- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章C++ 双链表的基本操作(详解)由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
1.概念 。
双向链表也叫双链表,是链表的一种,它的每个数据结点中都有两个指针,分别指向直接后继和直接前驱。所以,从双向链表中的任意一个结点开始,都可以很方便地访问它的前驱结点和后继结点。一般我们都构造双向循环链表.
结构图如下所示:
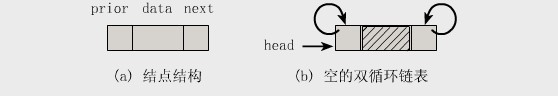
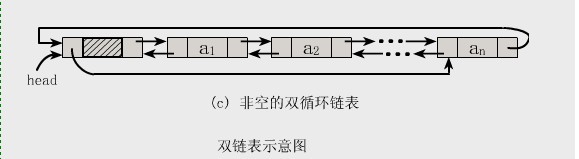
2.基本操作实例 。
DoubleList.cpp 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
|
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "DoubleList.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
DoubleList::DoubleList()
{
pDoubleListNode pDouList = NULL;
// 创建双链表
CreateDouList(pDouList);
PrintDouList(pDouList);
// 打印逆序链表
PrintDouReverseList(pDouList);
// 节点后插入节点
InsertNodeAfter(pDouList);
PrintDouList(pDouList);
// 节点前插入节点
InsertNodeBefore(pDouList);
PrintDouList(pDouList);
// 删除节点
DeleteNode(pDouList);
PrintDouList(pDouList);
// 删除链表
DeleteDouList(pDouList);
PrintDouList(pDouList);
system
(
"PAUSE"
);
}
DoubleList::~DoubleList()
{
}
//创建双向链表
void
DoubleList::CreateDouList(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
char
x;
// 定义成char型是用于输入'q'时可以退出,其实定义成int也能退出
pDoubleListNode p, s;
head = (pDoubleListNode)
malloc
(
sizeof
(DoubleListNode));
head->next = NULL;
head->prior = NULL;
// 构造头结点p
p = head;
printf
(
"\n输入双向链表的元素,每输入一个元素后按回车,输入q表示结束.\n"
);
fflush
(stdin);
//清空输入缓冲区
x =
getchar
();
while
(x !=
'q'
)
{
s = (pDoubleListNode)
malloc
(
sizeof
(DoubleListNode));
s->data = x -
'0'
;
// 得到的是输入字符的ASCII码,减去30H就变成想要的数字
s->next = NULL;
s->prior = p;
p->next = s;
p = s;
fflush
(stdin);
x =
getchar
();
}
if
(x ==
'q'
)
{
printf
(
"双向链表构造完毕!\n"
);
}
}
//打印双向链表
void
DoubleList::PrintDouList(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
pDoubleListNode p;
printf
(
"\n打印出双向链表数据为:\n"
);
if
(!IsDouListEmpty(head))
{
p = head->next;
while
(p)
{
printf
(
"%d\n"
, p->data);
p = p->next;
}
}
}
//逆序打印双向链表
void
DoubleList::PrintDouReverseList(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
pDoubleListNode p;
printf
(
"\n打印出逆序双向链表数据为:\n"
);
if
(!IsDouListEmpty(head))
{
p = head->next;
while
(p->next)
{
p = p->next;
}
while
(p->prior)
{
printf
(
"%d \n"
, p->data);
p = p->prior;
}
}
}
//求链表长度
int
DoubleList::GetDouListLength(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
int
length = 0;
if
(head == NULL)
{
printf
(
"链表不存在,请先初始化!\n"
);
}
else
{
pDoubleListNode p = head->next;
while
(p)
{
length++;
p = p->next;
}
}
return
length;
}
//判断链表是否为空
bool
DoubleList::IsDouListEmpty(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
if
(head == NULL)
{
printf
(
"链表不存在,请先初始化!\n"
);
return
true
;
}
else
if
(head->next == NULL)
{
printf
(
"链表为空!\n"
);
return
true
;
}
return
false
;
}
//把双向链表置空
void
DoubleList::ClearDouList(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
if
(head == NULL)
{
printf
(
"链表不存在,请先初始化!\n"
);
}
else
{
pDoubleListNode p, q;
p = q = head->next;
//是p、q指向第一个元素
head->next = NULL;
while
(p)
//逐个释放元素所占内存
{
p = p->next;
free
(q);
q = p;
}
}
}
// 删除双向链表
void
DoubleList::DeleteDouList(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
printf
(
"\n删除双向链表\n"
);
ClearDouList(head);
free
(head);
head = NULL;
}
// 在双向链表中第i个位置后面插入元素
void
DoubleList::InsertNodeAfter(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
int
data, pos;
pDoubleListNode p, s;
p = head;
int
i = 0;
printf
(
"\n在双向链表中第i个位置后面插入元素\n"
);
printf
(
"请输入要插入的元素和位置:\n"
);
scanf_s(
"%d%d"
, &data, &pos, 100);
if
(head == NULL)
{
printf
(
"链表不存在,请先初始化!\n"
);
}
else
if
(head->next == NULL)
{
printf
(
"链表为空,插入第一个元素!\n"
);
s = (pDoubleListNode)
malloc
(
sizeof
(DoubleListNode));
s->data = data;
s->prior = NULL;
s->next = NULL;
head->next = s;
// 将新结点插入head后
}
else
if
(pos<1 || pos>GetDouListLength(head) + 1)
{
printf
(
"插入位置错误!\n"
);
}
else
{
while
(i < pos)
{
p = p->next;
i++;
}
if
(i == GetDouListLength(head))
//如果在最后一个元素后面插入data
{
s = (pDoubleListNode)
malloc
(
sizeof
(DoubleListNode));
s->data = data;
s->next = NULL;
s->prior = p;
p->next = s;
}
else
{
s = (pDoubleListNode)
malloc
(
sizeof
(DoubleListNode));
s->data = data;
s->next = p->next;
p->next->prior = s;
p->next = s;
s->prior = p;
}
}
}
// 在双向链表中第i个位置前面插入元素
void
DoubleList::InsertNodeBefore(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
int
data, pos;
pDoubleListNode p, s;
p = head;
int
i = 0;
printf
(
"\n在双向链表中第i个位置前面插入元素\n"
);
printf
(
"请输入要插入的元素和位置:\n"
);
scanf_s(
"%d%d"
, &data, &pos, 100);
if
(head == NULL)
{
printf
(
"链表不存在,请先初始化!\n"
);
}
else
if
(head->next == NULL)
{
printf
(
"链表为空,插入第一个元素!\n"
);
s = (pDoubleListNode)
malloc
(
sizeof
(DoubleListNode));
s->data = data;
s->prior = NULL;
s->next = NULL;
head->next = s;
// 将新结点插入head后
}
else
if
(pos<1 || pos>GetDouListLength(head) + 1)
{
printf
(
"插入位置错误!\n"
);
}
else
{
while
(i < pos)
{
p = p->next;
i++;
}
if
(i == 1)
// 如果在第一个元素前面插入data
{
s = (pDoubleListNode)
malloc
(
sizeof
(DoubleListNode));
s->data = data;
head->next = s;
// 将新结点插入head后
s->prior = head;
// 新结点的前结点指向头结点
s->next = p;
// 新结点的后结点指向原head的后结点
p->prior = s ;
// 原第一个结点的前结点指向新结点
}
else
{
s = (pDoubleListNode)
malloc
(
sizeof
(DoubleListNode));
s->data = data;
s->prior = p->prior;
s->next = p;
p->prior->next = s;
p->prior = s;
}
}
}
//删除双向链表中的第i个元素
void
DoubleList::DeleteNode(pDoubleListNode &head)
{
int
pos;
int
i = 0;
pDoubleListNode p = head;
printf
(
"\n在双向链表中删除第i个位置的元素\n"
);
printf
(
"请输入要删除的位置:"
);
scanf_s(
"%d"
, &pos, 100);
if
(IsDouListEmpty(head))
{
return
;
}
else
if
(pos<1 || pos>GetDouListLength(head))
{
printf
(
"删除的位置不存在!\n"
);
}
else
{
while
(i < pos)
{
p = p->next;
i++;
}
if
(i == GetDouListLength(head))
{
p->prior->next = NULL;
free
(p);
}
else
{
p->prior->next = p->next;
p->next->prior = p->prior;
free
(p);
}
}
}
|
DoubleList.h 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
#pragma once
typedef
struct
DoubleListNode
{
int
data;
//数据
struct
DoubleListNode *prior;
//前驱
struct
DoubleListNode *next;
//后继
}DoubleListNode, *pDoubleListNode;
class
DoubleList
{
public
:
DoubleList();
~DoubleList();
//初始化双向链表
void
DoubleList::CreateDouList(pDoubleListNode &head);
//打印双向链表
void
DoubleList::PrintDouList(pDoubleListNode &head);
//逆序打印双向链表
void
DoubleList::PrintDouReverseList(pDoubleListNode &head);
//求链表长度
int
DoubleList::GetDouListLength(pDoubleListNode &head);
//判断链表是否为空
bool
DoubleList::IsDouListEmpty(pDoubleListNode &head);
//把双向链表置空
void
DoubleList::ClearDouList(pDoubleListNode &head);
//删除双向链表
void
DoubleList::DeleteDouList(pDoubleListNode &head);
//在双向链表中第i个位置后面插入元素m
void
DoubleList::InsertNodeAfter(pDoubleListNode &head);
// 在双向链表中第i个位置前面插入元素
void
DoubleList::InsertNodeBefore(pDoubleListNode &head);
//删除双向链表中的第i个元素
void
DoubleList::DeleteNode(pDoubleListNode &head);
};
|
3.对链表插入节点的理解 。
例如在节点i前插入一个新的节点(即上面代码中的InsertNodeBefore函数)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
typedef
struct
DoubleListNode
{
int
data;
// 数据
struct
DoubleListNode *prior;
// 前驱
struct
DoubleListNode *next;
// 后继
}DoubleListNode, *pDoubleListNode;
|
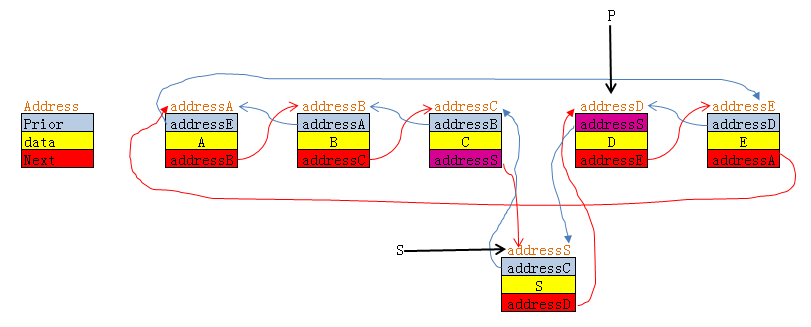
假设该链表由五个节点构成,分别为A,B,C,D,E 。

图中假设了A,B,C,D,E的地址分别为:addressA,addressB,addressC,addressD,addressE.
下面将分析链表的前插的例子
双链表的前插,下面这是在节点"D"前插入一个新的节点"S"的代码和分析 。
以上这篇C++ 双链表的基本操作(详解)就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我.
最后此篇关于C++ 双链表的基本操作(详解)的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于C++ 双链表的基本操作(详解)的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
大家好,我是汤师爷~ 什么是订单履约系统? 订单履约是从消费者下单支付到收到商品的全流程管理过程,包括订单接收、订单派单、库存分配、仓储管理和物流配送等环节,核心目标是确保商品准时、准确地送达消费
大家好,我是汤师爷~ 今天聊聊促销系统整体规划。 各类促销活动的系统流程,可以抽象为3大阶段: B端促销活动管理:商家运营人员在后台系统中配置和管理促销活动,包括设定活动基本信息、使用规则
全称“Java Virtual Machine statistics monitoring tool”(statistics 统计;monitoring 监控;tool 工具) 用于监控虚拟机的各种运
主要是讲下Mongodb的索引的查看、创建、删除、类型说明,还有就是Explain执行计划的解释说明。 可以转载,但请注明出处。
1>单线程或者单进程 相当于短链接,当accept之后,就开始数据的接收和数据的发送,不接受新的连接,即一个server,一个client 不存在并发。 2>循环服务器和并发服务器
详解 linux中的关机和重启命令 一 shutdown命令 shutdown [选项] 时间 选项: ?
首先,将json串转为一个JObject对象: ? 1
matplotlib官网 matplotlib库默认英文字体 添加黑体(‘SimHei')为绘图字体 代码: plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei'
在并发编程中,synchronized关键字是常出现的角色。之前我们都称呼synchronized关键字为重量锁,但是在jdk1.6中对synchronized进行了优化,引入了偏向锁、轻量锁。本篇
一般我们的项目中会使用1到2个数据库连接配置,同程艺龙的数据库连接配置被收拢到统一的配置中心,由DBA统一配置和维护,业务方通过某个字符串配置拿到的是Connection对象。
实例如下: ? 1
1. MemoryCahe NetCore中的缓存和System.Runtime.Caching很相似,但是在功能上做了增强,缓存的key支持object类型;提供了泛型支持;可以读缓存和单个缓存
argument是javascript中函数的一个特殊参数,例如下文,利用argument访问函数参数,判断函数是否执行 复制代码 代码如下: <script
一不小心装了一个Redis服务,开了一个全网的默认端口,一开始以为这台服务器没有公网ip,结果发现之后悔之莫及啊 某天发现cpu load高的出奇,发现一个minerd进程 占了大量cpu,googl
今天写这个是为了 提醒自己 编程过程 不仅要有逻辑 思想 还有要规范 代码 这样可读性 1、PHP 编程规范与编码习惯最主要的有以下几点: 1 文件说明 2 funct
摘要:虚拟机安装时一般都采用最小化安装,默认没有lspci工具。一台测试虚拟网卡性能的虚拟机,需要lspci工具来查看网卡的类型。本文描述了在一个虚拟机中安装lspci工具的具体步骤。 由于要测试
1、修改用户进程可打开文件数限制 在Linux平台上,无论编写客户端程序还是服务端程序,在进行高并发TCP连接处理时,最高的并发数量都要受到系统对用户单一进程同时可打开文件数量的限制(这是因为系统
目录 算术运算符 基本四则运算符 增量赋值运算符 自增/自减运算符 关系运算符 逻
如下所示: ? 1
MapperScannerConfigurer之sqlSessionFactory注入方式讲解 首先,Mybatis中的有一段配置非常方便,省去我们去写DaoImpl(Dao层实现类)的时间,这个

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!