- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章基于@ComponentScan注解的使用详解由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
。
。
@ComponentScan注解的定义如下:
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Target(ElementType.TYPE)@Documented@Repeatable(ComponentScans.class)public @interface ComponentScan { /** * 扫描路径 * @ComponentScan(value = "spring.annotation.componentscan") */ @AliasFor("basePackages") String[] value() default {}; /** * 扫描路径 */ @AliasFor("value") String[] basePackages() default {}; /** * 指定扫描类 * @ComponentScan(basePackageClasses = {BookDao.class, BookService.class}) */ Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {}; /** * 命名注册的Bean,可以自定义实现命名Bean, * 1、@ComponentScan(value = "spring.annotation.componentscan",nameGenerator = MyBeanNameGenerator.class) * MyBeanNameGenerator.class 需要实现 BeanNameGenerator 接口,所有实现BeanNameGenerator 接口的实现类都会被调用 * 2、使用 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 的 setBeanNameGenerator方法注入一个BeanNameGenerator * BeanNameGenerator beanNameGenerator = (definition,registry)-> String.valueOf(new Random().nextInt(1000)); * AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(); * annotationConfigApplicationContext.setBeanNameGenerator(beanNameGenerator); * annotationConfigApplicationContext.register(MainConfig2.class); * annotationConfigApplicationContext.refresh(); * 第一种方式只会重命名@ComponentScan扫描到的注解类 * 第二种只有是初始化的注解类就会被重命名 * 列如第一种方式不会重命名 @Configuration 注解的bean名称,而第二种就会重命名 @Configuration 注解的Bean名称 */ Class<? extends BeanNameGenerator> nameGenerator() default BeanNameGenerator.class; /** * 用于解析@Scope注解,可通过 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 的 setScopeMetadataResolver 方法重新设定处理类 * ScopeMetadataResolver scopeMetadataResolver = definition -> new ScopeMetadata(); 这里只是new了一个对象作为演示,没有做实际的逻辑操作 * AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(); * annotationConfigApplicationContext.setScopeMetadataResolver(scopeMetadataResolver); * annotationConfigApplicationContext.register(MainConfig2.class); * annotationConfigApplicationContext.refresh(); * 也可以通过@ComponentScan 的 scopeResolver 属性设置 *@ComponentScan(value = "spring.annotation.componentscan",scopeResolver = MyAnnotationScopeMetadataResolver.class) */ Class<? extends ScopeMetadataResolver> scopeResolver() default AnnotationScopeMetadataResolver.class; /** * 用来设置类的代理模式 */ ScopedProxyMode scopedProxy() default ScopedProxyMode.DEFAULT; /** * 扫描路径 如 resourcePattern = "**/*.class" * 使用 includeFilters 和 excludeFilters 会更灵活 */ String resourcePattern() default ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider.DEFAULT_RESOURCE_PATTERN; /** * 指示是否应启用对带有{@code @Component},{@ code @Repository}, * {@ code @Service}或{@code @Controller}注释的类的自动检测。 */ boolean useDefaultFilters() default true; /** * 对被扫描的包或类进行过滤,若符合条件,不论组件上是否有注解,Bean对象都将被创建 * @ComponentScan(value = "spring.annotation.componentscan",includeFilters = { * @ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION, classes = {Controller.class, Service.class}), * @ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE, classes = {SchoolDao.class}), * @ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = {MyTypeFilter.class}), * @ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ASPECTJ, pattern = "spring.annotation..*"), * @ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.REGEX, pattern = "^[A-Za-z.]+Dao$") * },useDefaultFilters = false) * useDefaultFilters 必须设为 false */ Filter[] includeFilters() default {}; /** * 指定哪些类型不适合进行组件扫描。 * 用法同 includeFilters 一样 */ Filter[] excludeFilters() default {}; /** * 指定是否应注册扫描的Bean以进行延迟初始化。 * @ComponentScan(value = "spring.annotation.componentscan",lazyInit = true) */ boolean lazyInit() default false; /** * 用于 includeFilters 或 excludeFilters 的类型筛选器 */ @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({}) @interface Filter { /** * 要使用的过滤器类型,默认为 ANNOTATION 注解类型 * @ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION, classes = {Controller.class, Service.class}) */ FilterType type() default FilterType.ANNOTATION; /** * 过滤器的参数,参数必须为class数组,单个参数可以不加大括号 * 只能用于 ANNOTATION 、ASSIGNABLE_TYPE 、CUSTOM 这三个类型 * @ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION, value = {Controller.class, Service.class}) * @ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE, classes = {SchoolDao.class}) * @ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = {MyTypeFilter.class}) */ @AliasFor("classes") Class<?>[] value() default {}; /** * 作用同上面的 value 相同 * ANNOTATION 参数为注解类,如 Controller.class, Service.class, Repository.class * ASSIGNABLE_TYPE 参数为类,如 SchoolDao.class * CUSTOM 参数为实现 TypeFilter 接口的类 ,如 MyTypeFilter.class * MyTypeFilter 同时还能实现 EnvironmentAware,BeanFactoryAware,BeanClassLoaderAware,ResourceLoaderAware * 这四个接口 * EnvironmentAware * 此方法用来接收 Environment 数据 ,主要为程序的运行环境,Environment 接口继承自 PropertyResolver 接口, * 详细内容在下方 * @Override * public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) { * String property = environment.getProperty("os.name"); * } * * BeanFactoryAware * BeanFactory Bean容器的根接口,用于操作容器,如获取bean的别名、类型、实例、是否单例的数据 * @Override * public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { * Object bean = beanFactory.getBean("BeanName") * } * * BeanClassLoaderAware * ClassLoader 是类加载器,在此方法里只能获取资源和设置加载器状态 * @Override * public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) { * ClassLoader parent = classLoader.getParent(); * } * * ResourceLoaderAware * ResourceLoader 用于获取类加载器和根据路径获取资源 * public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) { * ClassLoader classLoader = resourceLoader.getClassLoader(); * } */ @AliasFor("value") Class<?>[] classes() default {}; /** * 这个参数是 classes 或 value 的替代参数,主要用于 ASPECTJ 类型和 REGEX 类型 * ASPECTJ 为 ASPECTJ 表达式 * @ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ASPECTJ, pattern = "spring.annotation..*") * REGEX 参数为 正则表达式 * @ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.REGEX, pattern = "^[A-Za-z.]+Dao$") */ String[] pattern() default {}; }}
。
。
创建Maven项目,添加依赖:
<dependencies> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-context --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>4.3.26.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/junit/junit --> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies>
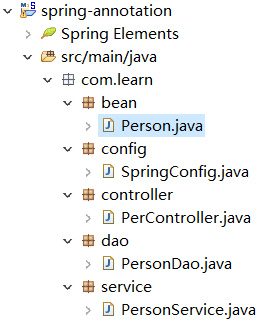
创建bean,controller,dao,service层,并在类上加上对应的注解,项目结构如下:
编写测试类,如下:
public class IoCTest { @Test public void test01() { //获取Spring的IOC容器 ApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class); //从容器中获取bean String[] names= applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames(); for(String i:names) { System.out.println(i); } }}
。
使用excludeFilters不扫描com.learn包中的Controller、Service注解,如下:
@Configuration@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.learn",excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class,Service.class})})public class SpringConfig {}
上面使用的excludeFilters用于设置排除的过滤条件,实现Filter接口的type属性用于设置过滤类型,默认值为FilterType.ANNOTATION,提供了这几个过滤类型:
FilterType.ANNOTATION:按照注解过滤FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE:按照给定的类型过滤FilterType.ASPECTJ:按照ASPECTJ表达式过滤FilterType.REGEX:按照正则表达式过滤FilterType.CUSTOM:按照自定义规则过滤classes和value属性为过滤器的参数,必须为class数组,类只能为以下三种类型:
ANNOTATION 参数为注解类,如 Controller.class, Service.class,Repository.classASSIGNABLE_TYPE 参数为类,如 SchoolDao.classCUSTOM 参数为实现 TypeFilter 接口的类 ,如 MyTypeFilter.class。
includeFilters属性用于定义扫描过滤条件,满足该条件才进行扫描。用法与excludeFilters一样.
但是因为useDefaultFilters属性默认为true,即使用默认的过滤器,启用对带有@Component,@Repository,@Service,@Controller注释的类的自动检测。会将带有这些注解的类注册为bean装配到IoC容器中。所以使用includeFilters时,需要把useDefaultFilters设置为false,如下:
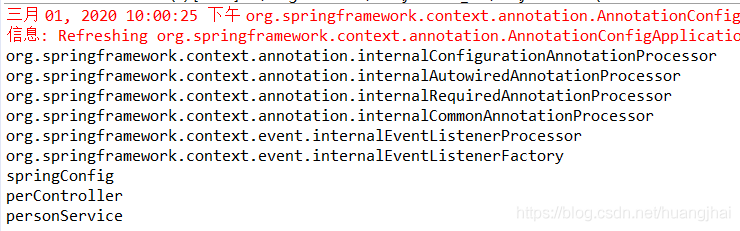
@Configuration@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.learn",includeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class,Service.class})},useDefaultFilters = false)public class SpringConfig {}
结果如下,只扫描了带有Controller,Service注解的自定义的类:
。
@ComponentScan注解扫描或解析的bean只能是Spring内部所定义的,比如@Component、@Service、@Controller或@Repository。如果要扫描一些自定义的注解,就可以自定义过滤规则来完成这个操作.
自定义一个类MyTypeFilter实现TypeFilter接口,这样这个TypeFilter就扫描所有类并只通过类名包含了controller的类,如下:
public class MyTypeFilter implements TypeFilter { /** * 两个参数的含义: * metadataReader:包含读取到的当前正在扫描的类的信息 * metadataReaderFactory:可以获取到当前正在扫描的类的其他类信息(如父类和接口) * match方法返回false即不通过过滤规则,true通过过滤规则 */ @Override public boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) throws IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub //获取当前类注解的信息 AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata(); //获取当前正在扫描的类的类信息 ClassMetadata classMetadata = metadataReader.getClassMetadata(); //获取当前类资源(类的路径) Resource resource = metadataReader.getResource(); String className = classMetadata.getClassName(); if(className.contains("controller")){ return true; } return false; }}
在@ComponentScan注解中进行配置,如下:
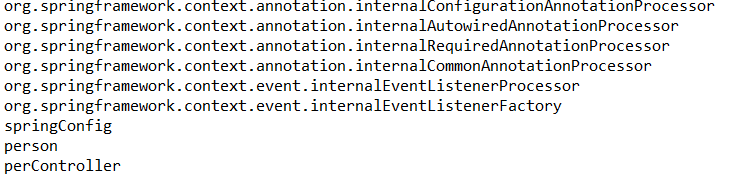
@Configuration@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.learn",includeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE,classes = {Person.class}), @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM,classes = {MyTypeFilter.class}),},useDefaultFilters = false)public class SpringConfig {}
经过上面的配置,第一个@Filter通过FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE规定了只扫描Person类型的类,第二个@Filter通过FilterType.CUSTOM自定义过滤规则规定了只扫描类名包含controller的类。结果:
。
@ComponentScan注解可以扫描 任意 类 或者 注解 中内部类bean; 。
要想被扫描的前提是内部类标注了@Component及其相关衍生注解、内部类必须是static修饰,否则扫描不到;如果是注解的内部类则只能是public static修饰 。
//@Configurationpublic class ProfileConfig { @Component("class1") private static class Class1 { @Bean public Class3 class3() { return new Class3(); } } @Component("class2") static class Class2 { } //@Component("class3") protected static class Class3 { }// @Component("class4") //出错// protected class Class4 {//// }}--------------------------------------------------------@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Target(ElementType.METHOD)//@Beanpublic @interface MyBean { public static final int age1=3; //常量可以 int age=2; public abstract String value() default "qwer"; //属性可以 //内部类可以 @Component @DependsOn("myBean.EventZ") //依赖事件bean的创建,保证该bean在事件bean之后创建 //细节:因为是内部类,所以默认bean的id是类名首字母小写,不是eventZ而是myBean.EventZ class EventSource { public EventSource(){ System.out.println("事件源创建了..."); } } @Component//("eventZ") public static class EventZ { public EventZ(){ System.out.println("事件创建了..."); } }}
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我.
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/huangjhai/article/details/104600328 。
最后此篇关于基于@ComponentScan注解的使用详解的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于基于@ComponentScan注解的使用详解的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
注解@CrossOrigin 出于安全原因,浏览器禁止Ajax调用驻留在当前原点之外的资源。例如,当你在一个标签中检查你的银行账户时,你可以在另一个选项卡上拥有EVILL网站。来自EVILL的脚本
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界. 这篇CFSDN的博客文章深入理解Java高级特性——注解由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,
概述 在这个快速教程中,我们将探索 Spring 的 @RequestParam 注解。 简单地说,我们可以使用 @RequestParam 从请求中提取查询参数、表单参数甚至文件。我们将讨论如何使用
我有一个关于 Spring @Async 注释的问题。我有一个 Controller 自动连接了一个服务(GnInsuranceDetailsService) @RequestMapping(va
我在使用注释来调用注释所属的方法时遇到了一些麻烦......我将举一个例子: class MyEventHandlers { @handler(id=“1”) public doSom
我是.Net程序员,但是这次我正在从事Java项目,并且遇到了一些困难。这个 java 项目不是我的,它是由其他开发人员开发的,并且使用 Hibernate。 当我运行 Ant 构建器时,我收到此错误
我在 Grails 文档(第 9 章:测试)中读到过这个注解。但是我不明白这是什么... 问题是我需要模拟 GORM 的动态方法,有一种方法可以自动模拟它们,而不必编写我需要的所有方法吗? 最佳答案
这个问题在这里已经有了答案: How to get annotation class name, attribute values using reflection (2 个答案) 关闭 5 年前。
如何了解 Java EE 6 JMS 注释规范支持的所有有效属性集@ActivationConfigProperty Java EE 6 Documentation for @ActivationCo
我认为这是不可能的,但也许我错了。所以我问你,如果可能的话。 ;-) 如果我定义了一个注释,它只接受类引用,它扩展了一些可能的接口(interface)或类: Class serviceIFProv
我正在尝试使用 javax.validation 验证一些 DTO,但似乎注释 @NotEmpty 没有检查参数是否为 null。 这是我的类(class): Person.class public
我是 hibernate 新手,我正在尝试学习它,但在尝试使一对多关系正常工作时遇到了问题。我尝试了几个例子,但似乎没有一个起作用。 有人可以看一下下面的代码并告诉我哪里出了问题吗?我尝试了很多不同的
这个问题已经有答案了: Why doesn't Java offer operator overloading? (17 个回答) 已关闭 9 年前。 每个人都知道 Java 中的简单算术如何用于基元
有人知道如何用 Python 处理这种 XML 注释,这是我第一次看到。 <?link id="752760" resource-uuid="UUID-9f0575a3-1847-1cde-fd
我遇到了这个link这解释了如何继承 bean。假设此示例中的 HelloWorld 类使用 @Component 注释作为 bean 公开,如何创建另一个继承此 bean 的 bean?我可以使用
谁能告诉我这段代码是否: public class OvTester { @Override public int hashCode() { return toStri
我有一个实体,它有一个非键列,我已将其设置为在我的数据库中自动生成。 我不能使用 @GeneratedValue,因为据我所知,它仅适用于关键字段。 在这种情况下,如何指示非键列是自动生成的? 最佳答
所以可能像很多人一样,我通常会临时注释掉代码,主要是为了调试目的。我目前放了类似 **DEBUG** 或任何容易搜索的内容,但我认为让编译器在发现临时注释掉的代码时输出警告(甚至错误)可能很有用。我想
此组件解决的问题是: 「谁」在「什么时间」对「什么」做了「什么事」 本组件目前针对 Spring-boot 做了 Autoconfig,如果是 SpringMVC,也可自己在 xml 初始化 b
配置全局乱码过滤器 参数绑定注解@RequestParam 注解@RequestParam的参数使用说明 获得Restful风格的参数 自定义类型转换器 自定义转换器的开发步骤: 获得Servlet相

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!