- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章Java之Jackson的基本使用案例讲解由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
Jackson 是当前用的比较广泛的,用来序列化和反序列化 json 的 Java 的开源框架。Jackson 社 区相对比较活跃,更新速度也比较快, 从 Github 中的统计来看,Jackson 是最流行的 json 解析器之一 。 Spring MVC 的默认 json 解析器便是 Jackson。 Jackson 优点很多。 Jackson 所依赖的 jar 包较少 ,简单易用。与其他 Java 的 json 的框架 Gson 等相比, Jackson 解析大的 json 文件速度比较快;Jackson 运行时占用内存比较低,性能比较好;Jackson 有灵活的 API,可以很容易进行扩展和定制.
Jackson 的 1.x 版本的包名是 org.codehaus.jackson ,当升级到 2.x 版本时,包名变为 com.fasterxml.jackson,本文讨论的内容是基于最新的 Jackson 的 2.9.1 版本.
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<
dependency
>
<
groupId
>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</
groupId
>
<
artifactId
>jackson-databind</
artifactId
>
<
version
>2.9.1</
version
>
</
dependency
>
|
jackson-databind 依赖 jackson-core 和 jackson-annotations,当添加 jackson-databind 之后, jackson-core 和 jackson-annotations 也随之添加到 Java 项目工程中。在添加相关依赖包之后,就可以使用 Jackson.
Jackson 最常用的 API 就是基于"对象绑定" 的 ObjectMapper。下面是一个 ObjectMapper 的使用的简单示例.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
ObjectMapper mapper =
new
ObjectMapper();
Person person =
new
Person();
person.setName(
"Tom"
);
person.setAge(
40
);
String jsonString = mapper.writerWithDefaultPrettyPrinter()
.writeValueAsString(person);
Person deserializedPerson = mapper.readValue(jsonString, Person.
class
);
|
ObjectMapper 通过 writeValue 系列方法 将 java 对 象序列化 为 json,并 将 json 存 储成不同的格式,String(writeValueAsString),Byte Array(writeValueAsString),Writer, File,OutStream 和 DataOutput.
ObjectMapper 通过 readValue 系列方法从不同的数据源像 String , Byte Array, Reader,File,URL, InputStream 将 json 反序列化为 java 对象.
在调用 writeValue 或调用 readValue 方法之前,往往需要设置 ObjectMapper 的相关配置信息。这些配置信息应用 java 对象的所有属性上。示例如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
//在反序列化时忽略在 json 中存在但 Java 对象不存在的属性
mapper.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES,
false
);
//在序列化时日期格式默认为 yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSZ
mapper.configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS,
false
)
//在序列化时忽略值为 null 的属性
mapper.setSerializationInclusion(Include.NON_NULL);
//忽略值为默认值的属性
mapper.setDefaultPropertyInclusion(Include.NON_DEFAULT);
|
更多配置信息可以查看 Jackson 的 DeserializationFeature,SerializationFeature 和 I nclude.
Jackson 根据它的默认方式序列化和反序列化 java 对象,若根据实际需要,灵活的调整它的默认方式,可以使用 Jackson 的注解。常用的注解及用法如下.
| 注解 | 用法 |
|---|---|
| @JsonProperty | 用于属性,把属性的名称序列化时转换为另外一个名称。示例: @JsonProperty("birth_ d ate") private Date birthDate; |
| @JsonFormat | 用于属性或者方法,把属性的格式序列化时转换成指定的格式。示例: @JsonFormat(timezone = "GMT+8", pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm") public Date getBirthDate() |
| @JsonPropertyOrder | 用于类, 指定属性在序列化时 json 中的顺序 , 示例: @JsonPropertyOrder({ "birth_Date", "name" }) public class Person |
| @JsonCreator | 用于构造方法,和 @JsonProperty 配合使用,适用有参数的构造方法。 示例: @JsonCreator public Person(@JsonProperty("name")String name) {…} |
| @JsonAnySetter | 用于属性或者方法,设置未反序列化的属性名和值作为键值存储到 map 中 @JsonAnySetter public void set(String key, Object value) { map.put(key, value); } |
| @JsonAnyGetter | 用于方法 ,获取所有未序列化的属性 public Map<String, Object> any() { return map; } |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
ObjectMapper objectMapper =
new
ObjectMapper();
String carJson =
"{ \"brand\" : \"Mercedes\", \"doors\" : 5 }"
;
try
{
Car car = objectMapper.readValue(carJson, Car.
class
);
System.out.println(
"car brand = "
+ car.getBrand());
System.out.println(
"car doors = "
+ car.getDoors());
}
catch
(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
public
class
Car {
private
String brand =
null
;
private
int
doors =
0
;
public
String getBrand() {
return
this
.brand; }
public
void
setBrand(String brand){
this
.brand = brand;}
public
int
getDoors() {
return
this
.doors; }
public
void
setDoors (
int
doors) {
this
.doors = doors; }
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
ObjectMapper objectMapper =
new
ObjectMapper();
String carJson =
"{ \"brand\" : \"Mercedes\", \"doors\" : 4 }"
;
Reader reader =
new
StringReader(carJson);
Car car = objectMapper.readValue(reader, Car.
class
);
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
ObjectMapper objectMapper =
new
ObjectMapper();
File file =
new
File(
"data/car.json"
);
Car car = objectMapper.readValue(file, Car.
class
);
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
ObjectMapper objectMapper =
new
ObjectMapper();
URL url =
new
URL(
"file:data/car.json"
);
Car car = objectMapper.readValue(url, Car.
class
);
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
ObjectMapper objectMapper =
new
ObjectMapper();
InputStream input =
new
FileInputStream(
"data/car.json"
);
Car car = objectMapper.readValue(input, Car.
class
);
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
ObjectMapper objectMapper =
new
ObjectMapper();
String carJson =
"{ \"brand\" : \"Mercedes\", \"doors\" : 5 }"
;
byte
[] bytes = carJson.getBytes(
"UTF-8"
);
Car car = objectMapper.readValue(bytes, Car.
class
);
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
String jsonArray =
"[{\"brand\":\"ford\"}, {\"brand\":\"Fiat\"}]"
;
ObjectMapper objectMapper =
new
ObjectMapper();
Car[] cars2 = objectMapper.readValue(jsonArray, Car[].
class
);
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
String jsonArray =“[{\”brand \“:\”ford \“},{\”brand \“:\”Fiat \“}]”;
ObjectMapper objectMapper =
new
ObjectMapper();
List <Car> cars1 = objectMapper.readValue(jsonArray,
new
TypeReference <List <Car >>(){});
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
String jsonObject =“{\”brand \“:\”ford \“,\”doors \“:
5
}”;
ObjectMapper objectMapper =
new
ObjectMapper();
Map <String,Object> jsonMap = objectMapper.readValue(jsonObject,
new
TypeReference <Map <String,Object >>(){});
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
String carJson =
"{ \"brand\" : \"Mercedes\", \"doors\" : 5 }"
;
ObjectMapper objectMapper =
new
ObjectMapper();
try
{
JsonNode jsonNode = objectMapper.readValue(carJson, JsonNode.
class
);
}
catch
(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
|
JSON字符串被解析为JsonNode对象而不是Car对象,只需将JsonNode.class第二个参数传递给readValue()方法而不是Car.class本教程前面的示例中使用的方法.
该ObjectMapper班也有一个特殊的readTree(),它总是返回一个方法 JsonNode。以下是JsonNode使用该ObjectMapper readTree()方法将JSON解析为a的示例:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
String carJson =
"{ \"brand\" : \"Mercedes\", \"doors\" : 5 }"
;
ObjectMapper objectMapper =
new
ObjectMapper();
try
{
JsonNode jsonNode = objectMapper.readTree(carJson);
}
catch
(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
|
JsonNode类 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
String carJson =
"{ \"brand\" : \"Mercedes\", \"doors\" : 5,"
+
" \"owners\" : [\"John\", \"Jack\", \"Jill\"],"
+
" \"nestedObject\" : { \"field\" : \"value\" } }"
;
ObjectMapper objectMapper =
new
ObjectMapper();
try
{
JsonNode jsonNode = objectMapper.readValue(carJson, JsonNode.
class
);
JsonNode brandNode = jsonNode.get(
"brand"
);
String brand = brandNode.asText();
System.out.println(
"brand = "
+ brand);
JsonNode doorsNode = jsonNode.get(
"doors"
);
int
doors = doorsNode.asInt();
System.out.println(
"doors = "
+ doors);
JsonNode array = jsonNode.get(
"owners"
);
JsonNode jsonNode = array.get(
0
);
String john = jsonNode.asText();
System.out.println(
"john = "
+ john);
JsonNode child = jsonNode.get(
"nestedObject"
);
JsonNode childField = child.get(
"field"
);
String field = childField.asText();
System.out.println(
"field = "
+ field);
}
catch
(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
ObjectMapper objectMapper =
new
ObjectMapper();
Car car =
new
Car();
car.brand =
"Cadillac"
;
car.doors =
4
;
JsonNode carJsonNode = objectMapper.valueToTree(car);
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
ObjectMapper objectMapper =
new
ObjectMapper();
String carJson =
"{ \"brand\" : \"Mercedes\", \"doors\" : 5 }"
;
JsonNode carJsonNode = objectMapper.readTree(carJson);
Car car = objectMapper.treeToValue(carJsonNode);
|
1.示例1(只是yaml字符串和对象的互转,不涉及yaml文件的处理) 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
import
com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import
com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import
com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.yaml.YAMLFactory;
import
java.io.IOException;
public
class
YamlJacksonExample {
public
static
void
main(String[] args) {
ObjectMapper objectMapper =
new
ObjectMapper(
new
YAMLFactory());
Employee employee =
new
Employee(
"John Doe"
,
"john@doe.com"
);
String yamlString =
null
;
try
{
yamlString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(employee);
}
catch
(JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// normally, rethrow exception here - or don't catch it at all.
}
}
}
|
该yamlString变量包含Employee在执行此代码后序列化为YAML数据格式的对象.
以下是Employee再次将YAML文本读入对象的示例:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
import
com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import
com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import
com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.yaml.YAMLFactory;
import
java.io.IOException;
public
class
YamlJacksonExample {
public
static
void
main(String[] args) {
ObjectMapper objectMapper =
new
ObjectMapper(
new
YAMLFactory());
Employee employee =
new
Employee(
"John Doe"
,
"john@doe.com"
);
String yamlString =
null
;
try
{
yamlString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(employee);
}
catch
(JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// normally, rethrow exception here - or don't catch it at all.
}
try
{
Employee employee2 = objectMapper.readValue(yamlString, Employee.
class
);
System.out.println(
"Done"
);
}
catch
(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
2. 示例2 (yaml文件的读取和写入) 。
2.1定义Employee实体类 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
package
com.example.jackjson;
import
lombok.Data;
/**
* @author: GuanBin
* @date: Created in 上午10:18 2020/6/15
*/
@Data
public
class
Employee {
public
Employee() {
}
public
Employee(String name, String email) {
this
.name = name;
this
.email = email;
}
String name;
String email;
}
|
2.2创建要读取的yml EmployeeYaml.yml文件,并初始化一条数据 。
|
1
2
|
name: test
email: test@qq.com
|
2.3创建要写入的yml文件,EmployeeYamlOutput.yml (空文件) 。
2.4 测试类 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
|
package
com.example.jackjson;
import
com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import
com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.SerializationFeature;
import
com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.yaml.YAMLFactory;
import
com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.yaml.YAMLGenerator;
import
java.io.File;
import
java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author: GuanBin
* @date: Created in 上午10:17 2020/6/15
*/
public
class
YamlJacksonExample {
public
static
void
main(String[] args) {
try
{
//从yaml文件读取数据
reaedYamlToEmployee();
//写入yaml文件
reaedEmployeeToYaml();
}
catch
(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 从yaml文件读取数据
* @throws IOException
*/
private
static
void
reaedYamlToEmployee()
throws
IOException {
ObjectMapper mapper =
new
ObjectMapper(
new
YAMLFactory());
Employee employee = mapper.readValue(
new
File(
"src/test/java/com/example/jackjson/EmployeeYaml.yml"
), Employee.
class
);
System.out.println(employee.getName() +
"********"
+ employee.getEmail());
}
/**
* 写入yaml文件
* @throws IOException
*/
private
static
void
reaedEmployeeToYaml()
throws
IOException {
//去掉三个破折号
ObjectMapper mapper =
new
ObjectMapper(
new
YAMLFactory().disable(YAMLGenerator.Feature.WRITE_DOC_START_MARKER));
//禁用掉把时间写为时间戳
mapper.disable(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS);
Employee employee =
new
Employee(
"test2"
,
"999@qq.com"
);
mapper.writeValue(
new
File(
"src/test/java/com/example/jackjson/EmployeeYamlOutput.yml"
), employee);
}
}
|
读取文件的打印输出 。
test********test@qq.com 。
Process finished with exit code 0 。
写入文件的输出 。
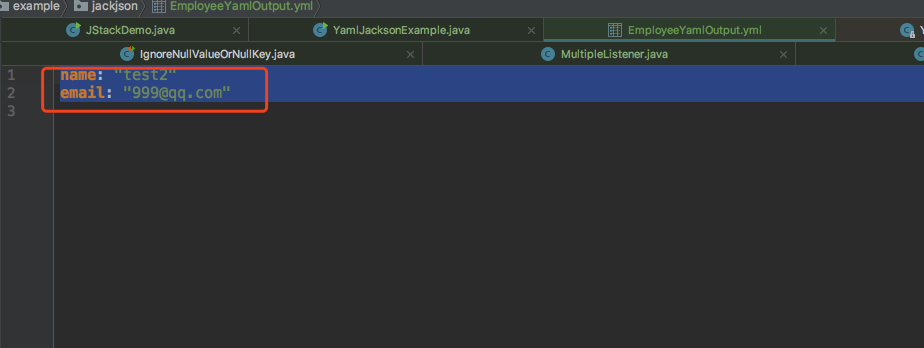
参考:
https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/jackson-advanced-application/index.html 。
http://tutorials.jenkov.com/java-json/jackson-objectmapper.html 。
https://www.baeldung.com/jackson-yaml 。
到此这篇关于Java之Jackson的基本使用案例讲解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java之Jackson的基本使用内容请搜索我以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我! 。
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/guanbin-529/p/11488869.html 。
最后此篇关于Java之Jackson的基本使用案例讲解的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于Java之Jackson的基本使用案例讲解的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我正在编写一个具有以下签名的 Java 方法。 void Logger(Method method, Object[] args); 如果一个方法(例如 ABC() )调用此方法 Logger,它应该
我是 Java 新手。 我的问题是我的 Java 程序找不到我试图用作的图像文件一个 JButton。 (目前这段代码什么也没做,因为我只是得到了想要的外观第一的)。这是我的主课 代码: packag
好的,今天我在接受采访,我已经编写 Java 代码多年了。采访中说“Java 垃圾收集是一个棘手的问题,我有几个 friend 一直在努力弄清楚。你在这方面做得怎么样?”。她是想骗我吗?还是我的一生都
我的 friend 给了我一个谜语让我解开。它是这样的: There are 100 people. Each one of them, in his turn, does the following
如果我将使用 Java 5 代码的应用程序编译成字节码,生成的 .class 文件是否能够在 Java 1.4 下运行? 如果后者可以工作并且我正在尝试在我的 Java 1.4 应用程序中使用 Jav
有关于why Java doesn't support unsigned types的问题以及一些关于处理无符号类型的问题。我做了一些搜索,似乎 Scala 也不支持无符号数据类型。限制是Java和S
我只是想知道在一个 java 版本中生成的字节码是否可以在其他 java 版本上运行 最佳答案 通常,字节码无需修改即可在 较新 版本的 Java 上运行。它不会在旧版本上运行,除非您使用特殊参数 (
我有一个关于在命令提示符下执行 java 程序的基本问题。 在某些机器上我们需要指定 -cp 。 (类路径)同时执行java程序 (test为java文件名与.class文件存在于同一目录下) jav
我已经阅读 StackOverflow 有一段时间了,现在我才鼓起勇气提出问题。我今年 20 岁,目前在我的家乡(罗马尼亚克卢日-纳波卡)就读 IT 大学。足以介绍:D。 基本上,我有一家提供簿记应用
我有 public JSONObject parseXML(String xml) { JSONObject jsonObject = XML.toJSONObject(xml); r
我已经在 Java 中实现了带有动态类型的简单解释语言。不幸的是我遇到了以下问题。测试时如下代码: def main() { def ks = Map[[1, 2]].keySet()
一直提示输入 1 到 10 的数字 - 结果应将 st、rd、th 和 nd 添加到数字中。编写一个程序,提示用户输入 1 到 10 之间的任意整数,然后以序数形式显示该整数并附加后缀。 public
我有这个 DownloadFile.java 并按预期下载该文件: import java.io.*; import java.net.URL; public class DownloadFile {
我想在 GUI 上添加延迟。我放置了 2 个 for 循环,然后重新绘制了一个标签,但这 2 个 for 循环一个接一个地执行,并且标签被重新绘制到最后一个。 我能做什么? for(int i=0;
我正在对对象 Student 的列表项进行一些测试,但是我更喜欢在 java 类对象中创建硬编码列表,然后从那里提取数据,而不是连接到数据库并在结果集中选择记录。然而,自从我这样做以来已经很长时间了,
我知道对象创建分为三个部分: 声明 实例化 初始化 classA{} classB extends classA{} classA obj = new classB(1,1); 实例化 它必须使用
我有兴趣使用 GPRS 构建车辆跟踪系统。但是,我有一些问题要问以前做过此操作的人: GPRS 是最好的技术吗?人们意识到任何问题吗? 我计划使用 Java/Java EE - 有更好的技术吗? 如果
我可以通过递归方法反转数组,例如:数组={1,2,3,4,5} 数组结果={5,4,3,2,1}但我的结果是相同的数组,我不知道为什么,请帮助我。 public class Recursion { p
有这样的标准方式吗? 包括 Java源代码-测试代码- Ant 或 Maven联合单元持续集成(可能是巡航控制)ClearCase 版本控制工具部署到应用服务器 最后我希望有一个自动构建和集成环境。
我什至不知道这是否可能,我非常怀疑它是否可能,但如果可以,您能告诉我怎么做吗?我只是想知道如何从打印机打印一些文本。 有什么想法吗? 最佳答案 这里有更简单的事情。 import javax.swin

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!