- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章详细说明关于Java的数据库连接(JDBC)由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
JDBC(JavaDataBase Connectivity) 就是Java数据库连接,说白了就是用Java语言来操作数据库。原来我们操作数据库是在控制台使用SQL语句来操作数据库,JDBC是用Java语言向数据库发送SQL语句.
早期SUN公司的天才们想编写一套可以连接天下所有数据库的API,但是当他们刚刚开始时就发现这是不可完成的任务,因为各个厂商的数据库服务器差异太大了。后来SUN开始与数据库厂商们讨论,最终得出的结论是,由SUN提供一套访问数据库的规范(就是一组接口),并提供连接数据库的协议标准,然后各个数据库厂商会遵循SUN的规范提供一套访问自己公司的数据库服务器的API出现。SUN提供的规范命名为JDBC,而各个厂商提供的,遵循了JDBC规范的,可以访问自己数据库的API被称之为驱动!JDBC是接口,而JDBC驱动才是接口的实现,没有驱动无法完成数据库连接!每个数据库厂商都有自己的驱动,用来连接自己公司的数据库.
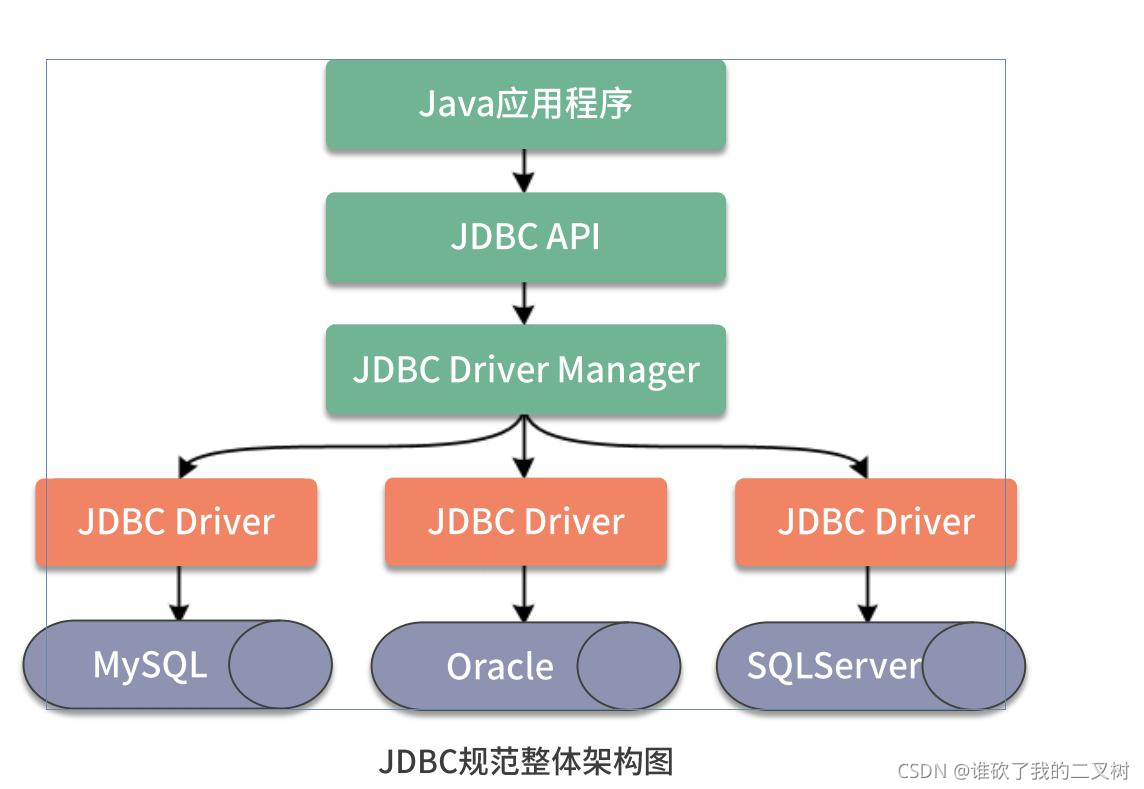
通过下载MySQL的驱动jar文件,将其添加到项目中间,在注册驱动时要指定为已经下载好的驱动.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
package
jdbc;
import
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver;
//这是我们驱动的路径
import
java.sql.Connection;
import
java.sql.SQLException;
import
java.sql.Statement;
import
java.util.Properties;
public
class
Jdbc01 {
public
static
void
main(String[] args)
throws
SQLException {
//1.注册驱动
Driver driver =
new
Driver();
//2.得到连接
//jdbc:mysql:// 规定好的协议 localhost 连接的地址 3306 监听的端口 test_table 连接的数据库
String url =
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test_table"
;
Properties properties =
new
Properties();
//user和password 规定好的不能随意改
properties.setProperty(
"user"
,
"root"
);
//
properties.setProperty(
"password"
,
"161142"
);
Connection connect = driver.connect(url, properties);
//相当于网络连接
//3.执行sql语句
//String sql = "insert into actor values(null,'syj','女','2000-05-26','110')";
String sql =
"update actor set name = 'xhj' where id = 2"
;
Statement statement = connect.createStatement();
int
rows = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
//返回影响的行数
if
(rows >
0
) System.out.println(
"添加成功"
);
else
System.out.println(
"添加失败"
);
//4.关闭连接资源
statement.close();
connect.close();
}
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
|
public
class
JdbcConn {
@Test
/* 第一种 */
public
void
testConn01()
throws
SQLException {
//获取Driver实现类对象
Driver driver =
new
Driver();
String url =
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test_table"
;
Properties properties =
new
Properties();
properties.setProperty(
"user"
,
"root"
);
properties.setProperty(
"password"
,
"161142"
);
Connection connect = driver.connect(url, properties);
System.out.println(connect);
}
@Test
/* 第二种 */
public
void
testConn02()
throws
Exception{
//使用反射加载Driver类,动态加载,可以通过配置文件灵活使用各种数据库
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(
"com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
);
Driver driver = (Driver) aClass.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
String url =
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test_table"
;
Properties properties =
new
Properties();
properties.setProperty(
"user"
,
"root"
);
properties.setProperty(
"password"
,
"161142"
);
Connection connect = driver.connect(url, properties);
System.out.println(connect);
}
@Test
/* 第三种 */
//DriverManager统一来管理Driver
public
void
testConn03()
throws
Exception{
//使用反射加载Driver类
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(
"com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
);
Driver driver = (Driver) aClass.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
//创建url和user和password
String url =
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test_table"
;
String user =
"root"
;
String password =
"161142"
;
DriverManager.registerDriver(driver);
//注册Driver驱动
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println(connection);
}
@Test
/* 第四种 */
public
void
testConn04()
throws
Exception{
//使用反射加载Driver类
Class.forName(
"com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
);
/* Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver")在底层加载Driver时自动完成注册驱动,简化代码
//在底层加载Driver时会自动加载静态代码块
static {
try {
DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());
} catch (SQLException var1) {
throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!");
}
}
*/
//Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
/* Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");这句话也可以去掉
mysql驱动5.1.6可以无需CLass.forName(“com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
从jdk1.5以后使用了jdbc4,不再需要显示调用class.forName()注册驱动而是自动调用驱动
jar包下META-INF\services\java.sqI.Driver文本中的类名称去注册
建议还是写上,更加明确
*/
//创建url和user和password
String url =
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test_table"
;
String user =
"root"
;
String password =
"161142"
;
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println(connection);
}
@Test
/* 第五种(推荐使用) */
public
void
testConn05()
throws
Exception{
//在方式4的情况下,将信息放到配置文件里,利于后续可持续操作
//获取配置文件信息
Properties properties =
new
Properties();
properties.load(
new
FileInputStream(
"src\\mysql.properties"
));
//获取相关信息
String user = properties.getProperty(
"user"
);
String password = properties.getProperty(
"password"
);
String url = properties.getProperty(
"url"
);
String driver = properties.getProperty(
"driver"
);
Class.forName(driver);
//加载Driver类,建议加上
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println(connection);
}
}
|
使用ResultSet 记录查询结果 ResultSet: 底层使用ArrayList 存放每一行数据(二维字节数组,每一维表示一行中的一个数据) Resultment: 用于执行静态SQL语句并返回其生成的结果的对象,是一个接口,需要各个数据库厂家来实现。(实际中我们一般不用这个) 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
public
class
jdbc03 {
public
static
void
main(String[] args)
throws
Exception {
Properties properties =
new
Properties();
properties.load(
new
FileInputStream(
"src\\mysql.properties"
));
String user = properties.getProperty(
"user"
);
String password = properties.getProperty(
"password"
);
String url = properties.getProperty(
"url"
);
String driver = properties.getProperty(
"driver"
);
Class.forName(driver);
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(
"select id,`name`,sex,borndate from actor;"
);
while
(resultSet.next()){
//resultSet.previous();//向上移动一行
int
id = resultSet.getInt(
1
);
//int id = resultSet.getInt("id"); //也可以按照列明来获取
String name = resultSet.getString(
2
);
String sex = resultSet.getString(
3
);
Date date = resultSet.getDate(
4
);
//Object object = resultSet.getObject(索引|列明); //对象形式操作(分情况考虑)
System.out.println(id +
"\t"
+ name +
"\t"
+ sex +
"\t"
+ date);
}
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
|
SQL注入: 是利用某些系统没有对用户输入的数据进行充分的检查,而在用户输入数据中注入非法的SQL语句段或命令,恶意攻击数据库。 例如下列代码实现了注入问题(而Statement就存在这个问题,所以实际开发过程中不用它) 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
create
table
admit(
name
varchar
(32),
password
varchar
(32));
insert
into
admit
values
(
'tom'
,
'1234'
);
select
*
from
admit
where
name
=
'tom'
and
password
=
'1234'
; # 输出 tom 1234
# 如果有人输入
name
为 1
' or password 为 or '
1
' = '
1
# 那么
select
就变成
select
*
from
admit
where
name
=
'1'
or
' and password = '
or
'1'
=
'1'
; # 其中
'1'
=
'1'
永远成立
|
使用PreparedStatement代替Statement就避免了注入问题,通过传入**?** 代替拼接 (PreparedStatement接口继承了Statement接口) 。
PreparedStatement的好处 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
public
class jdbc04 {
public
static
void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.
in
);
System.
out
.print(
"请输入用户名:"
);
String
name
= scanner.nextLine();
System.
out
.print(
"请输入密码:"
);
String pwd = scanner.nextLine();
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.
load
(new FileInputStream(
"src\\mysql.properties"
));
String
user
= properties.getProperty(
"user"
);
String
password
= properties.getProperty(
"password"
);
String url = properties.getProperty(
"url"
);
String driver = properties.getProperty(
"driver"
);
Class.forName(driver);
Connection
connection
= DriverManager.getConnection(url,
user
,
password
);
//Statement statement =
connection
.createStatement();
//preparedStatement是PreparedStatement实现类的对象
PreparedStatement preparedStatement =
connection
.prepareStatement(
"select `name` ,`password` "
+
"from admit where name = ? and password = ?"
);
preparedStatement.setString(1,
name
); //?号下标从1开始
preparedStatement.setString(2,pwd);
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
if (resultSet.
next
()) System.
out
.println(
"登录成功"
);
else
System.
out
.println(
"登陆失败"
);
preparedStatement.
close
();
connection
.
close
();
}
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
public
class jdbc05 {
public
static
void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.
in
);
System.
out
.print(
"请输入用户名:"
);
String
name
= scanner.nextLine();
System.
out
.print(
"请输入密码:"
);
String pwd = scanner.nextLine();
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.
load
(new FileInputStream(
"src\\mysql.properties"
));
String
user
= properties.getProperty(
"user"
);
String
password
= properties.getProperty(
"password"
);
String url = properties.getProperty(
"url"
);
String driver = properties.getProperty(
"driver"
);
Class.forName(driver);
Connection
connection
= DriverManager.getConnection(url,
user
,
password
);
//添加
String sql1 =
"insert into admit values(?,?)"
;
//修改
String sql2 =
"update admit set name = ? where name = ? and password = ?"
;
//删除
String sql3 =
"delete from admit where name = ? and password = ?"
;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement =
connection
.prepareStatement(sql3);
//preparedStatement.setString(1,
name
+
"plas"
); //?号下标从1开始
//preparedStatement.setString(2,
name
);
//preparedStatement.setString(3,pwd);
preparedStatement.setString(1,
name
);
preparedStatement.setString(2,pwd);
int
rows
= preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
if (
rows
> 0) System.
out
.println(
"操作成功"
);
else
System.
out
.println(
"操作失败"
);
preparedStatement.
close
();
connection
.
close
();
}
}
|
由于在进行数据库操作时,有些步骤是重复的,如连接,关闭资源等操作。 工具类 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
package utils;
import java.sql.*;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
public
class JDBCUtils {
private
static
String
user
; //用户名
private
static
String
password
; //密码
private
static
String url; //连接数据库的url
private
static
String driver; //驱动
//静态代码块进行行初始化
static
{
try {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.
load
(new FileInputStream(
"src\\mysql.properties"
));
user
= properties.getProperty(
"user"
);
password
= properties.getProperty(
"password"
);
url = properties.getProperty(
"url"
);
driver = properties.getProperty(
"driver"
);
} catch (Exception e) {
//实际开发过程中(将编译异常,改成运行异常,用户可以捕获异常,也可以默认处理该异常)
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//连接
public
static
Connection
getConnection(){
try {
return
DriverManager.getConnection(url,
user
,
password
);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//关闭资源
public
static
void
close
(ResultSet
set
, Statement statement,
Connection
connection
){
try {
if (
set
!=
null
)
set
.
close
();
if (statement !=
null
)statement.
close
();
if (
connection
!=
null
)
connection
.
close
();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
|
应用
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
|
public
class
JdbcUtilsTest {
@Test
//测试select操作
public
void
testSelect() {
Connection connection =
null
;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement =
null
;
ResultSet resultSet =
null
;
try
{
//得到连接
connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//设置sql
String sql =
"select * from actor where id = ?"
;
//创建PreparedStatement
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//占位赋值
preparedStatement.setInt(
1
,
2
);
//执行
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while
(resultSet.next()) {
/* 也可以这样写
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String name = resultSet.getString("name");
String sex = resultSet.getString("sex");
Date date = resultSet.getDate("borndate");
String phone = resultSet.getString("phone");
*/
int
id = resultSet.getInt(
1
);
String name = resultSet.getString(
2
);
String sex = resultSet.getString(
3
);
Date date = resultSet.getDate(
4
);
String phone = resultSet.getString(
5
);
System.out.println(id +
"\t"
+ name +
"\t"
+ sex +
"\t"
+ date +
"\t"
+ phone);
}
}
catch
(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally
{
JDBCUtils.close(resultSet, preparedStatement, connection);
}
}
@Test
//测试DML操作
public
void
testDML() {
Connection connection =
null
;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement =
null
;
try
{
//得到连接
connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//设置sql
String sql =
"update actor set name = ?,sex = ? where id = ?"
;
//创建PreparedStatement
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//占位符赋值
preparedStatement.setString(
1
,
"sxy"
);
preparedStatement.setString(
2
,
"男"
);
preparedStatement.setInt(
3
,
2
);
//执行
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
}
catch
(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally
{
JDBCUtils.close(
null
, preparedStatement, connection);
}
}
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
public
class
Jdbc06 {
public
static
void
main(String[] args) {
Connection connection =
null
;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement =
null
;
try
{
connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
connection.setAutoCommit(
false
);
//关闭自动提交(开启事务)
//第一个动作
String sql =
"update actor set phone = phone - 10 where id = 2"
;
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
//int i = 1/0; 异常
//第二个动作
sql =
"update actor set phone = phone + 10 where id = 1"
;
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
//提交事务
connection.commit();
}
catch
(Exception e) {
System.out.println(
"有异常存在,撤销sql服务"
);
try
{
connection.rollback();
//回滚到事务开始的地方
}
catch
(SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally
{
JDBCUtils.close(
null
, preparedStatement, connection);
}
}
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
|
public
class Jdbc07 {
@Test //普通处理5000条插入数据 执行时间169839
public
void test01() {
Connection
connection
=
null
;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement =
null
;
try {
connection
= JDBCUtils.getConnection();
String sql =
"insert into actor(id,`name`,sex) values (?,?,'男')"
;
preparedStatement =
connection
.prepareStatement(sql);
long
begin
= System.currentTimeMillis();
for
(
int
i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
preparedStatement.setString(1, 3 + i +
""
);
preparedStatement.setString(2,
"sxy"
+ (i + 1));
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
}
long
end
= System.currentTimeMillis();
System.
out
.println(
end
-
begin
);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.
close
(
null
, preparedStatement,
connection
);
}
}
@Test //批处理 执行时间429
public
void test02() {
Connection
connection
=
null
;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement =
null
;
try {
connection
= JDBCUtils.getConnection();
String sql =
"insert into actor(id,`name`,sex) values (?,?,'男')"
;
preparedStatement =
connection
.prepareStatement(sql);
long
begin
= System.currentTimeMillis();
for
(
int
i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
preparedStatement.setString(1, 3 + i +
""
);
preparedStatement.setString(2,
"sxy"
+ (i + 1));
//将sql语句加入批处理包中
preparedStatement.addBatch();
/*
preparedStatement.addBatch()在底层把每一条数据加入到ArrayList
执行过程:检查本条sql中的语法问题 -> 把本条sql语句加入到ArrayList -> 每1000条执行一次
批处理优点:减少了编译次数,又减少了运行次数,效率大大提高
还需要在properties配置文件中将url加上?rewriteBatchedStatements=
true
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test_table?rewriteBatchedStatements=
true
*/
//当有1000条时,在进行处理
if ((i + 1) % 1000 == 0) {
preparedStatement.executeBatch();
//清空批处理包
preparedStatement.clearBatch();
}
}
long
end
= System.currentTimeMillis();
System.
out
.println(
end
-
begin
);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.
close
(
null
, preparedStatement,
connection
);
}
}
}
|
由于有很多用户连接数据库,而数据库连接数量又是有限制的,而且就算连接并且关闭也是很耗时,所以就有了引入了数据库连接池可以很好的来解决这个问题。下面是普通连接数据库连接并且关闭5000次所耗时间6249毫秒,可以发下时间相对很长.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
public
class ConQuestion {
public
static
void main(String[] args) {
//看看连接-关闭
connection
会耗用多久
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.
out
.println(
"开始连接....."
);
for
(
int
i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
//使用传统的jdbc方式,得到连接
Connection
connection
= JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//做一些工作,比如得到PreparedStatement ,发送sql
//..........
//关闭
JDBCUtils.
close
(
null
,
null
,
connection
);
}
long
end
= System.currentTimeMillis();
System.
out
.println(
"传统方式5000次 耗时="
+ (
end
- start));//传统方式5000次 耗时=6249
}
}
|
JDBC的数据库连接池使用javax.sql.DataSource来表示,DataSource只是一个接口,该接口通常由第三方提供实现.
利用C3P0连接池再次尝试连接5000次数据库 可以发现耗时方式一仅仅花了456毫秒,第二种通过配置文件操作也是花了419毫秒差不多的时间,值得说的是这个连接池连接配置文件不能是我们自己写,官方有给定的模板(c3p0.config.xml).
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
|
public
class C3P0_ {
@Test //方式一: 相关参数,在程序中指定
user
,url,
password
等
public
void testC3P0_1() throws Exception {
//创建一个数据源对象
ComboPooledDataSource comboPooledDataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
//通过配合文件获取相关连接信息
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.
load
(new FileInputStream(
"src\\mysql.properties"
));
String
user
= properties.getProperty(
"user"
);
String
password
= properties.getProperty(
"password"
);
String url = properties.getProperty(
"url"
);
String driver = properties.getProperty(
"driver"
);
//给数据源(comboPooledDataSource)设置相关参数
//连接管理是由comboPooledDataSource(连接池)来管理的
comboPooledDataSource.setDriverClass(driver); //设置驱动
comboPooledDataSource.setJdbcUrl(url);
comboPooledDataSource.setUser(
user
);
comboPooledDataSource.setPassword(
password
);
//初始化数据源的连接数
comboPooledDataSource.setInitialPoolSize(10);
//数据库连接池最大容量,如果还有连接请求,那么就会将该请求放入等待队列中
comboPooledDataSource.setMaxPoolSize(50);
//测试连接池的效率, 测试对mysql 5000次操作
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for
(
int
i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
//getConnection()这个方法就是重写了DataSource接口的方法
Connection
connection
= comboPooledDataSource.getConnection();
connection
.
close
();
}
long
end
= System.currentTimeMillis();
//c3p0 5000连接mysql 耗时=456
System.
out
.println(
"c3p0 5000连接mysql 耗时="
+ (
end
- start));
comboPooledDataSource.
close
();
}
//第二种方式 使用配置文件模板来完成
//将C3P0 提供的 c3p0.config.xml 拷贝到 src目录下
//该文件指定了连接数据库和连接池的相关参数
@Test
public
void testC3P0_02() throws SQLException {
ComboPooledDataSource comboPooledDataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource(
"sxy"
);
//测试5000次连接mysql
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for
(
int
i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
Connection
connection
= comboPooledDataSource.getConnection();
connection
.
close
();
}
long
end
= System.currentTimeMillis();
//c3p0的第二种方式(5000) 耗时=419
System.
out
.println(
"c3p0的第二种方式(5000) 耗时="
+ (
end
- start));
}
}
|
在使用Druid连接池连接数据库500000次耗时643毫秒,而C3P0500000次连接耗时2373毫秒,很显然Druid连接速度更快.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
public
class
Druid_ {
@Test
public
void
testDruid()
throws
Exception {
//1.加入Druid jar包
//2.加入 配置文件 druid.properties 放到src目录下
//3.创建Properties对象
Properties properties =
new
Properties();
properties.load(
new
FileInputStream(
"src\\druid.properties"
));
//4.创建一个指定参数的数据库连接池
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
long
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for
(
int
i =
0
; i <
500000
; i++) {
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
connection.close();
}
long
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
//Druid的500000次创建 耗时=643
System.out.println(
"Druid的500000次创建 耗时="
+ (end - start));
}
}
|
对应的工具类 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
public
class JDBCUtilsByDruid {
private
static
DataSource ds;
//在静态代码块完成 ds初始化
static
{
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.
load
(new FileInputStream(
"src\\druid.properties"
));
ds = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//编写getConnection方法
public
static
Connection
getConnection() throws SQLException {
return
ds.getConnection();
}
//关闭连接:在数据库连接池技术中,
close
不是真的断掉连接,而是把使用的
Connection
对象放回连接池
public
static
void
close
(ResultSet resultSet, Statement statement,
Connection
connection
) {
try {
if (resultSet !=
null
) resultSet.
close
();
if (statement !=
null
) statement.
close
();
if (
connection
!=
null
)
connection
.
close
();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
|
使用工具类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
public
class TestUtilsByDruid {
@Test
public
void testSelect() {
Connection
connection
=
null
;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement =
null
;
ResultSet resultSet =
null
;
try {
//得到连接
connection
= JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
System.
out
.println(
connection
.getClass());
//
connection
的运行类型 class com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidPooledConnection
//设置sql
String sql =
"select * from actor where id = ?"
;
//创建PreparedStatement
preparedStatement =
connection
.prepareStatement(sql);
//占位赋值
preparedStatement.setInt(1, 2);
//执行
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.
next
()) {
int
id = resultSet.getInt(1);
String
name
= resultSet.getString(2);
String sex = resultSet.getString(3);
Date
date
= resultSet.getDate(4);
String phone = resultSet.getString(5);
System.
out
.println(id +
"\t"
+
name
+
"\t"
+ sex +
"\t"
+
date
+
"\t"
+ phone);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtilsByDruid.
close
(resultSet, preparedStatement,
connection
);
}
}
}
|
由于resultSet存放数据集合,在connection关闭时,resultSet结果集无法使用。所以为了使用这些数据,也有JDBC官方提供的文件Apache-DBUtils来存放数据.
ArrayList模拟Apache-DBUtils 。
Actor类 用来保存Actor表中的数据用的.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
public
class Actor { //Javabean, POJO, Domain对象
private
Integer
id;
private String
name
;
private String sex;
private
Date
borndate;
private String phone;
public
Actor() { //一定要给一个无参构造器[反射需要]
}
public
Actor(
Integer
id, String
name
, String sex,
Date
borndate, String phone) {
this.id = id;
this.
name
=
name
;
this.sex = sex;
this.borndate = borndate;
this.phone = phone;
}
public
Integer
getId() {
return
id; }
public
void setId(
Integer
id) { this.id = id; }
public
String getName() {
return
name
; }
public
void setName(String
name
) { this.
name
=
name
; }
public
String getSex() {
return
sex; }
public
void setSex(String sex) { this.sex = sex; }
public
Date
getBorndate() {
return
borndate; }
public
void setBorndate(
Date
borndate) { this.borndate = borndate; }
public
String getPhone() {
return
phone; }
public
void setPhone(String phone) { this.phone = phone; }
@Override
public
String toString() {
return
"\nActor{"
+
"id="
+ id +
", name='"
+
name
+ '\
''
+
", sex='"
+ sex + '\
''
+
", borndate="
+ borndate +
", phone='"
+ phone + '\
''
+
'}'
;
}
}
|
用ArrayList来存放数据 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
public
class LikeApDB {
@Test
public
/*也可以返回ArrayList<Actor>*/void testSelectToArrayList() {
Connection
connection
=
null
;
String sql =
"select * from actor where id >= ?"
;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement =
null
;
ResultSet resultSet =
null
;
ArrayList<Actor> list = new ArrayList<>();
try {
connection
= JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
System.
out
.println(
connection
.getClass());
preparedStatement =
connection
.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setInt(1, 1);
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.
next
()) {
int
id = resultSet.getInt(
"id"
);
String
name
= resultSet.getString(
"name"
);//getName()
String sex = resultSet.getString(
"sex"
);//getSex()
Date
borndate = resultSet.getDate(
"borndate"
);
String phone = resultSet.getString(
"phone"
);
//把得到的 resultSet 的记录,封装到 Actor对象,放入到list集合
list.
add
(new Actor(id,
name
, sex, borndate, phone));
}
System.
out
.println(
"list集合数据="
+ list);
for
(Actor actor : list) {
System.
out
.println(
"id="
+ actor.getId() +
"\t"
+ actor.getName());
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭资源
JDBCUtilsByDruid.
close
(resultSet, preparedStatement,
connection
);
}
//因为ArrayList 和
connection
没有任何关联,所以该集合可以复用.
//
return
list;
}
}
|
基本介绍 。
commons-dbutils是 Apache组织提供的一个开源JDBC工具类库,它是对JDBC的封装,使用dbutils能极大简化jdbc编码的工作量.
DbUtils类 。
应用实例 。
使用Apache-DBUtils工具+数据库连接池(Druid)方式,完成对一个表的增删改查.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
|
package datasourse;
import ApDB.Actor;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanHandler;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanListHandler;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.ScalarHandler;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.sql.
Connection
;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
public
class DBUtils_Use {
@Test //查询多条数据
public
void testQueryMany() throws Exception {
//1.得到连接(Druid)
Connection
connection
= JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
//2.使用 DBUtils 类和接口,先引入 DBUtils jar文件 ,放到src目录下
//3.创建QueryRunner
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
//4.执行相应的方法,返回ArrayList结果集
String sql =
"select * from actor where id >= ?"
;
//String sql =
"select id,`name` from actor where id >= ?"
;
/*
(1) query 方法就是执行sql 语句,得到resultSet
---封装到 --> ArrayList 集合中
(2) 返回集合
(3)
connection
: 连接
(4) sql : 执行的sql语句
(5) new BeanListHandler<>(Actor.class): 在将resultSet -> Actor 对象 -> 封装到 ArrayList
底层使用反射机制 去获取Actor 类的属性,然后进行封装
(6) 1 就是给 sql 语句中的? 赋值,可以有多个值,因为是可变参数Object... params
(7) 底层得到的resultSet ,会在query 关闭, 关闭PreparedStatement
*/
List<Actor> query =
queryRunner.query(
connection
, sql, new BeanListHandler<>(Actor.class), 1);
/**
* 分析 queryRunner.query方法源码分析
*
public
<T> T query(
Connection
conn, String sql, ResultSetHandler<T> rsh, Object... params) throws SQLException {
* PreparedStatement stmt =
null
;//定义PreparedStatement
* ResultSet rs =
null
;//接收返回的 ResultSet
* Object result =
null
;//返回ArrayList
*
* try {
* stmt = this.prepareStatement(conn, sql);//创建PreparedStatement
* this.fillStatement(stmt, params);//对sql 进行 ? 赋值
* rs = this.wrap(stmt.executeQuery());//执行sql,返回resultset
* result = rsh.handle(rs);//返回的resultset
--> arrayList[result] [使用到反射,对传入class对象处理]
* } catch (SQLException var33) {
* this.rethrow(var33, sql, params);
* } finally {
* try {
* this.
close
(rs);//关闭resultset
* } finally {
* this.
close
((Statement)stmt);//关闭preparedstatement对象
* }
* }
*
*
return
result;
* }
*/
for
(Actor actor : query) {
System.
out
.print(actor);
}
JDBCUtilsByDruid.
close
(
null
,
null
,
connection
);
}
@Test //查询单条记录
public
void testQuerySingle() throws SQLException {
Connection
connection
= JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
String sql =
"select * from actor where id = ?"
;
//已知查询的是单行,所以就用BeanHandler,返回一个对应的对象
Actor query = queryRunner.query(
connection
, sql, new BeanHandler<>(Actor.class), 2);
System.
out
.print(query);
JDBCUtilsByDruid.
close
(
null
,
null
,
connection
);
}
@Test //查询单行单列(某个信息) 返回一个Object对象
public
void testQuerySingleObject() throws SQLException {
Connection
connection
= JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
String sql =
"select `name` from actor where id = ?"
;
//已知查询的是单行单列,所以就用BeanHandler,返回一个Object
Object query = queryRunner.query(
connection
, sql, new ScalarHandler(), 1);
System.
out
.println(query);
JDBCUtilsByDruid.
close
(
null
,
null
,
connection
);
}
@Test //演示DML操作(
insert
,
update
,
delete
)
public
void testDML() throws SQLException {
Connection
connection
= JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
//String sql =
"update actor set phone = ? where id = ?"
;
//
int
affectedRow = queryRunner.
update
(
connection
, sql,
"110"
, 2);
String sql =
"insert into actor values(?,?,?,?,?)"
;
int
affectedRow = queryRunner.
update
(
connection
, sql, 3,
"xhj"
,
"女"
,
"2000-05-26"
,
"110"
);
//String sql =
"delete from actor where id = ?"
;
//
int
affectedRow = queryRunner.
update
(
connection
, sql, 5004);
System.
out
.println(affectedRow > 0 ?
"OK"
:
"NO"
);
JDBCUtilsByDruid.
close
(
null
,
null
,
connection
);
}
}
|
引入问题 。
所以在实际开发中,也有解决办法 —BasicDao 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
public
class BasicDAO<T> { //泛型指定具体的类型
private QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
//开发通用的DML,针对任意表
public
int
update
(String sql,Object... parameter){
Connection
connection
=
null
;
try {
connection
= JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
return
queryRunner.
update
(
connection
, sql, parameter);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);//将编译异常转化成运行异常,可以被捕获,也可以被抛出
}finally {
JDBCUtilsByDruid.
close
(
null
,
null
,
connection
);
}
}
/** 返回多个对象(多行结果)
*
* @param sql sql语句,可以存在?
* @param clazz 传入一个类的class对象 例如Actor.class
* @param parameter 传入?号具体的值,可以有多个
* @
return
根据类似Actor.class类型,返回对应的ArrayList集合
*/
public
List<T> QueryMultiply(String sql,Class<T> clazz, Object... parameter){
Connection
connection
=
null
;
try {
connection
= JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
return
queryRunner.query(
connection
,sql,new BeanListHandler<T>(clazz),parameter);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);//将编译异常转化成运行异常,可以被捕获,也可以被抛出
}finally {
JDBCUtilsByDruid.
close
(
null
,
null
,
connection
);
}
}
//返回单个对象(单行数据)
public
T querySingle(String sql,Class<T> clazz,Object... parameter){
Connection
connection
=
null
;
try {
connection
= JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
return
queryRunner.query(
connection
,sql,new BeanHandler<T>(clazz),parameter);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);//将编译异常转化成运行异常,可以被捕获,也可以被抛出
}finally {
JDBCUtilsByDruid.
close
(
null
,
null
,
connection
);
}
}
//返回单个对象的单个属性(单行中的单列)
public
Object queryScalar(String sql,Object... parameter){
Connection
connection
=
null
;
try {
connection
= JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
return
queryRunner.query(
connection
,sql,new ScalarHandler(),parameter);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);//将编译异常转化成运行异常,可以被捕获,也可以被抛出
}finally {
JDBCUtilsByDruid.
close
(
null
,
null
,
connection
);
}
}
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
public
class Actor { //Javabean, POJO, Domain对象
private
Integer
id;
private String
name
;
private String sex;
private
Date
borndate;
private String phone;
public
Actor() { //一定要给一个无参构造器[反射需要]
}
public
Actor(
Integer
id, String
name
, String sex,
Date
borndate, String phone) {
this.id = id;
this.
name
=
name
;
this.sex = sex;
this.borndate = borndate;
this.phone = phone;
}
public
Integer
getId() {
return
id; }
public
void setId(
Integer
id) { this.id = id; }
public
String getName() {
return
name
; }
public
void setName(String
name
) { this.
name
=
name
; }
public
String getSex() {
return
sex; }
public
void setSex(String sex) { this.sex = sex; }
public
Date
getBorndate() {
return
borndate; }
public
void setBorndate(
Date
borndate) { this.borndate = borndate; }
public
String getPhone() {
return
phone; }
public
void setPhone(String phone) { this.phone = phone; }
@Override
public
String toString() {
return
"\nActor{"
+
"id="
+ id +
", name='"
+
name
+ '\
''
+
", sex='"
+ sex + '\
''
+
", borndate="
+ borndate +
", phone='"
+ phone + '\
''
+
'}'
;
}
}
|
ActorDAO类继承BasicDAO类,这样的类可以有很多.
|
1
2
|
public
class ActorDAO extends BasicDAO<Actor> {
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
public
class TestDAO {
@Test//测试ActorDAO对actor表的操作
public
void testActorDAO() {
ActorDAO actorDAO = new ActorDAO();
//1.查询多行
List<Actor> actors = actorDAO.QueryMultiply(
"select * from actor where id >= ?"
, Actor.class, 1);
System.
out
.println(actors);
//2.查询单行
Actor actor = actorDAO.querySingle(
"select * from actor where id = ?"
, Actor.class, 1);
System.
out
.println(actor);
//3.查询单行单个数据
Object o = actorDAO.queryScalar(
"select name from actor where id = ?"
, 1);
System.
out
.println(o);
//4.DML操作 当前演示
update
int
affectedRow = actorDAO.
update
(
"update actor set phone = ? where id = ?"
,
"120"
, 3);
System.
out
.println(affectedRow > 0 ?
"OK"
:
"NO"
);
}
}
|
到此这篇关于详细说明关于Java的数据库连接(JDBC)的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java的数据库连接(JDBC)内容请搜索我以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我! 。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46687179/article/details/120105398 。
最后此篇关于详细说明关于Java的数据库连接(JDBC)的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于详细说明关于Java的数据库连接(JDBC)的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我的问题是如何在 python 中创建一个简单的数据库。我的例子是: User = { 'Name' : {'Firstname', 'Lastname'}, 'Address' : {'Street
我需要创建一个与远程数据库链接的应用程序! mysql 是最好的解决方案吗? Sqlite 是唯一的本地解决方案吗? 我使用下面的方法,我想知道它是否是最好的方法! NSString *evento
给定两台 MySQL 服务器,一台本地,一台远程。两者都有一个包含表 bohica 的数据库 foobar。本地服务器定义了用户 'myadmin'@'%' 和 'myadmin'@'localhos
我有以下灵活的搜索查询 Select {vt:code},{vt:productcode},{vw:code},{vw:productcode} from {abcd AS vt JOIN wxyz
好吧,我的电脑开始运行有点缓慢,所以我重置了 Windows,保留了我的文件。因为我的大脑还没有打开,所以我忘记事先备份我的 MySQL 数据库。我仍然拥有所有原始文件,因此我实际上仍然拥有数据库,但
如何将我的 Access 数据库 (.accdb) 转换为 SQLite 数据库 (.sqlite)? 请,任何帮助将不胜感激。 最佳答案 1)如果要转换 db 的结构,则应使用任何 DB 建模工具:
系统检查发现了一些问题: 警告:?:(mysql.W002)未为数据库连接“默认”设置 MySQL 严格模式 提示:MySQL 的严格模式通过将警告升级为错误来修复 MySQL 中的许多数据完整性问题
系统检查发现了一些问题: 警告:?:(mysql.W002)未为数据库连接“默认”设置 MySQL 严格模式 提示:MySQL 的严格模式通过将警告升级为错误来修复 MySQL 中的许多数据完整性问题
我想在相同的 phonegap 应用程序中使用 android 数据库。 更多说明: 我创建了 phonegap 应用程序,但 phonegap 应用程序不支持服务,所以我们已经在 java 中为 a
Time Tracker function clock() { var mytime = new Date(); var seconds
我需要在现有项目上实现一些事件的显示。我无法更改数据库结构。 在我的 Controller 中,我(从 ajax 请求)传递了一个时间戳,并且我需要显示之前的 8 个事件。因此,如果时间戳是(转换后)
我有一个可以收集和显示各种测量值的产品(不会详细介绍)。正如人们所期望的那样,显示部分是一个数据库+建立在其之上的网站(使用 Symfony)。 但是,我们可能还会创建一个 API 来向第三方公开数据
我们将 SQL Server 从 Azure VM 迁移到 Azure SQL 数据库。 Azure VM 为 DS2_V2、2 核、7GB RAM、最大 6400 IOPS Azure SQL 数据
我正在开发一个使用 MongoDB 数据库的程序,但我想问在通过 Java 执行 SQL 时是否可以使用内部数据库进行测试,例如 H2? 最佳答案 你可以尝试使用Testcontainers Test
已关闭。此问题不符合Stack Overflow guidelines 。目前不接受答案。 已关闭 9 年前。 此问题似乎与 a specific programming problem, a sof
我正在尝试使用 MSI 身份验证(无需用户名和密码)从 Azure 机器学习服务连接 Azure SQL 数据库。 我正在尝试在 Azure 机器学习服务上建立机器学习模型,目的是我需要数据,这就是我
我在我的 MySQL 数据库中使用这个查询来查找 my_column 不为空的所有行: SELECT * FROM my_table WHERE my_column != ""; 不幸的是,许多行在
我有那个基地:http://sqlfiddle.com/#!2/e5a24/2这是 WordPress 默认模式的简写。我已经删除了该示例不需要的字段。 如您所见,我的结果是“类别 1”的两倍。我喜欢
我有一张这样的 table : mysql> select * from users; +--------+----------+------------+-----------+ | userid
我有表: CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `category` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL, `name` varchar(255) NOT NULL

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!