- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章pandas针对excel处理的实现由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
本文主要介绍了pandas针对excel处理的实现,分享给大家,具体如下:
import padasdf = pd.read_csv("") #读取文件pd.read_clipboard() #读取粘贴板的内容#解决数据显示不完全的问题pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)pd.set_option('display.max_rows', None)#获取指定单元格的值datefirst = config.iloc[0,1]datename = config.iloc[0,2]#新建一列two,筛选料号一列的前俩个sheet["two"] = sheet["料号"].apply(lambda x:x[:2])
df["dog"] = df["dog"].replace(-1,0) #数值替换#apply理解函数作为一个对象,可以作为参数传递给其它参数,并且能作为函数的返回值df["price_new"] = df["price"].apply(lambda pri:pyi.lower()) #新列对老列处理df["pricee"] = df["price"] *2 #新列
data = df.head() #默认读取前行df = pd.read_excel("lemon.xlsx",sheet_name=["python","student"]) #可以通过表单名同时读取多个df = pd.read_excel("lemon.clsx",sheet_name=0) data = df.values #获取所有的数据print("获取到所有的值:\n{0}".format(data)) #格式化输出df = pd.read_excel("lemon.xlsx")data = df.ix[0].values #表示第一行,不包含表头print("获取到所有的值:\n{0}".format(data)) #格式化输出
loc[row,cloumn] 先行后列 : 是全部行或列,一般多行可以用中括号,连续的可以用a:c等iloc[index,columns] 行索引,列索引,索引都是从0开始,用法是一样的
多行嵌套df = pd.read_excel("lemon.xlsx")data = df.loc[1,2] #读取指定多行的话,就要在ix[]里面嵌套列表指定行数print("获取到所有的值:\n{0}".format(data)) #格式化输出多行df=pd.read_excel('lemon.xlsx')data=df.ix[1,2]#读取第一行第二列的值,这里不需要嵌套列表print("读取指定行的数据:\n{0}".format(data))多行多列嵌套df=pd.read_excel('lemon.xlsx')data=df.ix[[1,2],['title','data']].values#读取第一行第二行的title以及data列的值,这里需要嵌套列表print("读取指定行的数据:\n{0}".format(data))获取所有行和指定列df=pd.read_excel('lemon.xlsx')data=df.ix[:,['title','data']].values#读所有行的title以及data列的值,这里需要嵌套列表print("读取指定行的数据:\n{0}".format(data))
输出行号并打印输出df=pd.read_excel('lemon.xlsx')print("输出行号列表",df.index.values)输出结果是:输出行号列表 [0 1 2 3]输出列名并打印输出df=pd.read_excel('lemon.xlsx')print("输出列标题",df.columns.values)运行结果如下所示:输出列标题 ['case_id' 'title' 'data']获取指定行数的值df=pd.read_excel('lemon.xlsx')print("输出值",df.sample(3).values)#这个方法类似于head()方法以及df.values方法输出值 [[2 '输入错误的密码' '{"mobilephone":"18688773467","pwd":"12345678"}'] [3 '正常充值' '{"mobilephone":"18688773467","amount":"1000"}'] [1 '正常登录' '{"mobilephone":"18688773467","pwd":"123456"}']]
获取指定列的值df=pd.read_excel('lemon.xlsx')print("输出值\n",df['data'].values)excel数据转字典df=pd.read_excel('lemon.xlsx')test_data=[]for i in df.index.values:#获取行号的索引,并对其进行遍历: #根据i来获取每一行指定的数据 并利用to_dict转成字典 row_data=df.ix[i,['case_id','module','title','http_method','url','data','expected']].to_dict() test_data.append(row_data)print("最终获取到的数据是:{0}".format(test_data))
把带有空值的行全部去除df.dropna()对空置进行填充df.fillna(value=0)df["price"].fillna(df["price".mean()])去除字符串两边的空格df["city"] = df["city"].map(str.strip)大小写转换df["city"] = df["city"].map(str.lower)更改数据格式df["price"].fillna(0).astype("int")更改列的名称df.rename(columns={"category":"category_size"})删除重复项df["city"].drop_duplicates()df["city"].drop_duplicates(keep="last")数字修改和替换df["city"].replace("sh","shanghai")前3行数据df.tail(3)给出行数和列数data.describe()打印出第八行data.loc[8]打印出第八行[column_1]的列data.loc[8,column_1]第四到第六行(左闭右开)的数据子集data.loc[range(4,6)]统计出现的次数data[column_1].value_counts()len()函数被应用在column_1列中的每一个元素上map()运算给每一个元素应用一个的函数data[column_1].map(len).map(lambda x : x/100).plot() plot是绘图apply() 给一个列应用一个函数applymap() 会给dataframe中的所有单元格应用一个函数遍历行和列for i,row in data.iterrows(): print(i,row)选择指定数据的行important_dates = ['1/20/14', '1/30/14']data_frame_value_in_set = data_frame.loc[data_frame['Purchase Date']\.isin(important_dates), :]选择0-3列import pandas as pdimport sysinput_file = r"supplier_data.csv"output_file = r"output_files\6output.csv"data_frame = pd.read_csv(input_file)data_frame_column_by_index = data_frame.iloc[:, [0, 3]]data_frame_column_by_index.to_csv(output_file, index=False)添加行头import pandas as pdinput_file = r"supplier_data_no_header_row.csv"output_file = r"output_files\11output.csv"header_list = ['Supplier Name', 'Invoice Number', \'Part Number', 'Cost', 'Purchase Date']data_frame = pd.read_csv(input_file, header=None, names=header_list)data_frame.to_csv(output_file, index=False)
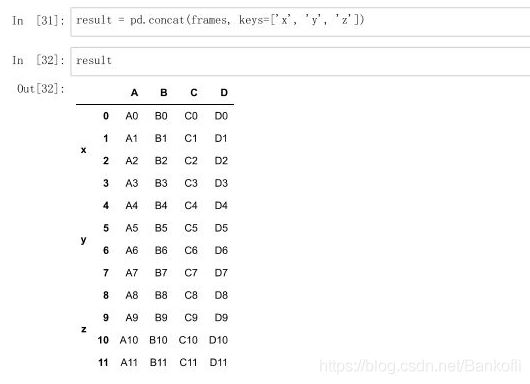
数据合并1.将表格通过concat()方法进行合并参数如下:objs(必须参数):参与连接的pandas对象的列表或字典axis:指明连接的轴向,默认为0join:选中inner或outer(默认),其它轴向上索引是按交集(inner)还是并集(outer)进行合并join_axes:指明用于其他N-1条轴的索引,不执行并集/交集运算keys:与连接对象有关的值,用于形成连接轴向上的层次化索引verify_integrity:是否去重ignore_index:是否忽略索引合并:eg:frames = [df1,df2,df3]result = pd.concat(frames)result = pd.concat(frames,keys=["x","y","z"]) #把每张表来个定义
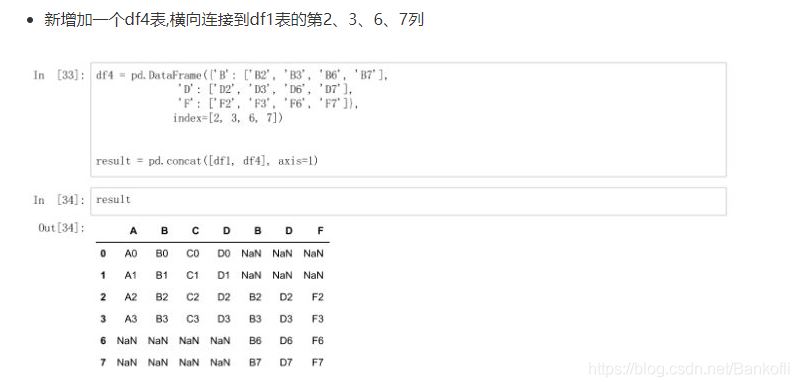
新增df4表,横向连接到df1表的第2367列,空置补nanindex:是新增的行axis=1是指列df4 = pd.DataFrame(["B":["sf"],"D":["'sf],index=[2,3,6,7]])result = pd.concat([df1,df4],axis=1)
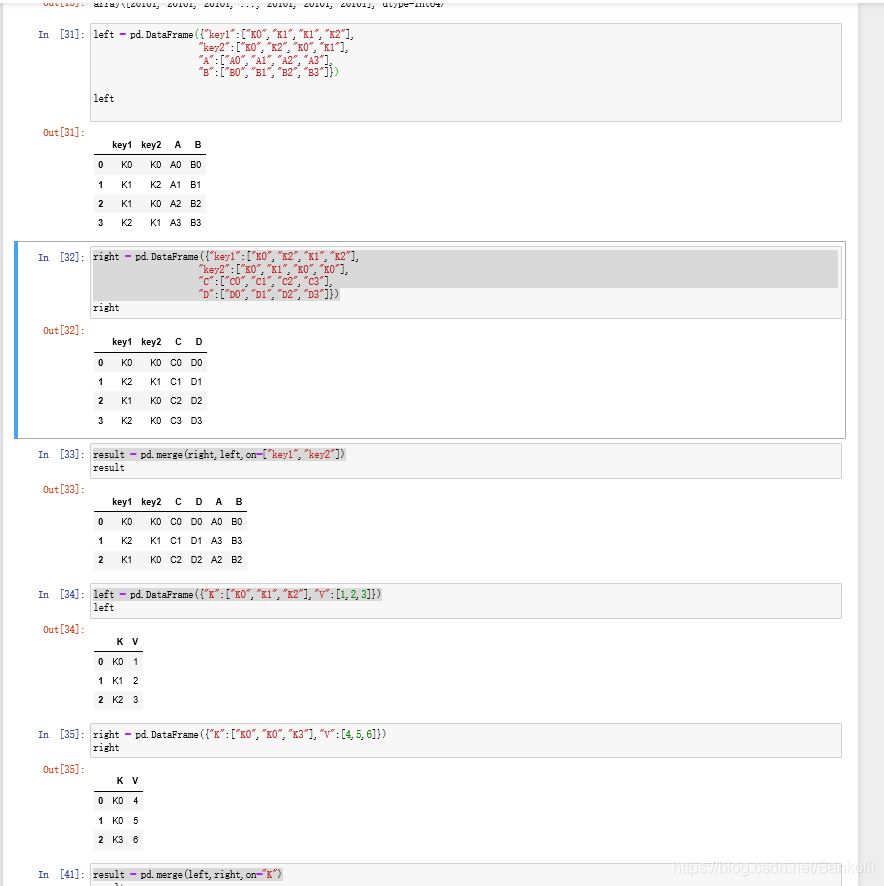
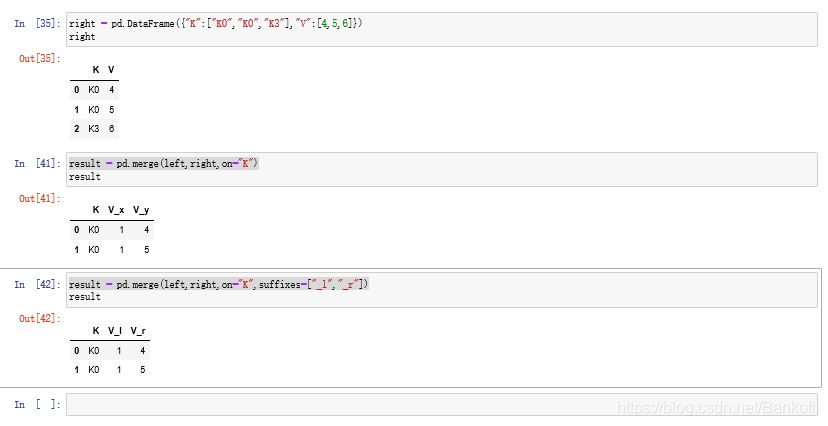
将df1和df4横向进行交集合并result = pd.concat([df1,df4],axis=1,join="inner") 列是增加,行是交集按照df1的索引进行df1表和df4表的横向索引pd.concat([df1,df4],axis=1,join_axes=[df1.index]) 列是增加,行以df1为准,空的为NaN通过append()方法连接表格result = df1.append(df2)result = df1.append(df4,ignore_index=True) 空格Nan补充新增一列s1表,并且跟df1进行横向合并s1 = pd.Series(["1","2","3","4"],name="x")result = pd.concat([df1,s1],axis=1) name是列,serise是一维列表,没有name,他会用索引0开始继续填充pd.concat([df1,s1],axis=1,ignore_index=True) 表格合并后不保留原来的索引列名将key作为两张表连接的中介result = pd.merge(left,right,on="key")result = pd.merge(right,left,on=["key1","key2"])key1和key2,只要有相同值就行,最后的排列是大的值为key1,小的key2通过左表索引连接右表right = pd.DataFrame({"key1":["K0","K2","K1","K2"], "key2":["K0","K1","K0","K0"], "C":["C0","C1","C2","C3"], "D":["D0","D1","D2","D3"]}, index = ["k0","k1","k2"])result = left.join(right) 以做索引为基准,right没有左索引的用Nan填充result = left.join(right,how='outer') how:连接方式on属性在merge中,以k为中心拼接,有相同的就拼result = pd.merge(left,right,on="K")result = pd.merge(left,right,on="K",suffixes=["_l","_r"]) 更改拼接后的neme属性
# 解决显示不完全的问题pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)pd.set_option('display.max_rows', None)config = pd.read_excel("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\数据\\文件名配置.xlsx", dtype=object)datefirst = config.iloc[0, 1]datename = config.iloc[0, 2]dateall = datefirst + r"\\" + datenametextfile = config.iloc[1, 1]textname = config.iloc[1, 2]textall = textfile + r"\\" + textnamesheet = pd.read_excel(dateall, sheet_name="Sheet2", dtype=object)sheet["two"] = sheet["料号"].apply(lambda x: x[:2])# 取出不包含的数据df = sheet[~sheet["two"].isin(["41", "48"])]df1 = df[~df["检验结果"].isin(["未验", "试产验证允收"])]# 删除不需要的列result = df1.iloc[:, :len(df1.columns) - 1]# 取出包含的数据DTR561 = result[result["机种"].isin(["DTR561"])]DTR562 = result[result["机种"].isin(["DTR562"])]HPS322 = result[result["机种"].isin(["HPS322"])]HPS829 = result[result["机种"].isin(["HPS829"])]writer = pd.ExcelWriter("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\数据\\数据筛选.xlsx")result.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="全部机种", index=False)DTR561.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="DTR561", index=False)DTR562.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="DTR562", index=False)HPS322.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="HPS322", index=False)HPS829.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="HPS829", index=False)writer.save()print("Data filtering completed")
到此这篇关于pandas针对excel处理的实现的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关pandas excel处理内容请搜索我以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我! 。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/Bankofli/article/details/107553739 。
最后此篇关于pandas针对excel处理的实现的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于pandas针对excel处理的实现的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
对于 Metal ,如果对主纹理进行 mipmap 处理,是否还需要对多采样纹理进行 mipmap 处理?我阅读了苹果文档,但没有得到任何相关信息。 最佳答案 Mipmapping 适用于您将从中
我正在使用的代码在后端 Groovy 代码中具有呈现 GSP(Groovy 服务器页面)的 Controller 。对于前端,我们使用 React-router v4 来处理路由。我遇到的问题是,通过
我们正在 build 一个巨大的网站。我们正在考虑是在服务器端(ASP .Net)还是在客户端进行 HTML 处理。 例如,我们有 HTML 文件,其作用类似于用于生成选项卡的模板。服务器端获取 HT
我正在尝试将图像加载到 void setup() 中的数组中,但是当我这样做时出现此错误:“类型不匹配,'processing .core.PImage' does not匹配“processing.
我正在尝试使用其私有(private)应用程序更新 Shopify 上的客户标签。我用 postman 尝试过,一切正常,但通过 AJAX,它带我成功回调而不是错误,但成功后我得到了身份验证链接,而不
如何更改我的 Processing appIconTest.exe 导出的默认图标在窗口中的应用程序? 默认一个: 最佳答案 经过一些研究,我能找到的最简单的解决方案是: 进入 ...\process
我在 Processing 中做了一个简单的小游戏,但需要一些帮助。我有一个 mp3,想将它添加到我的应用程序中,以便在后台循环运行。 这可能吗?非常感谢。 最佳答案 您可以使用声音库。处理已经自带
我有几个这样创建的按钮: 在 setup() PImage[] imgs1 = {loadImage("AREA1_1.png"),loadImage("AREA1_2.png"),loadImage
我正在尝试使用 Processing 创建一个多人游戏,但无法弄清楚如何将屏幕分成两个以显示玩家的不同情况? 就像在 c# 中一样,我们有Viewport leftViewport,rightView
我一直在尝试使用 Moore 邻域在处理过程中创建元胞自动机,到目前为止非常成功。我已经设法使基本系统正常工作,现在我希望通过添加不同的功能来使用它。现在,我检查细胞是否存活。如果是,我使用 fill
有没有办法用 JavaScript 代码检查资源使用情况?我可以检查脚本的 RAM 使用情况和 CPU 使用情况吗? 由于做某事有多种方法,我可能会使用不同的方法编写代码,并将其保存为两个不同的文件,
我想弄清楚如何处理这样的列表: [ [[4,6,7], [1,2,4,6]] , [[10,4,2,4], [1]] ] 这是一个整数列表的列表 我希望我的函数将此列表作为输入并返回列表中没有重复的整
有没有办法在不需要时处理 MethodChannel/EventChannel ?我问是因为我想为对象创建多个方法/事件 channel 。 例子: class Call { ... fields
我有一个关于在 Python3 中处理 ConnectionResetError 的问题。这通常发生在我使用 urllib.request.Request 函数时。我想知道如果我们遇到这样的错误是否可
我一直在努力解决这个问题几个小时,但无济于事。代码很简单,一个弹跳球(粒子)。将粒子的速度初始化为 (0, 0) 将使其保持上下弹跳。将粒子的初始化速度更改为 (0, 0.01) 或任何十进制浮点数都
我把自己弄得一团糟。 我想在我的系统中添加 python3.6 所以我决定在我的 Ubuntu 19.10 中卸载现有的。但是现在每次我想安装一些东西我都会得到这样的错误: dpkg: error w
我正在努力解决 Rpart 包中的 NA 功能。我得到了以下数据框(下面的代码) Outcome VarA VarB 1 1 1 0 2 1 1 1
我将 Java 与 JSF 一起使用,这是 Glassfish 3 容器。 在我的 Web 应用程序中,我试图实现一个文件(图像)管理系统。 我有一个 config.properties我从中读取上传
所以我一直在Processing工作几个星期以来,虽然我没有编程经验,但我已经转向更复杂的项目。我正在编写一个进化模拟器,它会产生具有随机属性的生物。 最终,我将添加复制,但现在这些生物只是在屏幕上漂
有人知道 Delphi 2009 对“with”的处理有什么不同吗? 我昨天解决了一个问题,只是将“with”解构为完整引用,如“with Datamodule、Dataset、MainForm”。

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!