- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章Python集成学习之Blending算法详解由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
普通机器学习:从训练数据中学习一个假设.
集成方法:试图构建一组假设并将它们组合起来,集成学习是一种机器学习范式,多个学习器被训练来解决同一个问题.
集成方法分类为:
Bagging(并行训练):随机森林 。
Boosting(串行训练):Adaboost; GBDT; XgBoost 。
Stacking
Blending
或者分类为串行集成方法和并行集成方法 。
1.串行模型:通过基础模型之间的依赖,给错误分类样本一个较大的权重来提升模型的性能.
2.并行模型的原理:利用基础模型的独立性,然后通过平均能够较大地降低误差 。
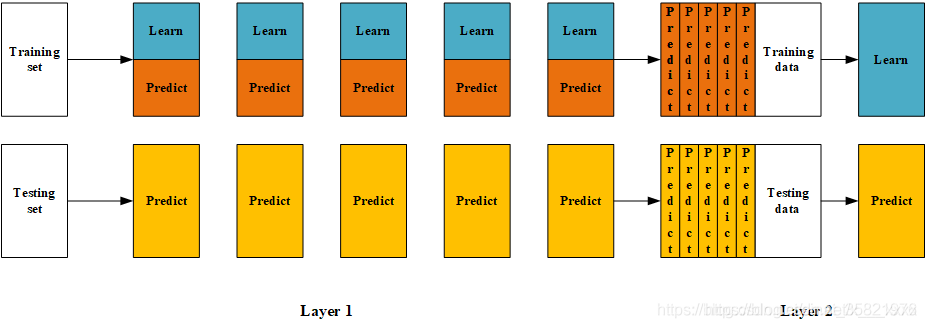
训练数据划分为训练和验证集+新的训练数据集和新的测试集 。
将训练数据进行划分,划分之后的训练数据一部分训练基模型,一部分经模型预测后作为新的特征训练元模型。 测试数据同样经过基模型预测,形成新的测试数据。最后,元模型对新的测试数据进行预测。Blending框架图如下所示: 注意:其是在stacking的基础上加了划分数据 。

相关工具包加载 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
import
numpy as np
import
pandas as pd
import
matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.style.use(
"ggplot"
)
%
matplotlib inline
import
seaborn as sns
|
创建数据 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
from
sklearn
import
datasets
from
sklearn.datasets
import
make_blobs
from
sklearn.model_selection
import
train_test_split
data, target
=
make_blobs(n_samples
=
10000
, centers
=
2
, random_state
=
1
, cluster_std
=
1.0
)
## 创建训练集和测试集
X_train1,X_test,y_train1,y_test
=
train_test_split(data, target, test_size
=
0.2
, random_state
=
1
)
## 创建训练集和验证集
X_train,X_val,y_train,y_val
=
train_test_split(X_train1, y_train1, test_size
=
0.3
, random_state
=
1
)
print
(
"The shape of training X:"
,X_train.shape)
print
(
"The shape of training y:"
,y_train.shape)
print
(
"The shape of test X:"
,X_test.shape)
print
(
"The shape of test y:"
,y_test.shape)
print
(
"The shape of validation X:"
,X_val.shape)
print
(
"The shape of validation y:"
,y_val.shape)
|
设置第一层分类器 。
|
1
2
3
|
from
sklearn.svm
import
SVC
from
sklearn.ensemble
import
RandomForestClassifier
from
sklearn.neighbors
import
KNeighborsClassifier
|
|
1
|
clfs
=
[SVC(probability
=
True
),RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators
=
5
,n_jobs
=
-
1
,criterion
=
'gini'
),KNeighborsClassifier()]
|
设置第二层分类器 。
|
1
2
|
from
sklearn.linear_model
import
LinearRegression
lr
=
LinearRegression()
|
第一层 。
|
1
2
|
val_features
=
np.zeros((X_val.shape[
0
],
len
(clfs)))
test_features
=
np.zeros((X_test.shape[
0
],
len
(clfs)))
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
for
i,clf
in
enumerate
(clfs):
clf.fit(X_train,y_train)
val_feature
=
clf.predict_proba(X_val)[:,
1
]
test_feature
=
clf.predict_proba(X_test)[:,
1
]
val_features[:,i]
=
val_feature
test_features[:,i]
=
test_feature
|
第二层 。
|
1
|
lr.fit(val_features,y_val)
|
输出预测的结果 。
|
1
2
3
4
|
lr.fit(val_features,y_val)
from
sklearn.model_selection
import
cross_val_score
cross_val_score(lr,test_features,y_test,cv
=
5
)
|
到此这篇关于Python集成学习之Blending算法详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python Blending算法内容请搜索我以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我! 。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36816848/article/details/116674754 。
最后此篇关于Python集成学习之Blending算法详解的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于Python集成学习之Blending算法详解的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
关闭。这个问题是opinion-based .它目前不接受答案。 想要改进这个问题? 更新问题,以便 editing this post 可以用事实和引用来回答它. 关闭 9 年前。 Improve
介绍篇 什么是MiniApis? MiniApis的特点和优势 MiniApis的应用场景 环境搭建 系统要求 安装MiniApis 配置开发环境 基础概念 MiniApis架构概述
我正在从“JavaScript 圣经”一书中学习 javascript,但我遇到了一些困难。我试图理解这段代码: function checkIt(evt) { evt = (evt) ? e
package com.fastone.www.javademo.stringintern; /** * * String.intern()是一个Native方法, * 它的作用是:如果字
您会推荐哪些资源来学习 AppleScript。我使用具有 Objective-C 背景的传统 C/C++。 我也在寻找有关如何更好地开发和从脚本编辑器获取更快文档的技巧。示例提示是“查找要编写脚本的
关闭。这个问题不满足Stack Overflow guidelines .它目前不接受答案。 想改善这个问题吗?更新问题,使其成为 on-topic对于堆栈溢出。 4年前关闭。 Improve thi
关闭。这个问题不满足Stack Overflow guidelines .它目前不接受答案。 想改善这个问题吗?更新问题,使其成为 on-topic对于堆栈溢出。 7年前关闭。 Improve thi
关闭。这个问题不符合 Stack Overflow guidelines 。它目前不接受答案。 想改善这个问题吗?更新问题,以便堆栈溢出为 on-topic。 6年前关闭。 Improve this
我是塞内加尔的阿里。我今年60岁(也许这是我真正的问题-笑脸!!!)。 我正在学习Flutter和Dart。今天,我想使用给定数据模型的列表(它的名称是Mortalite,请参见下面的代码)。 我尝试
关闭。这个问题是off-topic .它目前不接受答案。 想改进这个问题? Update the question所以它是on-topic对于堆栈溢出。 9年前关闭。 Improve this que
学习 Cappuccino 的最佳来源是什么?我从事“传统”网络开发,但我对这个新框架非常感兴趣。请注意,我对 Objective-C 毫无了解。 最佳答案 如上所述,该网站是一个好地方,但还有一些其
我正在学习如何使用 hashMap,有人可以检查我编写的这段代码并告诉我它是否正确吗?这个想法是有一个在公司工作的员工列表,我想从 hashMap 添加和删除员工。 public class Staf
我正在尝试将 jQuery 与 CoffeScript 一起使用。我按照博客中的说明操作,指示使用 $ -> 或 jQuery -> 而不是 .ready() 。我玩了一下代码,但我似乎无法理解我出错
还在学习,还有很多问题,所以这里有一些。我正在进行 javascript -> PHP 转换,并希望确保这些做法是正确的。是$dailyparams->$calories = $calories;一条
我目前正在学习 SQL,以便从我们的 Magento 数据库制作一个简单的 RFM 报告,我目前可以通过导出两个查询并将它们粘贴到 Excel 模板中来完成此操作,我想摆脱 Excel 模板。 我认为
我知道我很可能会因为这个问题而受到抨击,但没有人问,我求助于你。这是否是一个正确的 javascript > php 转换 - 在我开始不良做法之前,我想知道这是否是解决此问题的正确方法。 JavaS
除了 Ruby-Doc 之外,哪些来源最适合获取一些示例和教程,尤其是关于 Ruby 中的 Tk/Tile?我发现自己更正常了 http://www.tutorialspoint.com/ruby/r
我只在第一次收到警告。这正常吗? >>> cv=LassoCV(cv=10).fit(x,y) C:\Python27\lib\site-packages\scikit_learn-0.14.1-py
按照目前的情况,这个问题不适合我们的问答形式。我们希望答案得到事实、引用或专业知识的支持,但这个问题可能会引发辩论、争论、投票或扩展讨论。如果您觉得这个问题可以改进并可能重新打开,visit the
As it currently stands, this question is not a good fit for our Q&A format. We expect answers to be

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!