- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章Java线程通信及线程虚假唤醒知识总结由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
线程在内部运行时,线程调度具有一定的透明性,程序通常无法控制线程的轮换执行。但Java本身提供了一些机制来保证线程协调运行.
假设目前系统中有两个线程,分别代表存款和取钱。当钱存进去,立马就取出来挪入指定账户。这涉及到线程间的协作,使用到Object类提供的wait()、notify()、notifyAll()三个方法,其不属于Thread类,而属于Object,而这三个方法必须由监视器对象来调用:
三个方法解释如下:
现在用两个同步方法分别代表存钱取钱 。
调用方法:
结果没有什么问题 。
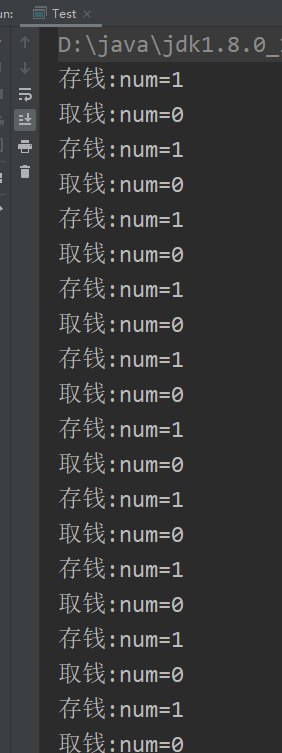
上述线程通信看起来似乎没有什么问题,但若此时将存钱和取钱的人数各增加1,再看运行结果 。
产生的结果已经不是最初的只有0和1 。
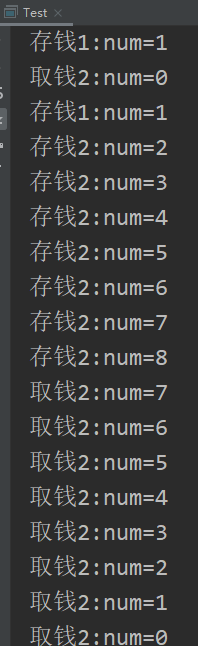
造成这个结果的原因就是线程间的虚假唤醒 。
由于目前分别有多个取款和存款线程。假设其中一个存款线程执行完毕,并使用wait释放同步监视器锁定,那其余多个取款线程将同时被唤醒,此时余额为1,如果有10个同时取钱,那余额会变为-9,造成结果错误.
因此,每次线程从wait中被唤醒,都必须再次测试是否符合唤醒条件,如果不符合那就继续等待.
由于多个线程被同时唤醒,在if(xxxx){wait();}处 if判断只会执行一次,当下一个被唤醒的线程过来时,由于if已经判断过,则直接从wait后面的语句继续执行,因此将if换成while可解决该问题,下次被唤醒的线程过来,while重新判断一下,发现上一个被唤醒的线程已经拿到锁,因此这个被虚假唤醒的线程将继续等待锁.
再次运行,结果正常:

到此这篇关于Java线程通信及线程虚假唤醒知识总结的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java线程通信及线程虚假唤醒内容请搜索我以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我! 。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_26012495/article/details/117908249 。
最后此篇关于Java线程通信及线程虚假唤醒知识总结的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于Java线程通信及线程虚假唤醒知识总结的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我试图弄清楚接受 OpenID 登录的网站如何无法通过简单的主机文件更新来指向伪造的 OpenID 提供商。 假设我想侵入 Joe Smith 的帐户,在这个例子中,假设他的 OpenID 提供商是
#include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #define P
根据此讨论 - "RESTful API - Correct behavior when spurious/not requested parameters are passed in the req
如果编译为 Cand C++ 源代码,这个简单的代码片段会使用 g++ 4.7.0 生成“函数调用中缺少标记”警告。我相信这是编译器的错误,因为最终的 NULL值(value)就在那里。 #inclu
我读到,有时 && 运算符用于“短路”JavaScript,使其相信返回值 0 是 0 而不是 NaN,因为 0 在 JavaScript 中是一个虚假数字。我一直在四处寻找,想弄清楚这一切意味着什么
我正在使用 Borland(又名“Embarcodegearland”)C++Builder 2007 编译器,它有一个小错误,系统头文件中的某些 static const 项可能导致虚假的 "xyz

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!