- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章Java IO流学习总结之文件传输基础由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
|
package
pkg1;
import
java.io.file;
import
java.io.ioexception;
/**
* @author administrator
* @date 2021/4/2
*/
public
class
filedemo {
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
// 了解构造函数,可查看api
file file =
new
file(
"d:\\javaio\\cook"
);
// 设置分隔符,不同系统也可以认识
//file file=new file("d:"+file.separator);
//system.out.println(file.exists());
if
(!file.exists()) {
file.mkdirs();
}
else
{
file.delete();
}
// 是否是一个目录,如果是目录返回true,如果不是目录或目录不存在返回false
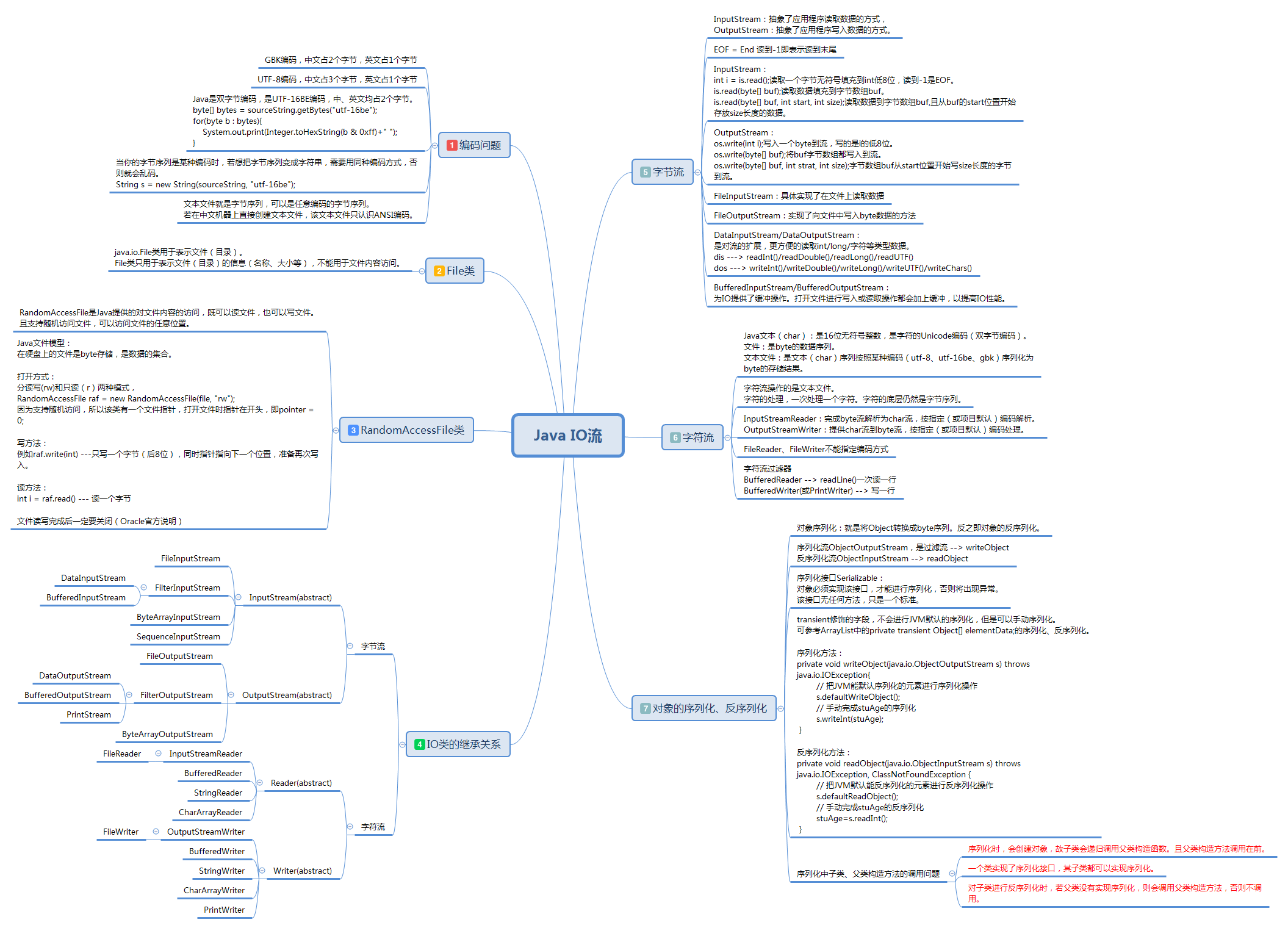
system.out.println(file.isdirectory());
// 如果是一个文件
system.out.println(file.isfile());
//file file2 = new file("d:\\javaio\\日记1.txt");
file file2 =
new
file(
"d:\\javaio"
,
"日记1.txt"
);
if
(!file2.exists()) {
try
{
file2.createnewfile();
}
catch
(ioexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
else
{
file2.delete();
}
// 常用file对象的api
system.out.println(file);
// file.tostring()的内容
system.out.println(file.getabsolutepath());
system.out.println(file.getname());
system.out.println(file2.getname());
system.out.println(file.getparent());
system.out.println(file2.getparent());
system.out.println(file.getparentfile().getabsolutepath());
}
}
|
测试结果:
其他api:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
package
pkg1;
import
java.io.*;
import
java.util.randomaccess;
/**
* @author administrator
* @date 2021/4/7
*/
class
filedemo2 {
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
file file =
new
file(
"d:\\javaio\\example"
);
if
(!file.exists()) {
file.mkdir();
}
/*string[] filenames = file.list(new filenamefilter() {
@override
public boolean accept(file dir, string name) {
system.out.println("文件是:"+dir + "\\" + name);
return name.endswith("java");
}
});
for (string filename : filenames != null ? filenames : new string[0]) {
system.out.println(filename);
}*/
/*file[] files = file.listfiles(new filenamefilter() {
@override
public boolean accept(file dir, string name) {
system.out.println("文件是:" + dir + "\\" + name);
return false;
}
});
for (file filename : files) {
system.out.println(filename.tostring());
}*/
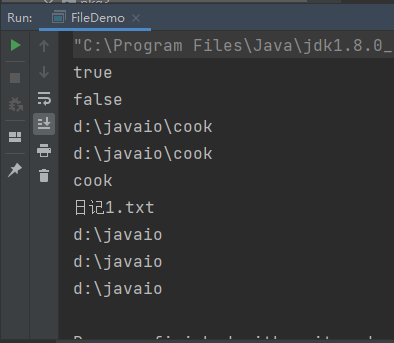
file[] files = file.listfiles(
new
filefilter() {
@override
public
boolean
accept(file pathname) {
system.out.println(pathname);
return
false
;
}
});
for
(file filename : files) {
system.out.println(filename.tostring());
}
}
}
|
测试:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
package
pkg2;
import
java.io.file;
/**
* 列出file的一些常用操作,如过滤、遍历
*/
public
class
fileutils {
/**
* 列出指定目录(包括其子目录)下的所有文件
*/
public
static
void
listdirectory(file dir)
throws
illegalaccessexception {
if
(!dir.exists()) {
throw
new
illegalargumentexception(
"目录:"
+ dir +
"不存在"
);
}
if
(!dir.isdirectory()) {
throw
new
illegalargumentexception(dir +
"不存在"
);
}
// list()用于列出当前目录下的子目录(不包含子目录下的内容)和文件。返回的是字符串数组。
/*string[] filenames = dir.list();
for (string string : filenames) {
system.out.println(dir + "\\" + string);
}*/
// 若要遍历子目录下的内容,就要构造成file对象进行递归操作。file提供了直接返回file对象的api
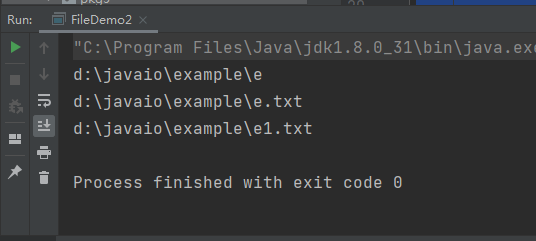
file[] files = dir.listfiles();//返回直接子目录(文件)的抽象
/*for (file file : files) {
system.out.println(file);
}*/
if
(files !=
null
&& files.length >
0
) {
for
(file file : files) {
if
(file.isdirectory()) {
// 递归
listdirectory(file);
}
else
{
system.out.println(file);
}
}
}
}
}
|
测试类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
package
pkg2;
import
java.io.file;
public
class
fileutilstest {
public
static
void
main(string[] args)
throws
illegalaccessexception {
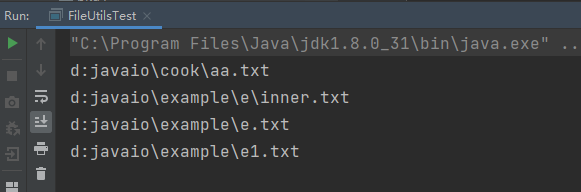
fileutils.listdirectory(
new
file(
"d:javaio"
));
}
}
|
测试结果:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
package
pkg3;
import
java.io.*;
import
java.util.arrays;
public
class
rafdemo {
public
static
void
main(string[] args)
throws
ioexception {
// 若没有指定路径,则表示相对路径,即项目所在路径。
file demo =
new
file(
"demo"
);
if
(!demo.exists()) {
demo.mkdir();
}
file file =
new
file(demo,
"raf.dat"
);
if
(!file.exists()) {
file.createnewfile();
}
randomaccessfile raf =
new
randomaccessfile(file,
"rw"
);
// 查看指针位置
system.out.println(raf.getfilepointer());
// 0
raf.writeint(
'a'
);
// 只写了一个字节
system.out.println(raf.getfilepointer());
raf.writeint(
'b'
);
int
i =
0x7fffffff
;
// 用write方法每次只能写一个字节,如果要把i写进去就要写4次
raf.writeint(i >>>
24
);
//高8位
raf.writeint(i >>>
16
);
raf.writeint(i >>>
8
);
raf.writeint(i);
// 低8位
system.out.println(raf.getfilepointer());
// 直接写一个int ,与上述4步操作等效
raf.writeint(i);
string s =
"中"
;
byte
[] gbk = s.getbytes(
"gbk"
);
raf.write(gbk);
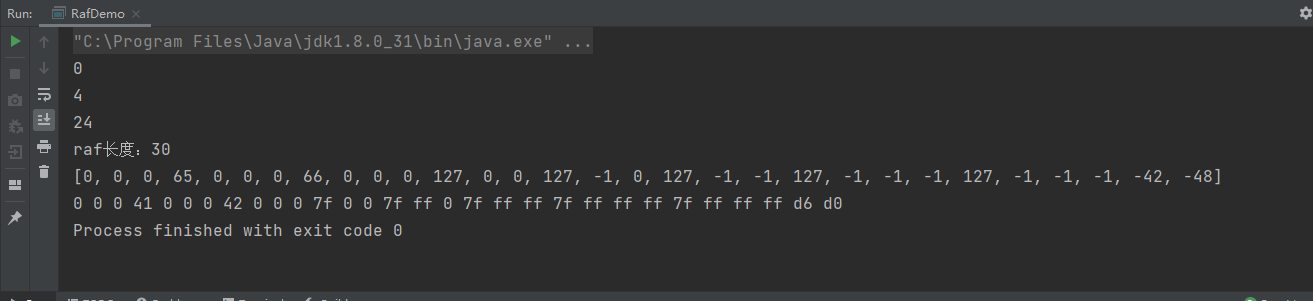
system.out.println(
"raf长度:"
+ raf.length());
// 读文件,必须把指针移到头部
raf.seek(
0
);
// 一次性读取,把文件中的内容都读到字节数组汇总
byte
[] buf =
new
byte
[(
int
) raf.length()];
raf.read(buf);
system.out.println(arrays.tostring(buf));
// 转为字符串
/*string s1=new string(buf,"utf-8");
system.out.println(s1);*/
for
(
byte
b : buf) {
system.out.print(integer.tohexstring(b &
0xff
) +
" "
);
}
raf.close();
}
}
|
测试结果:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
|
package
pkg4;
import
java.io.*;
public
class
ioutil {
/**
* 读取指定文件内容, 按照十六进制输出到控制台,
* 且每输出10个byte换行
*
* @param filename
*/
public
static
void
printhex(string filename)
throws
ioexception {
// 把文件作为字节流进行操作
fileinputstream fis =
new
fileinputstream(filename);
int
b;
int
i =
1
;
while
((b = fis.read()) != -
1
) {
if
(b <=
0xf
) {
// 单位数前补0
system.out.print(
"0"
);
}
// 将整型b转换为16进制表示的字符串
system.out.print(integer.tohexstring(b) +
" "
);
if
(i++ %
10
==
0
) {
system.out.println();
}
}
fis.close();
}
public
static
void
printhexbybytearray(string filename)
throws
ioexception {
fileinputstream fis =
new
fileinputstream(filename);
/*byte[] buf = new byte[20 * 1024];
//从fis中批量读取字节,放入到buf字节数组中,从第0个位置开始放,最多放buf.length个,返回的是读到的字节个数
int bytes = fis.read(buf, 0, buf.length);// 一次性读完,说明字节数组足够大
int j = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < bytes; i++) {
if (buf[i] <= 0xf) {
system.out.print("0");
}
system.out.println(integer.tohexstring(buf[i]) + " ");
if (j++ % 10 == 0) {
system.out.println();
}
}*/
// 当字节数组容量不够,一次读不完时
byte[] buf = new byte[8 * 1024];
int bytes = 0;
int j = 1;
while ((bytes = fis.read(buf, 0, buf.length)) != -1) {
for (int i = 0; i < bytes; i++) {
// byte是8位,int类型是32位,为了避免数据转换错误,通过&0xff将高24位清零
system.out.print(integer.tohexstring(buf[i] & 0xff) + " ");
if (j++ % 10 == 0) {
system.out.println();
}
}
}
fis.close();
}
/**
* 文件拷贝操作 -> 字节批量读取式拷贝,效率最优
*/
public static void copyfile(file srcfile, file destfile) throws ioexception {
if (!srcfile.exists()) {
throw new illegalargumentexception("文件:" + srcfile + "不存在");
}
if (!srcfile.isfile()) {
throw new illegalargumentexception(srcfile + "不是文件");
}
fileinputstream fis = new fileinputstream(srcfile);
fileoutputstream fos = new fileoutputstream(destfile);
byte[] buf = new byte[8 * 1024];
int b;
while ((b = fis.read(buf, 0, buf.length)) != -1) {
fos.write(buf, 0, b);
fos.flush();//最好加上这个
}
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
/**
* 用带缓冲的字节流,进行文件拷贝,效率居中
*/
public static void copyfilebybuffer(file srcfile, file destfile) throws ioexception {
if (!srcfile.exists()) {
throw new illegalargumentexception("文件:" + srcfile + "不存在");
}
if (!srcfile.isfile()) {
throw new illegalargumentexception(srcfile + "不是文件");
}
bufferedinputstream bis = new bufferedinputstream(new fileinputstream(srcfile));
bufferedoutputstream bos = new bufferedoutputstream(new fileoutputstream(destfile));
int c;
while ((c = bis.read()) != -1) {
bos.write(c);
// 刷新缓冲区。不能省略,否则无法写入
bos.flush();
}
bis.close();
bos.close();
}
/**
* 文件拷贝操作 -> 单字节,不带缓冲式拷贝,效率最差
*/
public
static
void
copyfilebybyte(file srcfile, file destfile)
throws
ioexception {
if
(!srcfile.exists()) {
throw
new
illegalargumentexception(
"文件:"
+ srcfile +
"不存在"
);
}
if
(!srcfile.isfile()) {
throw
new
illegalargumentexception(srcfile +
"不是文件"
);
}
fileinputstream fis =
new
fileinputstream(srcfile);
fileoutputstream fos =
new
fileoutputstream(destfile);
int
b;
while
((b = fis.read()) != -
1
) {
fos.write(b);
fos.flush();
}
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
}
|
测试类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
package
pkg4;
import
java.io.ioexception;
public
class
ioutiltest1 {
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
try
{
ioutil.printhex(
"d:\\javaio\\fileutils.java"
);
}
catch
(ioexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
package
pkg5;
import
pkg4.ioutil;
import
java.io.filenotfoundexception;
import
java.io.fileoutputstream;
import
java.io.ioexception;
public
class
fileoutdemo {
public
static
void
main(string[] args)
throws
ioexception {
// 如果该文件不存在,则直接创建,如果存在,则删除后创建。若要在后面追加内容,参数中加一个true
fileoutputstream fos =
new
fileoutputstream(
"demo/out.dat"
);
// 写入a的低8位
fos.write(
'a'
);
fos.write(
'b'
);
// write只能写8位,那么写一个int需要4次,每次8位
int
a =
10
;
fos.write(a >>>
24
);
fos.write(a >>>
16
);
fos.write(a >>>
8
);
fos.write(a);
byte
[] gbk =
"中国"
.getbytes(
"gbk"
);
fos.write(gbk);
fos.close();
ioutil.printhex(
"demo/out.dat"
);
}
}
|
测试类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
package
pkg5;
import
pkg4.ioutil;
import
java.io.datainputstream;
import
java.io.dataoutputstream;
import
java.io.file;
import
java.io.ioexception;
public
class
ioutiltest3 {
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
try
{
ioutil.copyfile(
new
file(
"d:\\javaio\\abc.txt"
),
new
file(
"d:\\javaio\\abc1.txt"
));
}
catch
(ioexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
}
|
输入流:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
package
pkg6;
import
pkg4.ioutil;
import
java.io.datainputstream;
import
java.io.fileinputstream;
import
java.io.ioexception;
public
class
disdemo {
public
static
void
main(string[] args)
throws
ioexception {
string file =
"demo/dos.dat"
;
ioutil.printhex(file);
datainputstream dis =
new
datainputstream(
new
fileinputstream(file));
int
i = dis.readint();
system.out.println(i);
i = dis.readint();
system.out.println(i);
long
l = dis.readlong();
system.out.println(l);
double
d = dis.readdouble();
system.out.println(d);
string s = dis.readutf();
system.out.println(s);
dis.close();
}
}
|
输出流:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
package
pkg6;
import
pkg4.ioutil;
import
java.io.dataoutputstream;
import
java.io.filenotfoundexception;
import
java.io.fileoutputstream;
import
java.io.ioexception;
public
class
dosdemo {
public
static
void
main(string[] args)
throws
ioexception {
string file =
"demo/dos.dat"
;
dataoutputstream dos =
new
dataoutputstream(
new
fileoutputstream(file));
dos.writeint(
10
);
dos.writeint(-
10
);
dos.writelong(10l);
dos.writedouble(
10.5
);
// 采用utf-8写入
dos.writeutf(
"中国"
);
// 采用utf-16be写入
dos.writechars(
"中国"
);
dos.close();
ioutil.printhex(file);
}
}
|
工具类在4.1小节的ioutil.java中.
测试类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
package
pkg7;
import
pkg4.ioutil;
import
java.io.file;
import
java.io.ioexception;
public
class
ioutiltest4 {
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
// 效率最高
try
{
long
start = system.currenttimemillis();
ioutil.copyfile(
new
file(
"d:\\javaio\\alpha.mp3"
),
new
file(
"d:\\javaio\\alpha1.mp3"
));
long
end = system.currenttimemillis();
system.out.println(
"耗时1:"
+ (end - start));
}
catch
(ioexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
// 效率居中
try
{
long
start = system.currenttimemillis();
ioutil.copyfilebybuffer(
new
file(
"d:\\javaio\\alpha.mp3"
),
new
file(
"d:\\javaio\\alpha2.mp3"
));
long
end = system.currenttimemillis();
system.out.println(
"耗时2:"
+ (end - start));
}
catch
(ioexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
// 效率最差
try
{
long
start = system.currenttimemillis();
ioutil.copyfilebybyte(
new
file(
"d:\\javaio\\alpha.mp3"
),
new
file(
"d:\\javaio\\alpha3.mp3"
));
long
end = system.currenttimemillis();
system.out.println(
"耗时3:"
+ (end - start));
}
catch
(ioexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
package
pkg8;
import
java.io.*;
public
class
israndoswdemo {
public
static
void
main(string[] args)
throws
ioexception {
fileinputstream fis =
new
fileinputstream(
"d:\\javaio\\aa.txt"
);
inputstreamreader isr =
new
inputstreamreader(fis);
//未指定编码格式,即按照项目默认编码操作
fileoutputstream fos =
new
fileoutputstream(
"d:\\javaio\\aa.txt"
);
outputstreamwriter osw =
new
outputstreamwriter(fos);
//未指定编码格式,即按照项目默认编码操作
/*int c;
while ((c=isr.read())!=-1){
system.out.print((char)c);
}*/
/*
批量读取。
放入buffer这个字节数组,从第0个位置开始放,最多放buffer.length个,返回读到的字符个数。
*/
char[] buffer = new char[8 * 1024];
int c;
while ((c = isr.read(buffer, 0, buffer.length)) != -1) {
string s = new string(buffer, 0, c);
system.out.print(s);
/*osw.write(buffer,0,c);
osw.flush();*/
}
isr.close();
osw.close();
}
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
package
pkg8;
import
java.io.filenotfoundexception;
import
java.io.filereader;
import
java.io.filewriter;
import
java.io.ioexception;
public
class
frandfwdemo {
/**
* 注意:filereader、filewriter不能指定编码方式
*/
public
static
void
main(string[] args)
throws
ioexception {
filereader fr =
new
filereader(
"d:\\javaio\\aa.txt"
);
// 指定参数,也可以追加内容:filewriter(string filename, boolean append)
filewriter fw =
new
filewriter(
"d:\\javaio\\bb.txt"
);
char
[] buffer =
new
char
[
8
*
1024
];
int
c;
while
((c = fr.read(buffer,
0
, buffer.length)) != -
1
) {
fw.write(buffer,
0
, c);
fw.flush();
}
fr.close();
fw.close();
}
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
package
pkg9;
import
java.io.*;
public
class
brandbworpwdemo {
public
static
void
main(string[] args)
throws
ioexception {
// 对文件进行读写操作
bufferedreader br =
new
bufferedreader(
new
inputstreamreader(
new
fileinputstream(
"d:\\javaio\\aa.txt"
)));
//bufferedwriter bw = new bufferedwriter(new outputstreamwriter(new fileoutputstream("d:\\javaio\\cc.txt")));
// printwriter可以替换bufferedwriter
printwriter pw =
new
printwriter(
"d:\\javaio\\cc.txt"
);
string line;
while
((line = br.readline()) !=
null
) {
// 一次读一行,不能识别换行
system.out.println(line);
/*bw.write(line);
// 手动给出换行
bw.newline();
bw.flush();*/
pw.println(line);
pw.flush();
}
br.close();
//bw.close();
pw.close();
}
}
|
实体类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
|
package
pkg10;
import
java.io.serializable;
public
class
student
implements
serializable {
private
string stuno;
private
string stuname;
// 该元素不会 进行jvm默认的序列化,但可以手动序列化
private
transient
int
stuage;
public
student(string stuno, string stuname,
int
stuage) {
this
.stuno = stuno;
this
.stuname = stuname;
this
.stuage = stuage;
}
public
string getstuno() {
return
stuno;
}
public
void
setstuno(string stuno) {
this
.stuno = stuno;
}
public
string getstuname() {
return
stuname;
}
public
void
setstuname(string stuname) {
this
.stuname = stuname;
}
public
int
getstuage() {
return
stuage;
}
public
void
setstuage(
int
stuage) {
this
.stuage = stuage;
}
@override
public
string tostring() {
return
"student{"
+
"stuno='"
+ stuno + '\
''
+
", stuname='"
+ stuname + '\
''
+
", stuage="
+ stuage +
'}'
;
}
/**
* 序列化
*/
private
void
writeobject(java.io.objectoutputstream s)
throws
java.io.ioexception {
// 把jvm能默认序列化的元素进行序列化操作
s.defaultwriteobject();
// 手动完成stuage的序列化
s.writeint(stuage);
}
/**
* 反序列化
*/
private
void
readobject(java.io.objectinputstream s)
throws
java.io.ioexception, classnotfoundexception {
// 把jvm默认能反序列化的元素进行反序列化操作
s.defaultreadobject();
// 手动完成stuage的反序列化
stuage = s.readint();
}
}
|
测试类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
package
pkg10;
import
java.io.*;
import
java.util.arraylist;
public
class
objectseriademo {
public
static
void
main(string[] args)
throws
ioexception, classnotfoundexception {
string file =
"demo/obj.dat"
;
// 1、对象的序列化
/*objectoutputstream oos = new objectoutputstream(new fileoutputstream(file));
student student = new student("10001", "张三", 20);
oos.writeobject(student);
oos.flush();
oos.close();*/
// 2、对象的反序列化
objectinputstream ois =
new
objectinputstream(
new
fileinputstream(file));
student stu = (student) ois.readobject();
system.out.println(stu);
ois.close();
}
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
|
package
pkg11;
import
java.io.*;
import
java.sql.sqloutput;
public
class
objectseriademo {
public
static
void
main(string[] args)
throws
ioexception, classnotfoundexception {
// 序列化
/*objectoutputstream oos=new objectoutputstream(new fileoutputstream("demo/obj1.dat"));
foo2 foo2=new foo2();
oos.writeobject(foo2);
oos.flush();
oos.close();*/
// 反序列化
/*objectinputstream ois=new objectinputstream(new fileinputstream("demo/obj1.dat"));
foo2 foo2= (foo2) ois.readobject();
system.out.println(foo2);
ois.close();*/
/*objectoutputstream oos=new objectoutputstream(new fileoutputstream("demo/obj1.dat"));
bar2 bar2=new bar2();
oos.writeobject(bar2);
oos.flush();
oos.close();*/
/*objectinputstream ois = new objectinputstream(new fileinputstream("demo/obj1.dat"));
bar2 bar2 = (bar2) ois.readobject();
system.out.println(bar2);
ois.close();*/
/*objectoutputstream oos=new objectoutputstream(new fileoutputstream("demo/obj1.dat"));
ccc2 ccc2=new ccc2();
oos.writeobject(ccc2);
oos.flush();
oos.close();*/
objectinputstream ois = new objectinputstream(new fileinputstream("demo/obj1.dat"));
ccc2 ccc2 = (ccc2) ois.readobject();
system.out.println(ccc2);
ois.close();
}
}
/**
* 一个类实现了序列化接口,其子类都可以实现序列化。
*/
class foo implements serializable {
public foo() {
system.out.println("foo...");
}
}
class foo1 extends foo {
public foo1() {
system.out.println("foo1...");
}
}
class foo2 extends foo1 {
public foo2() {
system.out.println("foo2...");
}
}
/**
* 对子类对象进行反序列化操作时,
* 如果其父类没有实现序列化接口
* 那么其父类的构造函数会被调用
*/
class
bar {
public
bar() {
system.out.println(
"bar..."
);
}
}
class
bar1
extends
bar
implements
serializable {
public
bar1() {
system.out.println(
"bar1..."
);
}
}
class
bar2
extends
bar1 {
public
bar2() {
system.out.println(
"bar2..."
);
}
}
class
ccc {
public
ccc() {
system.out.println(
"ccc..."
);
}
}
class
ccc1
extends
ccc {
public
ccc1() {
system.out.println(
"ccc1..."
);
}
}
class
ccc2
extends
ccc1
implements
serializable {
public
ccc2() {
system.out.println(
"ccc2..."
);
}
}
|
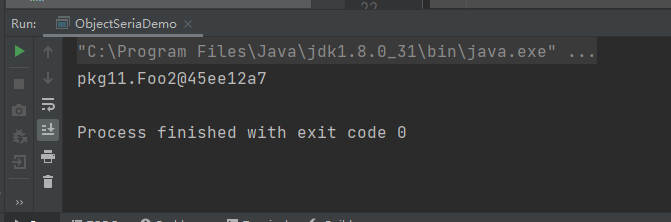
foo2类反序列化时不打印构造方法:
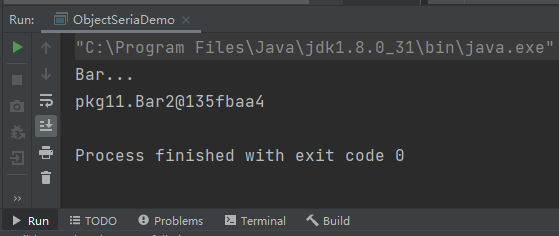
bar2类反序列化时打印了bar的构造方法:
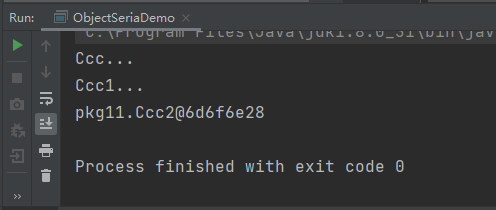
ccc2类反序列化时打印了ccc、ccc1的构造方法:
结论(详见导图标红部分):
对子类对象进行反序列化操作时,如果其父类没有实现序列化接口,那么其父类的构造函数会被调用.
到此这篇关于java io流学习总结之文件传输基础的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关java io流文件传输内容请搜索我以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我! 。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/ykmeory/article/details/115682087 。
最后此篇关于Java IO流学习总结之文件传输基础的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于Java IO流学习总结之文件传输基础的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
这个问题在这里已经有了答案: Why filter() after flatMap() is "not completely" lazy in Java streams? (8 个答案) 关闭 6
我正在创建一个应用程序来从 Instagram 收集数据。我正在寻找像 Twitter 流 API 这样的流 API,这样我就可以自动实时收集数据而无需发送请求。 Instagram 有类似的 API
我正在使用 Apache Commons 在 Google App Engine 中上传一个 .docx 文件,如此链接中所述 File upload servlet .上传时,我还想使用 Apach
我尝试使用 DynamoDB 流和 AWS 提供的 Java DynamoDB 流 Kinesis 适配器捕获 DynamoDB 表更改。我正在 Scala 应用程序中使用 AWS Java 开发工具
我目前有一个采用 H.264 编码的 IP 摄像机流式视频 (RTSP)。 我想使用 FFmpeg 将此 H.264 编码流转换为另一个 RTSP 流,但 MPEG-2 编码。我该怎么做?我应该使用哪
Redis 流是否受益于集群模式?假设您有 10 个流,它们是分布在整个集群中还是都分布在同一节点上?我计划使用 Redis 流来实现真正的高吞吐量(200 万条消息/秒),所以我担心这种规模的 Re
这件事困扰了我一段时间。 所以我有一个 Product 类,它有一个 Image 列表(该列表可能为空)。 我想做 product.getImages().stream().filter(...) 但
是否可以使用 具有持久存储的 Redis 流 还是流仅限于内存数据? 我知道可以将 Redis 与核心数据结构的持久存储一起使用,但我已经能够理解是否也可以使用 Redis 中的流的持久存储。 最佳答
我开始学习 Elixir 并遇到了一个我无法轻松解决的挑战。 我正在尝试创建一个函数,该函数接受一个 Enumerable.t 并返回另一个 Enumerable.t ,其中包含下 n 个项目。它与
我试图从 readLine 调用创建一个无限的字符串流: import java.io.{BufferedReader, InputStreamReader} val in = new Buffere
你能帮我使用 Java 8 流 API 编写以下代码吗? SuperUser superUser = db.getSuperUser; for (final Client client : super
我正在尝试服用补品routeguide tutorial,并将客户端变成rocket服务器。我只是接受响应并将gRPC转换为字符串。 service RouteGuide { rpc GetF
流程代码可以是run here. 使用 flow,我有一个函数,它接受一个键值对对象并获取它的值 - 它获取的值应该是字符串、数字或 bool 值。 type ValueType = string
如果我有一个函数返回一个包含数据库信息的对象或一个空对象,如下所示: getThingFromDB: async function(id:string):Promise{ const from
我正在尝试使用javascript api和FB.ui将ogg音频文件发布到流中, 但是我不知道该怎么做。 这是我给FB.ui的电话: FB.ui( { method: '
我正在尝试删除工作区(或克隆它以使其看起来像父工作区,但我似乎两者都做不到)。但是,当我尝试时,我收到此消息:无法删除工作区 test_workspace,因为它有一个非空的默认组。 据我所知,这意味
可以使用 Stream|Map 来完成此操作,这样我就不需要将结果放入外部 HashMap 中,而是使用 .collect(Collectors.toMap(...)); 收集结果? Map rep
当我们从集合列表中获取 Stream 时,幕后到底发生了什么?我发现很多博客都说Stream不存储任何数据。如果这是真的,请考虑代码片段: List list = new ArrayList(); l
我对流及其工作方式不熟悉,我正在尝试获取列表中添加的特定对象的出现次数。 我找到了一种使用Collections来做到这一点的方法。其过程如下: for (int i = 0; i p.conten
我希望将一个 map 列表转换为另一个分组的 map 列表。 所以我有以下 map 列表 - List [{ "accId":"1", "accName":"TestAcc1", "accNumber

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!