- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章java中常见的死锁以及解决方法代码由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
在java中我们常常使用加锁机制来确保线程安全,但是如果过度使用加锁,则可能导致锁顺序死锁。同样,我们使用线程池和信号量来限制对资源的使用,但是这些被限制的行为可能会导致资源死锁。java应用程序无法从死锁中恢复过来,因此设计时一定要排序那些可能导致死锁出现的条件.
1.一个最简单的死锁案例 当一个线程永远地持有一个锁,并且其他线程都尝试获得这个锁时,那么它们将永远被阻塞。在线程a持有锁l并想获得锁m的同时,线程b持有锁m并尝试获得锁l,那么这两个线程将永远地等待下去。这种就是最简答的死锁形式(或者叫做"抱死").
2.锁顺序死锁 。
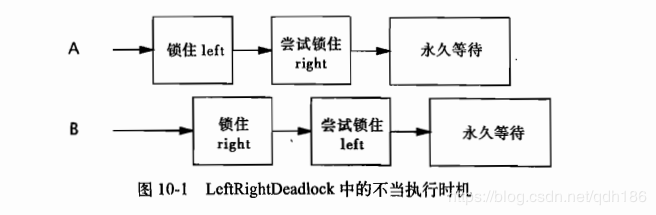
如图:leftright和rightleft这两个方法分别获得left锁和right锁。如果一个线程调用了leftright,而另一个线程调用了rightleft,并且这两个线程的操作是交互执行,那么它们就会发生死锁.
死锁的原因就是两个线程试图以不同的顺序来获得相同的锁。所以,如果所有的线程以固定的顺序来获得锁,那么在程序中就不会出现锁顺序死锁的问题.
2.1.动态的锁顺序死锁 。
我以一个经典的转账案例来进行说明,我们知道转账就是将资金从一个账户转入另一个账户。在开始转账之前,首先需要获得这两个账户对象得锁,以确保通过原子方式来更新两个账户中的余额,同时又不破坏一些不变形条件,例如 账户的余额不能为负数.
所以写出的代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
|
//动态的锁的顺序死锁
public
class
dynamicorderdeadlock {
public
static
void
transfermoney(account fromaccount,account toaccount,
int
amount,
int
from_index,
int
to_index)
throws
exception {
system.out.println(
"账户 "
+ from_index+
"~和账户~"
+to_index+
" ~请求锁"
);
synchronized
(fromaccount) {
system.out.println(
" 账户 >>>"
+from_index+
" <<<获得锁"
);
synchronized
(toaccount) {
system.out.println(
" 账户 "
+from_index+
" & "
+to_index+
"都获得锁"
);
if
(fromaccount.compareto(amount) <
0
) {
throw
new
exception();
}
else
{
fromaccount.debit(amount);
toaccount.credit(amount);
}
}
}
}
static
class
account {
private
int
balance =
100000
;
//这里假设每个人账户里面初始化的钱
private
final
int
accno;
private
static
final
atomicinteger sequence =
new
atomicinteger();
public
account() {
accno = sequence.incrementandget();
}
void
debit(
int
m)
throws
interruptedexception {
thread.sleep(
5
);
//模拟操作时间
balance = balance + m;
}
void
credit(
int
m)
throws
interruptedexception {
thread.sleep(
5
);
//模拟操作时间
balance = balance - m;
}
int
getbalance() {
return
balance;
}
int
getaccno() {
return
accno;
}
public
int
compareto(
int
money) {
if
(balance > money) {
return
1
;
}
else
if
(balance < money) {
return
-
1
;
}
else
{
return
0
;
}
}
}
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
public
class
demonstratedeadlock {
private
static
final
int
num_threads =
5
;
private
static
final
int
num_accounts =
5
;
private
static
final
int
num_iterations =
100000
;
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
final
random rnd =
new
random();
final
account[] accounts =
new
account[num_accounts];
for
(
int
i =
0
;i < accounts.length;i++) {
accounts[i] =
new
account();
}
class
transferthread
extends
thread{
@override
public
void
run() {
for
(
int
i =
0
;i < num_iterations;i++) {
int
fromacct = rnd.nextint(num_accounts);
int
toacct =rnd.nextint(num_accounts);
int
amount = rnd.nextint(
100
);
try
{
dynamicorderdeadlock.transfermoney(accounts[fromacct],accounts[toacct], amount,fromacct,toacct);
//inducelockorder.transfermoney(accounts[fromacct],accounts[toacct], amount);
//inducelockorder2.transfermoney(accounts[fromacct],accounts[toacct], amount);
}
catch
(exception e) {
system.out.println(
"发生异常-------"
+e);
}
}
}
}
for
(
int
i =
0
;i < num_threads;i++) {
new
transferthread().start();
}
}
}
|
打印结果如下: 注意:这里的结果是我把已经执行完的给删除后,只剩下导致死锁的请求. 。

从打印结果的图片中可以的得到结论:由于我们无法控制transfermoney中的参数的顺序,而这些参数顺序取决于外部的输入。所以两个线程同时调用transfermoney,一个线程从x向y转账,另一个线程从y向x转账,那么就会发生互相等待锁的情况,导致死锁.
解决问题方案:定义锁的顺序,并且整个应用中都按照这个顺序来获取锁.
方案一 。
使用system.identityhashcode方法,该方法返回有object.hashcode返回的值,此时可以通过某种任意方法来决定锁的顺序。但是在极少数情况下,两个对象可能拥有相同的散列值,在这种情况下,通过给公共变量加锁来实现给锁制定顺序。所以这种方法也是用最小的代价,换来了最大的安全性。 具体代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
|
//通过锁顺序来避免死锁
public
class
inducelockorder {
private
static
final
object tielock =
new
object();
public
static
void
transfermoney(
final
account fromacct,
final
account toacct,
final
int
amount)
throws
exception {
class
helper {
public
void
transfer()
throws
exception {
if
(fromacct.compareto(amount) <
0
) {
throw
new
exception();
}
else
{
fromacct.debit(amount);
toacct.credit(amount);
}
}
}
int
fromhash = system.identityhashcode(fromacct);
int
tohash = system.identityhashcode(toacct);
if
(fromhash < tohash) {
synchronized
(fromacct) {
synchronized
(toacct) {
new
helper().transfer();
}
}
}
else
if
(fromhash > tohash) {
synchronized
(toacct) {
synchronized
(fromacct) {
new
helper().transfer();
}
}
}
else
{
synchronized
(tielock) {
synchronized
(fromacct) {
synchronized
(toacct) {
new
helper().transfer();
}
}
}
}
}
static
class
account {
private
int
balance =
100000
;
public
account() {
}
void
debit(
int
m)
throws
interruptedexception {
thread.sleep(
5
);
balance = balance + m;
}
void
credit(
int
m)
throws
interruptedexception {
thread.sleep(
5
);
balance = balance - m;
}
int
getbalance() {
return
balance;
}
public
int
compareto(
int
money) {
if
(balance > money) {
return
1
;
}
else
if
(balance < money) {
return
-
1
;
}
else
{
return
0
;
}
}
}
}
|
经过我测试,此方案可行,不会造成死锁.
方案二 。
在account中包含一个唯一的,不可变的,值。比如说账号等。通过对这个值对对象进行排序。 具体代码如下 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
|
public
class
inducelockorder2 {
public
static
void
transfermoney(
final
account fromacct,
final
account toacct,
final
int
amount)
throws
exception {
class
helper {
public
void
transfer()
throws
exception {
if
(fromacct.compareto(amount) <
0
) {
throw
new
exception();
}
else
{
fromacct.debit(amount);
toacct.credit(amount);
}
}
}
int
fromhash = fromacct.getaccno();
int
tohash = toacct.getaccno();
if
(fromhash < tohash) {
synchronized
(fromacct) {
synchronized
(toacct) {
new
helper().transfer();
}
}
}
else
if
(fromhash > tohash) {
synchronized
(toacct) {
synchronized
(fromacct) {
new
helper().transfer();
}
}
}
}
static
class
account {
private
int
balance =
100000
;
private
final
int
accno;
private
static
final
atomicinteger sequence =
new
atomicinteger();
public
account() {
accno = sequence.incrementandget();
}
void
debit(
int
m)
throws
interruptedexception {
thread.sleep(
6
);
balance = balance + m;
}
void
credit(
int
m)
throws
interruptedexception {
thread.sleep(
6
);
balance = balance - m;
}
int
getbalance() {
return
balance;
}
int
getaccno() {
return
accno;
}
public
int
compareto(
int
money) {
if
(balance > money) {
return
1
;
}
else
if
(balance < money) {
return
-
1
;
}
else
{
return
0
;
}
}
}
}
|
经过测试此方案也可行.
2.2在协作对象之间发生的死锁 如果在持有锁时调用某外部的方法,那么将出现活跃性问题。在这个外部方法中可能会获取其他的锁(这个可能产生死锁),或阻塞时间过长,导致其他线程无法及时获得当前持有的锁.
场景如下:taxi代表出租车对象,包含当前位置和目的地。dispatcher代表车队。当一个线程收到gps更新事件时掉用setlocation,那么它首先更新出租车的位置,然后判断它是否到达目的地。如果已经到达,它会通知dispatcher:它需要一个新的目的地。因为setlocation和notifyavailable都是同步方法,因此掉用setlocation线程首先获取taxi的锁,然后在获取dispatcher的锁。同样,掉用getimage的线程首先获取dispatcher的锁,再获取每一个taxi的锁,这两个线程按照不同的顺序来获取锁,因此可能导致死锁.
能造成死锁的代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
|
//会发生死锁
public
class
cooperatingdeadlock {
// 坐标类
class
point {
private
final
int
x;
private
final
int
y;
public
point(
int
x,
int
y) {
this
.x = x;
this
.y = y;
}
public
int
getx() {
return
x;
}
public
int
gety() {
return
y;
}
}
// 出租车类
class
taxi {
private
point location, destination;
private
final
dispatcher dispatcher;
public
taxi(dispatcher dispatcher) {
this
.dispatcher = dispatcher;
}
public
synchronized
point getlocation() {
return
location;
}
public
synchronized
void
setlocation(point location) {
this
.location = location;
if
(location.equals(destination)) {
dispatcher.notifyavailable(
this
);
}
}
public
synchronized
point getdestination() {
return
destination;
}
public
synchronized
void
setdestination(point destination) {
this
.destination = destination;
}
}
class
dispatcher {
private
final
set<taxi> taxis;
private
final
set<taxi> availabletaxis;
public
dispatcher() {
taxis =
new
hashset<>();
availabletaxis =
new
hashset<>();
}
public
synchronized
void
notifyavailable(taxi taxi) {
availabletaxis.add(taxi);
}
public
synchronized
image getimage() {
image image =
new
image();
for
(taxi t:taxis) {
image.drawmarker(t.getlocation());
}
return
image;
}
}
class
image{
public
void
drawmarker(point p) {
}
}
}
|
解决方案:使用开放掉用。 如果再调用某个方法时不需要持有锁,那么这种调用就被称为开放掉用。这种调用能有效的避免死锁,并且易于分析线程安全.
修改后的代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
|
//此方案不会造成死锁
public
class
cooperatingnodeadlock {
// 坐标类
class
point {
private
final
int
x;
private
final
int
y;
public
point(
int
x,
int
y) {
this
.x = x;
this
.y = y;
}
public
int
getx() {
return
x;
}
public
int
gety() {
return
y;
}
}
// 出租车类
class
taxi {
private
point location, destination;
private
final
dispatcher dispatcher;
public
taxi(dispatcher dispatcher) {
this
.dispatcher = dispatcher;
}
public
synchronized
point getlocation() {
return
location;
}
public
void
setlocation(point location) {
boolean
reacheddestination;
synchronized
(
this
) {
this
.location = location;
reacheddestination = location.equals(destination);
}
if
(reacheddestination) {
dispatcher.notifyavailable(
this
);
}
}
public
synchronized
point getdestination() {
return
destination;
}
public
synchronized
void
setdestination(point destination) {
this
.destination = destination;
}
}
class
dispatcher {
private
final
set<taxi> taxis;
private
final
set<taxi> availabletaxis;
public
dispatcher() {
taxis =
new
hashset<>();
availabletaxis =
new
hashset<>();
}
public
synchronized
void
notifyavailable(taxi taxi) {
availabletaxis.add(taxi);
}
public
image getimage() {
set<taxi> copy;
synchronized
(
this
) {
copy =
new
hashset<>(taxis);
}
image image =
new
image();
for
(taxi t:copy) {
image.drawmarker(t.getlocation());
}
return
image;
}
}
class
image{
public
void
drawmarker(point p) {
}
}
}
|
总结:活跃性故障是一个非常严重的问题,因为当出现活跃性故障时,除了终止应用程序之外没有其他任何机制可以帮助从这种故障中恢复过来。最常见的活跃性故障就是锁顺序死锁。在设计时应该避免产生顺序死锁:确保线程在获取多个锁时采用一直的顺序。最好的解决方案是在程序中始终使用开放掉用。这将大大减小需要同时持有多个锁的地方,也更容易发现这些地方.
以上所述是小编给大家介绍的java中常见的死锁以及解决方法详解整合,希望对大家有所帮助,如果大家有任何疑问请给我留言,小编会及时回复大家的。在此也非常感谢大家对我网站的支持! 。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qdh186/article/details/86497809 。
最后此篇关于java中常见的死锁以及解决方法代码的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于java中常见的死锁以及解决方法代码的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我正在编写一个具有以下签名的 Java 方法。 void Logger(Method method, Object[] args); 如果一个方法(例如 ABC() )调用此方法 Logger,它应该
我是 Java 新手。 我的问题是我的 Java 程序找不到我试图用作的图像文件一个 JButton。 (目前这段代码什么也没做,因为我只是得到了想要的外观第一的)。这是我的主课 代码: packag
好的,今天我在接受采访,我已经编写 Java 代码多年了。采访中说“Java 垃圾收集是一个棘手的问题,我有几个 friend 一直在努力弄清楚。你在这方面做得怎么样?”。她是想骗我吗?还是我的一生都
我的 friend 给了我一个谜语让我解开。它是这样的: There are 100 people. Each one of them, in his turn, does the following
如果我将使用 Java 5 代码的应用程序编译成字节码,生成的 .class 文件是否能够在 Java 1.4 下运行? 如果后者可以工作并且我正在尝试在我的 Java 1.4 应用程序中使用 Jav
有关于why Java doesn't support unsigned types的问题以及一些关于处理无符号类型的问题。我做了一些搜索,似乎 Scala 也不支持无符号数据类型。限制是Java和S
我只是想知道在一个 java 版本中生成的字节码是否可以在其他 java 版本上运行 最佳答案 通常,字节码无需修改即可在 较新 版本的 Java 上运行。它不会在旧版本上运行,除非您使用特殊参数 (
我有一个关于在命令提示符下执行 java 程序的基本问题。 在某些机器上我们需要指定 -cp 。 (类路径)同时执行java程序 (test为java文件名与.class文件存在于同一目录下) jav
我已经阅读 StackOverflow 有一段时间了,现在我才鼓起勇气提出问题。我今年 20 岁,目前在我的家乡(罗马尼亚克卢日-纳波卡)就读 IT 大学。足以介绍:D。 基本上,我有一家提供簿记应用
我有 public JSONObject parseXML(String xml) { JSONObject jsonObject = XML.toJSONObject(xml); r
我已经在 Java 中实现了带有动态类型的简单解释语言。不幸的是我遇到了以下问题。测试时如下代码: def main() { def ks = Map[[1, 2]].keySet()
一直提示输入 1 到 10 的数字 - 结果应将 st、rd、th 和 nd 添加到数字中。编写一个程序,提示用户输入 1 到 10 之间的任意整数,然后以序数形式显示该整数并附加后缀。 public
我有这个 DownloadFile.java 并按预期下载该文件: import java.io.*; import java.net.URL; public class DownloadFile {
我想在 GUI 上添加延迟。我放置了 2 个 for 循环,然后重新绘制了一个标签,但这 2 个 for 循环一个接一个地执行,并且标签被重新绘制到最后一个。 我能做什么? for(int i=0;
我正在对对象 Student 的列表项进行一些测试,但是我更喜欢在 java 类对象中创建硬编码列表,然后从那里提取数据,而不是连接到数据库并在结果集中选择记录。然而,自从我这样做以来已经很长时间了,
我知道对象创建分为三个部分: 声明 实例化 初始化 classA{} classB extends classA{} classA obj = new classB(1,1); 实例化 它必须使用
我有兴趣使用 GPRS 构建车辆跟踪系统。但是,我有一些问题要问以前做过此操作的人: GPRS 是最好的技术吗?人们意识到任何问题吗? 我计划使用 Java/Java EE - 有更好的技术吗? 如果
我可以通过递归方法反转数组,例如:数组={1,2,3,4,5} 数组结果={5,4,3,2,1}但我的结果是相同的数组,我不知道为什么,请帮助我。 public class Recursion { p
有这样的标准方式吗? 包括 Java源代码-测试代码- Ant 或 Maven联合单元持续集成(可能是巡航控制)ClearCase 版本控制工具部署到应用服务器 最后我希望有一个自动构建和集成环境。
我什至不知道这是否可能,我非常怀疑它是否可能,但如果可以,您能告诉我怎么做吗?我只是想知道如何从打印机打印一些文本。 有什么想法吗? 最佳答案 这里有更简单的事情。 import javax.swin

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!