- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章SpringBoot整个启动过程的分析由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
前言 。
前一篇分析了springboot如何启动以及内置web容器,这篇我们一起看一下springboot的整个启动过程,废话不多说,正文开始.
正文 。
1、springboot的启动类是**application,以注解@springbootapplication注明.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
@springbootapplication
public
class
cmsapplication {
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
springapplication.run(cmsapplication.
class
, args);
}
}
|
springbootapplication注解是@configuration,@enableautoconfiguration,@componentscan三个注解的集成,分别表示springbean的配置bean,开启自动配置spring的上下文,组件扫描的路径,这也是为什么*application.java需要放在根路径的原因,这样@componentscan扫描的才是整个项目.
2、该启动类默认只有一个main方法,调用的是springapplication.run方法,下面我们来看一下springapplication这个类.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
public
static
configurableapplicationcontext run(object source, string... args) {
return
run(
new
object[]{source}, args);
}
...
public
static
configurableapplicationcontext run(object[] sources, string[] args) {
return
(
new
springapplication(sources)).run(args);
//sources为具体的cmsapplication.class类
}
...
|
抽出其中两个直接调用的run方法,可以看出静态方法springapplication.run最终创建了一个springapplication,并运行其中run方法.
查看起构造方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public
springapplication(object... sources) {
this
.bannermode = mode.console;
this
.logstartupinfo =
true
;
this
.addcommandlineproperties =
true
;
this
.headless =
true
;
this
.registershutdownhook =
true
;
this
.additionalprofiles =
new
hashset();
this
.initialize(sources);
}
...
|
构造方法设置了基础值后调用initialize方法进行初始化,如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
private
void
initialize(object[] sources) {
if
(sources !=
null
&& sources.length >
0
) {
this
.sources.addall(arrays.aslist(sources));
}
this
.webenvironment =
this
.deducewebenvironment();
this
.setinitializers(
this
.getspringfactoriesinstances(applicationcontextinitializer.
class
));
this
.setlisteners(
this
.getspringfactoriesinstances(applicationlistener.
class
));
this
.mainapplicationclass =
this
.deducemainapplicationclass();
}
...
|
初始化方法主要做了几步:
1.将source放入springapplication的sources属性中管理,sources是一个linkedhashset(),这意味着我们可以同时创建多个自定义不重复的application,但是目前只有一个.
2.判断是否是web程序(javax.servlet.servlet和org.springframework.web.context.configurablewebapplicationcontext都必须在类加载器中存在),并设置到webenvironment属性中.
3.从spring.factories中找出applicationcontextinitializer并设置到初始化器initializers.
4.从spring.factories中找出applicationlistener,并实例化后设置到springapplication的监听器listeners属性中。这个过程就是找出所有的应用程序事件监听器.
5.找出的main方法的类(这里是cmsapplication),并返回class对象.
默认情况下,initialize方法从spring.factories文件中找出的key为applicationcontextinitializer的类有:
key为applicationlistener的有:
3、springapplication构造和初始化完成后,便是运行其run方法 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
public
configurableapplicationcontext run(string... args) {
stopwatch stopwatch =
new
stopwatch();
// 构造一个任务执行观察器
stopwatch.start();
// 开始执行,记录开始时间
configurableapplicationcontext context =
null
;
failureanalyzers analyzers =
null
;
this
.configureheadlessproperty();
// 获取springapplicationrunlisteners,内部只有一个eventpublishingrunlistener
springapplicationrunlisteners listeners =
this
.getrunlisteners(args);
// 封装成springapplicationevent事件然后广播出去给springapplication中的listeners所监听,启动监听
listeners.starting();
try
{
// 构造一个应用程序参数持有类
applicationarguments applicationarguments =
new
defaultapplicationarguments(args);
// 加载配置环境
configurableenvironment environment =
this
.prepareenvironment(listeners, applicationarguments);
banner printedbanner =
this
.printbanner(environment);
// 创建spring容器(使用beanutils.instantiate)
context =
this
.createapplicationcontext();
// 若容器创建失败,分析输出失败原因
new
failureanalyzers(context);
// 设置容器配置环境,监听等
this
.preparecontext(context, environment, listeners, applicationarguments, printedbanner);
// 刷新容器
this
.refreshcontext(context);
this
.afterrefresh(context, applicationarguments);
// 广播出applicationreadyevent事件给相应的监听器执行
listeners.finished(context, (throwable)
null
);
stopwatch.stop();
// 执行结束,记录执行时间
if
(
this
.logstartupinfo) {
(
new
startupinfologger(
this
.mainapplicationclass)).logstarted(
this
.getapplicationlog(), stopwatch);
}
return
context;
// 返回spring容器
}
catch
(throwable var9) {
this
.handlerunfailure(context, listeners, (failureanalyzers)analyzers, var9);
throw
new
illegalstateexception(var9);
}
}
|
run方法过程分析如上,该方法几个关键步骤如下:
1.创建了应用的监听器springapplicationrunlisteners并开始监听 。
2.加载springboot配置环境(configurableenvironment),如果是通过web容器发布,会加载standardenvironment,其最终也是继承了configurableenvironment,类图如下 。
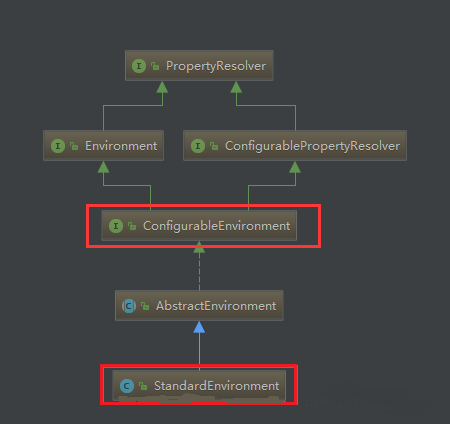
可以看出,*environment最终都实现了propertyresolver接口,我们平时通过environment对象获取配置文件中指定key对应的value方法时,就是调用了propertyresolver接口的getproperty方法.
3.配置环境(environment)加入到监听器对象中(springapplicationrunlisteners) 。
4.创建spring容器:configurableapplicationcontext(应用配置上下文),我们可以看一下创建方法 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
protected
configurableapplicationcontext createapplicationcontext() {
class
<?> contextclass =
this
.applicationcontextclass;
if
(contextclass ==
null
) {
try
{
contextclass =
class
.forname(
this
.webenvironment ?
"org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.annotationconfigembeddedwebapplicationcontext"
:
"org.springframework.context.annotation.annotationconfigapplicationcontext"
);
}
catch
(classnotfoundexception var3) {
throw
new
illegalstateexception(
"unable create a default applicationcontext, please specify an applicationcontextclass"
, var3);
}
}
return
(configurableapplicationcontext)beanutils.instantiate(contextclass);
}
|
方法会先获取显式设置的应用上下文(applicationcontextclass),如果不存在,再加载默认的环境配置(通过是否是web environment判断),默认选择annotationconfigapplicationcontext注解上下文(通过扫描所有注解类来加载bean),最后通过beanutils实例化上下文对象,并返回,configurableapplicationcontext类图如下 。
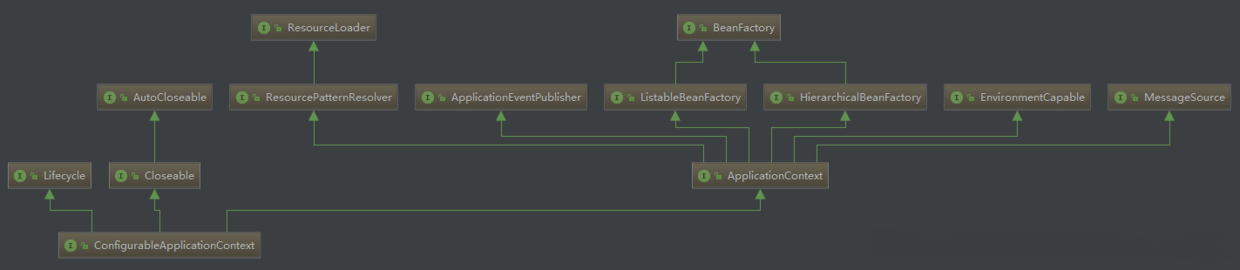
主要看其继承的两个方向:
5.回到run方法内,设置容器preparecontext方法,将listeners、environment、applicationarguments、banner等重要组件与上下文对象关联 。
6.刷新容器,refresh()方法,初始化方法如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
public
void
refresh()
throws
beansexception, illegalstateexception {
object var1 =
this
.startupshutdownmonitor;
synchronized
(
this
.startupshutdownmonitor) {
this
.preparerefresh();
configurablelistablebeanfactory beanfactory =
this
.obtainfreshbeanfactory();
this
.preparebeanfactory(beanfactory);
try
{
this
.postprocessbeanfactory(beanfactory);
this
.invokebeanfactorypostprocessors(beanfactory);
this
.registerbeanpostprocessors(beanfactory);
this
.initmessagesource();
this
.initapplicationeventmulticaster();
this
.onrefresh();
this
.registerlisteners();
this
.finishbeanfactoryinitialization(beanfactory);
this
.finishrefresh();
}
catch
(beansexception var9) {
if
(
this
.logger.iswarnenabled()) {
this
.logger.warn(
"exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: "
+ var9);
}
this
.destroybeans();
this
.cancelrefresh(var9);
throw
var9;
}
finally
{
this
.resetcommoncaches();
}
}
}
|
refresh()方法做了很多核心工作比如beanfactory的设置,beanfactorypostprocessor接口的执行、beanpostprocessor接口的执行、自动化配置类的解析、spring.factories的加载、bean的实例化、条件注解的解析、国际化的初始化等等。这部分内容会在之后的文章中分析.
7.广播出applicationreadyevent,执行结束返回configurableapplicationcontext.
至此,springboot启动完成,回顾整体流程,springboot的启动,主要创建了配置环境(environment)、事件监听(listeners)、应用上下文(applicationcontext),并基于以上条件,在容器中开始实例化我们需要的bean.
总结 。
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,谢谢大家对我的支持。如果你想了解更多相关内容请查看下面相关链接 。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/u011961421/article/details/80227453 。
最后此篇关于SpringBoot整个启动过程的分析的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于SpringBoot整个启动过程的分析的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
如果我声明了类似的类型 type test(NSIZE) integer, len :: NSIZE real :: dummy(NSIZE) contains procedure,
我知道这是一个不太可能的事情,但是由于“选项私有(private)模块”的限制,甚至更糟糕的“私有(private)子/函数”的限制,有谁知道是否有一种方法可以从 Excel 应用程序隐藏 VBA 过
我有两个表,property 和 component。 component.id_property = property.id。 我正在尝试创建一个过程,该过程对所选属性的组件进行计数,如果所选属性没
我有一份报告,它是在 SSRS 2005 中开发的,我正在使用存储过程从数据库中获取结果。报告输出的结果非常简单,如下图所示。 如果假设我正在寻找不同的成员 例如:- MemberID c108 c
我需要一个通用函数/过程,该函数/过程将根据提供的数据计算出我的淡入淡出时间和值,如下所示: 我将字节值保存在字节数组中:这些是起始值。然后,我在其他数组中存储了一些值:这些将是新值。然后我有时间要提
我想在界面的多个按钮上创建相同的操作。是否只能通过创建单独的操作监听器方法并调用执行操作的方法才可行,还是还有其他方法?是否可以将按钮放在一个组中并执行以下操作:- groupButton.setOn
我有以下情况: procedure Test; begin repeat TryAgain := FALSE; try // Code // Code if this an
我正在尝试执行以下操作;假设我在 Oracle 中创建了一个对象类型 create type test as object( name varchar2(12), member procedure p
问题: 如果可能的话,如何声明一个用于任何类型参数的函数 T其中 T 的唯一约束是它被定义为 1D array如 type T is array ( integer range <> ) of a_r
我正在尝试创建这个 mysql 过程来制作一个包含今年所有日期和所有时间的表(以一小时为间隔。) CREATE TABLE FECHAS ( created_at datetime ); CREA
所以, 我在这里面临一个问题,这让我发疯,我认为这是一个愚蠢的错误,所以我不是 MySQL 的新手,但它并不像我想象的那样工作。 尝试将此语句部署到 MySQL 后,我收到此错误: ERROR 106
我有一个架构,其中包含星球大战中的人物列表、他们出现的电影、他们访问的行星等。这是架构: CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `starwarsFINAL` /*!40100
我一直在为一家慈善机构创建一款应用程序,允许家庭在节日期间注册接收礼物。数据库组织有多个表。下面列出了这些表(及其架构/创建语句): CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS ValidD
正如上面标题所解释的,我正在尝试编写一个sql函数来按日期删除表而不删除系统表。我在此消息下方放置了一张图片,以便直观地解释我的问题。任何帮助将不胜感激!感谢您的时间! 最佳答案 您可以通过查询INF
DELIMITER $$ CREATE PROCEDURE INSERT_NONE_HISTORY_CHECKBOX() BEGIN DECLARE note_id bigint(20); F
是否可以编写一个存储过程或触发器,在特定时间在数据库内部自动执行,而无需来自应用程序的任何调用?如果是,那么任何人都可以给我一个例子或链接到一些我可以阅读如何做到这一点的资源。 最佳答案 查看 pgA
我需要创建一个过程:1)从表中的字段中选择一些文本并将其存储在变量中2) 更新相同的记录字段,仅添加 yyyymmdd 格式的日期以及过程中的附加文本输入...类似这样的... delimiter /
好的,这就是我想做的: 如果条目已存在(例如基于字段name),则只需返回其id 如果没有,请添加 这是我迄今为止所管理的(对于“如果不存在,则创建它”部分): INSERT INTO `object
以下是我编写的程序,用于找出每位客户每天购买的前 10 件商品。 这是我尝试过的第一个 PL/SQL 操作。它没有达到我预期的效果。 我使用的逻辑是接受开始日期、结束日期以及我对每个客户感兴趣的前“x
我正在尝试在MySQL中创建一个过程那insert week s(当年)发送至我的 week table 。但存在一个问题,因为在为下一行添加第一行后,我收到错误: number column can

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!