- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章C语言二叉树常见操作详解【前序,中序,后序,层次遍历及非递归查找,统计个数,比较,求深度】由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
本文实例讲述了C语言二叉树常见操作。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
1、基本概念 。
每个结点最多有两棵子树,左子树和右子树,次序不可以颠倒.
性质:
1、非空二叉树的第n层上至多有2^(n-1)个元素.
2、深度为h的二叉树至多有2^h-1个结点.
满二叉树:所有终端都在同一层次,且非终端结点的度数为2.
在满二叉树中若其深度为h,则其所包含的结点数必为2^h-1.
完全二叉树:除了最大的层次即成为一颗满二叉树且层次最大那层所有的结点均向左靠齐,即集中在左面的位置上,不能有空位置.
对于完全二叉树,设一个结点为i则其父节点为i/2,2i为左子节点,2i+1为右子节点.
2、存储结构 。
顺序存储:
将数据结构存在一块固定的数组中.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
#define LENGTH 100
typedef
char
datatype;
typedef
struct
node{
datatype data;
int
lchild,rchild;
int
parent;
}Node;
Node tree[LENGTH];
int
length;
int
root;
|
虽然在遍历速度上有一定的优势,但因所占空间比较大,是非主流二叉树。二叉树通常以链式存储.
链式存储:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
typedef
char
datatype;
typedef
struct
BinNode{
datatype data;
struct
BinNode* lchild;
struct
BinNode* rchild;
}BinNode;
typedef
BinNode* bintree;
//bintree本身是个指向结点的指针
|
3、二叉树的遍历 。
遍历即将树的所有结点访问且仅访问一次。按照根节点位置的不同分为前序遍历,中序遍历,后序遍历.
前序遍历:根节点->左子树->右子树 。
中序遍历:左子树->根节点->右子树 。
后序遍历:左子树->右子树->根节点 。
例如:求下面树的三种遍历 。
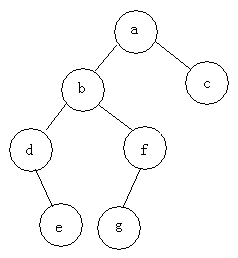
前序遍历:abdefgc 。
中序遍历:debgfac 。
后序遍历:edgfbca 。
4、遍历的实现 。
递归实现(以前序遍历为例,其他的只是输出的位置稍有不同) 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
void
preorder(bintree t){
if
(t){
printf
(
"%c "
,t->data);
preorder(t->lchild);
preorder(t->rchild);
}
}
|
非递归的实现 。
因为当遍历过根节点之后还要回来,所以必须将其存起来。考虑到后进先出的特点,选用栈存储。数量确定,以顺序栈存储.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
#define SIZE 100
typedef
struct
seqstack{
bintree data[SIZE];
int
tag[SIZE];
//为后续遍历准备的
int
top;
//top为数组的下标
}seqstack;
void
push(seqstack *s,bintree t){
if
(s->top == SIZE){
printf
(
"the stack is full\n"
);
}
else
{
s->top++;
s->data[s->top]=t;
}
}
bintree pop(seqstack *s){
if
(s->top == -1){
return
NULL;
}
else
{
s->top--;
return
s->data[s->top+1];
}
}
|
1、前序遍历 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
void
preorder_dev(bintree t){
seqstack s;
s.top = -1;
//因为top在这里表示了数组中的位置,所以空为-1
if
(!t){
printf
(
"the tree is empty\n"
);
}
else
{
while
(t || s.stop != -1){
while
(t){
//只要结点不为空就应该入栈保存,与其左右结点无关
printf
(
"%c "
,t->data);
push(&s,t);
t= t->lchild;
}
t=pop(&s);
t=t->rchild;
}
}
}
|
2、中序遍历 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
void
midorder(bintree t){
seqstack s;
s.top = -1;
if
(!t){
printf
(
"the tree is empty!\n"
);
}
else
{
while
(t ||s.top != -1){
while
(t){
push(&s,t);
t= t->lchild;
}
t=pop(&s);
printf
(
"%c "
,t->data);
t=t->rchild;
}
}
}
|
3、后序遍历 。
因为后序遍历最后还要要访问根结点一次,所以要访问根结点两次。采取夹标志位的方法解决这个问题.
这段代码非常纠结,对自己有信心的朋友可以尝试独立写一下。反正我是写了很长时间。逻辑不难,我画了一张逻辑图:
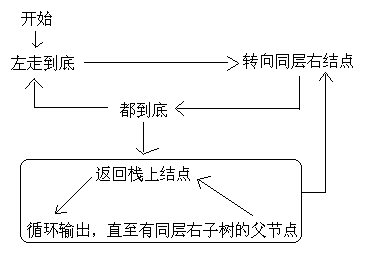
代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
void
postorder_dev(bintree t){
seqstack s;
s.top = -1;
if
(!t){
printf
(
"the tree is empty!\n"
);
}
else
{
while
(t || s.top != -1){
//栈空了的同时t也为空。
while
(t){
push(&s,t);
s.tag[s.top] = 0;
//设置访问标记,0为第一次访问,1为第二次访问
t= t->lchild;
}
if
(s.tag[s.top] == 0){
//第一次访问时,转向同层右结点
t= s.data[s.top];
//左走到底时t是为空的,必须有这步!
s.tag[s.top]=1;
t=t->rchild;
}
else
{
while
(s.tag[s.top] == 1){
//找到栈中下一个第一次访问的结点,退出循环时并没有pop所以为其左子结点
t = pop(&s);
printf
(
"%c "
,t->data);
}
t = NULL;
//必须将t置空。跳过向左走,直接向右走
}
}
}
}
|
4、层次遍历:即每一层从左向右输出 。
元素需要储存有先进先出的特性,所以选用队列存储.
队列的定义:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
#define MAX 1000
typedef
struct
seqqueue{
bintree data[MAX];
int
front;
int
rear;
}seqqueue;
void
enter(seqqueue *q,bintree t){
if
(q->rear == MAX){
printf
(
"the queue is full!\n"
);
}
else
{
q->data[q->rear] = t;
q->rear++;
}
}
bintree del(seqqueue *q){
if
(q->front == q->rear){
return
NULL;
}
else
{
q->front++;
return
q->data[q->front-1];
}
}
|
遍历实现 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
void
level_tree(bintree t){
seqqueue q;
bintree temp;
q.front = q.rear = 0;
if
(!t){
printf
(
"the tree is empty\n"
);
return
;
}
enter(&q,t);
while
(q.front != q.rear){
t=del(&q);
printf
(
"%c "
,t->data);
if
(t->lchild){
enter(&q,t->lchild);
}
if
(t->rchild){
enter(&q,t->rchild);
}
}
}
|
5、利用前序遍历的结果生成二叉树 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
//递归调用,不存点,想的时候只关注于一个点,因为还会回来的,不要跟踪程序运行,否则容易多加循环
void
createtree(bintree *t){
datatype c;
if
((c=
getchar
()) ==
'#'
)
*t = NULL;
else
{
*t = (bintree)
malloc
(
sizeof
(BinNode));
(*t)->data = c;
createtree(&(*t)->lchild);
createtree(&(*t)->rchild);
}
}
|
6、二叉树的查找 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
bintree search_tree(bintree t,datatype x){
if
(!t){
return
NULL;
}
if
(t->data == x){
return
t;
}
else
{
if
(!search_tree(t->lchild,x)){
return
search_tree(t->rchild,x);
}
return
t;
}
}
|
7、统计结点个数 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
int
count_tree(bintree t){
if
(t){
return
(count_tree(t->lchild)+count_tree(t->rchild)+1);
}
return
0;
}
|
8、比较两个树是否相同 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
int
is_equal(bintree t1,bintree t2){
if
(!t1 && !t2){
//都为空就相等
return
1;
}
if
(t1 && t2 && t1->data == t2->data){
//有一个为空或数据不同就不判断了
if
(is_equal(t1->lchild,t2->lchild))
if
(is_equal(t1->rchild,t2->rchild)){
return
1;
}
}
return
0;
}
|
9、求二叉树的深度 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
int
hight_tree(bintree t){
int
h,left,right;
if
(!t){
return
0;
}
left = hight_tree(t->lchild);
right = hight_tree(t->rchild);
h = (left>right?left:right)+1;
return
h;
}
|
希望本文所述对大家C语言程序设计有所帮助.
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/fansongy/article/details/6798278/ 。
最后此篇关于C语言二叉树常见操作详解【前序,中序,后序,层次遍历及非递归查找,统计个数,比较,求深度】的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于C语言二叉树常见操作详解【前序,中序,后序,层次遍历及非递归查找,统计个数,比较,求深度】的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
这个问题在这里已经有了答案: Prolog - count repetitions in list (3 个答案) 关闭 7 年前。 所以我正在尝试创建一种方法来确定列表中 N 的数量。我已经试验了
使用 sscanf 或任何其他命令从分号后的文件读取的最佳方法是什么,例如,如果我的文件有 5: 4 5 6 7。如何将冒号后的值存储在数组中。此外,分号后面的整数数量可能会有所不同,即在上面给出的示
我正在尝试返回第 n 个数字。如果数字是 3 或 7 的倍数,则从 1 开始,则跳过该数字并获取下一个数字。但是,如果数字是 3 和 7 的倍数,则不会跳过该数字。 public int Multip
如何有效地从末尾获取一定数量的元素? 1 looks like 2 three!! 例如,如何获取最后 2 个 div 的内容? 最佳答案 $(document).ready(function(){
//Generate Food Personality for(i=0; i
我试图在给定的排序数组中找到最大的 K 个数。 例如:输入 -> [ 5, 12, 45, 32, 9, 20, 15]输出 -> K = 3, [45, 32, 20] 到目前为止我编写的代码返回最
两个数字表 a 和 b 被写入并按升序合并在一起,并删除重复项。现在的问题是在这个 super 表中找到比 O(n) 复杂度更好的 nth 数。 Limits 1 #include using nam
给定一个包含 N 个元素的数组 A,我需要找到对 (i,j) 使得 i 不等于 j 并且如果我们为所有对 (i, j) 然后它来到第k个位置。 示例:让 N=4 和数组 A=[1 2 3 4] 如果
给定一组跳过的数字,我需要找到该组中不存在的第 N 个数字。示例: 给定一组 [1, 4, 5] 一些结果: 对于 N = 1 结果 0 对于 N = 2 结果 2(因为 1 被跳过) 对于 N =
几个月前在亚马逊的招聘挑战中遇到了这个问题。 给定两个数字 a 和 b 及其倍数的升序列表,找出第 n 个倍数。 例如,如果 a = 4 , b = 6 和 n = 6 那么答案是 18因为列表是 4
所以我最近一直在研究 Python,我试图找到一种方法来在单个表达式中输出斐波那契数列的第 n 个数。这是我到目前为止编写的代码: (lambda f: f if f 1 # n == 2 -> 1
作业是编写一个 C++ 程序,它接受输入数字 n 并输出序列中的第 n 个数字: 1 1 2 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 ... 这是我到目前为止想出的:
问题很简单(答案很可能):如何找到数组中最小的 2 个数字? for ( i = 1; i 关于c++ - 数组中最小的 2 个数,我们在Stack Overflow上找到一个类似的问题: ht
您可以调用Nokogiri::XML::Node#ancestors.size 来查看节点的嵌套深度。但是有没有办法确定嵌套最深的子节点的嵌套深度呢? 或者,您如何找到从一个节点下降的所有叶节点? 最
这个任务是找到n个数字的fibanocci。任务: 1.找出n个数的斐波那契数。 2.使用变量n,first=0,second=1,next,c。输入格式:使用 printf 语句。使用 scanf
我想添加每 10 个元素的数量。 例如, function myFunction() { for (var i = 1; i "; } } 输出: 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,
我想编写一个程序来计算斐波那契数列的第 n 个数,这是我使用 printf 和 scanf 完成的。但我希望更改我的程序,以便在命令行中输入序列号,而不是在程序提示时输入。这就是我想出的。它可以编译,
我有一个方案中的对象列表。每个对象都与一个可以在运行时计算的置信度值相关联。我想找到具有最高置信度值的前 50 个此类对象。示例:((WordPair1) (WordPair2)) 等等都是我的对象。
我正在寻找一种给定目标的算法,返回目标位为 0 的第 N 个数字。 例如,对于n={0,1,2,3}和target=1的输入,输出将是(二进制) 000,001,100,101 最佳答案 只写值N-1
我正在尝试创建一个函数来获取 vector 中的 3 个最大数字。例如:数字:1 6 2 5 3 7 4结果:5 6 7 我想我可以对它们进行 DESC 排序,在开始时获取 3 个数字,然后再对它们进

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!