- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章pytorch 禁止/允许计算局部梯度的操作由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
torch.autogard.no_grad: 禁用梯度计算的上下文管理器.
当确定不会调用Tensor.backward()计算梯度时,设置禁止计算梯度会减少内存消耗。如果需要计算梯度设置Tensor.requires_grad=True 。
将不用计算梯度的变量放在with torch.no_grad()里 。
>>> x = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True)>>> with torch.no_grad():... y = x * 2>>> y.requires_gradOut[12]:False
使用装饰器 @torch.no_gard()修饰的函数,在调用时不允许计算梯度 。
>>> @torch.no_grad()... def doubler(x):... return x * 2>>> z = doubler(x)>>> z.requires_gradOut[13]:False
torch.autogard.enable_grad :允许计算梯度的上下文管理器 。
在一个no_grad上下文中使能梯度计算。在no_grad外部此上下文管理器无影响. 。
使用with torch.enable_grad()允许计算梯度 。
>>> x = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True)>>> with torch.no_grad():... with torch.enable_grad():... y = x * 2>>> y.requires_gradOut[14]:True >>> y.backward() # 计算梯度>>> x.gradOut[15]: tensor([2.])
在禁止计算梯度下调用被允许计算梯度的函数,结果可以计算梯度 。
>>> @torch.enable_grad()... def doubler(x):... return x * 2 >>> with torch.no_grad():... z = doubler(x)>>> z.requires_grad Out[16]:True
torch.autograd.set_grad_enable()
可以作为一个函数使用:
>>> x = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True)>>> is_train = False>>> with torch.set_grad_enabled(is_train):... y = x * 2>>> y.requires_gradOut[17]:False >>> torch.set_grad_enabled(True)>>> y = x * 2>>> y.requires_gradOut[18]:True >>> torch.set_grad_enabled(False)>>> y = x * 2>>> y.requires_gradOut[19]:False
单独使用这三个函数时没有什么,但是若是嵌套,遵循就近原则.
x = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True) with torch.enable_grad(): torch.set_grad_enabled(False) y = x * 2 print(y.requires_grad)Out[20]: False torch.set_grad_enabled(True)with torch.no_grad(): z = x * 2 print(z.requires_grad)Out[21]:False
补充:pytorch局部范围内禁用梯度计算,no_grad、enable_grad、set_grad_enabled使用举例 。
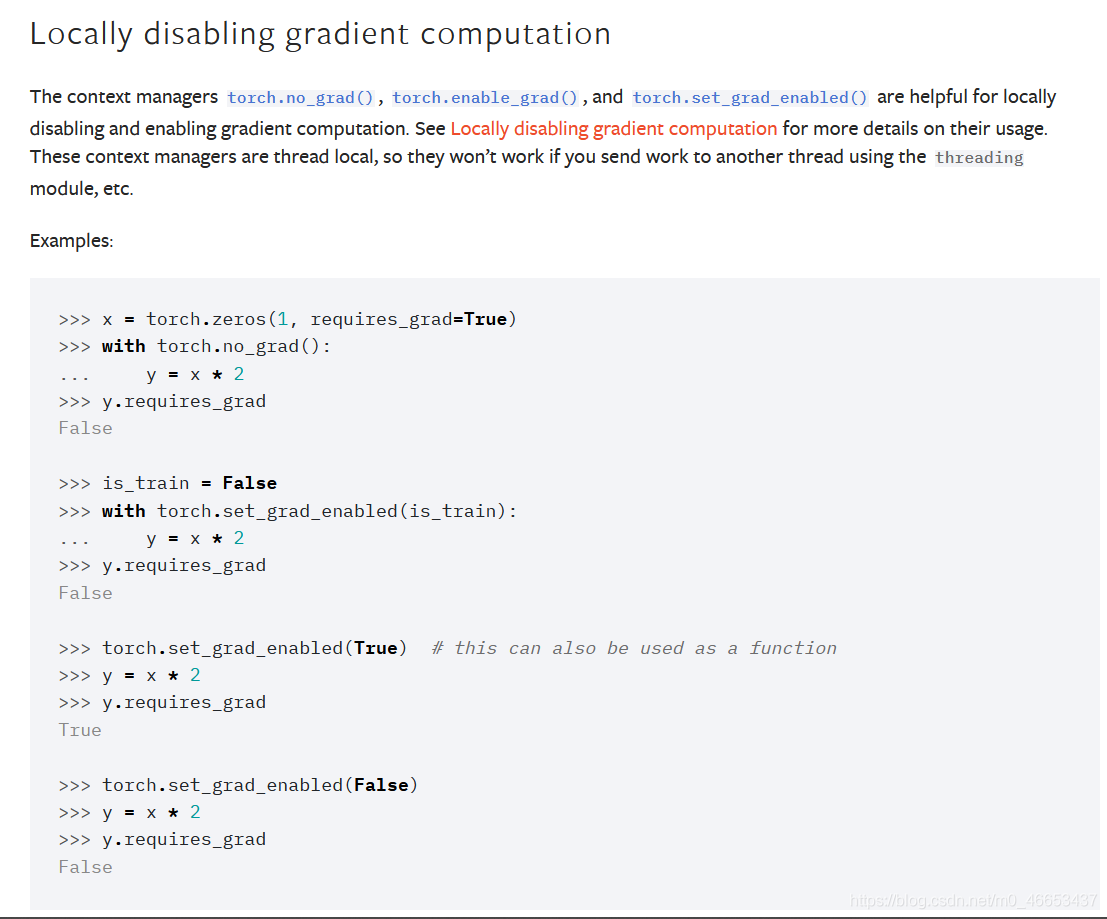
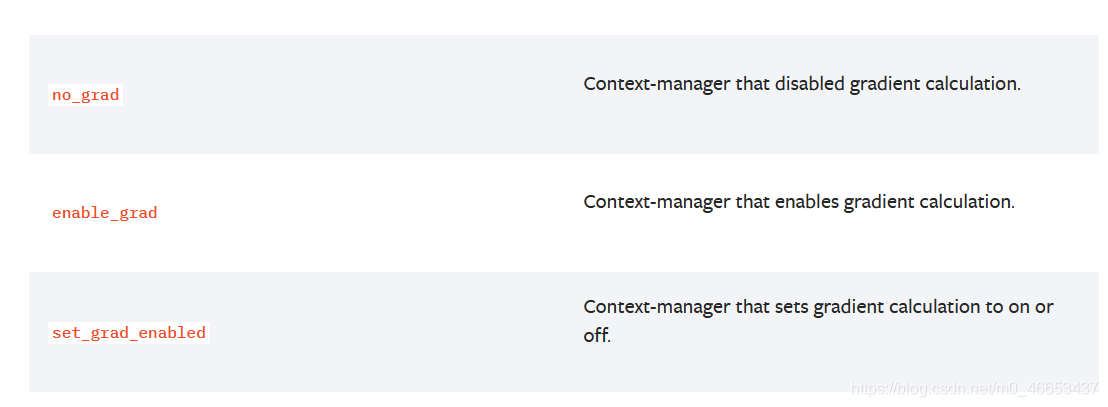
Locally disabling gradient computation在局部区域内关闭(禁用)梯度的计算.The context managers torch.no_grad(), torch.enable_grad(), and torch.set_grad_enabled() are helpful for locally disabling and enabling gradient computation. See Locally disabling gradient computation for more details on their usage. These context managers are thread local, so they won"t work if you send work to another thread using the threading module, etc.上下文管理器torch.no_grad()、torch.enable_grad()和torch.set_grad_enabled()可以用来在局部范围内启用或禁用梯度计算.在Locally disabling gradient computation章节中详细介绍了局部禁用梯度计算的使用方式.这些上下文管理器具有线程局部性,因此,如果你使用threading模块来将工作负载发送到另一个线程,这些上下文管理器将不会起作用.no_grad Context-manager that disabled gradient calculation.no_grad 用于禁用梯度计算的上下文管理器.enable_grad Context-manager that enables gradient calculation.enable_grad 用于启用梯度计算的上下文管理器.set_grad_enabled Context-manager that sets gradient calculation to on or off.set_grad_enabled 用于设置梯度计算打开或关闭状态的上下文管理器.
Microsoft Windows [版本 10.0.18363.1440](c) 2019 Microsoft Corporation。保留所有权利。C:Userschenxuqi>conda activate pytorch_1.7.1_cu102(pytorch_1.7.1_cu102) C:Userschenxuqi>pythonPython 3.7.9 (default, Aug 31 2020, 17:10:11) [MSC v.1916 64 bit (AMD64)] :: Anaconda, Inc. on win32Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.>>> import torch>>> torch.manual_seed(seed=20200910)<torch._C.Generator object at 0x000001A2E55A8870>>>> a = torch.randn(3,4,requires_grad=True)>>> atensor([[ 0.2824, -0.3715, 0.9088, -1.7601], [-0.1806, 2.0937, 1.0406, -1.7651], [ 1.1216, 0.8440, 0.1783, 0.6859]], requires_grad=True)>>> b = a * 2>>> btensor([[ 0.5648, -0.7430, 1.8176, -3.5202], [-0.3612, 4.1874, 2.0812, -3.5303], [ 2.2433, 1.6879, 0.3567, 1.3718]], grad_fn=<MulBackward0>)>>> b.requires_gradTrue>>> b.grad__main__:1: UserWarning: The .grad attribute of a Tensor that is not a leaf Tensor is being accessed. Its .grad attribute won"t be populated during autograd.backward(). If you indeed want the gradient for a non-leaf Tensor, use .retain_grad() on the non-leaf Tensor. If you access the non-leaf Tensor by mistake, make sure you access the leaf Tensor instead. See github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/30531 for more informations.>>> print(b.grad)None>>> a.requires_gradTrue>>> a.grad>>> print(a.grad)None>>>>>> with torch.no_grad():... c = a * 2...>>> ctensor([[ 0.5648, -0.7430, 1.8176, -3.5202], [-0.3612, 4.1874, 2.0812, -3.5303], [ 2.2433, 1.6879, 0.3567, 1.3718]])>>> c.requires_gradFalse>>> print(c.grad)None>>> a.grad>>>>>> print(a.grad)None>>> c.sum()tensor(6.1559)>>>>>> c.sum().backward()Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> File "D:Anaconda3envspytorch_1.7.1_cu102libsite-packages orch ensor.py", line 221, in backward torch.autograd.backward(self, gradient, retain_graph, create_graph) File "D:Anaconda3envspytorch_1.7.1_cu102libsite-packages orchautograd\__init__.py", line 132, in backward allow_unreachable=True) # allow_unreachable flagRuntimeError: element 0 of tensors does not require grad and does not have a grad_fn>>>>>>>>> b.sum()tensor(6.1559, grad_fn=<SumBackward0>)>>> b.sum().backward()>>>>>>>>> a.gradtensor([[2., 2., 2., 2.], [2., 2., 2., 2.], [2., 2., 2., 2.]])>>> a.requires_gradTrue>>>>>>
Microsoft Windows [版本 10.0.18363.1440](c) 2019 Microsoft Corporation。保留所有权利。C:Userschenxuqi>conda activate pytorch_1.7.1_cu102(pytorch_1.7.1_cu102) C:Userschenxuqi>pythonPython 3.7.9 (default, Aug 31 2020, 17:10:11) [MSC v.1916 64 bit (AMD64)] :: Anaconda, Inc. on win32Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.>>> import torch>>> torch.manual_seed(seed=20200910)<torch._C.Generator object at 0x000002109ABC8870>>>>>>> a = torch.randn(3,4,requires_grad=True)>>> atensor([[ 0.2824, -0.3715, 0.9088, -1.7601], [-0.1806, 2.0937, 1.0406, -1.7651], [ 1.1216, 0.8440, 0.1783, 0.6859]], requires_grad=True)>>> a.requires_gradTrue>>>>>> with torch.set_grad_enabled(False):... b = a * 2...>>> btensor([[ 0.5648, -0.7430, 1.8176, -3.5202], [-0.3612, 4.1874, 2.0812, -3.5303], [ 2.2433, 1.6879, 0.3567, 1.3718]])>>> b.requires_gradFalse>>>>>> with torch.set_grad_enabled(True):... c = a * 3...>>> ctensor([[ 0.8472, -1.1145, 2.7263, -5.2804], [-0.5418, 6.2810, 3.1219, -5.2954], [ 3.3649, 2.5319, 0.5350, 2.0576]], grad_fn=<MulBackward0>)>>> c.requires_gradTrue>>>>>> d = a * 4>>> d.requires_gradTrue>>>>>> torch.set_grad_enabled(True) # this can also be used as a function<torch.autograd.grad_mode.set_grad_enabled object at 0x00000210983982C8>>>>>>> # 以函数调用的方式来使用>>>>>> e = a * 5>>> etensor([[ 1.4119, -1.8574, 4.5439, -8.8006], [-0.9030, 10.4684, 5.2031, -8.8257], [ 5.6082, 4.2198, 0.8917, 3.4294]], grad_fn=<MulBackward0>)>>> e.requires_gradTrue>>>>>> dtensor([[ 1.1296, -1.4859, 3.6351, -7.0405], [-0.7224, 8.3747, 4.1625, -7.0606], [ 4.4866, 3.3759, 0.7133, 2.7435]], grad_fn=<MulBackward0>)>>>>>> torch.set_grad_enabled(False) # 以函数调用的方式来使用<torch.autograd.grad_mode.set_grad_enabled object at 0x0000021098394C48>>>>>>> f = a * 6>>> ftensor([[ 1.6943, -2.2289, 5.4527, -10.5607], [ -1.0836, 12.5621, 6.2437, -10.5908], [ 6.7298, 5.0638, 1.0700, 4.1153]])>>> f.requires_gradFalse>>>>>>>>>
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我。如有错误或未考虑完全的地方,望不吝赐教.
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/Answer3664/article/details/99460175 。
最后此篇关于pytorch 禁止/允许计算局部梯度的操作的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于pytorch 禁止/允许计算局部梯度的操作的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我正在尝试调整 tf DeepDream 教程代码以使用另一个模型。现在当我调用 tf.gradients() 时: t_grad = tf.gradients(t_score, t_input)[0
考虑到 tensorflow 中 mnist 上的一个简单的小批量梯度下降问题(就像在这个 tutorial 中),我如何单独检索批次中每个示例的梯度。 tf.gradients()似乎返回批次中所有
当我在 numpy 中计算屏蔽数组的梯度时 import numpy as np import numpy.ma as ma x = np.array([100, 2, 3, 5, 5, 5, 10,
除了数值计算之外,是否有一种快速方法来获取协方差矩阵(我的网络激活)的导数? 我试图将其用作深度神经网络中成本函数中的惩罚项,但为了通过我的层反向传播误差,我需要获得导数。 在Matlab中,如果“a
我有一个计算 3D 空间标量场值的函数,所以我为它提供 x、y 和 z 坐标(由 numpy.meshgrid 获得)的 3D 张量,并在各处使用元素运算。这按预期工作。 现在我需要计算标量场的梯度。
我正在使用内核密度估计 (KDE) ( http://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/generated/scipy.stats.gaussian_kde.htm
我对 tensorflow gradient documentation 中的示例感到困惑用于计算梯度。 a = tf.constant(0.) b = 2 * a g = tf.gradients(
我有一个 softmax 层(只有激活本身,没有将输入乘以权重的线性部分),我想对其进行向后传递。 我找到了很多关于 SO 的教程/答案来处理它,但它们似乎都使用 X 作为 (1, n_inputs)
仅供引用,我正在尝试使用 Tensorflow 实现梯度下降算法。 我有一个矩阵X [ x1 x2 x3 x4 ] [ x5 x6 x7 x8 ] 我乘以一些特征向量 Y 得到 Z [ y
我目前有一个由几百万个不均匀分布的粒子组成的体积,每个粒子都有一个属性(对于那些好奇的人来说是潜在的),我想为其计算局部力(加速度)。 np.gradient 仅适用于均匀间隔的数据,我在这里查看:S
我正在寻找有关如何实现 Gradient (steepest) Descent 的建议在 C 中。我正在寻找 f(x)=||Ax-y||^2 的最小值,其中给出了 A(n,n) 和 y(n)。 这在
我正在查看 SVM 损失和导数的代码,我确实理解了损失,但我无法理解如何以矢量化方式计算梯度 def svm_loss_vectorized(W, X, y, reg): loss = 0.0 dW
我正在寻找一种有效的方法来计算 Julia 中多维数组的导数。准确地说,我想要一个等效的 numpy.gradient在 Julia 。但是,Julia 函数 diff : 仅适用于二维数组 沿微分维
我在cathesian 2D 系统中有两个点,它们都给了我向量的起点和终点。现在我需要新向量和 x 轴之间的角度。 我知道梯度 = (y2-y1)/(x2-x1) 并且我知道角度 = arctan(g
我有一个 2D 数组正弦模式,想要绘制该函数的 x 和 y 梯度。我有一个二维数组 image_data : def get_image(params): # do some maths on
假设我有一个针对 MNIST 数据的简单 TensorFlow 模型,如下所示 import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.m
我想查看我的 Tensorflow LSTM 随时间变化的梯度,例如,绘制从 t=N 到 t=0 的梯度范数。问题是,如何从 Tensorflow 中获取每个时间步长的梯度? 最佳答案 在图中定义:
我有一个简单的神经网络,我试图通过使用如下回调使用张量板绘制梯度: class GradientCallback(tf.keras.callbacks.Callback): console =
在CIFAR-10教程中,我注意到变量被放置在CPU内存中,但它在cifar10-train.py中有说明。它是使用单个 GPU 进行训练的。 我很困惑..图层/激活是否存储在 GPU 中?或者,梯度
我有一个 tensorflow 模型,其中层的输出是二维张量,例如 t = [[1,2], [3,4]] . 下一层需要一个由该张量的每一行组合组成的输入。也就是说,我需要把它变成t_new = [[

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!