- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章python geopandas读取、创建shapefile文件的方法由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
shapefile是GIS中非常重要的一种数据类型,在ArcGIS中被称为要素类(Feature Class),主要包括点(point)、线(polyline)和多边形(polygon)。作为一种十分常见的矢量文件格式,geopandas对shapefile提供了很好的读取和写出支持,其DataFrame结构相当于GIS数据中的一张属性表,使得可以直接操作矢量数据属性表,使得在python中操作地理数据更方便。本文给大家介绍下用Python脚本中对Shapefile文件(.shp,.shx,.dbf等格式)进行读写操作.
由于geopandas有好几个依赖库,推荐大家使用 Miniconda或是 Anaconda来安装geopandas.
安装命令:
conda install -c conda-forge geopandas
国内镜像:
conda install -c https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud/conda-forge geopandas
使用导入:import geopandas 。
我这里用的是geopandas 0.7的版本,版本间差异是不太大,最新0.8版本新增了一些查询、入库方面的特性.
相比pyshp库,geopandas库的数据读取、展示、分析、拓展的效果要更好。它可以读取zip中的shapefile,还可以读取GeoJson、ArcGIS中地理数据库gdb,以及QGIS中GeoPackage 存放的矢量数据.
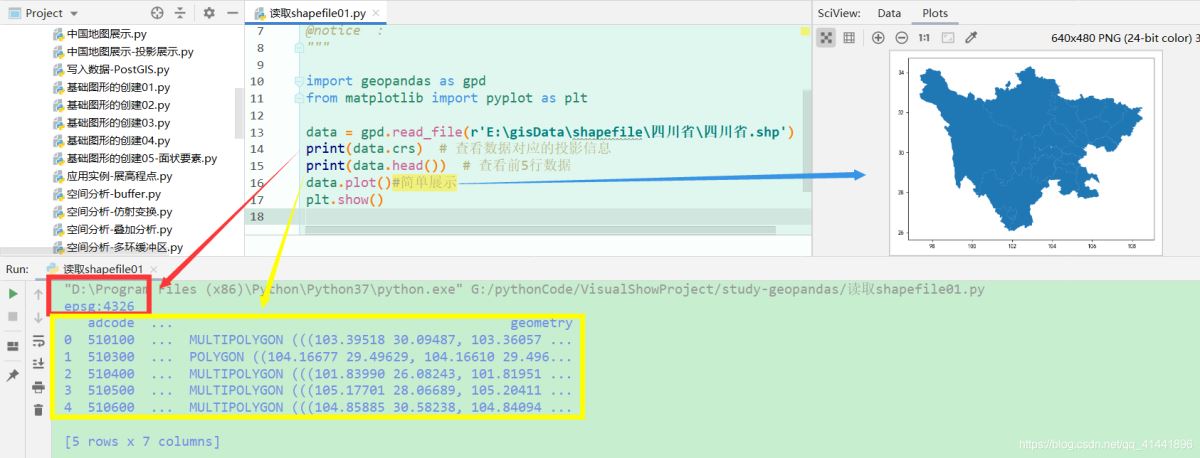
import geopandas as gpdfrom matplotlib import pyplot as pltdata = gpd.read_file(r"E:gisData行政区划数据2019省.shp")#读取磁盘上的矢量文件#data = gpd.read_file("shapefile/china.gdb", layer="province")#读取gdb中的矢量数据print(data.crs) # 查看数据对应的投影信息print(data.head()) # 查看前5行数据data.plot()plt.show()#简单展示
显示效果:
要素类的创建效率很高,既能创建要素实体,也能写入属性信息和定义投影。下面先简单介绍下三种要素类的创建方法.
点状要素类的创建 。
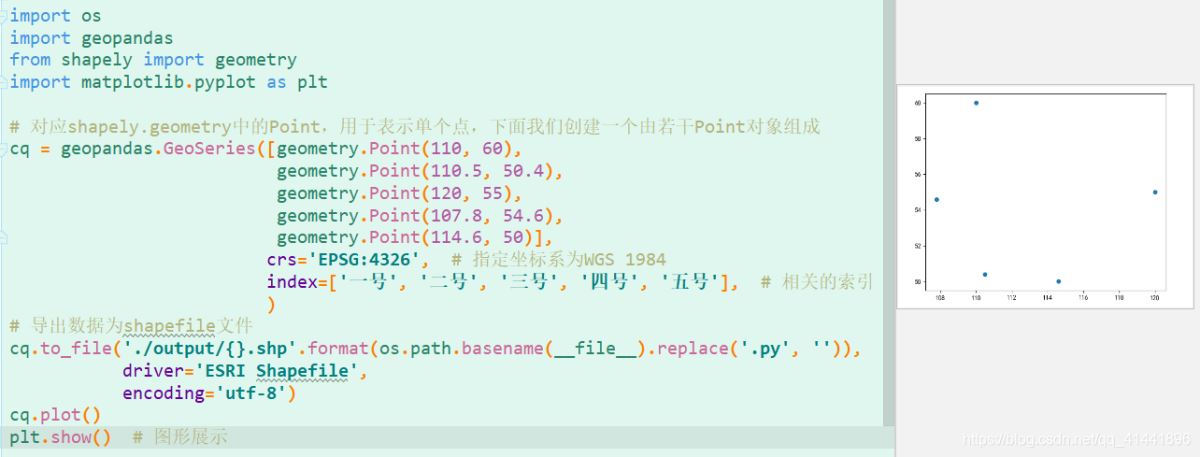
核心代码:
# 对应shapely.geometry中的Point,用于表示单个点,下面我们创建一个由若干Point对象组成cq = geopandas.GeoSeries([geometry.Point(110, 60), geometry.Point(110.5, 50.4), geometry.Point(120, 55), geometry.Point(107.8, 54.6), geometry.Point(114.6, 50)], crs="EPSG:4326", # 指定坐标系为WGS 1984 index=["一号", "二号", "三号", "四号", "五号"], # 相关的索引 )# 导出数据为shapefile文件cq.to_file("./output/{}.shp".format(os.path.basename(__file__).replace(".py", "")), driver="ESRI Shapefile", encoding="utf-8")
线状要素类的创建 。

核心代码:
# 这里shapely.geometry.LineString([(x1, y1), (x2, y2), ...])用于创建多点按顺序连接而成的线段cq = geopandas.GeoSeries([geometry.LineString([(0, 0), (1, 1), (1, 0)]), geometry.LineString([(0.5, 2), (0, 1), (-1, 0)])], crs="EPSG:4326", index=["一号线", "b"])cq.to_file("./output/{}.shp".format(os.path.basename(__file__).replace(".py", "")), driver="ESRI Shapefile", encoding="utf-8")
面状要素类的创建 。

核心代码:
# 对应shapely.geometry中的Polygon,用于表示面,下面我们创建一个由若干Polygon对象组成cq = geopandas.GeoSeries([geometry.Polygon([(14, 14), (13, 18), (20, 11), (18, 10)]), geometry.Polygon([(0, 0), (10, 0), (10, 10), (0, 10)], [((1, 3), (5, 3), (5, 1), (1, 1)), ((9, 9), (9, 8), (8, 8), (8, 9))]), geometry.Polygon([(11, 2), (11, 10), (12, 10), (12, 2)]) ], index=["简单面", "复杂面", "c区"], # 构建一个索引字段 crs="EPSG:4326", # 坐标系是:WGS 1984 )cq.to_file("./output/{}.shp".format(os.path.basename(__file__).replace(".py", "")), driver="ESRI Shapefile", encoding="utf-8")
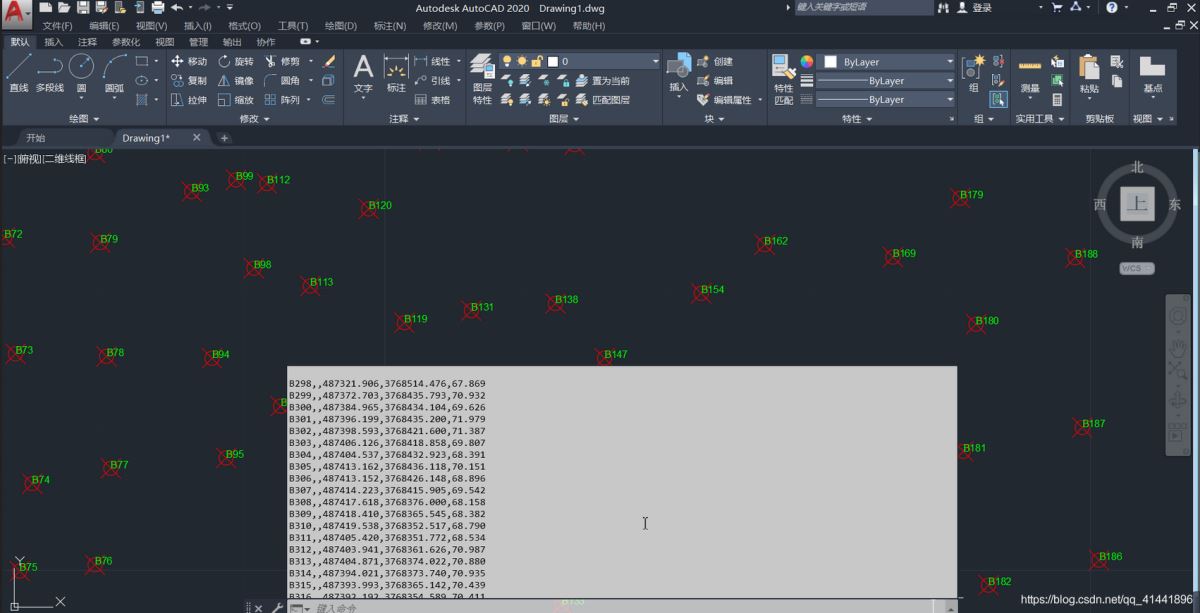
展高程点 。
高程点文件存储格式与CASS中读取的DAT格式一致,示例:【1,ZDH ,450000.000,4100000,20002,DYG,450000.000,4100000,2000 】其中,“1”代表的是“点号”,“ZDH”代表的是“代码”,之后的分别是“东坐标、北坐标、高程值”即“Y、X、H ”或者是“X、Y、H ” 。
AutoCAD中展点效果 。
geopandas中展点效果 。
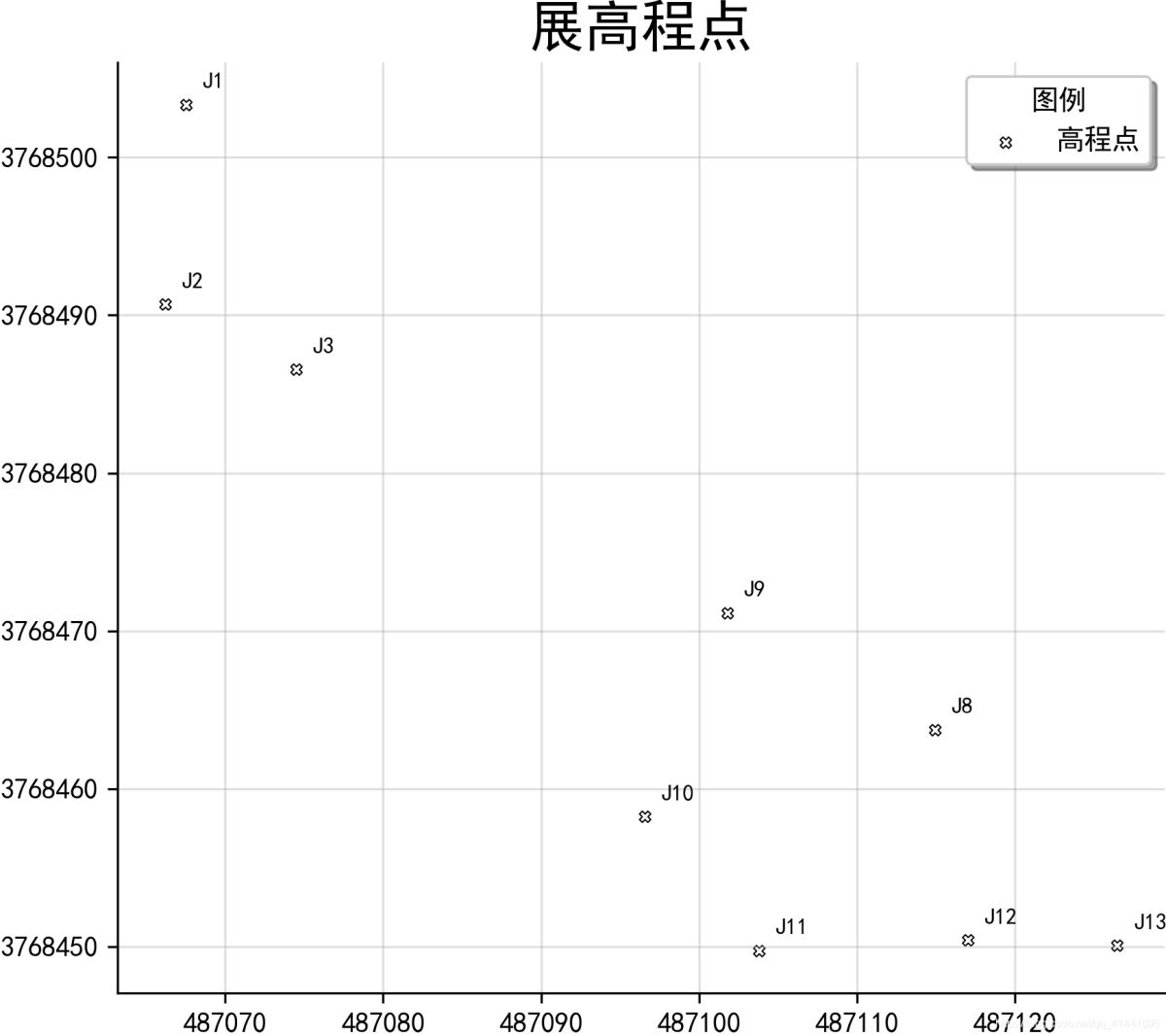
实现代码 。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-import pandas as pdimport geopandas as gpdfrom shapely.geometry import Pointfrom matplotlib import pyplot as pltfrom matplotlib.ticker import FuncFormatter# 读取数据file_path = "./data-use/高程数据.csv"rankings_colname = ["name", "mark", "longitude", "latitude", "height"];df = pd.read_csv(file_path, header=None, names=rankings_colname)# print(df.head(5))#输出前五行数据查看xy = [Point(xy) for xy in zip(df["longitude"], df["latitude"])]pts = gpd.GeoSeries(xy) # 创建点要素数据集#保存为SHP文件pts.to_file("./output/展高程点.shp", driver="ESRI Shapefile", encoding="utf-8")"""fig是用来设置图像大小参数,ax是行列有多少个点"""fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 6)) # 返回一个包含figure和axes对象的元组ax = pts.plot(ax=ax, facecolor="white", edgecolor="black", marker="X", linewidth=0.5, # 内外符号比例系数 markersize=12, label="高程点")# 地图标注new_texts = [plt.text(x_ + 1, y_ + 1, text, fontsize=8) for x_, y_, text in zip(df["longitude"], df["latitude"], df["name"])]# 设置坐标轴def formatnum(x, pos): # return "$%.1f$x$10^{4}$" % (x / 10000)#科学计数法显示 return int(x) # 取整显示formatter = FuncFormatter(formatnum)ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(formatter)# 美观起见隐藏顶部与右侧边框线ax.spines["right"].set_visible(False)ax.spines["top"].set_visible(False)plt.grid(True, alpha=0.4) # 显示网格,透明度为50%ax.legend(title="图例", loc="lower right", ncol=1, shadow=True) # 添加图例plt.title("展高程点", fontdict={"weight": "normal", "size": 20}) # 设置图名&改变图标题字体# 保存图片plt.savefig("images/展高程点.png", dpi=300, bbox_inches="tight", pad_inches=0)plt.show()
点集转面 。
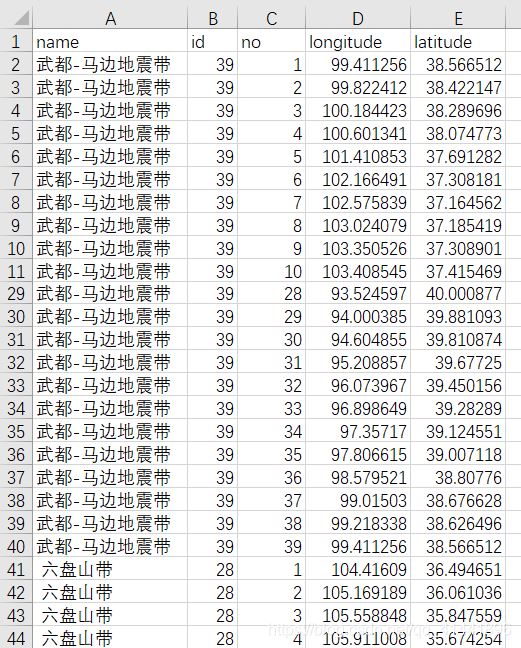
将一系列点的集合转为面状要素类,下面以甘肃省的地震带为例(字段对应:名称,面索引,点索引,经度,纬度).
数据预览 。
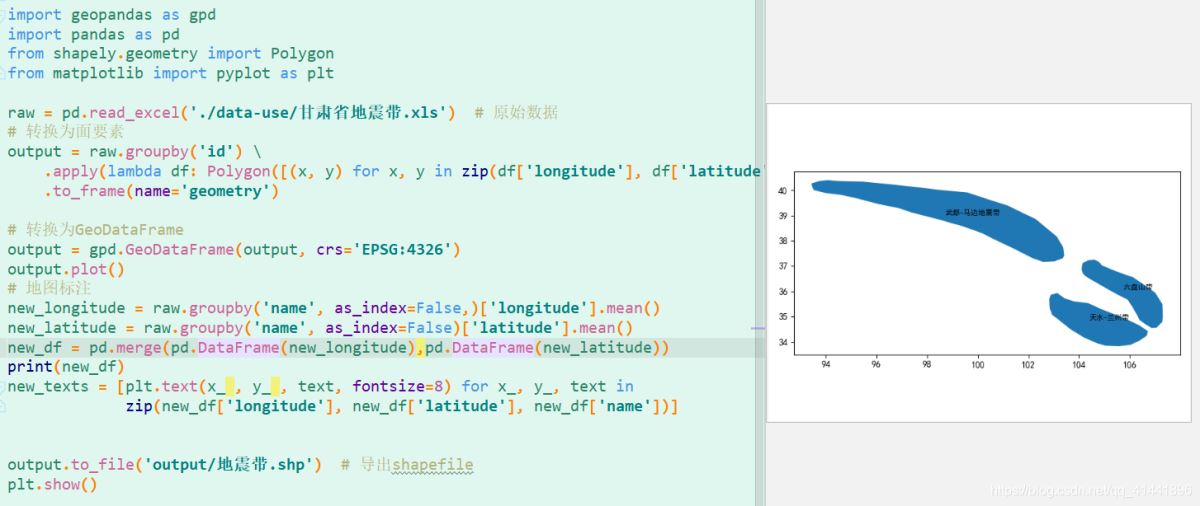
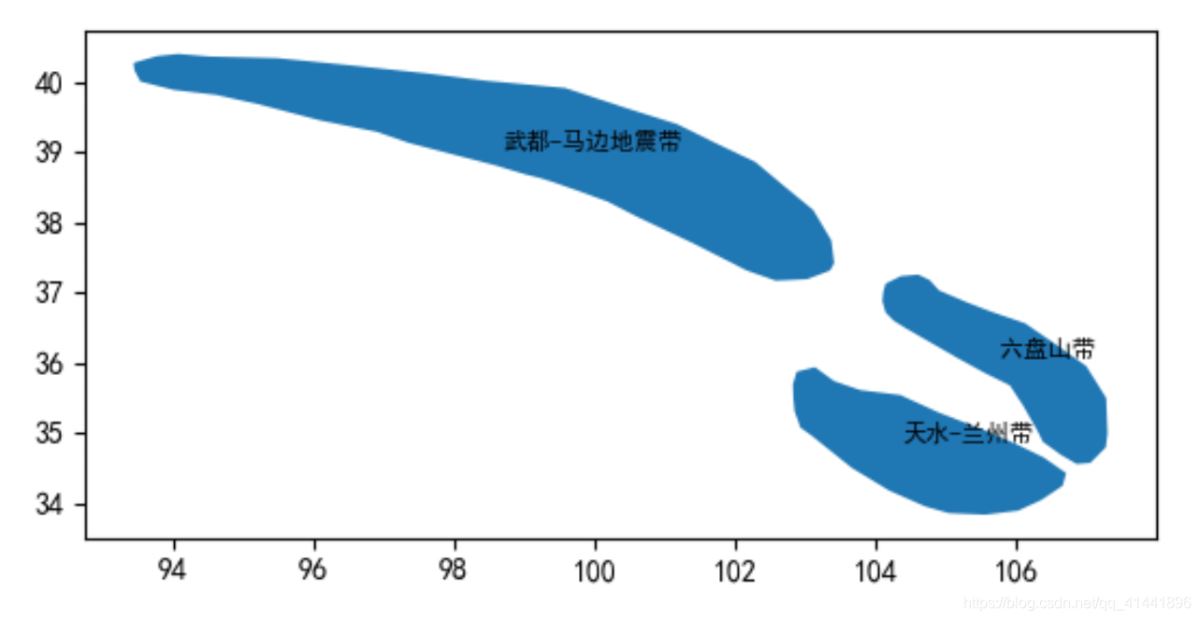
效果预览 。
实现代码 。
import geopandas as gpdimport pandas as pdfrom shapely.geometry import Polygonfrom matplotlib import pyplot as pltraw = pd.read_excel("./data-use/甘肃省地震带.xls") # 原始数据# 转换为面要素output = raw.groupby("id") .apply(lambda df: Polygon([(x, y) for x, y in zip(df["longitude"], df["latitude"])])) .to_frame(name="geometry")# 转换为GeoDataFrameoutput = gpd.GeoDataFrame(output, crs="EPSG:4326")output.plot()# 地图标注new_longitude = raw.groupby("name", as_index=False,)["longitude"].mean()new_latitude = raw.groupby("name", as_index=False)["latitude"].mean()new_df = pd.merge(pd.DataFrame(new_longitude),pd.DataFrame(new_latitude))new_texts = [plt.text(x_ , y_ , text, fontsize=8) for x_, y_, text in zip(new_df["longitude"], new_df["latitude"], new_df["name"])]# 导出shapefileoutput.to_file("output/地震带.shp") plt.show()
创建缓冲区、多环缓冲区 。
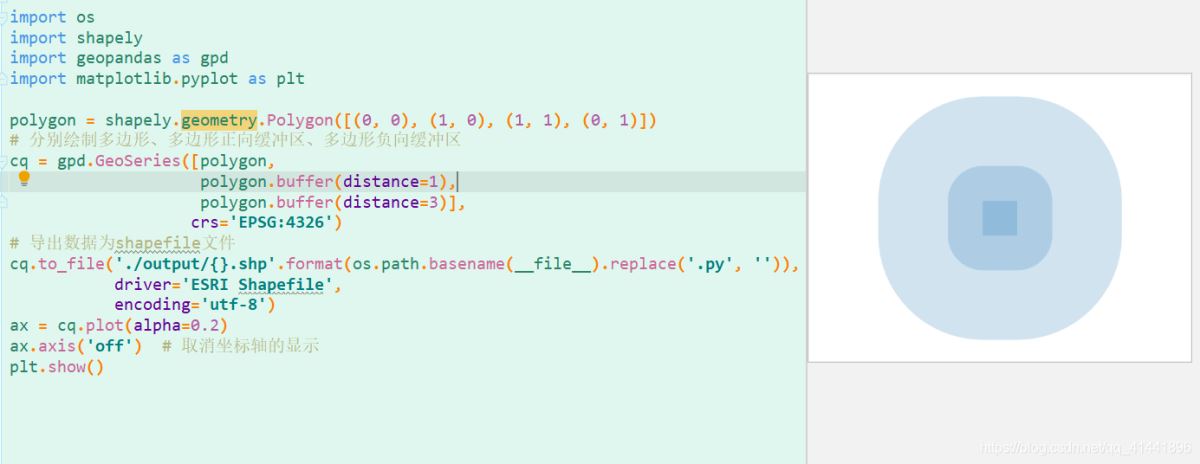
实现代码:
import osimport shapelyimport geopandas as gpdimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltpolygon = shapely.geometry.Polygon([(0, 0), (1, 0), (1, 1), (0, 1)])# 分别绘制多边形、多边形正向缓冲区,坐标系是WGS1984,单位是度cq = gpd.GeoSeries([polygon, polygon.buffer(distance=1), polygon.buffer(distance=3)], crs="EPSG:4326")# 导出数据为shapefile文件cq.to_file("./output/{}.shp".format(os.path.basename(__file__).replace(".py", "")), driver="ESRI Shapefile", encoding="utf-8")ax = cq.plot(alpha=0.2)ax.axis("off") # 取消坐标轴的显示plt.show()
附相关完整代码的下载,还有更多有趣的内容,感兴趣的朋友们可以自行实践。喜欢的朋友们可以点个关注,后续将持续更新,精彩无限^ - ^ 。
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1g7G8sQ17-9XIhojyQ1M7Ww 。
提取码: 59vz 。
最后给大家强烈安利一个geopandas学习博客: https://www.cnblogs.com/feffery/tag/geopandas/ 。
以上就是python geopandas读取、创建shapefile文件的方法的详细内容,更多关于python读取shapefile文件的资料请关注我其它相关文章! 。
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/fungis/p/14946013.html 。
最后此篇关于python geopandas读取、创建shapefile文件的方法的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于python geopandas读取、创建shapefile文件的方法的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我使用来自 OpenStreetMap (link) 的形状文件创建了一个简单的 geopandas map 。 import geopandas as gpd map_gdf = gpd.read_
我正在尝试更改 geopandas 数据框的 CRS。目前的 CRS 是: Name: unknown Axis Info [ellipsoidal]: - lon[east]: Longitude
是否有在 Windows PC 上安装 geopandas 的教程(逐步)?或者哪种方式效果更好? 我已经使用 anaconda 尝试了文档中的解决方案,但最终收到错误(甚至按照建议创建环境)。我什至
我正在尝试按照描述设置 geopandas 对象的 crs here . 示例文件可以从here下载。 import geopandas as gdp df = pd.read_pickle('myS
我目前在 Python 中结合使用 Pandas 和 ArcPy 来完成我的 GIS 工作。我最近听说了 Geopandas 并且有兴趣学习使用它作为 ArcPy 的替代品来进行基本的地理处理操作(空
我读了 .csv文件作为数据框,如下所示: import pandas as pd df = pd.read_csv('myFile.csv') df.head() BoroName g
将 geojson 文件加载到 GeoPandas 后,我得到了预期的名为“几何”的列/特征,其中包含多边形和多边形。 如何将此对象作为 json 或 Python 字典再次取出? 在当前形式下,它是
我正在尝试使用 ANACONDA spyder 运行一个简单的 geopandas 代码。但是,我遇到了错误。 我已经包含了代码和错误如下: —— 这是代码: import geopandas as
我有一个点,我想知道哪个多边形最接近该点。我有点和多边形的地理数据。 最佳答案 您可以使用 distance查找到每个多边形的距离并对它们进行排序以检索最近的。 示例 >>> from shapely
如果我有下面的图,如何将颜色图/图例转换为对数刻度? import geopandas as gpd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt world = gpd.read_
我有一个 geopandas 数据框 geometry idx 0 POLYGON ((-74.2555
我在 python 中使用 GeoPandas 并且有一个有效的多边形 GeoDataframe。 0 POLYGON Z ((68.70999999999999 623.1 0, 3
假设我有以下包含 3 个多边形对象的地理数据框。 import geopandas as gpd from shapely.geometry import Polygon p1=Polygon([(0
我有一个 geopandas 数据框,由 id 和由 2D 点填充的几何列组成。我想连接每个唯一 id 的点来创建一个多边形,以便我的新数据框将多边形作为其几何形状。我的代码目前看起来像这样: pol
我想使用geopandas.rotate()函数根据列中的属性旋转geodataframe中的所有要素。如果我只选择一项功能,我就会成功。然而,对于多行,我相信我需要创建一个 for 循环。 new_
我正在尝试在我的 Mac OS X 上安装 geopandas。 我做了什么: • 下载并安装了适用于 Python 2.7 的 Anaconda here .图形安装程序。 • python --v
我一直收到这个错误,并且已经阅读了其他人的在线访问, ImportError: geopandas, pyshp and shapely must be installed for this figu
您好,我正在尝试将 X 和 Y 坐标列表转换为直线。我想通过 groupby ID 和时间来映射这些数据。只要我 grouby 一列,我的代码就可以成功执行,但是两列是我遇到错误的地方。我引用了这个q
我在使用 read_file 函数时遇到了一些关于 geopandas 和 fiona 的问题。这是我的回溯: df = gpd.read_file('/Users/danqing0703/githu
我有一个在 mapshaper 上看起来像这样的 shapefile: 但是当我尝试用下面的代码在 pandas 中绘制它时 police = gpd.read_file('srilanka_poli

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!