- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章java String类功能、原理与应用案例【统计、判断、转换等】由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
本文实例讲述了java string类功能、原理与应用。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
string构造方法 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
|
package
cn.itcast_01;
/*
* 字符串:就是由多个字符组成的一串数据。也可以看成是一个字符数组。
* 通过查看api,我们可以知道
* a:字符串字面值"abc"也可以看成是一个字符串对象。
* b:字符串是常量,一旦被赋值,就不能被改变。
*
* 构造方法:
* public string():空构造
* public string(byte[] bytes):把字节数组转成字符串
* public string(byte[] bytes,int index,int length):把字节数组的一部分转成字符串
* public string(char[] value):把字符数组转成字符串
* public string(char[] value,int index,int count):把字符数组的一部分转成字符串
* public string(string original):把字符串常量值转成字符串
*
* 字符串的方法:
* public int length():返回此字符串的长度。
*/
public
class
stringdemo {
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
// public string():空构造
string s1 =
new
string();
system.out.println(
"s1:"
+ s1);
system.out.println(
"s1.length():"
+ s1.length());
system.out.println(
"--------------------------"
);
//s1:
//s1.length():0
// public string(byte[] bytes):把字节数组转成字符串
byte
[] bys = {
97
,
98
,
99
,
100
,
101
};
string s2 =
new
string(bys);
system.out.println(
"s2:"
+ s2);
//abcde
system.out.println(
"s2.length():"
+ s2.length());
//
system.out.println(
"--------------------------"
);
// public string(byte[] bytes,int index,int length):把字节数组的一部分转成字符串
// 我想得到字符串"bcd"
string s3 =
new
string(bys,
1
,
3
);
system.out.println(
"s3:"
+ s3);
system.out.println(
"s3.length():"
+ s3.length());
system.out.println(
"--------------------------"
);
// public string(char[] value):把字符数组转成字符串
char
[] chs = {
'a'
,
'b'
,
'c'
,
'd'
,
'e'
,
'爱'
,
'林'
,
'亲'
};
string s4 =
new
string(chs);
system.out.println(
"s4:"
+ s4);
system.out.println(
"s4.length():"
+ s4.length());
system.out.println(
"--------------------------"
);
// public string(char[] value,int index,int count):把字符数组的一部分转成字符串
string s5 =
new
string(chs,
2
,
4
);
system.out.println(
"s5:"
+ s5);
system.out.println(
"s5.length():"
+ s5.length());
system.out.println(
"--------------------------"
);
//public string(string original):把字符串常量值转成字符串
string s6 =
new
string(
"abcde"
);
system.out.println(
"s6:"
+ s6);
system.out.println(
"s6.length():"
+ s6.length());
system.out.println(
"--------------------------"
);
//字符串字面值"abc"也可以看成是一个字符串对象。
string s7 =
"abcde"
;
system.out.println(
"s7:"
+s7);
system.out.println(
"s7.length():"
+s7.length());
}
}
|
字符串的特点:一旦被赋值,就不能改变.
但是引用可以改变 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
package
cn.itcast_02;
/*
* 字符串的特点:一旦被赋值,就不能改变。
*/
public
class
stringdemo {
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
string s =
"hello"
;
s +=
"world"
;
system.out.println(
"s:"
+ s);
// helloworld
}
}
|
图解:
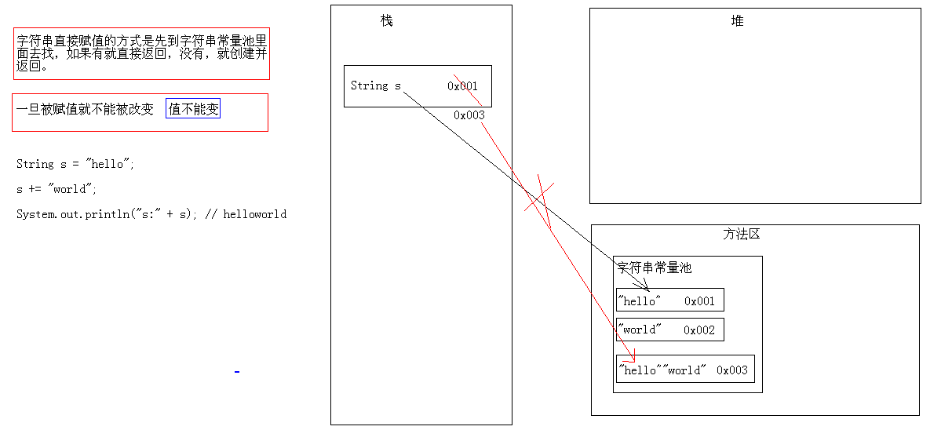
string s = new string("hello")和 string s = "hello";的区别?
string字面值对象和构造方法创建对象的区别 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
package
cn.itcast_02;
/*
* string s = new string("hello")和string s = "hello";的区别?
* 有。前者会创建2个对象,后者创建1个对象。
*
* ==:比较引用类型比较的是地址值是否相同
* equals:比较引用类型默认也是比较地址值是否相同,而string类重写了equals()方法,比较的是内容是否相同。
*/
public
class
stringdemo2 {
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
string s1 =
new
string(
"hello"
);
string s2 =
"hello"
;
system.out.println(s1 == s2);
// false
system.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
// true
}
}
|
图解:

|
1
2
3
4
|
string s5 =
"hello"
;
string s6 =
"hello"
;
system.out.println(s5 == s6);
// 字符串字面量,直接从内存找,所以true
system.out.println(s5.equals(s6));
// true
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
package
cn.itcast_02;
/*
* 看程序写结果
* 字符串如果是变量相加,先开空间,在拼接。
* 字符串如果是常量相加,是先加,然后在常量池找,如果有就直接返回,否则,就创建。
*/
public
class
stringdemo4 {
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
string s1 =
"hello"
;
string s2 =
"world"
;
string s3 =
"helloworld"
;
system.out.println(s3 == s1 + s2);
// false。字符串如果是变量相加,先开空间,再拼接。
system.out.println(s3.equals((s1 + s2)));
// true
system.out.println(s3 ==
"hello"
+
"world"
);
//true。字符串如果是常量相加,是先加,然后在常量池找,如果有就直接返回,否则,就创建。
system.out.println(s3.equals(
"hello"
+
"world"
));
// true
// 通过反编译看源码,我们知道这里已经做好了处理。
// system.out.println(s3 == "helloworld");
// system.out.println(s3.equals("helloworld"));
}
}
|
string类的判断功能:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
package
cn.itcast_03;
/*
* string类的判断功能:
* boolean equals(object obj):比较字符串的内容是否相同,区分大小写
* boolean equalsignorecase(string str):比较字符串的内容是否相同,忽略大小写
* boolean contains(string str):判断大字符串中是否包含小字符串
* boolean startswith(string str):判断字符串是否以某个指定的字符串开头
* boolean endswith(string str):判断字符串是否以某个指定的字符串结尾
* boolean isempty():判断字符串是否为空。
*
* 注意:
* 字符串内容为空和字符串对象为空。
* string s = "";//对象存在,所以可以调方法
* string s = null;//对象不存在,不能调方法
*/
public
class
stringdemo {
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
// 创建字符串对象
string s1 =
"helloworld"
;
string s2 =
"helloworld"
;
string s3 =
"helloworld"
;
// boolean equals(object obj):比较字符串的内容是否相同,区分大小写
system.out.println(
"equals:"
+ s1.equals(s2));
system.out.println(
"equals:"
+ s1.equals(s3));
system.out.println(
"-----------------------"
);
// boolean equalsignorecase(string str):比较字符串的内容是否相同,忽略大小写
system.out.println(
"equals:"
+ s1.equalsignorecase(s2));
system.out.println(
"equals:"
+ s1.equalsignorecase(s3));
system.out.println(
"-----------------------"
);
// boolean contains(string str):判断大字符串中是否包含小字符串
system.out.println(
"contains:"
+ s1.contains(
"hello"
));
system.out.println(
"contains:"
+ s1.contains(
"hw"
));
system.out.println(
"-----------------------"
);
// boolean startswith(string str):判断字符串是否以某个指定的字符串开头
system.out.println(
"startswith:"
+ s1.startswith(
"h"
));
system.out.println(
"startswith:"
+ s1.startswith(
"hello"
));
system.out.println(
"startswith:"
+ s1.startswith(
"world"
));
system.out.println(
"-----------------------"
);
// 练习:boolean endswith(string str):判断字符串是否以某个指定的字符串结尾这个自己玩
// boolean isempty():判断字符串是否为空。
system.out.println(
"isempty:"
+ s1.isempty());
string s4 =
""
;
string s5 =
null
;
system.out.println(
"isempty:"
+ s4.isempty());
// nullpointerexception
// s5对象都不存在,所以不能调用方法,空指针异常
// system.out.println("isempty:" + s5.isempty());
}
}
|
string类的判断功能---使用---键盘录入猜字小游戏 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
|
package
cn.itcast_03;
import
java.util.scanner;
/*
* 模拟登录,给三次机会,并提示还有几次。如果登录成功,就可以玩猜数字小游戏了。
*
* 分析:
* a:定义用户名和密码。已存在的。
* b:键盘录入用户名和密码。
* c:比较用户名和密码。
* 如果都相同,则登录成功
* 如果有一个不同,则登录失败
* d:给三次机会,用循环改进,最好用for循环。
*/
public
class
stringtest2 {
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
// 定义用户名和密码。已存在的。
string username =
"admin"
;
string password =
"admin"
;
// 给三次机会,用循环改进,最好用for循环。
for
(
int
x =
0
; x <
3
; x++) {
// x=0,1,2
// 键盘录入用户名和密码。
scanner sc =
new
scanner(system.in);
system.out.println(
"请输入用户名:"
);
string name = sc.nextline();
system.out.println(
"请输入密码:"
);
string pwd = sc.nextline();
// 比较用户名和密码。
if
(name.equals(username) && pwd.equals(password)) {
// 如果都相同,则登录成功
system.out.println(
"登录成功,开始玩游戏"
);
//猜数字游戏
guessnumbergame.start();
break
;
}
else
{
// 如果有一个不同,则登录失败
// 2,1,0
// 如果是第0次,应该换一种提示
if
((
2
- x) ==
0
) {
system.out.println(
"帐号被锁定,请与班长联系"
);
}
else
{
system.out.println(
"登录失败,你还有"
+ (
2
- x) +
"次机会"
);
}
}
}
}
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
package
cn.itcast_03;
import
java.util.scanner;
/*
* 这时猜数字小游戏的代码
*/
public
class
guessnumbergame {
private
guessnumbergame() {
}
public
static
void
start() {
// 产生一个随机数
int
number = (
int
) (math.random() *
100
) +
1
;
while
(
true
) {
// 键盘录入数据
scanner sc =
new
scanner(system.in);
system.out.println(
"请输入你要猜的数据(1-100):"
);
int
guessnumber = sc.nextint();
// 判断
if
(guessnumber > number) {
system.out.println(
"你猜的数据"
+ guessnumber +
"大了"
);
}
else
if
(guessnumber < number) {
system.out.println(
"你猜的数据"
+ guessnumber +
"小了"
);
}
else
{
system.out.println(
"恭喜你,猜中了"
);
break
;
}
}
}
}
|
string类的获取功能 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
|
package
cn.itcast_04;
/*
* string类的获取功能
* int length():获取字符串的长度。
* char charat(int index):获取指定索引位置的字符
* int indexof(int ch):返回指定字符在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引。
* 为什么这里是int类型,而不是char类型?
* 原因是:'a'和97其实都可以代表'a'。如果里面写char,就不能写数字97了
* int indexof(string str):返回指定字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引。
* int indexof(int ch,int fromindex):返回指定字符在此字符串中从指定位置后第一次出现处的索引。
* int indexof(string str,int fromindex):返回指定字符串在此字符串中从指定位置后第一次出现处的索引。
* string substring(int start):从指定位置开始截取字符串,默认到末尾。
* string substring(int start,int end):从指定位置开始到指定位置结束截取字符串。
*/
public
class
stringdemo {
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
// 定义一个字符串对象
string s =
"helloworld"
;
// int length():获取字符串的长度。
system.out.println(
"s.length:"
+ s.length());
//10
system.out.println(
"----------------------"
);
// char charat(int index):获取指定索引位置的字符
system.out.println(
"charat:"
+ s.charat(
7
));
//
system.out.println(
"----------------------"
);
// int indexof(int ch):返回指定字符在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引。
system.out.println(
"indexof:"
+ s.indexof(
'l'
));
system.out.println(
"----------------------"
);
// int indexof(string str):返回指定字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引。
system.out.println(
"indexof:"
+ s.indexof(
"owo"
));
system.out.println(
"----------------------"
);
// int indexof(int ch,int fromindex):返回指定字符在此字符串中从指定位置后第一次出现处的索引。
system.out.println(
"indexof:"
+ s.indexof(
'l'
,
4
));
system.out.println(
"indexof:"
+ s.indexof(
'k'
,
4
));
// -1
system.out.println(
"indexof:"
+ s.indexof(
'l'
,
40
));
// -1
system.out.println(
"----------------------"
);
// 自己练习:int indexof(string str,int
// fromindex):返回指定字符串在此字符串中从指定位置后第一次出现处的索引。
// string substring(int start):从指定位置开始截取字符串,默认到末尾。包含start这个索引
system.out.println(
"substring:"
+ s.substring(
5
));
system.out.println(
"substring:"
+ s.substring(
0
));
system.out.println(
"----------------------"
);
// string substring(int start,intend):从指定位置开始到指定位置结束截取字符串。
//包括start索引但是不包end索引
system.out.println(
"substring:"
+ s.substring(
3
,
8
));
system.out.println(
"substring:"
+ s.substring(
0
, s.length()));
}
}
|
字符串遍历:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
package
cn.itcast_04;
/*
* 需求:遍历获取字符串中的每一个字符
*
* 分析:
* a:如何能够拿到每一个字符呢?
* char charat(int index)
* b:我怎么知道字符到底有多少个呢?
* int length()
*/
public
class
stringtest {
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
// 定义字符串
string s =
"helloworld"
;
for
(
int
x =
0
; x < s.length(); x++) {
system.out.println(s.charat(x));
}
}
}
|
统计大写字母,小写字母,数字在字符串中的个数 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
|
package
cn.itcast_04;
/*
* 需求:统计一个字符串中大写字母字符,小写字母字符,数字字符出现的次数。(不考虑其他字符)
* 举例:
* "hello123world"
* 结果:
* 大写字符:2个
* 小写字符:8个
* 数字字符:3个
*
* 分析:
* 前提:字符串要存在
* a:定义三个统计变量
* bigcount=0
* smallcount=0
* numbercount=0
* b:遍历字符串,得到每一个字符。
* length()和charat()结合
* c:判断该字符到底是属于那种类型的
* 大:bigcount++
* 小:smallcount++
* 数字:numbercount++
*
* 这道题目的难点就是如何判断某个字符是大的,还是小的,还是数字的。
* ascii码表:
* 0 48
* a 65
* a 97
* 虽然,我们按照数字的这种比较是可以的,但是想多了,有比这还简单的
* char ch = s.charat(x);
*
* if(ch>='0' && ch<='9') numbercount++
* if(ch>='a' && ch<='z') smallcount++
* if(ch>='a' && ch<='z') bigcount++
* d:输出结果。
*
* 练习:把给定字符串的方式,改进为键盘录入字符串的方式。
*/
public
class
stringtest2 {
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
//定义一个字符串
string s =
"hello123world"
;
//定义三个统计变量
int
bigcount =
0
;
int
smallcount =
0
;
int
numbercount =
0
;
//遍历字符串,得到每一个字符。
for
(
int
x=
0
; x<s.length(); x++){
char
ch = s.charat(x);
//判断该字符到底是属于那种类型的,char类型会转成int类型
if
(ch>=
'a'
&& ch<=
'z'
){
smallcount++;
}
else
if
(ch>=
'a'
&& ch<=
'z'
){
bigcount++;
}
else
if
(ch>=
'0'
&& ch<=
'9'
){
numbercount++;
}
}
//输出结果。
system.out.println(
"大写字母"
+bigcount+
"个"
);
system.out.println(
"小写字母"
+smallcount+
"个"
);
system.out.println(
"数字"
+numbercount+
"个"
);
}
}
|
string的转换功能:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
package
cn.itcast_05;
/*
* string的转换功能:
* byte[] getbytes():把字符串转换为字节数组。
* char[] tochararray():把字符串转换为字符数组。
* static string valueof(char[] chs):把字符数组转成字符串。
* static string valueof(int i):把int类型的数据转成字符串。
* 注意:string类的valueof方法可以把任意类型的数据转成字符串。
* string tolowercase():把字符串转成小写。
* string touppercase():把字符串转成大写。
* string concat(string str):把字符串拼接。
*/
public
class
stringdemo {
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
// 定义一个字符串对象
string s =
"javase"
;
// byte[] getbytes():把字符串转换为字节数组。
byte
[] bys = s.getbytes();
for
(
int
x =
0
; x < bys.length; x++) {
system.out.println(bys[x]);
}
system.out.println(
"----------------"
);
// char[] tochararray():把字符串转换为字符数组。
char
[] chs = s.tochararray();
for
(
int
x =
0
; x < chs.length; x++) {
system.out.println(chs[x]);
}
system.out.println(
"----------------"
);
// static string valueof(char[] chs):把字符数组转成字符串。
string ss = string.valueof(chs);
system.out.println(ss);
system.out.println(
"----------------"
);
// static string valueof(int i):把int类型的数据转成字符串。
int
i =
100
;
string sss = string.valueof(i);
system.out.println(sss);
system.out.println(
"----------------"
);
// string tolowercase():把字符串转成小写。
system.out.println(
"tolowercase:"
+ s.tolowercase());
system.out.println(
"s:"
+ s);
// system.out.println("----------------");
// string touppercase():把字符串转成大写。
system.out.println(
"touppercase:"
+ s.touppercase());
system.out.println(
"----------------"
);
// string concat(string str):把字符串拼接。
string s1 =
"hello"
;
string s2 =
"world"
;
string s3 = s1 + s2;
string s4 = s1.concat(s2);
system.out.println(
"s3:"
+s3);
system.out.println(
"s4:"
+s4);
}
}
|
把一个字符串的首字母转成大写,其余为小写。(只考虑英文大小写字母字符) 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
package
cn.itcast_05;
/*
* 需求:把一个字符串的首字母转成大写,其余为小写。(只考虑英文大小写字母字符)
* 举例:
* helloworld
* 结果:
* helloworld
*
* 分析:
* a:先获取第一个字符
* b:获取除了第一个字符以外的字符
* c:把a转成大写
* d:把b转成小写
* e:c拼接d
*/
public
class
stringtest {
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
// 定义一个字符串
string s =
"helloworld"
;
// 先获取第一个字符
string s1 = s.substring(
0
,
1
);
// 获取除了第一个字符以外的字符
string s2 = s.substring(
1
);
// 把a转成大写
string s3 = s1.touppercase();
// 把b转成小写
string s4 = s2.tolowercase();
// c拼接d
string s5 = s3.concat(s4);
system.out.println(s5);
// 优化后的代码
// 链式编程
string result = s.substring(
0
,
1
).touppercase()
.concat(s.substring(
1
).tolowercase());
system.out.println(result);
}
}
|
string类的其他功能:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
package
cn.itcast_06;
/*
* string类的其他功能:
*
* 替换功能:
* string replace(char old,char new)
* string replace(string old,string new)
*
* 去除字符串两空格
* string trim()
*
* 按字典顺序比较两个字符串
* int compareto(string str)
* int comparetoignorecase(string str)
*/
public
class
stringdemo {
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
// 替换功能
string s1 =
"helloworld"
;
string s2 = s1.replace(
'l'
,
'k'
);
string s3 = s1.replace(
"owo"
,
"ak47"
);
system.out.println(
"s1:"
+ s1);
system.out.println(
"s2:"
+ s2);
system.out.println(
"s3:"
+ s3);
system.out.println(
"---------------"
);
// 去除字符串两空格
string s4 =
" hello world "
;
string s5 = s4.trim();
system.out.println(
"s4:"
+ s4 +
"---"
);
system.out.println(
"s5:"
+ s5 +
"---"
);
// 按字典顺序比较两个字符串
string s6 =
"hello"
;
string s7 =
"hello"
;
string s8 =
"abc"
;
string s9 =
"xyz"
;
system.out.println(s6.compareto(s7));
// 0
system.out.println(s6.compareto(s8));
// 7
system.out.println(s6.compareto(s9));
// -16
}
}
|
compareto源码解析 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
public
int
compareto(string anotherstring) {
//this -- s1 -- "hello"
//anotherstring -- s2 -- "hel"
int
len1 = value.length;
//this.value.length--s1.tochararray().length--5
int
len2 = anotherstring.value.length;
//s2.value.length -- s2.tochararray().length--3
int
lim = math.min(len1, len2);
//math.min(5,3); -- lim=3;
char
v1[] = value;
//s1.tochararray()
char
v2[] = anotherstring.value;
//char v1[] = {'h','e','l','l','o'};
//char v2[] = {'h','e','l'};
int
k =
0
;
while
(k < lim) {
char
c1 = v1[k];
//c1='h','e','l'
char
c2 = v2[k];
//c2='h','e','l'
if
(c1 != c2) {
return
c1 - c2;
}
k++;
}
return
len1 - len2;
//5-3=2;
}
string s1 =
"hello"
;
string s2 =
"hel"
;
system.out.println(s1.compareto(s2));
// 2
|
把数组中的数据按照指定个格式拼接成一个字符串 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
|
package
cn.itcast_07;
/*
* 需求:把数组中的数据按照指定个格式拼接成一个字符串
* 举例:
* int[] arr = {1,2,3};
* 输出结果:
* "[1, 2, 3]"
* 分析:
* a:定义一个字符串对象,只不过内容为空
* b:先把字符串拼接一个"["
* c:遍历int数组,得到每一个元素
* d:先判断该元素是否为最后一个
* 是:就直接拼接元素和"]"
* 不是:就拼接元素和逗号以及空格
* e:输出拼接后的字符串
*
* 把代码用功能实现。
*/
public class stringtest2 {
public static void main(string[] args) {
// 前提是数组已经存在
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3 };
// 写一个功能,实现结果
string result = arraytostring(arr);
system.out.println("最终结果是:" + result);
}
/*
* 两个明确: 返回值类型:string 参数列表:int[] arr
*/
public
static
string arraytostring(
int
[] arr) {
// 定义一个字符串
string s =
""
;
// 先把字符串拼接一个"["
s +=
"["
;
// 遍历int数组,得到每一个元素
for
(
int
x =
0
; x < arr.length; x++) {
// 先判断该元素是否为最后一个
if
(x == arr.length -
1
) {
// 就直接拼接元素和"]"
s += arr[x];
s +=
"]"
;
}
else
{
// 就拼接元素和逗号以及空格
s += arr[x];
s +=
", "
;
}
}
return
s;
}
}
|
字符串反转 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
package
cn.itcast_07;
import
java.util.scanner;
/*
* 字符串反转
* 举例:键盘录入"abc"
* 输出结果:"cba"
*
* 分析:
* a:键盘录入一个字符串
* b:定义一个新字符串
* c:倒着遍历字符串,得到每一个字符
* a:length()和charat()结合
* b:把字符串转成字符数组
* d:用新字符串把每一个字符拼接起来
* e:输出新串
*/
public class stringtest3 {
public static void main(string[] args) {
// 键盘录入一个字符串
scanner sc = new scanner(system.in);
system.out.println("请输入一个字符串:");
string line = sc.nextline();
string s = myreverse(line);
system.out.println("实现功能后的结果是:" + s);
}
/*
* 两个明确: 返回值类型:string 参数列表:string
*/
public
static
string myreverse(string s) {
// 定义一个新字符串
string result =
""
;
// 把字符串转成字符数组
char
[] chs = s.tochararray();
// 倒着遍历字符串,得到每一个字符
for
(
int
x = chs.length -
1
; x >=
0
; x--) {
// 用新字符串把每一个字符拼接起来
result += chs[x];
}
return
result;
}
}
|
统计大串中小串出现的次数 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
package
cn.itcast_07;
/*
* 统计大串中小串出现的次数
* 举例:
* 在字符串"woaijavawozhenaijavawozhendeaijavawozhendehenaijavaxinbuxinwoaijavagun"
* 结果:
* java出现了5次
*
* 分析:
* 前提:是已经知道了大串和小串。
*
* a:定义一个统计变量,初始化值是0
* b:先在大串中查找一次小串第一次出现的位置
* a:索引是-1,说明不存在了,就返回统计变量
* b:索引不是-1,说明存在,统计变量++
* c:把刚才的索引+小串的长度作为开始位置截取上一次的大串,返回一个新的字符串,并把该字符串的值重新赋值给大串
* d:回到b
*/
public class stringtest5 {
public static void main(string[] args) {
// 定义大串
string maxstring = "woaijavawozhenaijavawozhendeaijavawozhendehenaijavaxinbuxinwoaijavagun";
// 定义小串
string minstring = "java";
// 写功能实现
int count = getcount(maxstring, minstring);
system.out.println("java在大串中出现了:" + count + "次");
}
/*
* 两个明确: 返回值类型:int 参数列表:两个字符串
*/
public
static
int
getcount(string maxstring, string minstring) {
// 定义一个统计变量,初始化值是0
int
count =
0
;
int
index;
//先查,赋值,判断
while
((index=maxstring.indexof(minstring))!=-
1
){
count++;
maxstring = maxstring.substring(index + minstring.length());
}
return
count;
}
}
|
希望本文所述对大家java程序设计有所帮助.
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/baiyangyuanzi/p/6855703.html 。
最后此篇关于java String类功能、原理与应用案例【统计、判断、转换等】的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于java String类功能、原理与应用案例【统计、判断、转换等】的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
本文全面深入地探讨了Docker容器通信技术,从基础概念、网络模型、核心组件到实战应用。详细介绍了不同网络模式及其实现,提供了容器通信的技术细节和实用案例,旨在为专业从业者提供深入的技术洞见和实
📒博客首页:崇尚学技术的科班人 🍣今天给大家带来的文章是《Dubbo快速上手 -- 带你了解Dubbo使用、原理》🍣 🍣希望各位小伙伴们能够耐心的读完这篇文章🍣 🙏博主也在学习阶段,如若发
一、写在前面 我们经常使用npm install ,但是你是否思考过它内部的原理是什么? 1、执行npm install 它背后帮助我们完成了什么操作? 2、我们会发现还有一个成为package-lo
Base64 Base64 是什么?是将字节流转换成可打印字符、将可打印字符转换为字节流的一种算法。Base64 使用 64 个可打印字符来表示转换后的数据。 准确的来说,Base64 不算
目录 协程定义 生成器和yield语义 Future类 IOLoop类 coroutine函数装饰器 总结 tornado中的
切片,这是一个在go语言中引入的新的理念。它有一些特征如下: 对数组抽象 数组长度不固定 可追加元素 切片容量可增大 容量大小成片增加 我们先把上面的理念整理在这
文章来源:https://sourl.cn/HpZHvy 引 言 本文主要论述的是“RPC 实现原理”,那么首先明确一个问题什么是 RPC 呢?RPC 是 Remote Procedure Call
源码地址(包含所有与springmvc相关的,静态文件路径设置,request请求入参接受,返回值处理converter设置等等): spring-framework/WebMvcConfigurat
请通过简单的java类向我展示一个依赖注入(inject)原理的小例子虽然我已经了解了spring,但是如果我需要用简单的java类术语来解释它,那么你能通过一个简单的例子向我展示一下吗?提前致谢。
1、背景 我们平常使用手机和电脑上网,需要访问公网上的网络资源,如逛淘宝和刷视频,那么手机和电脑是怎么知道去哪里去拿到这个网络资源来下载到本地的呢? 就比如我去食堂拿吃的,我需要
大家好,我是飞哥! 现在 iptables 这个工具的应用似乎是越来越广了。不仅仅是在传统的防火墙、NAT 等功能出现,在今天流行的的 Docker、Kubernets、Istio 项目中也经
本篇涉及到的所有接口在公开文档中均无,需要下载 GitHub 上的源码,自己创建私有类的文档。 npm run generateDocumentation -- --private yarn gene
我最近在很多代码中注意到人们将硬编码的配置(如端口号等)值放在类/方法的深处,使其难以找到,也无法配置。 这是否违反了 SOLID 原则?如果不是,我是否可以向我的团队成员引用另一个“原则”来说明为什
我是 C#、WPF 和 MVVM 模式的新手。很抱歉这篇很长的帖子,我试图设定我所有的理解点(或不理解点)。 在研究了很多关于 WPF 提供的命令机制和 MVVM 模式的文本之后,我在弄清楚如何使用这
可比较的 jQuery 函数 $.post("/example/handler", {foo: 1, bar: 2}); 将创建一个带有 post 参数 foo=1&bar=2 的请求。鉴于 $htt
如果Django不使用“延迟查询执行”原则,主要问题是什么? q = Entry.objects.filter(headline__startswith="What") q = q.filter(
我今天发现.NET框架在做计算时遵循BODMAS操作顺序。即计算按以下顺序进行: 括号 订单 部门 乘法 添加 减法 但是我四处搜索并找不到任何文档确认 .NET 绝对 遵循此原则,是否有此类文档?如
已结束。此问题不符合 Stack Overflow guidelines .它目前不接受答案。 我们不允许提出有关书籍、工具、软件库等方面的建议的问题。您可以编辑问题,以便用事实和引用来回答它。 关闭
API 回顾 在创建 Viewer 时可以直接指定 影像供给器(ImageryProvider),官方提供了一个非常简单的例子,即离屏例子(搜 offline): new Cesium.Viewer(
As it currently stands, this question is not a good fit for our Q&A format. We expect answers to be

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!