- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章在Java中使用redisTemplate操作缓存的方法示例由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
背景 。
在最近的项目中,有一个需求是对一个很大的数据库进行查询,数据量大概在几千万条。但同时对查询速度的要求也比较高.
这个数据库之前在没有使用presto的情况下,使用的是hive,使用hive进行一个简单的查询,速度可能在几分钟。当然几分钟也并不完全是跑sql的时间,这里面包含发请求,查询数据并且返回数据的时间的总和。但是即使这样,这样的速度明显不能满足交互式的查询需求.
我们的下一个解决方案就是presto,在使用了presto之后,查询速度降到了秒级。但是对于一个前端查询界面的交互式查询来说,十几秒仍然是一个不能接受的时间.
虽然presto相比hive已经快了很多(facebook官方宣称的是10倍),但是对分页的支持不是很友好。我在使用的时候是自己在后端实现的分页.
在这种情况下应用缓存实属无奈之举。讲道理,优化应从底层开始,自底而上。上层优化的方式和效率感觉都很有局限.
<!--more--> 。
为什么要使用缓存 。
前端查询中,单次查询的匹配数据量有可能会达到上百甚至上千条,在前端中肯定是需要分页展示的。就算每次查询10条数据,整个查询也要耗时6-8s的时间。想象一下,每翻一页等10s的场景.
所以,此时使用redis缓存。减少请求数据库的次数。将匹配的数据一并存入数据库。这样只有在第一次查询时耗费长一点,一旦查询完成,用户点击下一页就是毫秒级别的操作了.
使用redistemplate 。
spring封装了一个比较强大的模板,也就是redistemplate,方便在开发的时候操作redis缓存。在redis中可以存储string、list、set、hash、zset。下面将针对list和hash分别介绍.
list 。
redis中的list为简单的字符串列表,常见的有下面几种操作.
haskey 。
判断一个键是否存在,只需要调用haskey就可以了。假设这个key是test,具体用法如下.
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
if
(redistemplate.haskey(
"test"
)) {
system.out.println(
"存在"
);
}
else
{
system.out.println(
"不存在"
);
}
|
range 。
该函数用于从redis缓存中获取指定区间的数据。具体用法如下.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
if
(redistemplate.haskey(
"test"
)) {
// 该键的值为 [4, 3, 2, 1]
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().range(
"test"
,
0
,
0
));
// [4]
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().range(
"test"
,
0
,
1
));
// [4, 3]
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().range(
"test"
,
0
,
2
));
// [4, 3, 2]
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().range(
"test"
,
0
,
3
));
// [4, 3, 2, 1]
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().range(
"test"
,
0
,
4
));
// [4, 3, 2, 1]
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().range(
"test"
,
0
,
5
));
// [4, 3, 2, 1]
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().range(
"test"
,
0
, -
1
));
// [4, 3, 2, 1] 如果结束位是-1, 则表示取所有的值
}
|
delete 。
删除某个键.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
list<string> test =
new
arraylist<>();
test.add(
"1"
);
test.add(
"2"
);
test.add(
"3"
);
test.add(
"4"
);
redistemplate.opsforlist().rightpushall(
"test"
, test);
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().range(
"test"
,
0
, -
1
));
// [1, 2, 3, 4]
redistemplate.delete(
"test"
);
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().range(
"test"
,
0
, -
1
));
// []
|
size 。
获取该键的集合长度.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
list<string> test =
new
arraylist<>();
test.add(
"1"
);
test.add(
"2"
);
test.add(
"3"
);
test.add(
"4"
);
redistemplate.opsforlist().rightpushall(
"test"
, test);
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().size(
"test"
));
// 4
|
leftpush 。
我们把存放这个值的地方想象成如图所示的容器.
container 。
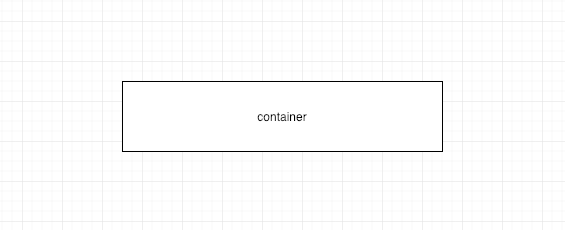
并且取数据总是从左边取,但是存数据可以从左也可以从右。左就是leftpush,右就是rightpush。leftpush如下图所示.
left-push 。
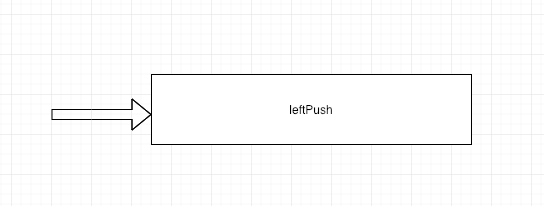
用法如下.
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
for
(
int
i =
0
; i <
4
; i++) {
integer value = i +
1
;
redistemplate.opsforlist().leftpush(
"test"
, value.tostring());
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().range(
"test"
,
0
, -
1
));
}
|
控制台输出的结果如下.
[1] [2, 1] [3, 2, 1] [4, 3, 2, 1] 。
leftpushall 。
基本和leftpush一样,只不过是一次性的将list入栈.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
list<string> test =
new
arraylist<>();
test.add(
"1"
);
test.add(
"2"
);
test.add(
"3"
);
test.add(
"4"
);
redistemplate.opsforlist().leftpushall(
"test"
, test);
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().range(
"test"
,
0
, -
1
));
// [4, 3, 2, 1]
|
当然你也可以这样 。
|
1
2
|
redistemplate.opsforlist().leftpushall(
"test"
, test);
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().range(
"test"
,
0
, -
1
));
// [4, 3, 2, 1]
|
leftpushifpresent 。
跟leftpush是同样的操作,唯一的不同是,当且仅当key存在时,才会更新key的值。如果key不存在则不会对数据进行任何操作.
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
redistemplate.delete(
"test"
);
redistemplate.opsforlist().leftpushifpresent(
"test"
,
"1"
);
redistemplate.opsforlist().leftpushifpresent(
"test"
,
"2"
);
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().range(
"test"
,
0
, -
1
));
// []
|
leftpop 。
该函数用于移除上面我们抽象的容器中的最左边的一个元素.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
list<string> test =
new
arraylist<>();
test.add(
"1"
);
test.add(
"2"
);
test.add(
"3"
);
test.add(
"4"
);
redistemplate.opsforlist().rightpushall(
"test"
, test);
redistemplate.opsforlist().leftpop(
"test"
);
// [2, 3, 4]
redistemplate.opsforlist().leftpop(
"test"
);
// [3, 4]
redistemplate.opsforlist().leftpop(
"test"
);
// [4]
redistemplate.opsforlist().leftpop(
"test"
);
// []
redistemplate.opsforlist().leftpop(
"test"
);
// []
|
值得注意的是,当返回为空后,在redis中这个key也不复存在了。如果此时再调用leftpushifpresent,是无法再添加数据的。有代码有真相.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
list<string> test =
new
arraylist<>();
test.add(
"1"
);
test.add(
"2"
);
test.add(
"3"
);
test.add(
"4"
);
redistemplate.opsforlist().rightpushall(
"test"
, test);
redistemplate.opsforlist().leftpop(
"test"
);
// [2, 3, 4]
redistemplate.opsforlist().leftpop(
"test"
);
// [3, 4]
redistemplate.opsforlist().leftpop(
"test"
);
// [4]
redistemplate.opsforlist().leftpop(
"test"
);
// []
redistemplate.opsforlist().leftpop(
"test"
);
// []
redistemplate.opsforlist().leftpushifpresent(
"test"
,
"1"
);
// []
redistemplate.opsforlist().leftpushifpresent(
"test"
,
"1"
);
// []
|
rightpush 。
rightpush如下图所示.
right-push 。
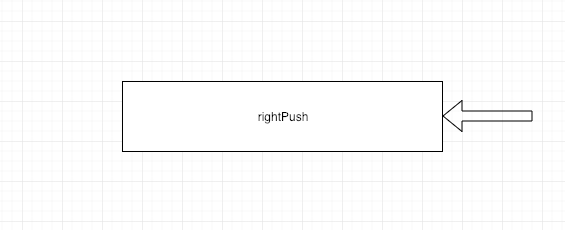
用法如下.
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
for
(
int
i =
0
; i <
4
; i++) {
integer value = i +
1
;
redistemplate.opsforlist().leftpush(
"test"
, value.tostring());
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().range(
"test"
,
0
, -
1
));
}
|
控制台输出的结果如下.
[1] [1, 2] [1, 2, 3] [1, 2, 3, 4] 。
rightpushall 。
同rightpush,一次性将list存入.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
list<string> test =
new
arraylist<>();
test.add(
"1"
);
test.add(
"2"
);
test.add(
"3"
);
test.add(
"4"
);
redistemplate.opsforlist().leftpushall(
"test"
, test);
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().range(
"test"
,
0
, -
1
));
// [1, 2, 3, 4]
|
当然你也可以这样.
|
1
2
|
redistemplate.opsforlist().rightpushall(
"test"
,
"1"
,
"2"
,
"3"
,
"4"
);
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().range(
"test"
,
0
, -
1
));
// [1, 2, 3, 4]
|
rightpushifpresent 。
跟rightpush是同样的操作,唯一的不同是,当且仅当key存在时,才会更新key的值。如果key不存在则不会对数据进行任何操作.
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
redistemplate.delete(
"test"
);
redistemplate.opsforlist().rightpushifpresent(
"test"
,
"1"
);
redistemplate.opsforlist().rightpushifpresent(
"test"
,
"2"
);
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().range(
"test"
,
0
, -
1
));
// []
|
rightpop 。
该函数用于移除上面我们抽象的容器中的最右边的一个元素.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
list<string> test =
new
arraylist<>();
test.add(
"1"
);
test.add(
"2"
);
test.add(
"3"
);
test.add(
"4"
);
redistemplate.opsforlist().rightpushall(
"test"
, test);
redistemplate.opsforlist().rightpop(
"test"
);
// [1, 2, 3]
redistemplate.opsforlist().rightpop(
"test"
);
// [1, 2]
redistemplate.opsforlist().rightpop(
"test"
);
// [1]
redistemplate.opsforlist().rightpop(
"test"
);
// []
redistemplate.opsforlist().rightpop(
"test"
);
// []
|
与leftpop一样,返回空之后,再调用rightpushifpresent,是无法再添加数据的.
index 。
获取list中指定位置的元素.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
if
(redistemplate.haskey(
"test"
)) {
// 该键的值为 [1, 2, 3, 4]
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().index(
"test"
, -
1
));
// 4
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().index(
"test"
,
0
));
// 1
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().index(
"test"
,
1
));
// 2
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().index(
"test"
,
2
));
// 3
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().index(
"test"
,
3
));
// 4
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().index(
"test"
,
4
));
// null
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().index(
"test"
,
5
));
// null
}
|
值得注意的有两点。一个是如果下标是-1的话,则会返回list最后一个元素,另一个如果数组下标越界,则会返回null.
trim 。
用于截取指定区间的元素,可能你会理解成与range是一样的作用。看了下面的代码之后应该就会立刻理解.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
list<string> test =
new
arraylist<>();
test.add(
"1"
);
test.add(
"2"
);
test.add(
"3"
);
test.add(
"4"
);
redistemplate.opsforlist().rightpushall(
"test"
, test);
// [1, 2, 3, 4]
redistemplate.opsforlist().trim(
"test"
,
0
,
2
);
// [1, 2, 3]
|
其实作用完全不一样。range是获取指定区间内的数据,而trim是留下指定区间的数据,删除不在区间的所有数据。trim是void,不会返回任何数据.
remove 。
用于移除键中指定的元素。接受3个参数,分别是缓存的键名,计数事件,要移除的值。计数事件可以传入的有三个值,分别是-1、0、1.
-1代表从存储容器的最右边开始,删除一个与要移除的值匹配的数据;0代表删除所有与传入值匹配的数据;1代表从存储容器的最左边开始,删除一个与要移除的值匹配的数据.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
list<string> test =
new
arraylist<>();
test.add(
"1"
);
test.add(
"2"
);
test.add(
"3"
);
test.add(
"4"
);
test.add(
"4"
);
test.add(
"3"
);
test.add(
"2"
);
test.add(
"1"
);
redistemplate.opsforlist().rightpushall(
"test"
, test);
// [1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 3, 2, 1]
// 当计数事件是-1、传入值是1时
redistemplate.opsforlist().remove(
"test"
, -
1
,
"1"
);
// [1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 3, 2]
// 当计数事件是1,传入值是1时
redistemplate.opsforlist().remove(
"test"
,
1
,
"1"
);
// [2, 3, 4, 4, 3, 2]
// 当计数事件是0,传入值是4时
redistemplate.opsforlist().remove(
"test"
,
0
,
"4"
);
// [2, 3, 3, 2]
|
rightpopandleftpush 。
该函数用于操作两个键之间的数据,接受三个参数,分别是源key、目标key。该函数会将源key进行rightpop,再将返回的值,作为输入参数,在目标key上进行leftpush。具体代码如下.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
list<string> test =
new
arraylist<>();
test.add(
"1"
);
test.add(
"2"
);
test.add(
"3"
);
test.add(
"4"
);
list<string> test2 =
new
arraylist<>();
test2.add(
"1"
);
test2.add(
"2"
);
test2.add(
"3"
);
redistemplate.opsforlist().rightpushall(
"test"
, test);
// [1, 2, 3, 4]
redistemplate.opsforlist().rightpushall(
"test2"
, test2);
// [1, 2, 3]
redistemplate.opsforlist().rightpopandleftpush(
"test"
,
"test2"
);
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().range(
"test"
,
0
, -
1
));
// [1, 2, 3]
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforlist().range(
"test2"
,
0
, -
1
));
// [4, 1, 2, 3]
|
hash 。
存储类型为hash其实很好理解。在上述的list中,一个redis的key可以理解为一个list,而在hash中,一个redis的key可以理解为一个hashmap.
put 。
用于写入数据.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
list<string> list =
new
arraylist<>();
list.add(
"1"
);
list.add(
"2"
);
list.add(
"3"
);
list.add(
"4"
);
redistemplate.opsforhash().put(
"test"
,
"map"
, list.tostring());
// [1, 2, 3, 4]
redistemplate.opsforhash().put(
"test"
,
"isadmin"
,
true
);
// true
|
putall 。
用于一次性向一个hash键中添加多个key.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
list<string> list =
new
arraylist<>();
list.add(
"1"
);
list.add(
"2"
);
list.add(
"3"
);
list.add(
"4"
);
list<string> list2 =
new
arraylist<>();
list2.add(
"5"
);
list2.add(
"6"
);
list2.add(
"7"
);
list2.add(
"8"
);
map<string, string> valuemap =
new
hashmap<>();
valuemap.put(
"map1"
, list.tostring());
valuemap.put(
"map2"
, list2.tostring());
redistemplate.opsforhash().putall(
"test"
, valuemap);
// {map2=[5, 6, 7, 8], map1=[1, 2, 3, 4]}
|
putifabsent 。
用于向一个hash键中写入数据。当key在hash键中已经存在时,则不会写入任何数据,只有在hash键中不存在这个key时,才会写入数据.
同时,如果连这个hash键都不存在,redistemplate会新建一个hash键,再写入key.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
list<string> list =
new
arraylist<>();
list.add(
"1"
);
list.add(
"2"
);
list.add(
"3"
);
list.add(
"4"
);
redistemplate.opsforhash().putifabsent(
"test"
,
"map"
, list.tostring());
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforhash().entries(
"test"
));
// {map=[1, 2, 3, 4]}
|
get 。
用于获取数据.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
list<string> list =
new
arraylist<>();
list.add(
"1"
);
list.add(
"2"
);
list.add(
"3"
);
list.add(
"4"
);
redistemplate.opsforhash().put(
"test"
,
"map"
, list.tostring());
redistemplate.opsforhash().put(
"test"
,
"isadmin"
,
true
);
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforhash().get(
"test"
,
"map"
));
// [1, 2, 3, 4]
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforhash().get(
"test"
,
"isadmin"
));
// true
boolean
bool = (
boolean
) redistemplate.opsforhash().get(
"test"
,
"isadmin"
);
system.out.println(bool);
// true
string str = redistemplate.opsforhash().get(
"test"
,
"map"
).tostring();
list<string> array = jsonarray.parsearray(str, string.
class
);
system.out.println(array.size());
// 4
|
值得注意的是,使用get函数获取的数据都是object类型.
所以需要使用类型与上述例子中的布尔类型的话,则需要强制转换一次。list类型则可以使用fastjson这种工具来进行转换。转换的例子已列举在上述代码中.
delete 。
用于删除一个hash键中的key。可以理解为删除一个map中的某个key.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
list<string> list =
new
arraylist<>();
list.add(
"1"
);
list.add(
"2"
);
list.add(
"3"
);
list.add(
"4"
);
list<string> list2 =
new
arraylist<>();
list2.add(
"5"
);
list2.add(
"6"
);
list2.add(
"7"
);
list2.add(
"8"
);
map<string, string> valuemap =
new
hashmap<>();
valuemap.put(
"map1"
, list.tostring());
valuemap.put(
"map2"
, list2.tostring());
redistemplate.opsforhash().putall(
"test"
, valuemap);
// {map2=[5, 6, 7, 8], map1=[1, 2, 3, 4]}
redistemplate.opsforhash().delete(
"test"
,
"map1"
);
// {map2=[5, 6, 7, 8]}
|
values 。
用于获取一个hash类型的键的所有值.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
list<string> list =
new
arraylist<>();
list.add(
"1"
);
list.add(
"2"
);
list.add(
"3"
);
list.add(
"4"
);
redistemplate.opsforhash().put(
"test"
,
"map"
, list.tostring());
redistemplate.opsforhash().put(
"test"
,
"isadmin"
,
true
);
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforhash().values(
"test"
));
// [[1, 2, 3, 4], true]
|
entries 。
用于以map的格式获取一个hash键的所有值.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
list<string> list =
new
arraylist<>();
list.add(
"1"
);
list.add(
"2"
);
list.add(
"3"
);
list.add(
"4"
);
redistemplate.opsforhash().put(
"test"
,
"map"
, list.tostring());
redistemplate.opsforhash().put(
"test"
,
"isadmin"
,
true
);
map<string, string> map = redistemplate.opsforhash().entries(
"test"
);
system.out.println(map.get(
"map"
));
// [1, 2, 3, 4]
system.out.println(map.get(
"map"
)
instanceof
string);
// true
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforhash().entries(
"test"
));
// {a=[1, 2, 3, 4], isadmin=true}
|
haskey 。
用于获取一个hash键中是否含有某个键.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
ist<string> list =
new
arraylist<>();
list.add(
"1"
);
list.add(
"2"
);
list.add(
"3"
);
list.add(
"4"
);
redistemplate.opsforhash().put(
"test"
,
"map"
, list.tostring());
redistemplate.opsforhash().put(
"test"
,
"isadmin"
,
true
);
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforhash().haskey(
"test"
,
"map"
));
// true
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforhash().haskey(
"test"
,
"b"
));
// false
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforhash().haskey(
"test"
,
"isadmin"
));
// true
|
keys 。
用于获取一个hash键中所有的键.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
list<string> list =
new
arraylist<>();
list.add(
"1"
);
list.add(
"2"
);
list.add(
"3"
);
list.add(
"4"
);
redistemplate.opsforhash().put(
"test"
,
"map"
, list.tostring());
redistemplate.opsforhash().put(
"test"
,
"isadmin"
,
true
);
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforhash().keys(
"test"
));
// [a, isadmin]
|
size 。
用于获取一个hash键中包含的键的数量.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
list<string> list =
new
arraylist<>();
list.add(
"1"
);
list.add(
"2"
);
list.add(
"3"
);
list.add(
"4"
);
redistemplate.opsforhash().put(
"test"
,
"map"
, list.tostring());
redistemplate.opsforhash().put(
"test"
,
"isadmin"
,
true
);
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforhash().size(
"test"
));
// 2
|
increment 。
用于让一个hash键中的某个key,根据传入的值进行累加。传入的数值只能是double或者long,不接受浮点型 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
redistemplate.opsforhash().increment(
"test"
,
"a"
,
3
);
redistemplate.opsforhash().increment(
"test"
,
"a"
, -
3
);
redistemplate.opsforhash().increment(
"test"
,
"a"
,
1
);
redistemplate.opsforhash().increment(
"test"
,
"a"
,
0
);
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforhash().entries(
"test"
));
// {a=1}
|
multiget 。
用于批量的获取一个hash键中多个key的值.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
list<string> list =
new
arraylist<>();
list.add(
"1"
);
list.add(
"2"
);
list.add(
"3"
);
list.add(
"4"
);
list<string> list2 =
new
arraylist<>();
list2.add(
"5"
);
list2.add(
"6"
);
list2.add(
"7"
);
list2.add(
"8"
);
redistemplate.opsforhash().put(
"test"
,
"map1"
, list.tostring());
// [1, 2, 3, 4]
redistemplate.opsforhash().put(
"test"
,
"map2"
, list2.tostring());
// [5, 6, 7, 8]
list<string> keys =
new
arraylist<>();
keys.add(
"map1"
);
keys.add(
"map2"
);
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforhash().multiget(
"test"
, keys));
// [[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8]]
system.out.println(redistemplate.opsforhash().multiget(
"test"
, keys)
instanceof
list);
// true
|
scan 。
获取所以匹配条件的hash键中key的值。我查过一些资料,大部分写的是无法模糊匹配,我自己尝试了一下,其实是可以的。如下,使用scan模糊匹配hash键的key中,带scan的key.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
list<string> list =
new
arraylist<>();
list.add(
"1"
);
list.add(
"2"
);
list.add(
"3"
);
list.add(
"4"
);
list<string> list2 =
new
arraylist<>();
list2.add(
"5"
);
list2.add(
"6"
);
list2.add(
"7"
);
list2.add(
"8"
);
list<string> list3 =
new
arraylist<>();
list3.add(
"9"
);
list3.add(
"10"
);
list3.add(
"11"
);
list3.add(
"12"
);
map<string, string> valuemap =
new
hashmap<>();
valuemap.put(
"map1"
, list.tostring());
valuemap.put(
"scan_map2"
, list2.tostring());
valuemap.put(
"map3"
, list3.tostring());
redistemplate.opsforhash().putall(
"test"
, valuemap);
// {scan_map2=[5, 6, 7, 8], map3=[9, 10, 11, 12], map1=[1, 2, 3, 4]}
cursor<map.entry<string, string>> cursor = redistemplate.opsforhash().scan(
"test"
, scanoptions.scanoptions().match(
"*scan*"
).build());
if
(cursor.hasnext()) {
while
(cursor.hasnext()) {
map.entry<string, string> entry = cursor.next();
system.out.println(entry.getvalue());
// [5, 6, 7, 8]
}
}
|
引入redistemplate 。
如果大家看懂了怎么用,就可以将redistemplate引入项目中了.
引入pom依赖 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactid>
<version>
2.0
.
5
.release</version>
</dependency>
|
新建配置文件 。
然后需要新建一个redisconfig配置文件.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
package
com.detectivehlh;
import
com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.jsonautodetect;
import
com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.propertyaccessor;
import
com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.objectmapper;
import
org.springframework.context.annotation.bean;
import
org.springframework.context.annotation.configuration;
import
org.springframework.data.redis.connection.redisconnectionfactory;
import
org.springframework.data.redis.core.redistemplate;
import
org.springframework.data.redis.core.stringredistemplate;
import
org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.jackson2jsonredisserializer;
/**
* redisconfig
*
* @author lunhao hu
* @date 2019-01-17 15:12
**/
@configuration
public
class
redisconfig {
@bean
public
redistemplate<string, string> redistemplate(redisconnectionfactory factory) {
objectmapper om =
new
objectmapper();
om.setvisibility(propertyaccessor.all, jsonautodetect.visibility.any);
om.enabledefaulttyping(objectmapper.defaulttyping.non_final);
//redis序列化
jackson2jsonredisserializer jackson2jsonredisserializer =
new
jackson2jsonredisserializer(object.
class
);
jackson2jsonredisserializer.setobjectmapper(om);
stringredistemplate template =
new
stringredistemplate(factory);
template.setvalueserializer(jackson2jsonredisserializer);
template.sethashkeyserializer(jackson2jsonredisserializer);
template.sethashvalueserializer(jackson2jsonredisserializer);
template.setvalueserializer(jackson2jsonredisserializer);
template.afterpropertiesset();
return
template;
}
}
|
注入 。
将redistemplate注入到需要使用的地方.
|
1
2
|
@autowired
private
redistemplate redistemplate;
|
写在后面 。
github 。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我.
原文链接:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000017940126#leftPush 。
最后此篇关于在Java中使用redisTemplate操作缓存的方法示例的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于在Java中使用redisTemplate操作缓存的方法示例的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我正在努力做到这一点 在我的操作中从数据库获取对象列表(确定) 在 JSP 上打印(确定) 此列表作为 JSP 中的可编辑表出现。我想修改然后将其提交回同一操作以将其保存在我的数据库中(失败。当我使用
我有以下形式的 Linq to Entities 查询: var x = from a in SomeData where ... some conditions ... select
我有以下查询。 var query = Repository.Query() .Where(p => !p.IsDeleted && p.Article.ArticleSections.Cou
我正在编写一个应用程序包,其中包含一个主类,其中主方法与GUI类分开,GUI类包含一个带有jtabbedpane的jframe,它有两个选项卡,第一个选项卡包含一个jtable,称为jtable1,第
以下代码产生错误 The nested query is not supported. Operation1='Case' Operation2='Collect' 问题是我做错了什么?我该如何解决?
我已经为 HA redis 集群(2 个副本、1 个主节点、3 个哨兵)设置了本地 docker 环境。只有哨兵暴露端口(10021、10022、10023)。 我使用的是 stackexchange
我正在 Desk.com 中构建一个“集成 URL”,它使用 Shopify Liquid 模板过滤器语法。对于开始日期为 7 天前而结束日期为现在的查询,此 URL 需要包含“开始日期”和“结束日期
你一定想过。然而情况却不理想,python中只能使用类似于 i++/i--等操作。 python中的自增操作 下面代码几乎是所有程序员在python中进行自增(减)操作的常用
我需要在每个使用 github 操作的手动构建中显示分支。例如:https://gyazo.com/2131bf83b0df1e2157480e5be842d4fb 我应该显示分支而不是一个。 最佳答
我有一个关于 Perl qr 运算符的问题: #!/usr/bin/perl -w &mysplit("a:b:c", /:/); sub mysplit { my($str, $patt
我已经使用 ArgoUML 创建了一个 ERD(实体关系图),我希望在一个类中创建两个操作,它们都具有 void 返回类型。但是,我只能创建一个返回 void 类型的操作。 例如: 我能够将 book
Github 操作仍处于测试阶段并且很新,但我希望有人可以提供帮助。我认为可以在主分支和拉取请求上运行 github 操作,如下所示: on: pull_request push: b
我正在尝试创建一个 Twilio 工作流来调用电话并记录用户所说的内容。为此,我正在使用 Record,但我不确定要在 action 参数中放置什么。 尽管我知道 Twilio 会发送有关调用该 UR
我不确定这是否可行,但值得一试。我正在使用模板缓冲区来减少使用此算法的延迟渲染器中光体积的过度绘制(当相机位于体积之外时): 使用廉价的着色器,将深度测试设置为 LEQUAL 绘制背面,将它们标记在模
有没有聪明的方法来复制 和 重命名 文件通过 GitHub 操作? 我想将一些自述文件复制到 /docs文件夹(:= 同一个 repo,不是远程的!),它们将根据它们的 frontmatter 重命名
我有一个 .csv 文件,其中第一列包含用户名。它们采用 FirstName LastName 的形式。我想获取 FirstName 并将 LastName 的第一个字符添加到它上面,然后删除空格。然
Sitecore 根据 Sitecore 树中定义的项目名称生成 URL, http://samplewebsite/Pages/Sample Page 但我们的客户有兴趣降低所有 URL(页面/示例
我正在尝试进行一些计算,但是一旦我输入金额,它就会完成。我只是希望通过单击按钮而不是自动发生这种情况。 到目前为止我做了什么: Angular JS - programming-fr
我的公司创建了一种在环境之间移动文件的复杂方法,现在我们希望将某些构建的 JS 文件(已转换和缩小)从一个 github 存储库移动到另一个。使用 github 操作可以实现这一点吗? 最佳答案 最简
在我的代码中,我创建了一个 JSONArray 对象。并向 JSONArray 对象添加了两个 JSONObject。我使用的是 json-simple-1.1.jar。我的代码是 package j

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!