作者热门文章
- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章Python 作图实现坐标轴截断(打断)的效果由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
主题:利用python画图实现坐标轴截断或打断 。
关键词:python, plot, matplotlib, break axes 。
首先介绍一种简单快速的方法――调用包 brokenaxes.
详细请点击参考 。
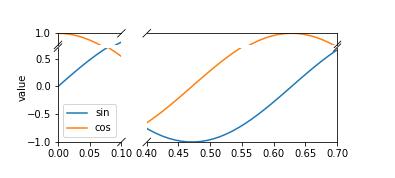
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom brokenaxes import brokenaxesimport numpy as npfig = plt.figure(figsize=(5,2))bax = brokenaxes(xlims=((0, .1), (.4, .7)), ylims=((-1, .7), (.79, 1)), hspace=.05, despine=False)x = np.linspace(0, 1, 100)bax.plot(x, np.sin(10 * x), label="sin")bax.plot(x, np.cos(10 * x), label="cos")bax.legend(loc=3)bax.set_xlabel("time")bax.set_ylabel("value")
效果如下:
拼接法,该种方法代码更繁琐,但更有可能满足个性化的需求.
请点击参考链接 。
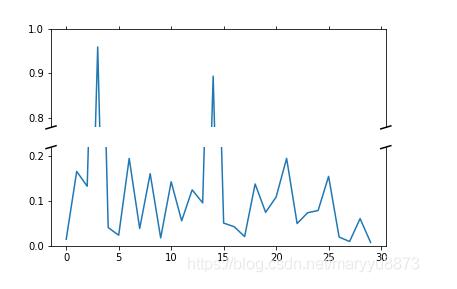
"""Broken axis example, where the y-axis will have a portion cut out."""import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as np# 30 points between [0, 0.2) originally made using np.random.rand(30)*.2pts = np.array([ 0.015, 0.166, 0.133, 0.159, 0.041, 0.024, 0.195, 0.039, 0.161, 0.018, 0.143, 0.056, 0.125, 0.096, 0.094, 0.051, 0.043, 0.021, 0.138, 0.075, 0.109, 0.195, 0.050, 0.074, 0.079, 0.155, 0.020, 0.010, 0.061, 0.008])# Now let"s make two outlier points which are far away from everything.pts[[3, 14]] += .8# If we were to simply plot pts, we"d lose most of the interesting# details due to the outliers. So let"s "break" or "cut-out" the y-axis# into two portions - use the top (ax) for the outliers, and the bottom# (ax2) for the details of the majority of our dataf, (ax, ax2) = plt.subplots(2, 1, sharex=True)# plot the same data on both axesax.plot(pts)ax2.plot(pts)# zoom-in / limit the view to different portions of the dataax.set_ylim(.78, 1.) # outliers onlyax2.set_ylim(0, .22) # most of the data# hide the spines between ax and ax2ax.spines["bottom"].set_visible(False)ax2.spines["top"].set_visible(False)ax.xaxis.tick_top()ax.tick_params(labeltop="off") # don"t put tick labels at the topax2.xaxis.tick_bottom()# This looks pretty good, and was fairly painless, but you can get that# cut-out diagonal lines look with just a bit more work. The important# thing to know here is that in axes coordinates, which are always# between 0-1, spine endpoints are at these locations (0,0), (0,1),# (1,0), and (1,1). Thus, we just need to put the diagonals in the# appropriate corners of each of our axes, and so long as we use the# right transform and disable clipping.d = .015 # how big to make the diagonal lines in axes coordinates# arguments to pass to plot, just so we don"t keep repeating themkwargs = dict(transform=ax.transAxes, color="k", clip_on=False)ax.plot((-d, +d), (-d, +d), **kwargs) # top-left diagonalax.plot((1 - d, 1 + d), (-d, +d), **kwargs) # top-right diagonalkwargs.update(transform=ax2.transAxes) # switch to the bottom axesax2.plot((-d, +d), (1 - d, 1 + d), **kwargs) # bottom-left diagonalax2.plot((1 - d, 1 + d), (1 - d, 1 + d), **kwargs) # bottom-right diagonal# What"s cool about this is that now if we vary the distance between# ax and ax2 via f.subplots_adjust(hspace=...) or plt.subplot_tool(),# the diagonal lines will move accordingly, and stay right at the tips# of the spines they are "breaking"plt.show()
效果如下:
补充:python绘制折线图--纵坐标y轴截断 。
看代码吧~ 。
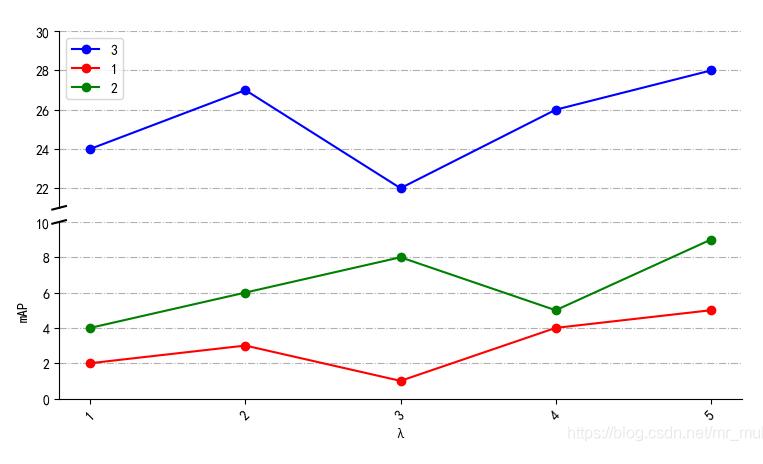
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-"""Created on Wed Dec 4 21:50:38 2019@author: muli"""import matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom pylab import * mpl.rcParams["font.sans-serif"] = ["SimHei"] #支持中文 names = ["1","2","3","4","5"] # 刻度值命名x = [1,2,3,4,5] # 横坐标y3= [2,3,1,4,5] # 纵坐标y4= [4,6,8,5,9] # 纵坐标y5=[24,27,22,26,28] # 纵坐标f, (ax3, ax) = plt.subplots(2, 1, sharex=False) # 绘制两个子图plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0,hspace=0.08) # 设置 子图间距ax.plot(x, y3, color="red", marker="o", linestyle="solid",label=u"1") # 绘制折线ax.plot(x, y4, color="g", marker="o", linestyle="solid",label=u"2") # 绘制折线plt.xticks(x, names, rotation=45) # 刻度值ax3.xaxis.set_major_locator(plt.NullLocator()) # 删除坐标轴的刻度显示ax3.plot(x, y5, color="blue", marker="o", linestyle="solid",label=u"3") # 绘制折线ax3.plot(x, y3, color="red", marker="o", linestyle="solid",label=u"1") # 起图例作用ax3.plot(x, y4, color="g", marker="o", linestyle="solid",label=u"2") # 起图例作用ax3.set_ylim(21, 30) # 设置纵坐标范围ax.set_ylim(0, 10) # 设置纵坐标范围ax3.grid(axis="both",linestyle="-.") # 打开网格线ax.grid(axis="y",linestyle="-.") # 打开网格线ax3.legend() # 让图例生效plt.xlabel(u"λ") #X轴标签plt.ylabel("mAP") #Y轴标签ax.spines["top"].set_visible(False) # 边框控制ax.spines["bottom"].set_visible(True) # 边框控制ax.spines["right"].set_visible(False) # 边框控制ax3.spines["top"].set_visible(False) # 边框控制ax3.spines["bottom"].set_visible(False) # 边框控制ax3.spines["right"].set_visible(False) # 边框控制ax.tick_params(labeltop="off") # 绘制断层线d = 0.01 # 断层线的大小kwargs = dict(transform=ax3.transAxes, color="k", clip_on=False)ax3.plot((-d, +d), (-d, +d), **kwargs) # top-left diagonalkwargs.update(transform=ax.transAxes, color="k") # switch to the bottom axesax.plot((-d, +d), (1 - d, 1 + d), **kwargs) # bottom-left diagonalplt.show()
结果如图所示:
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我。如有错误或未考虑完全的地方,望不吝赐教.
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/maryyu8873/article/details/84313423 。
最后此篇关于Python 作图实现坐标轴截断(打断)的效果的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于Python 作图实现坐标轴截断(打断)的效果的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
如标题所述,我正在尝试使用 R 中的 Shiny 创建一个程序来读取用户上传的 csv 文件,之后用户可以从该文件中选择一个变量来查看绘制的图通过 ggplot。我试图通过两个选项卡实现这一点,第一个
嗨,关于 plotly 的“简单”问题,我想删除当数据集包含大于 10000 的数字时似乎自动出现在 y 轴上的 k。我尝试将数据上传到 plotly 在线,它把 ' k' 也一样。 例如使用数据的子

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!