- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章一篇文章带你了解Java中ThreadPool线程池由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
线程池做的工作主要是控制运行的线程数量,处理过程中将任务放入队列,然后在线程创建后启动这些任务,如果线程数量超过了最大数量,超出的线程排队等候,等待其他线程执行完毕,再从队列中取出任务来执行 。
线程复用、控制最大并发数、管理线程 。
。
执行长期任务性能好,创建一个线程池,一池有n个固定的线程,可以控制线程最大并发数,有固定线程数的线程池[ 。
|
1
|
executorservice threadpool = executors.newfixedthreadpool(n);
|
单个任务执行,它只会使用单个工作线程,一池一线程 。
|
1
|
executorservice threadpool = executors.newsinglethreadexecutor();
|
执行短期异步任务,可缓存线程池,线程池根据需要创建新线程,但在先前构造的线程可以复用,也可灵活回收空闲的线程,可扩容的池 。
|
1
|
executorservice threadpool = executors.newcachedthreadpool();
|
周期性线程池;支持定时及周期性任务执行 。
|
1
|
executorservice threadpool = executors.newscheduledthreadpool();
|
可以控制线程最大并发数的线程池:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
public
class
fixedthreadpool {
private
static
atomicinteger num =
new
atomicinteger(
0
);
private
static
executorservice executorservice = executors.newfixedthreadpool(
2
);
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
countsum c=
new
countsum();
//将coutsum作为task,submit至线程池
for
(
int
i =
0
; i <
2
; i++) {
executorservice.submit(c);
}
//task执行完成后关闭
executorservice.shutdown();
}
static
class
countsum
implements
runnable{
@override
public
void
run() {
for
(
int
i =
0
; i <
500
; i++) {
try
{
system.out.println(
"thread - "
+thread.currentthread().getname()+
" count= "
+ num.getandincrement());
thread.sleep(
100
);
}
catch
(exception e){
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
}
}
}
|
结果:
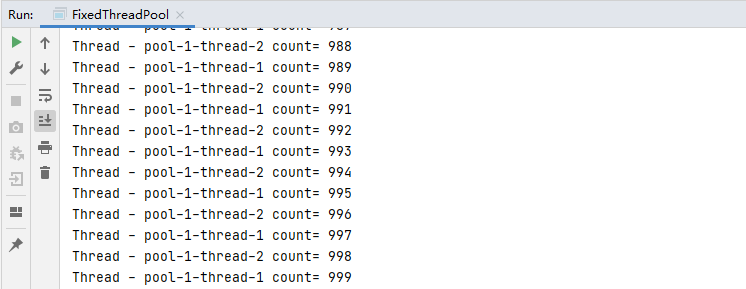
只会使用唯一的工作线程执行任务的线程池:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
public
class
singlethreadexecutor {
private
static
atomicinteger num =
new
atomicinteger(
0
);
private
static
executorservice executorservice = executors.newsinglethreadexecutor();
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
//将coutsum作为task,submit至线程池
for
(
int
i =
0
; i <
2
; i++) {
executorservice.submit(
new
countsum());
}
//task执行完成后关闭
executorservice.shutdown();
}
static
class
countsum
implements
runnable{
@override
public
void
run() {
for
(
int
i =
0
; i <
500
; i++) {
try
{
system.out.println(
"thread - "
+thread.currentthread().getname()+
" count= "
+ num.getandincrement());
thread.sleep(
100
);
}
catch
(exception e){
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
}
}
}
|
结果:
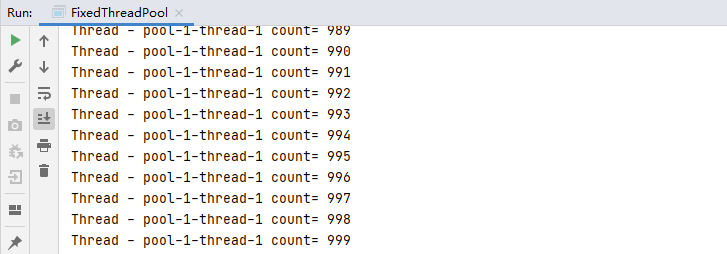
传参值为corepoolsize大小,支持定时及周期性任务执行 。
延期执行示例:调用schedule方法,三个参数:task,delay,timeunit 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
public
class
scheduledthreadpool {
// corepoolsize = 2
private
static
scheduledexecutorservice service = executors.newscheduledthreadpool(
2
);
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
system.out.println(
"thread - "
+thread.currentthread().getname()+
" begin "
+
new
date());
service.schedule(
new
print(),
5
, timeunit.seconds);
service.shutdown();
}
static
class
print
implements
runnable{
@override
public
void
run() {
for
(
int
i =
0
; i <
10
; i++) {
try
{
system.out.println(
"thread - "
+thread.currentthread().getname()+
" delay 5 second and sleep 2 second "
+
new
date());
thread.sleep(
2000
);
}
catch
(exception e){
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
}
}
}
|
结果:

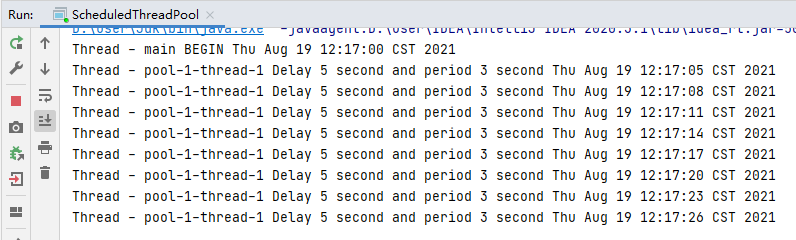
定时执行示例:调用scheduleatfixedrate方法,四个参数:task,initialdelay,period,timeunit 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
public
class
scheduledthreadpool {
// corepoolsize = 1
private
static
scheduledexecutorservice service = executors.newscheduledthreadpool(
1
);
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
system.out.println(
"thread - "
+thread.currentthread().getname()+
" begin "
+
new
date());
service.scheduleatfixedrate(
new
print(),
5
,
3
,timeunit.seconds);
}
static
class
print
implements
runnable{
@override
public
void
run() {
system.out.println(
"thread - "
+thread.currentthread().getname()+
" delay 5 second and period 3 second "
+
new
date());
}
}
}
|
结果:
可缓存线程池,如果线程池长度超过处理需要,回收空闲线程,若无可回收,则新建线程。即若前一个任务已完成,则会接着复用该线程:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
public
class
cachedthreadpool {
private
static
atomicinteger num =
new
atomicinteger(
0
);
private
static
executorservice service = executors.newcachedthreadpool();
public
static
void
main(string[] args) {
countsum c =
new
countsum();
for
(
int
i =
0
; i <
3
; i++) {
try
{
service.submit(c);
thread.sleep(
1000
);
}
catch
(exception e){
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
service.shutdown();
}
static
class
countsum
implements
runnable{
@override
public
void
run() {
for
(
int
i =
0
; i <
1000
; i++) {
system.out.println(
"thread - "
+thread.currentthread().getname()+
" countsum= "
+num.getandincrement());
}
}
}
}
|
结果:thread.sleep(1000)即sleep一秒,上个任务完成可继续复用该线程,不需要创建新的线程 。
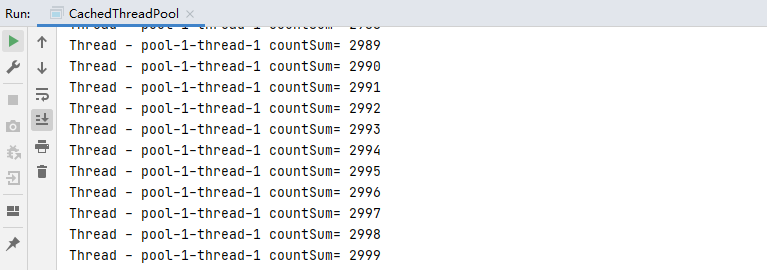
若将tread.sleep(1000)注释掉,你会发现有3个线程在跑 。
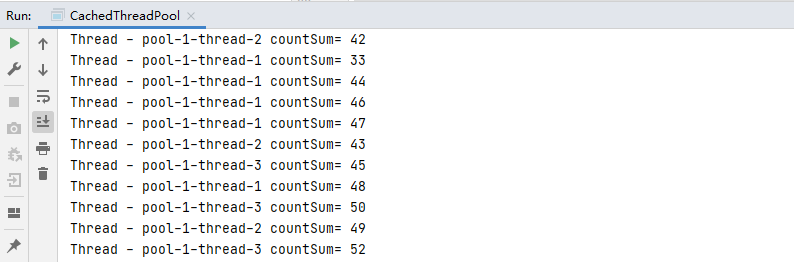
若感兴趣可以去了解一下它们的底层源码,对于cachedthreadpool而言,可新建线程最大数量为integer.maximum 。
以newfixedthreadpool为例 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
public
static
executorservice newfixedthreadpool(
int
nthreads) {
return
new
threadpoolexecutor(nthreads, nthreads,
0l, timeunit.milliseconds,
new
linkedblockingqueue<runnable>());
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
public
threadpoolexecutor(
int
corepoolsize,
int
maximumpoolsize,
long
keepalivetime,
timeunit unit,
blockingqueue<runnable> workqueue) {
this
(corepoolsize, maximumpoolsize, keepalivetime, unit, workqueue,executors.defaultthreadfactory(), defaulthandler);
}
|
线程池七大参数 。
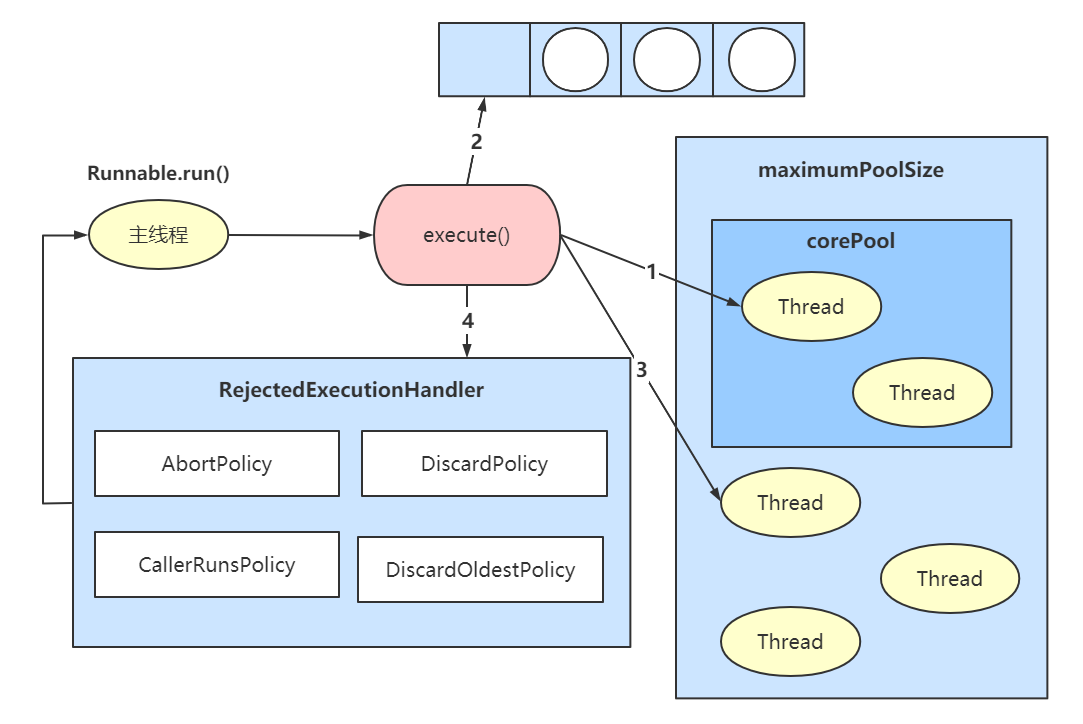
线程池四大流程 。
1)创建线程池后,开始等待请求 。
2)当调用execute()方法添加一个请求任务时,线程池会做以下判断:
3)当一个线程完成任务时,会从等待队列中取下一个任务来执行 。
4)当空闲线程超过keepalivetime定义时间,会判断:
。
note:阿里巴巴java开发手册:线程池不允许使用executors去创建线程池,而是通过使用threadpoolexecutor的方式自定义线程池,规避资源耗尽的风险 。
executors返回的线程池对象的弊端:
1)fixedthreadpool和singlethreadpool:
允许请求队列长度为integer.max_value,可能会堆积大量请求导致oom 。
2)cachedthreadpool和scheduledthreadpool:
允许创建线程数量为integer.max_value,可能会创建大量的线程导致oom 。
。
1)abortpolicy 。
直接抛出rejectedexecutionexception异常阻止系统正常运行 。
2)callerrunspolicy 。
"调用者运行"的调节机制,该策略既不会抛弃任务,也不会抛出异常,而是将某些任务回退到调用者,从而降低新任务的流量 。
3)discardpolicy 。
该策略抛弃无法处理的任务,不予任何处理也不抛出异常。如果允许任务丢失,这是最好的一种策略 。
4)discardoldestpolicy 。
抛弃队列中等待最久的任务,然后把当前任务加入队列中尝试再次提交当前任务 。
。
runtime.getruntime().availableprocessors()方法获取核数 。
cpu密集型 。
maximumpoolsize设为核数+1 。
io密集型 。
maximumpoolsize设为核数/阻塞系数 。
以上就是一篇文章-带你了解threadpool线程池的详细内容,更多关于threadpool线程池的资料请关注我其它相关文章! 。
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/torima/p/15159336.html 。
最后此篇关于一篇文章带你了解Java中ThreadPool线程池的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于一篇文章带你了解Java中ThreadPool线程池的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
运行 PostgreSQL(7.4 和 8.x),我认为这是可行的,但现在我遇到了错误。 我可以单独运行查询,它工作得很好,但如果我使用 UNION 或 UNION ALL,它会抛出错误。 这个错误:
我试图为我的应用程序创建一个导航,使用抽屉导航我的 fragment 之一(HomeFragment)有一个 ViewPager,可容纳 3 个 fragment (Bundy Clock、Annou
以我目前正在开发的应用为例: - 它有一个包含多个项目的抽屉导航;现在有两个项目让我感兴趣,我将它们称为 X 和 Y。 X 和 Y 都在单击时显示包含 x 元素或 y 元素列表的 fragment 选
我有一个形状为 (370,275,210) 的 NumPy 数组,我想将其重新整形为 (275,210,370)。我将如何在 Python 中实现这一点? 370是波段数,275是行数,210是图像包
我们如何与被子 UIViewController 阻止的父 UIViewController(具有按钮)交互。显然,触摸事件不会通过子 Nib 。 (启用用户交互) 注意:我正在加载默认和自定义 NI
我是 Jpa 新手,我想执行过程 我的代码如下 private static final String PERSISTENCE_UNIT_NAME = "todos"; private static
与安装了 LAMP 的 GCE 相比,选择与 Google Cloud SQL 链接的 GCE 实例有哪些优势? 我确定 GCE 是可扩展的,但是安装在其上的 mysql 数据库的可扩展性如何? 使用
这个问题在这里已经有了答案: Value receiver vs. pointer receiver (3 个答案) 关闭 3 年前。 我刚接触 golang。只是想了解为 Calc 类型声明的两种
我不小心按了一个快捷键,一个非常漂亮的断线出现在日期上。 有点像 # 23 Jun 2010 -------------------- 有人知道有问题的快捷方式吗?? (我在 mac 上工作!) 在
我正在Scala中编写正则表达式 val regex = "^foo.*$".r 这很好,但是如果我想做 var x = "foo" val regex = s"""^$x.*$""".r 现在我们有
以下 XML 文档在技术上是否相同? James Dean 19 和: James Dean 19 最佳答案 这两个文档在语义上是相同的。在 X
我在对数据帧列表运行稳健的线性回归模型(使用 MASS 库中的 rlm)时遇到问题。 可重现的示例: var1 <- c(1:100) var2 <- var1*var1 df1 <- data.f
好的,我有一个自定义数字键盘,可以在标签(numberField)中将数字显示为 0.00,现在我需要它显示 $0.00。 NSString *digit = sender.currentTitle;
在基于文档的应用程序中,使用 XIB 文件,创建新窗口时其行为是: 根据最后一个事件的位置进行定位和调整大小 window 。 如果最后一个事件窗口仍然可见,则新窗口 窗口应该是级联的,这样它就不会直
我想使用参数进行查询,如下所示: SELECT * FROM MATABLE WHERE MT_ID IN (368134, 181956) 所以我考虑一下 SELECT * FROM MATABLE
我遇到一些性能问题。 我有一个大约有 200 万行的表。 CREATE TABLE [dbo].[M8]( [M8_ID] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
我在 jquery 中的按键功能遇到问题。我不知道为什么按键功能不起作用。我已经使用了正确的 key 代码。在我的函数中有 2 个代码,其中包含 2 个事件键,按一个键表示 (+) 代码 107 和(
我想显示音频波形,我得到了此代码,它需要.raw音频输入并显示音频波形,但是当我放入.3gp,.mp3音频时,我得到白噪声,有人可以帮助我如何使其按需与.3gp一起使用使用.3gp音频运行它。 Inp
我无法让 stristr 函数返回真值,我相信这是因为我的搜索中有一个 $ 字符。 当我这样做时: var_dump($nopricecart); 完整的 $nopricecart 值是 $0 ,我得
如果我有这样的循环: for(int i=0;i O(n) 次。所以do some执行了O(n)次。如果做某事是线性时间,那么代码片段的复杂度是O(n^2)。 关于algorithm - 带 If 语

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!