- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章Spring @Cacheable redis异常不影响正常业务方案由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
项目中,使用@Cacheable进行数据缓存。发现:当redis宕机之后,@Cacheable注解的方法并未进行缓存冲突,而是直接抛出异常。而这样的异常会导致服务不可用.
我们是通过@EnableCaching进行缓存启用的,因此可以先看@EnableCaching的相关注释 。
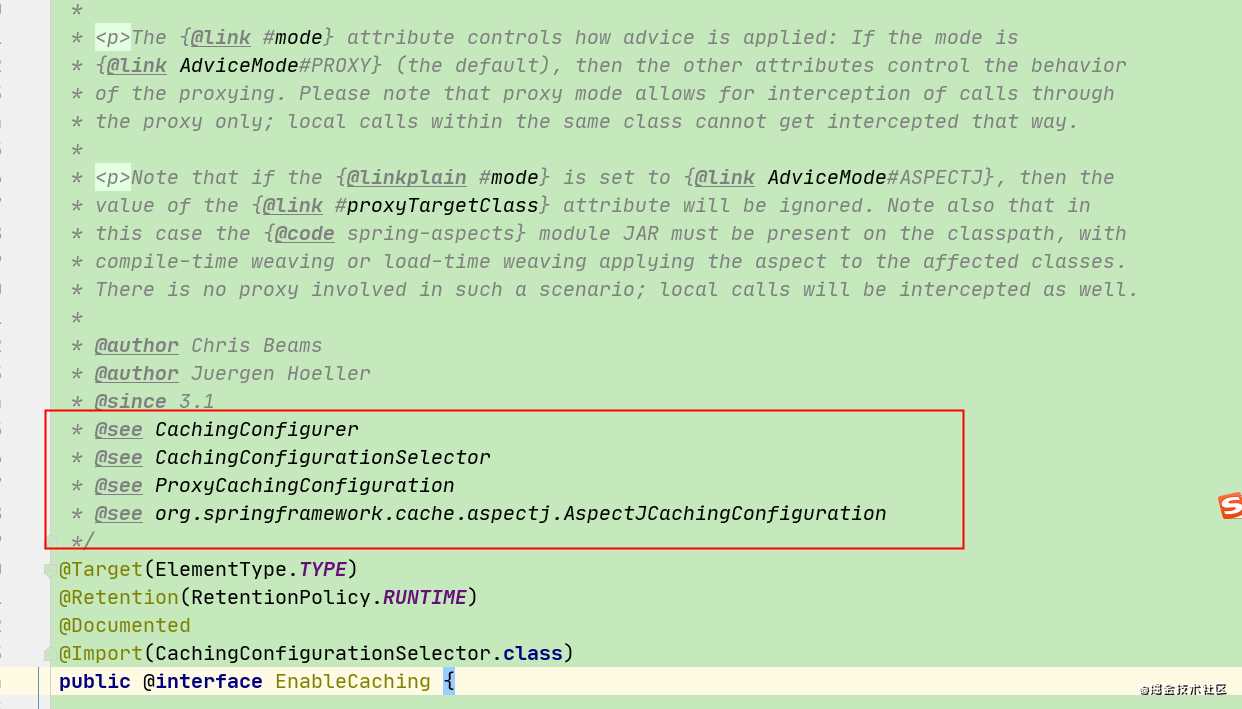
通过@EnableCaching的类注释可发现,spring cache的核心配置接口为:org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurer 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
|
/**
* Interface to be implemented by @{@link org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration
* Configuration} classes annotated with @{@link EnableCaching} that wish or need to
* specify explicitly how caches are resolved and how keys are generated for annotation-driven
* cache management. Consider extending {@link CachingConfigurerSupport}, which provides a
* stub implementation of all interface methods.
*
* <p>See @{@link EnableCaching} for general examples and context; see
* {@link #cacheManager()}, {@link #cacheResolver()} and {@link #keyGenerator()}
* for detailed instructions.
*
* @author Chris Beams
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @since 3.1
* @see EnableCaching
* @see CachingConfigurerSupport
*/
public
interface
CachingConfigurer {
/**
* Return the cache manager bean to use for annotation-driven cache
* management. A default {@link CacheResolver} will be initialized
* behind the scenes with this cache manager. For more fine-grained
* management of the cache resolution, consider setting the
* {@link CacheResolver} directly.
* <p>Implementations must explicitly declare
* {@link org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean @Bean}, e.g.
* <pre class="code">
* Configuration
* EnableCaching
* public class AppConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
* Bean // important!
* Override
* public CacheManager cacheManager() {
* // configure and return CacheManager instance
* }
* // ...
* }
* </pre>
* See @{@link EnableCaching} for more complete examples.
*/
CacheManager cacheManager();
/**
* Return the {@link CacheResolver} bean to use to resolve regular caches for
* annotation-driven cache management. This is an alternative and more powerful
* option of specifying the {@link CacheManager} to use.
* <p>If both a {@link #cacheManager()} and {@code #cacheResolver()} are set,
* the cache manager is ignored.
* <p>Implementations must explicitly declare
* {@link org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean @Bean}, e.g.
* <pre class="code">
* Configuration
* EnableCaching
* public class AppConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
* Bean // important!
* Override
* public CacheResolver cacheResolver() {
* // configure and return CacheResolver instance
* }
* // ...
* }
* </pre>
* See {@link EnableCaching} for more complete examples.
*/
CacheResolver cacheResolver();
/**
* Return the key generator bean to use for annotation-driven cache management.
* Implementations must explicitly declare
* {@link org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean @Bean}, e.g.
* <pre class="code">
* Configuration
* EnableCaching
* public class AppConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
* Bean // important!
* Override
* public KeyGenerator keyGenerator() {
* // configure and return KeyGenerator instance
* }
* // ...
* }
* </pre>
* See @{@link EnableCaching} for more complete examples.
*/
KeyGenerator keyGenerator();
/**
* Return the {@link CacheErrorHandler} to use to handle cache-related errors.
* <p>By default,{@link org.springframework.cache.interceptor.SimpleCacheErrorHandler}
* is used and simply throws the exception back at the client.
* <p>Implementations must explicitly declare
* {@link org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean @Bean}, e.g.
* <pre class="code">
* Configuration
* EnableCaching
* public class AppConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
* Bean // important!
* Override
* public CacheErrorHandler errorHandler() {
* // configure and return CacheErrorHandler instance
* }
* // ...
* }
* </pre>
* See @{@link EnableCaching} for more complete examples.
*/
CacheErrorHandler errorHandler();
}
|
该接口errorHandler方法可配置异常的处理方式。通过该方法上的注释可以发现,默认的CacheErrorHandler实现类是org.springframework.cache.interceptor.SimpleCacheErrorHandler 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
/**
* A simple {@link CacheErrorHandler} that does not handle the
* exception at all, simply throwing it back at the client.
*
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @since 4.1
*/
public
class
SimpleCacheErrorHandler
implements
CacheErrorHandler {
@Override
public
void
handleCacheGetError(RuntimeException exception, Cache cache, Object key) {
throw
exception;
}
@Override
public
void
handleCachePutError(RuntimeException exception, Cache cache, Object key, Object value) {
throw
exception;
}
@Override
public
void
handleCacheEvictError(RuntimeException exception, Cache cache, Object key) {
throw
exception;
}
@Override
public
void
handleCacheClearError(RuntimeException exception, Cache cache) {
throw
exception;
}
}
|
SimpleCacheErrorHandler类注释上说明的很清楚:对cache的异常不做任何处理,直接将该异常抛给客户端。因此默认的情况下,redis服务器异常后,直接就阻断了正常业务 。
通过上面的分析可知,我们可以通过自定义CacheErrorHandler来干预@Cacheable的异常处理逻辑。具体代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
public
class
RedisConfig
extends
CachingConfigurerSupport {
/**
* redis数据操作异常处理。该方法处理逻辑:在日志中打印出错误信息,但是放行。
* 保证redis服务器出现连接等问题的时候不影响程序的正常运行
*/
@Override
public
CacheErrorHandler errorHandler() {
return
new
CacheErrorHandler() {
@Override
public
void
handleCachePutError(RuntimeException exception, Cache cache,
Object key, Object value) {
handleRedisErrorException(exception, key);
}
@Override
public
void
handleCacheGetError(RuntimeException exception, Cache cache,
Object key) {
handleRedisErrorException(exception, key);
}
@Override
public
void
handleCacheEvictError(RuntimeException exception, Cache cache,
Object key) {
handleRedisErrorException(exception, key);
}
@Override
public
void
handleCacheClearError(RuntimeException exception, Cache cache) {
handleRedisErrorException(exception,
null
);
}
};
}
protected
void
handleRedisErrorException(RuntimeException exception, Object key) {
log.error(
"redis异常:key=[{}]"
, key, exception);
}
}
|
到此这篇关于Spring @Cacheable redis异常不影响正常业务方案的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Spring @Cacheable redis异常内容请搜索我以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我! 。
原文链接:https://juejin.cn/post/6930545205036875784 。
最后此篇关于Spring @Cacheable redis异常不影响正常业务方案的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于Spring @Cacheable redis异常不影响正常业务方案的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
关闭。这个问题是opinion-based 。目前不接受答案。 想要改进这个问题吗?更新问题,以便 editing this post 可以用事实和引文来回答它。 . 已关闭 9 年前。 Improv
我在这里感觉有些不对劲,所以我希望社区提供意见 - 也许我以错误的方式处理这个问题...... 问:是否适合使用传统的基础架构日志框架(如 log4net)来记录业务事件? 当我说业务事件时,我的意思
技术也好,业务也罢; 01 【什么是业务?】 对于那些久经职场的人,也很难一句话说明白; 业务,作为工作中绝对的核心点,即便在一个公司待的足够久,
三天研发,两天设计; 01 【优先做设计方案】 职场中的那些魔幻操作,研发最烦的是哪个? 作为一个数年且资深的互联网普通开发,可以来说明一下为什么
业务、系统、接口(interface)、持久化类是什么意思?用一些例子解释一下? 最佳答案 业务可能是应用程序中所有功能部分发生的部分(即计算或规则) 系统是您的操作系统 接口(interface),
我无法创建带有指向移动应用的外部链接的简单广告。我已正确设置访问权限,可以创建广告系列、广告集、加载图像,但在创建广告期间出现错误: Ads and ad creatives must be asso
我是软件工程专业的学生,现在我正在为我的期末项目工作,安排在交易日进行商务配对。 这个想法是将卖家(开发人员)和买家(有经济能力的人)在一起。 算法应该像“快速约会”。 假设我有 15 张 table
我们只需按照以下说明在 AWS Cloudformation 上部署企业 WhatsApp API: AWS WhatsApp API 所以一切正常,部署正确完成,问题出在“SSL 配置”选项上,我们
我的应用因为以下原因被拒绝了 Guideline 3.2 - Business We found that your app is not appropriate for the App Store
您好,我想在我的网络应用程序中使用 WhatsApp 业务 API。我已经在 postman 中测试过了。 每当在 WhatsApp 选项卡下的 Facebook 业务页面中运行示例 curl 代码时
我是 Skype for Business 技术的新手,我正在尝试部署一个我愿意与 Skype WebSDK 和 AppSDK 一起使用的服务器。 起初我尝试使用Skype进行在线商务,但websdk
Apple 开发人员以此为由拒绝了我的应用。 “业务 - 3.1.1您的应用程序包含一个帐户注册功能,该功能被视为对外部机制的访问,以便在应用程序中使用购买或订阅。此功能不符合 App Store 审
我正在玩 Realm for Android。 我喜欢自动更新对象的想法,但我对它的软件架构有顾虑。 我已经看到许多提议的架构都指定了一个层来处理数据/数据库访问,理想情况下,更高层不会知道有关数据库
关闭。这个问题不符合Stack Overflow guidelines .它目前不接受答案。 这个问题似乎与 help center 中定义的范围内的编程无关。 . 关闭 10 个月前。 Impro
我正在尝试设置 Whatsapp 业务 API。 引用Link用于设置。 我正在使用 Windows 10 操作系统。 -- 仅供引用。 在初始设置部分,使用命令 docker-compose up
我正在尝试使用 Facebook Business SDK 创建一个 facebook Adaccount .但是当我使用方法 createAdAccount 时,它会给我一个错误。请参阅下面的图片。
我想写一个概念证明 MonoMac使用 c# 和 Razor 呈现 html“ View ”的应用程序。 这可能吗? 如果没有,是否有人推荐与 Razor 的简单性相比的任何其他模板引擎。如果必须的话
无法解析 ':business:diary@debug/compileClasspath': Could not resolve project :fun:push. 的依赖关系 无法解析项目:fun
当我尝试在 Visual Studio Professional 2015 14.0.23107.0 中打开某些 XML 文件时,XML 编辑器出现白屏并显示以下文本: 为什么我不能编辑这个文件?此项

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!