- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章python运行加速的几种方式由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
1、使用pypy 2、减少函数化调用 3、减少文件的打开即with的调用,将这一调用放在for循环前面,然后传递至后面需要用到的地方 4、if函数判断条件多的尽量在前面 全面加速(pypy) 。
将python换为pypy,在纯python代码下,pypy的兼容性就不影响使用了,因为一些纯python的代码常常会用pypy进行一下加速 。
测试代码,for循环10000000次 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
start
=
time.time()
for
i
in
range
(
10000000
):
print
(i,end
=
"\r"
)
end
=
time.time()
print
(f
"耗费时间{end-start}秒>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
)
|
pypy的耗时为:
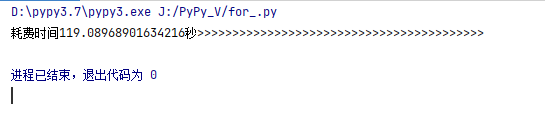
而python耗时为 。
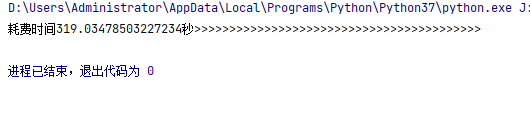
大致三倍,但是循环越多估计越快,据说有6倍左右 。
原代码的with在调用函数内,即每次调用函数都要打开并关闭文件,造成大量耗时 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
def
bmes(word,tag):
with
open
(r
"j:\pycharm项目\学习进行中\nlp教程\nlp教程\数据集\词性标注\nature2ner.txt"
,
"a+"
,encoding
=
"utf-8"
)as f_:
if
len
(word)
=
=
1
:
"""单字"""
f_.write(word
+
" "
+
f
"s-{tag.upper()}"
+
"\n"
)
else
:
"""多字"""
for
index, word_
in
enumerate
(word):
if
index
=
=
0
:
f_.write(word_
+
" "
+
f
"b-{tag.upper()}"
+
"\n"
)
elif
0
< index <
len
(word)
-
1
:
f_.write(word_
+
" "
+
f
"m-{tag.upper()}"
+
"\n"
)
else
:
f_.write(word_
+
" "
+
f
"e-{tag.upper()}"
+
"\n"
)
#后续在多个if-elif-else中调用
|
耗时为 。
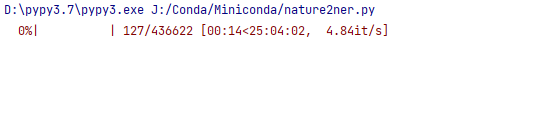
tqdm预估时间在15~25个小时左右跳动 。
将with放在循环前面 。
如 。
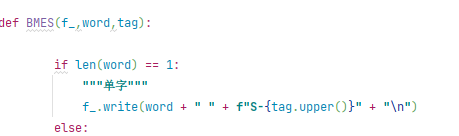
将with的内容作为f_传递进来 。

后的耗时为:
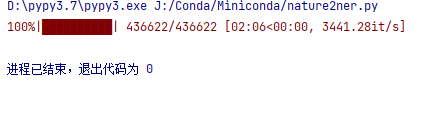
测试如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
import
os, warnings,time,tqdm
def
txt(word):
with
open
(
"ceshi.txt"
,
"a+"
,encoding
=
"utf-8"
)as f:
if
len
(
str
(word))<
=
2
:
word
+
=
100
f.write(
str
(word)
+
"\n"
)
elif
2
<
len
(
str
(word))<
=
4
:
word
+
=
200
f.write(
str
(word)
+
"\n"
)
else
:
f.write(
str
(word)
+
"\n"
)
if
__name__
=
=
"__main__"
:
start
=
time.time()
for
i
in
tqdm.tqdm(
range
(
100000
)):
txt(i)
end
=
time.time()
print
(f
"耗费时间{end-start}秒>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
)
|
耗时结果为:
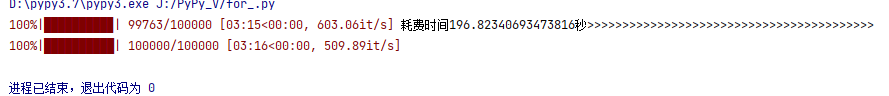
将文件的打开即with的调用放在外面 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
import
os, warnings,time,tqdm
def
txt(f,word):
if
len
(
str
(word))<
=
2
:
word
+
=
100
f.write(
str
(word)
+
"\n"
)
elif
2
<
len
(
str
(word))<
=
4
:
word
+
=
200
f.write(
str
(word)
+
"\n"
)
else
:
f.write(
str
(word)
+
"\n"
)
if
__name__
=
=
"__main__"
:
start
=
time.time()
with
open
(
"ceshi.txt"
,
"a+"
, encoding
=
"utf-8"
)as f:
for
i
in
tqdm.tqdm(
range
(
100000
)):
txt(f,i)
end
=
time.time()
print
(f
"耗费时间{end-start}秒>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
)
|
耗时为 。
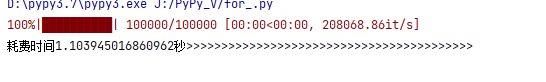
结论:快了119倍,而实际加速远远大于这个倍数 。
如:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
if
tag
in
[
"nts"
,
"nto"
,
"ntc"
,
"ntcb"
,
"ntcf"
,
"ntch"
,
"nth"
,
"ntu"
,
"nt"
]:
bmes(f_,i2, tag
=
"org"
)
elif
tag
in
[
"nb"
,
"nba"
,
"nbc"
,
"nbp"
,
"nf"
,
"nm"
,
"nmc"
,
"nhm"
,
"nh"
]:
bmes(f_,i2, tag
=
"obj"
)
elif
tag
in
[
"nnd"
,
"nnt"
,
"nn"
]:
bmes(f_,i2, tag
=
"job"
)
elif
tag
in
[
"nr"
,
"nrf"
]:
bmes(f_,i2, tag
=
"per"
)
elif
tag
in
[
"t"
]:
bmes(f_,i2, tag
=
"time"
)
elif
tag
in
[
"ns"
,
"nsf"
]:
bmes(f_,i2, tag
=
"loc"
)
else
:
for
i3
in
list
(i2):
f_.write(i3
+
" "
+
f
"o"
+
"\n"
)
|
满足条件的可以先跳出判断 。
到此这篇关于python运行加速的几种方式的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python运行加速的几种方式内容请搜索我以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我! 。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/python__reported/article/details/118660689 。
最后此篇关于python运行加速的几种方式的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于python运行加速的几种方式的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
好的,所以我想从批处理文件运行我的整个工作环境... 我想要实现什么...... 打开新的 powershell,打开我的 API 文件夹并从该文件夹运行 VS Code 编辑器(cd c:\xy;
我正在查看 Cocoa Controls 上的示例并下载了一些演示。我遇到的问题是一些例子,比如 BCTabBarController ,不会在我的设备上构建或启动。当我打开项目时,它看起来很正常,没
我刚刚开始学习 C 语言(擅长 Java 和 Python)。 当编写 C 程序(例如 hello world)时,我在 ubuntu cmd 行上使用 gcc hello.c -o hello 编译
我在 php 脚本从 cron 开始运行到超时后注意到了这个问题,但是当它从命令行手动运行时这不是问题。 (对于 CLI,PHP 默认的 max_execution_time 是 0) 所以我尝试运行
我可以使用命令行运行测试 > ./node_modules/.bin/wdio wdio.conf.js 但是如果我尝试从 IntelliJ 的运行/调试配置运行它,我会遇到各种不同的错误。 Fea
Error occurred during initialization of VM. Could not reserve enough space for object heap. Error: C
将 Anaconda 安装到 C:\ 后,我无法打开 jupyter 笔记本。无论是在带有 jupyter notebook 的 Anaconda Prompt 中还是在导航器中。我就是无法让它工作。
我遇到一个问题,如果我双击我的脚本 (.py),或者使用 IDLE 打开它,它将正确编译并运行。但是,如果我尝试在 Windows 命令行中运行脚本,请使用 C:\> "C:\Software_Dev
情况 我正在使用 mysql 数据库。查询从 phpmyadmin 和 postman 运行 但是当我从 android 发送请求时(它返回零行) 我已经记录了从 android 发送的电子邮件是正确
所以这个有点奇怪 - 为什么从 Java 运行 .exe 文件会给出不同的输出而不是直接运行 .exe。 当 java 在下面的行执行时,它会调用我构建的可与 3CX 电话系统配合使用的 .exe 文
这行代码 Environment.Is64BitProcess 当我的应用单独运行时评估为真。 但是当它在我的 Visual Studio 单元测试中运行时,相同的表达式的计算结果为 false。 我
关闭。这个问题是opinion-based .它目前不接受答案。 想要改进这个问题? 更新问题,以便 editing this post 可以用事实和引用来回答它. 关闭 8 年前。 Improve
我写了一个使用 libpq 连接到 PostgreSQL 数据库的演示。 我尝试通过包含将 C 文件连接到 PostgreSQL #include 在我将路径添加到系统变量 I:\Program F
如何从 Jenkins 运行 Android 模拟器来运行我的测试?当我在 Execiute Windows bath 命令中写入时,运行模拟器的命令: emulator -avd Tester 然后
我已经配置好东西,这样我就可以使用 ssl 登录和访问在 nginx 上运行的 errbit 我的问题是我不知道如何设置我的 Rails 应用程序的 errbit.rb 以便我可以运行测试 nginx
我编写了 flutter 应用程序,我通过 xcode 打开了 ios 部分并且应用程序正在运行,但是当我通过 flutter build ios 通过 vscode 运行应用程序时,我得到了这个错误
我有一个简短的 python 脚本,它使用日志记录模块和 configparser 模块。我在Win7下使用PyCharm 2.7.1和Python 3.3。 当我使用 PyCharm 运行我的脚本时
我在这里遇到了一些难题。 我的开发箱是 64 位的,windows 7。我所有的项目都编译为“任何 CPU”。该项目引用了 64 位版本的第 3 方软件 当我运行不使用任何 Web 引用的单元测试时,
当我注意到以下问题时,我正在做一些 C++ 练习。给定的代码将不会在 Visual Studio 2013 或 Qt Creator 5.4.1 中运行/编译 报错: invalid types 'd
假设我有一个 easteregg.py 文件: from airflow import DAG from dateutil import parser from datetime import tim

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!