- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章java 如何扫描指定包下类(包括jar中的java类)由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
在很多的实际场景中,我们需要得到某个包名下面所有的类, 。
包括我们自己在src里写的java类和一些第三方提供的jar包里的类,那么怎么来实现呢?
今天带大家来完成这件事.
首先,比较简单的是得到我们自己写的类,我们先来完成这个, 。
项目的结构图如下:

我故意创建了这么个比较复杂的项目结构,现在我们就来获取com.baibin包下所有的类,并且打印他们,代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
import
org.junit.Test;
import
java.io.File;
import
java.util.ArrayList;
import
java.util.List;
public
class
Main {
List<String> classPaths =
new
ArrayList<String>();
@Test
public
void
searchClass()
throws
ClassNotFoundException {
//包名
String basePack =
"com.baibin"
;
//先把包名转换为路径,首先得到项目的classpath
String classpath = Main.
class
.getResource(
"/"
).getPath();
//然后把我们的包名basPach转换为路径名
basePack = basePack.replace(
"."
, File.separator);
//然后把classpath和basePack合并
String searchPath = classpath + basePack;
doPath(
new
File(searchPath));
//这个时候我们已经得到了指定包下所有的类的绝对路径了。我们现在利用这些绝对路径和java的反射机制得到他们的类对象
for
(String s : classPaths) {
//把 D:\work\code\20170401\search-class\target\classes\com\baibin\search\a\A.class 这样的绝对路径转换为全类名com.baibin.search.a.A
s = s.replace(classpath.replace(
"/"
,
"\\"
).replaceFirst(
"\\\\"
,
""
),
""
).replace(
"\\"
,
"."
).replace(
".class"
,
""
);
Class cls = Class.forName(s);
System.out.println(cls);
}
}
/**
* 该方法会得到所有的类,将类的绝对路径写入到classPaths中
* @param file
*/
private
void
doPath(File file) {
if
(file.isDirectory()) {
//文件夹
//文件夹我们就递归
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for
(File f1 : files) {
doPath(f1);
}
}
else
{
//标准文件
//标准文件我们就判断是否是class文件
if
(file.getName().endsWith(
".class"
)) {
//如果是class文件我们就放入我们的集合中。
classPaths.add(file.getPath());
}
}
}
}
|
效果如下:
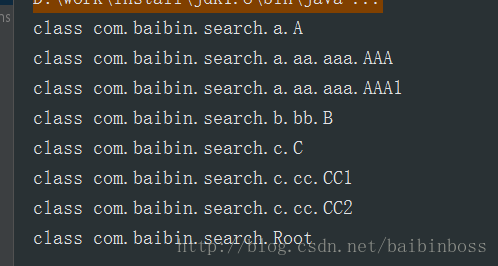
总结:这样的src下面的都比较容易处理,也很容易想到,但是jar包下面的就没这么简单了, 。
但是还是有办法的.
jar下的类我们可以通过JarURLConnection类来或者,代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
import
org.junit.Test;
import
java.io.IOException;
import
java.net.JarURLConnection;
import
java.net.URL;
import
java.util.Enumeration;
import
java.util.jar.JarEntry;
import
java.util.jar.JarFile;
public
class
JarMain {
@Test
public
void
searchClass()
throws
IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
String basePack =
"org.junit"
;
//通过当前线程得到类加载器从而得到URL的枚举
Enumeration<URL> urlEnumeration = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResources(basePack.replace(
"."
,
"/"
));
while
(urlEnumeration.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urlEnumeration.nextElement();
//得到的结果大概是:jar:file:/C:/Users/ibm/.m2/repository/junit/junit/4.12/junit-4.12.jar!/org/junit
String protocol = url.getProtocol();
//大概是jar
if
(
"jar"
.equalsIgnoreCase(protocol)) {
//转换为JarURLConnection
JarURLConnection connection = (JarURLConnection) url.openConnection();
if
(connection !=
null
) {
JarFile jarFile = connection.getJarFile();
if
(jarFile !=
null
) {
//得到该jar文件下面的类实体
Enumeration<JarEntry> jarEntryEnumeration = jarFile.entries();
while
(jarEntryEnumeration.hasMoreElements()) {
/*entry的结果大概是这样:
org/
org/junit/
org/junit/rules/
org/junit/runners/*/
JarEntry entry = jarEntryEnumeration.nextElement();
String jarEntryName = entry.getName();
//这里我们需要过滤不是class文件和不在basePack包名下的类
if
(jarEntryName.contains(
".class"
) && jarEntryName.replaceAll(
"/"
,
"."
).startsWith(basePack)) {
String className = jarEntryName.substring(
0
, jarEntryName.lastIndexOf(
"."
)).replace(
"/"
,
"."
);
Class cls = Class.forName(className);
System.out.println(cls);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
|
通过这两种方式我们就可以得到指定包名下面所有的类了,这个还是挺有用的, 。
比如spring中经常用来扫描指定包注解的实现等.
补充:获取指定包名下的所有类 。
写了一个工具类,用于获取指定包名下的所有类,支持递归遍历,支持注解过滤,可从 classpath (class 文件与 jar 包)中获取.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
|
import
java.io.File;
import
java.io.FileFilter;
import
java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import
java.net.JarURLConnection;
import
java.net.URL;
import
java.util.ArrayList;
import
java.util.Enumeration;
import
java.util.List;
import
java.util.jar.JarEntry;
import
java.util.jar.JarFile;
public
class
ClassUtil {
// 获取指定包名下的所有类
public
static
List<Class<?>> getClassList(String packageName,
boolean
isRecursive) {
List<Class<?>> classList =
new
ArrayList<Class<?>>();
try
{
Enumeration<URL> urls = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResources(packageName.replaceAll(
"\\."
,
"/"
));
while
(urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
if
(url !=
null
) {
String protocol = url.getProtocol();
if
(protocol.equals(
"file"
)) {
String packagePath = url.getPath();
addClass(classList, packagePath, packageName, isRecursive);
}
else
if
(protocol.equals(
"jar"
)) {
JarURLConnection jarURLConnection = (JarURLConnection) url.openConnection();
JarFile jarFile = jarURLConnection.getJarFile();
Enumeration<JarEntry> jarEntries = jarFile.entries();
while
(jarEntries.hasMoreElements()) {
JarEntry jarEntry = jarEntries.nextElement();
String jarEntryName = jarEntry.getName();
if
(jarEntryName.endsWith(
".class"
)) {
String className = jarEntryName.substring(
0
, jarEntryName.lastIndexOf(
"."
)).replaceAll(
"/"
,
"."
);
if
(isRecursive || className.substring(
0
, className.lastIndexOf(
"."
)).equals(packageName)) {
classList.add(Class.forName(className));
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
catch
(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return
classList;
}
// 获取指定包名下的所有类(可根据注解进行过滤)
public
static
List<Class<?>> getClassListByAnnotation(String packageName, Class<?
extends
Annotation> annotationClass) {
List<Class<?>> classList =
new
ArrayList<Class<?>>();
try
{
Enumeration<URL> urls = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResources(packageName.replaceAll(
"\\."
,
"/"
));
while
(urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
if
(url !=
null
) {
String protocol = url.getProtocol();
if
(protocol.equals(
"file"
)) {
String packagePath = url.getPath();
addClassByAnnotation(classList, packagePath, packageName, annotationClass);
}
else
if
(protocol.equals(
"jar"
)) {
JarURLConnection jarURLConnection = (JarURLConnection) url.openConnection();
JarFile jarFile = jarURLConnection.getJarFile();
Enumeration<JarEntry> jarEntries = jarFile.entries();
while
(jarEntries.hasMoreElements()) {
JarEntry jarEntry = jarEntries.nextElement();
String jarEntryName = jarEntry.getName();
if
(jarEntryName.endsWith(
".class"
)) {
String className = jarEntryName.substring(
0
, jarEntryName.lastIndexOf(
"."
)).replaceAll(
"/"
,
"."
);
Class<?> cls = Class.forName(className);
if
(cls.isAnnotationPresent(annotationClass)) {
classList.add(cls);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
catch
(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return
classList;
}
private
static
void
addClass(List<Class<?>> classList, String packagePath, String packageName,
boolean
isRecursive) {
try
{
File[] files = getClassFiles(packagePath);
if
(files !=
null
) {
for
(File file : files) {
String fileName = file.getName();
if
(file.isFile()) {
String className = getClassName(packageName, fileName);
classList.add(Class.forName(className));
}
else
{
if
(isRecursive) {
String subPackagePath = getSubPackagePath(packagePath, fileName);
String subPackageName = getSubPackageName(packageName, fileName);
addClass(classList, subPackagePath, subPackageName, isRecursive);
}
}
}
}
}
catch
(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private
static
File[] getClassFiles(String packagePath) {
return
new
File(packagePath).listFiles(
new
FileFilter() {
@Override
public
boolean
accept(File file) {
return
(file.isFile() && file.getName().endsWith(
".class"
)) || file.isDirectory();
}
});
}
private
static
String getClassName(String packageName, String fileName) {
String className = fileName.substring(
0
, fileName.lastIndexOf(
"."
));
if
(StringUtil.isNotEmpty(packageName)) {
className = packageName +
"."
+ className;
}
return
className;
}
private
static
String getSubPackagePath(String packagePath, String filePath) {
String subPackagePath = filePath;
if
(StringUtil.isNotEmpty(packagePath)) {
subPackagePath = packagePath +
"/"
+ subPackagePath;
}
return
subPackagePath;
}
private
static
String getSubPackageName(String packageName, String filePath) {
String subPackageName = filePath;
if
(StringUtil.isNotEmpty(packageName)) {
subPackageName = packageName +
"."
+ subPackageName;
}
return
subPackageName;
}
private
static
void
addClassByAnnotation(List<Class<?>> classList, String packagePath, String packageName, Class<?
extends
Annotation> annotationClass) {
try
{
File[] files = getClassFiles(packagePath);
if
(files !=
null
) {
for
(File file : files) {
String fileName = file.getName();
if
(file.isFile()) {
String className = getClassName(packageName, fileName);
Class<?> cls = Class.forName(className);
if
(cls.isAnnotationPresent(annotationClass)) {
classList.add(cls);
}
}
else
{
String subPackagePath = getSubPackagePath(packagePath, fileName);
String subPackageName = getSubPackageName(packageName, fileName);
addClassByAnnotation(classList, subPackagePath, subPackageName, annotationClass);
}
}
}
}
catch
(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我。如有错误或未考虑完全的地方,望不吝赐教.
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/baibinboss/article/details/68947929 。
最后此篇关于java 如何扫描指定包下类(包括jar中的java类)的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于java 如何扫描指定包下类(包括jar中的java类)的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
tl;博士:我们的 Spring Boot jar 中的类似乎可以看到捆绑的 jar 中的类,但它们的内容似乎无法看到。为什么? 我们的主要产品是一个网络应用程序,但所有的业务逻辑都集中在一个核心 m
我有一个适用于 Java 8 的 jar。 我想创建一个新 jar,它将是多版本 JAR 但为空,只有 META-INF/versions 中的“修补”类. 我想要一个单独的 jar,这样人们就可以在
免责声明: 在我得到“这个问题已经被问了 1000 次”的标准之前,让我说,是的,我知道。我读了又读又读。看了 JarJar 和 One-JAR,但问题是:我是自学成才的,只有几个月的经验,而且我不熟
我知道要组合多个 jar 并创建一个可执行 jar,我需要使用像 OneJar 这样的工具如果我不想解压相关的 jar 。 OneJar 有自己的自定义类加载器,可以在关联的 jar 中找到所需的类并
在我的项目中,我使用许多 jar 文件来支持该项目。随着 jar 文件数量的增加,我想将所有 jar 文件移动到一个 jar 中并利用它。您能给我提供有用的链接吗?可以帮助我做到这一点。 最佳答案 有
我有一个脚本可以删除目录中的低版本 jars 文件。 #!/bin/bash #Script to remove lower version jar files. for PREFIX in `ls
可执行 jar 文件可以自行重启吗?例如,在用户做出一些选择后,程序会说“重新启动应用程序?”并且用户单击"is",然后 jar 关闭并自行重新启动。 最佳答案 需要重新启动应用程序是糟糕设计的标志。
过去两年我一直有这个问题。 我有一个从 Internet 下载的 .jar 文件。它应该是一个魔方计时器。 当我双击这个 .jar 文件时,没有任何反应。如果我将 .jar 文件设置为使用 java.
我正在尝试在多项目Gradle构建中创建一个胖jar文件,如下所示: root +-- project1 +-- project2 project1提供了基本功能,然后project2将其用于
我需要 Maven 的配置,其中项目内的所有库都以 jar 格式保存在最终的 jar 中...所以我需要在最终的 jar 中包含 jar。为此我只能使用maven。我已经尝试过像 one-jar 这样
JAR、Fat JAR 和 Executable JAR 之间有什么区别?它们是如何从命令行和 gradle.build 任务创建的(如果是 gradle 项目)? 除了上面提到的以外,还有其他的JA
我阅读了很多构建具有依赖项的可执行 jar 的解决方案(maven 阴影插件、maven 依赖项插件、maven 程序集插件)和所有这些插件解压依赖项 jar 并将它们重新打包到可执行 jar 中。唯
我想问一下java命令中-jar选项前后传递参数有什么区别。考虑 $SOME_ENV_VAR=-Dinstance=qa 最佳答案 取决于SOME_ENV_VAR的内容;假设它包含有效的命令行参数,例
我试图了解如何打包用 Clojure 编写的命令行应用程序进行分发。我不希望用户不得不使用 java -jar myproject.jar arg1 arg2运行程序。 PHP 有一个叫做“Phar”
在 gradle 中 - 如何将 jar 嵌入到 lib 中的构建输出 jar 中目录(特别是 lib/enttoolkit.jar 和 lib/mail.jar)? 最佳答案 如果您的项目中的一个目
查看 Google gson 2.8.5 ,我看到这里分发了几个 jar https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/com/google/code/gson/gson/2.8.5/
我正在将 jar 文件和一个主类合并到一个 jar 中。问题是我的主类使用这些 jar ,如果它在一个 jar 中,它就会抛出找不到类定义。如何让类(class)看到 jar 里的 jar ? 最佳答
我正在使用 Maven 进行开发。我有一个要求,我想在我的项目 jar 中包含一些第三方 jar 并排除 pom.xml 文件中指定的其他 jar。下面是我的 pom.xml 文件。 4.0.0 c
我正在开发一个 GUI 应用程序,宁愿只分发一个 jar 而不是多个。 你能用 list 来控制它吗? 最佳答案 另一种选择是使用自定义类加载器,例如这个: http://one-jar.source
我看到许多 Java 包都有 api、impl 和 bundle jar(name-api.jar、name-impl.jar、name-bundle.jar)。有人可以解释这些是什么意思吗?应用程序

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!