- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章linux下的通配符与正则表达式由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
通配符 。
* 任意字符,可重复多次 ? 任意字符,重复一次 [] 代表一个字符 。
举例: [a,b,c] 表示abc中任意一个 。
通配符的作用是用来匹配文件名的 。
正则表达式 。
正则表达式是在文件中匹配符合条件的字符串的 。
ls find cp是不支持正则表达式的 。
但是grep awk sed支持正则表达式 。
[root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# touch aa [root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# touch aab aabb [root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# ll total 0 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 May 16 19:47 aa -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 May 16 19:47 aab -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 May 16 19:47 aabb [root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# ls aa aa [root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# ls aa? aab [root@hadoop-bigdata01 test]# ls aa* aa aab aabb 。
正则表达式特殊字符 。
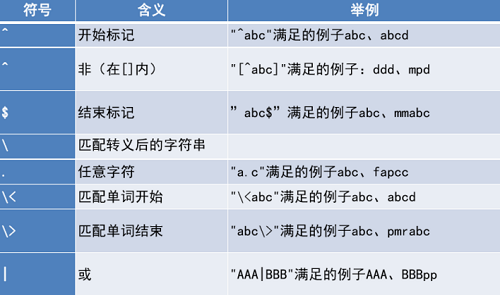
正则表达式匹配范围 。
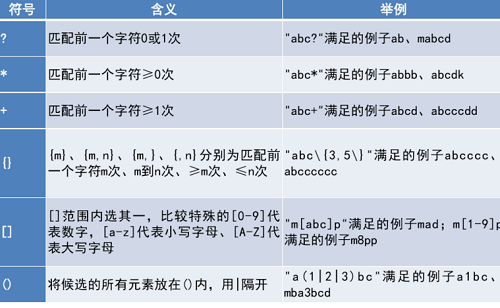
正则表达式标准字符 。
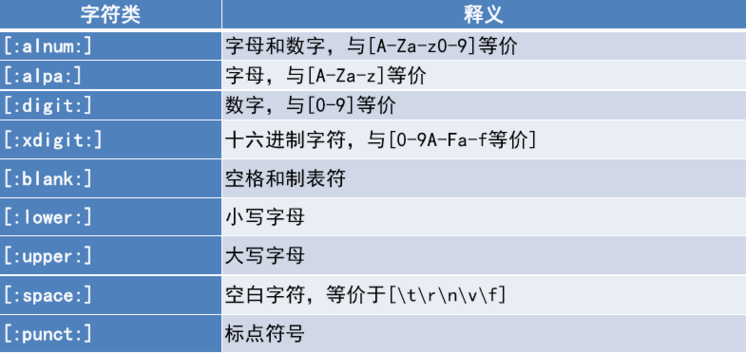
使用正则表达式 。
|
1
|
grep
"1"
/etc/passwd
|
包含关键字1的行,grep只要包含就行,不想通配符,要完全一致 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
[root@hadoop-bigdata01
test
]
# grep "1" /etc/passwd
bin:x:1:1:bin:
/bin
:
/sbin/nologin
mail:x:8:12:mail:
/var/spool/mail
:
/sbin/nologin
uucp:x:10:14:uucp:
/var/spool/uucp
:
/sbin/nologin
operator:x:11:0:operator:
/root
:
/sbin/nologin
games:x:12:100:games:
/usr/games
:
/sbin/nologin
gopher:x:13:30:gopher:
/var/gopher
:
/sbin/nologin
ftp
:x:14:50:FTP User:
/var/ftp
:
/sbin/nologin
dbus:x:81:81:System message bus:/:
/sbin/nologin
usbmuxd:x:113:113:usbmuxd user:/:
/sbin/nologin
avahi-autoipd:x:170:170:Avahi IPv4LL Stack:
/var/lib/avahi-autoipd
:
/sbin/nologin
abrt:x:173:173::
/etc/abrt
:
/sbin/nologin
wang:x:501:501::
/home/wang
:
/bin/bash
grep
'root'
/etc/passwd
cat
/etc/passwd
|
grep
'root'
|
都是同样的道理,但是管道符更吃资源 。
所以 。
1.匹配含有数字的行 。
|
1
|
grep
'[0-9]'
/etc/passwd
|
2.匹配连续含有三个数字的行 。
|
1
|
grep
'[0-9][0-9][0-9]'
/etc/passwd
或者
grep
':[0-9][0-9][0-9]:'
/etc/passwd
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
[root@hadoop-bigdata01
test
]
# grep '[0-9][0-9][0-9]' /etc/passwd
games:x:12:100:games:
/usr/games
:
/sbin/nologin
usbmuxd:x:113:113:usbmuxd user:/:
/sbin/nologin
rtkit:x:499:497:RealtimeKit:
/proc
:
/sbin/nologin
avahi-autoipd:x:170:170:Avahi IPv4LL Stack:
/var/lib/avahi-autoipd
:
/sbin/nologin
abrt:x:173:173::
/etc/abrt
:
/sbin/nologin
nfsnobody:x:65534:65534:Anonymous NFS User:
/var/lib/nfs
:
/sbin/nologin
saslauth:x:498:76:
"Saslauthd user"
:
/var/empty/saslauth
:
/sbin/nologin
pulse:x:497:496:PulseAudio System Daemon:
/var/run/pulse
:
/sbin/nologin
liucheng:x:500:500::
/home/liucheng
:
/bin/bash
wang:x:501:501::
/home/wang
:
/bin/bas
|
3.匹配以r开头 n结尾的行 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
grep
'^r.*n$'
/etc/passwd
.*代表所有
[root@hadoop-bigdata01
test
]
# grep '^r.*n$' /etc/passwd
rpc:x:32:32:Rpcbind Daemon:
/var/cache/rpcbind
:
/sbin/nologin
rtkit:x:499:497:RealtimeKit:
/proc
:
/sbin/nologin
rpcuser:x:29:29:RPC Service User:
/var/lib/nfs
:
/sbin/nologin
|
4.过滤ifconfig ,截取ip 。
grep -v 代表反向截取,意思就是去除带有某关键字的行 sed有替换的意思 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
[root@hadoop-bigdata01
test
]
# ifconfig | grep 'inet addr:'
inet addr:192.168.126.191 Bcast:192.168.126.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
[root@hadoop-bigdata01
test
]
#
[root@hadoop-bigdata01
test
]
# ifconfig | grep 'inet addr:' | grep -v '127.0.0.1'
inet addr:192.168.126.191 Bcast:192.168.126.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
[root@hadoop-bigdata01
test
]
# ifconfig | grep 'inet addr:' | grep -v '127.0.0.1' | sed 's/inet addr://g'
192.168.126.191 Bcast:192.168.126.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
[root@hadoop-bigdata01
test
]
# ifconfig | grep 'inet addr:' | grep -v '127.0.0.1' | sed 's/inet addr://g' | sed 's/Bcast.*//g'
192.168.126.191
|
误区 。
这里有个误区,想了好久,是正则表达式和通配符的区别 。
我们知道通配符的*指的是任意字符,可重复多次 正则表达式的*指的是匹配前一个字符>=0次 。
这两个是完全不同的,那如何知道我用的*是通配符还是正则表达式 。
起初我陷入一个误区,看下面这串命令 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
[root@hadoop-bigdata01
test
]
# touch ac aac abc abbc
[root@hadoop-bigdata01
test
]
# ll
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 May 16 19:55 aac
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 May 16 19:55 abbc
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 May 16 19:55 abc
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 May 16 19:55 ac
[root@hadoop-bigdata01
test
]
# ls | grep 'a*c'
aac
abbc
abc
ac
[root@hadoop-bigdata01
test
]
# ls | grep 'a.*c'
aac
abbc
abc
ac
[root@hadoop-bigdata01
test
]
# ls | grep '^a.*c'
aac
abbc
abc
ac
[root@hadoop-bigdata01
test
]
# ls | grep '^a*c'
aac
ac
|
为什么grep 'a*c' 和 grep '^a*c$' 的结果会不一样,我以为一个是通配符,一个是正则,因为a*c显示的四个结果,正好 。
不就是匹配任意多个字符吗?
其实不然 。
通配符的作用是用来匹配文件名的 。
正则表达式是在文件中匹配符合条件的字符串的 。
交给管道符之后使用grep已经不是匹配文件名了,这是对文件的操作,所以说,他完全就是正则表达式 。
grep 'a*c' 表示的是匹配a>=0个所以只要含有c就是可以的 。
而grep '^a*c$'也是正则,表示的是以a开头,且第二个字符匹配a零次或者多次,接下来是c字母的 。
所以只有aac 和ac 符合条件 。
所以看这个例子 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
[root@hadoop-bigdata01
test
]
# ls
a aac abb abbc abc ac b bb c cb
[root@hadoop-bigdata01
test
]
# ls | grep 'a*b'
abb
abbc
abc
b
bb
cb
|
这里grep 'a*b' 指的可不是含有a和b 而是a重复0次或者多次然后含有b 。
以上所述是小编给大家介绍的linux下的通配符与正则表达式,希望对大家有所帮助,如果大家有任何疑问请给我留言,小编会及时回复大家的。在此也非常感谢大家对我网站的支持! 。
最后此篇关于linux下的通配符与正则表达式的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于linux下的通配符与正则表达式的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
关闭。这个问题不符合Stack Overflow guidelines .它目前不接受答案。 要求我们推荐或查找工具、库或最喜欢的场外资源的问题对于 Stack Overflow 来说是偏离主题的,
Linux 管道可以缓冲多少数据?这是可配置的吗? 如果管道的两端在同一个进程中,但线程不同,这会有什么不同吗? 请注意:这个“同一个进程,两个线程”的问题是理论上的边栏,真正的问题是关于缓冲的。 最
我找到了here [最后一页] 一种有趣的通过 Linux 启动 Linux 的方法。不幸的是,它只是被提及,我在网上找不到任何有用的链接。那么有人听说过一种避免引导加载程序而使用 Linux 的方法
很难说出这里要问什么。这个问题模棱两可、含糊不清、不完整、过于宽泛或夸夸其谈,无法以目前的形式得到合理的回答。如需帮助澄清此问题以便重新打开,visit the help center . 关闭 1
我试图了解 ld-linux.so 如何在 Linux 上解析对版本化符号的引用。我有以下文件: 测试.c: void f(); int main() { f(); } a.c 和 b.c:
与 RetroPie 的工作原理类似,我可以使用 Linux 应用程序作为我的桌面环境吗?我实际上并不需要像实际桌面和安装应用程序这样的东西。我只需要一种干净简单的方法来在 RaspberryPi 上
关闭。这个问题不符合Stack Overflow guidelines .它目前不接受答案。 这个问题似乎不是关于 a specific programming problem, a softwar
关闭。这个问题是off-topic .它目前不接受答案。 想改进这个问题吗? Update the question所以它是on-topic用于堆栈溢出。 关闭 10 年前。 Improve thi
有什么方法可以覆盖现有的源代码,我应该用 PyQt、PyGTK、Java 等从头开始构建吗? 最佳答案 如果您指的是软件本身而不是它所连接的存储库,那么自定义应用程序的方法就是 fork 项目。据我所
我的情况是:我在一个磁盘上安装了两个 linux。我将第一个安装在/dev/sda1 中,然后在/dev/sda2 中安装第二个然后我运行第一个系统,我写了一个脚本来在第一个系统运行时更新它。
我在 i2c-0 总线上使用地址为 0x3f 的系统监视器设备。该设备在设备树中配置有 pmbus 驱动程序。 问题是,加载 linux 内核时,这个“Sysmon”设备没有供电。因此,当我在总线 0
关闭。这个问题是off-topic .它目前不接受答案。 想改进这个问题吗? Update the question所以它是on-topic用于堆栈溢出。 关闭 11 年前。 Improve thi
我正试图在 linux 模块中分配一大块内存,而 kalloc 做不到。 我知道唯一的方法是使用 alloc_bootmem(unsigned long size) 但我只能从 linux 内核而不是
关闭。这个问题不符合Stack Overflow guidelines .它目前不接受答案。 这个问题似乎不是关于 a specific programming problem, a softwar
我有 .sh 文件来运行应用程序。在该文件中,我想动态设置服务器名称,而不是每次都配置。 我尝试了以下方法,它在 CentOS 中运行良好。 nohup /voip/java/jdk1.8.0_71/
我是在 Linux 上开发嵌入式 C++ 程序的新手。我有我的 Debian 操作系统,我在其中开发和编译了我的 C++ 项目(一个简单的控制台进程)。 我想将我的应用程序放到另一个 Debian 操
关闭。这个问题需要多问focused 。目前不接受答案。 想要改进此问题吗?更新问题,使其仅关注一个问题 editing this post . 已关闭 4 年前。 Improve this ques
我使用4.19.78版本的稳定内核,我想找到带有企鹅二进制数据的C数组。系统启动时显示。我需要在哪里搜索该内容? 我在 include/linux/linux_logo.h 文件中只找到了一些 Log
我知道可以使用 gdb 的服务器模式远程调试代码,我知道可以调试针对另一种架构交叉编译的代码,但是是否可以更进一步,从远程调试 Linux 应用程序OS X 使用 gdbserver? 最佳答案 当然
是否有任何可能的方法来运行在另一个 Linux 上编译的二进制文件?我知道当然最简单的是在另一台机器上重建它,但假设我们唯一能得到的是一个二进制文件,那么这可能与否? (我知道这可能并不容易,但我只是

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!