
我使用 Windows 身份验证创建了一个新的 Blazor(服务器端)应用程序,并使用 IIS Express 运行它。它将显示一条消息“Hello Domain\User!”来自右上方的以下 Ra
这是我的方法 void login(Event event);我想知道 Kotlin 中应该如何 最佳答案 在 Kotlin 中通配符运算符是 * 。它指示编译器它是未知的,但一旦知道,就不会有其他类
看下面的代码 for story in book if story.title.length < 140 - var story
我正在尝试用 C 语言学习字符串处理。我写了一个程序,它存储了一些音乐轨道,并帮助用户检查他/她想到的歌曲是否存在于存储的轨道中。这是通过要求用户输入一串字符来完成的。然后程序使用 strstr()
我正在学习 sscanf 并遇到如下格式字符串: sscanf("%[^:]:%[^*=]%*[*=]%n",a,b,&c); 我理解 %[^:] 部分意味着扫描直到遇到 ':' 并将其分配给 a。:
def char_check(x,y): if (str(x) in y or x.find(y) > -1) or (str(y) in x or y.find(x) > -1):
我有一种情况,我想将文本文件中的现有行包含到一个新 block 中。 line 1 line 2 line in block line 3 line 4 应该变成 line 1 line 2 line
我有一个新项目,我正在尝试设置 Django 调试工具栏。首先,我尝试了快速设置,它只涉及将 'debug_toolbar' 添加到我的已安装应用程序列表中。有了这个,当我转到我的根 URL 时,调试
在 Matlab 中,如果我有一个函数 f,例如签名是 f(a,b,c),我可以创建一个只有一个变量 b 的函数,它将使用固定的 a=a1 和 c=c1 调用 f: g = @(b) f(a1, b,
我不明白为什么 ForEach 中的元素之间有多余的垂直间距在 VStack 里面在 ScrollView 里面使用 GeometryReader 时渲染自定义水平分隔线。 Scrol
我想知道,是否有关于何时使用 session 和 cookie 的指南或最佳实践? 什么应该和什么不应该存储在其中?谢谢! 最佳答案 这些文档很好地了解了 session cookie 的安全问题以及
我在 scipy/numpy 中有一个 Nx3 矩阵,我想用它制作一个 3 维条形图,其中 X 轴和 Y 轴由矩阵的第一列和第二列的值、高度确定每个条形的 是矩阵中的第三列,条形的数量由 N 确定。
假设我用两种不同的方式初始化信号量 sem_init(&randomsem,0,1) sem_init(&randomsem,0,0) 现在, sem_wait(&randomsem) 在这两种情况下
我怀疑该值如何存储在“WORD”中,因为 PStr 包含实际输出。? 既然Pstr中存储的是小写到大写的字母,那么在printf中如何将其给出为“WORD”。有人可以吗?解释一下? #include
我有一个 3x3 数组: var my_array = [[0,1,2], [3,4,5], [6,7,8]]; 并想获得它的第一个 2
我意识到您可以使用如下方式轻松检查焦点: var hasFocus = true; $(window).blur(function(){ hasFocus = false; }); $(win

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!