- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章java 实现Comparable接口排序,升序、降序、倒叙由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
本人由于项目开发中需要对查询结果list进行排序,这里根据的是每一个对象中的创建时间降序排序。本人讲解不深,只实现目的,如需理解原理还需查阅更深的资料.
1.实现的效果 。
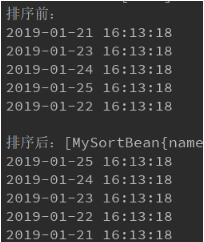
2.创建排序的对象 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
|
package
com.practice.test.comparable;
import
java.util.Date;
/**
* 描述:要比较的对象
*
* @author cui
* @create 2018-12-18 14:07
*/
public
class
MySortBean
implements
Comparable<MySortBean> {
private
String name;
private
int
age;
private
Date createTime;
public
String getName() {
return
name;
}
public
void
setName(String name) {
this
.name = name;
}
public
int
getAge() {
return
age;
}
public
void
setAge(
int
age) {
this
.age = age;
}
public
Date getCreateTime() {
return
createTime;
}
public
void
setCreateTime(Date createTime) {
this
.createTime = createTime;
}
// @Override
// public int compareTo(MySortBean o) {
// if (this.age>o.age){
// return -1;
// }else if (this.age==o.age){
// return 0;
// }
// return 1;
// }
@Override
public
int
compareTo(MySortBean o) {
if
(
this
.createTime.compareTo(o.getCreateTime())>
0
){
return
-
1
;
}
else
if
(
this
.createTime.compareTo(o.getCreateTime())==
0
){
return
0
;
}
return
1
;
}
@Override
public
String toString() {
return
"MySortBean{"
+
"name='"
+ name + '\
''
+
", age="
+ age +
'}'
;
}
}
|
3.编写test方法 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
|
package
com.practice.test;
import
com.practice.test.comparable.MySortBean;
import
com.spring.testlist.util.DateUtil;
import
org.junit.Test;
import
org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import
org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import
java.util.ArrayList;
import
java.util.Date;
import
java.util.List;
/**
* 描述:
* 测试比较器
*
* @author cui
* @create 2018-12-18 14:10
*/
@RunWith
(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.
class
)
public
class
TestCompare {
@Test
public
void
testComparable(){
MySortBean m1 =
new
MySortBean();
m1.setAge(
1
);
m1.setCreateTime(DateUtil.parseDate(
"2019-01-21 16:13:18"
));
MySortBean m2 =
new
MySortBean();
m2.setAge(
2
);
m2.setCreateTime(DateUtil.parseDate(
"2019-01-23 16:13:18"
));
MySortBean m3 =
new
MySortBean();
m3.setAge(
3
);
m3.setCreateTime(DateUtil.parseDate(
"2019-01-22 16:13:18"
));
MySortBean m4 =
new
MySortBean();
m4.setAge(
4
);
m4.setCreateTime(DateUtil.parseDate(
"2019-01-24 16:13:18"
));
MySortBean m5 =
new
MySortBean();
m5.setAge(
5
);
m5.setCreateTime(DateUtil.parseDate(
"2019-01-25 16:13:18"
));
List<MySortBean> l =
new
ArrayList<>(
5
);
l.add(m1);
l.add(m2);
l.add(m4);
l.add(m5);
l.add(m3);
System.out.println(
"排序前:"
);
for
(MySortBean i:l) {
System.out.println(DateUtil.formatDate(i.getCreateTime(),
"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
));
}
/**
* 自定义排序
* 直接return -1 倒叙排列,list顺序颠倒输出
*
* if (o1.getAge()>o2.getAge()){
* return 1;
* }
* return -1;
* 以上升序输出
*
* if (o1.getAge()>o2.getAge()){
* return -1;
* }
* return 1;
* 以上降序输出
*
*
*/
/* Comparator<MySortBean> comparator = new Comparator<MySortBean>() {
@Override
public int compare(MySortBean o1,MySortBean o2) {
if (o1.getAge()>o2.getAge()){
return -1;
}
return 1;
}
};
l.sort(comparator);*/
l.sort(MySortBean::compareTo);
System.out.println(
"--------"
);
System.out.println(
"排序后:"
);
for
(MySortBean i:l) {
System.out.println(DateUtil.formatDate(i.getCreateTime(),
"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
));
}
}
}
|
4.时间格式化工具类 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
|
package
com.spring.testlist.util;
import
org.apache.commons.lang3.time.DateFormatUtils;
import
java.text.ParseException;
import
java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import
java.util.Calendar;
import
java.util.Date;
/**
* 日期工具类, 继承org.apache.commons.lang.time.DateUtils类
*
* @author cui
* @create 2018-10-26 15:30
**/
public
class
DateUtil
extends
org.apache.commons.lang3.time.DateUtils{
private
static
String[] parsePatterns = {
"yyyy-MM-dd"
,
"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
,
"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm"
,
"yyyy-MM"
,
"yyyy/MM/dd"
,
"yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss"
,
"yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm"
,
"yyyy/MM"
,
"yyyy.MM.dd"
,
"yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss"
,
"yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm"
,
"yyyy.MM"
};
/**
* 得到当前日期字符串 格式(yyyy-MM-dd)
*/
public
static
String getDate() {
return
getDate(
"yyyy-MM-dd"
);
}
/**
* 得到当前日期字符串 格式(yyyyMMdd)
*/
public
static
String getSizeDate() {
return
getDate(
"yyyyMMdd"
);
}
/**
* 得到当前日期字符串 格式(yyyy-MM-dd) pattern可以为:"yyyy-MM-dd" "HH:mm:ss" "E"
*/
public
static
String getDate(String pattern) {
return
DateFormatUtils.format(
new
Date(), pattern);
}
/**
* 得到日期字符串 默认格式(yyyy-MM-dd) pattern可以为:"yyyy-MM-dd" "HH:mm:ss" "E"
*/
public
static
String formatDate(Date date, Object... pattern) {
if
(date ==
null
) {
return
null
;
}
String formatDate =
null
;
if
(pattern !=
null
&& pattern.length >
0
) {
formatDate = DateFormatUtils.format(date, pattern[
0
].toString());
}
else
{
formatDate = DateFormatUtils.format(date,
"yyyy-MM-dd"
);
}
return
formatDate;
}
/**
* 得到日期时间字符串,转换格式(yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss)
*/
public
static
String formatDateTime(Date date) {
return
formatDate(date,
"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
);
}
/**
* 得到当前时间字符串 格式(HH:mm:ss)
*/
public
static
String getTime() {
return
formatDate(
new
Date(),
"HH:mm:ss"
);
}
/**
* 得到当前日期和时间字符串 格式(yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss)
*/
public
static
String getDateTime() {
return
formatDate(
new
Date(),
"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
);
}
/**
* 得到当前年份字符串 格式(yyyy)
*/
public
static
String getYear() {
return
formatDate(
new
Date(),
"yyyy"
);
}
/**
* 得到当前月份字符串 格式(MM)
*/
public
static
String getMonth() {
return
formatDate(
new
Date(),
"MM"
);
}
/**
* 得到当天字符串 格式(dd)
*/
public
static
String getDay() {
return
formatDate(
new
Date(),
"dd"
);
}
/**
* 得到当前星期字符串 格式(E)星期几
*/
public
static
String getWeek() {
return
formatDate(
new
Date(),
"E"
);
}
/**
* 日期型字符串转化为日期 格式
* { "yyyy-MM-dd", "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss", "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm",
* "yyyy/MM/dd", "yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss", "yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm",
* "yyyy.MM.dd", "yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm:ss", "yyyy.MM.dd HH:mm" }
*/
public
static
Date parseDate(Object str) {
if
(str ==
null
) {
return
null
;
}
try
{
return
parseDate(str.toString(), parsePatterns);
}
catch
(ParseException e) {
return
null
;
}
}
/**
* 获取过去的天数
*
* @param date
* @return
*/
public
static
long
pastDays(Date date) {
long
t = System.currentTimeMillis()- date.getTime();
return
t / (
24
*
60
*
60
*
1000
);
}
/**
* 获取过去的小时
*
* @param date
* @return
*/
public
static
long
pastHour(Date date) {
long
t =System.currentTimeMillis() - date.getTime();
return
t / (
60
*
60
*
1000
);
}
/**
* 获取过去的分钟
*
* @param date
* @return
*/
public
static
long
pastMinutes(Date date) {
long
t = System.currentTimeMillis() - date.getTime();
return
t / (
60
*
1000
);
}
/**
* 转换为时间(天,时:分:秒.毫秒)
*
* @param timeMillis
* @return
*/
public
static
String formatDateTime(
long
timeMillis) {
long
day = timeMillis / (
24
*
60
*
60
*
1000
);
long
hour = (timeMillis / (
60
*
60
*
1000
) - day *
24
);
long
min = ((timeMillis / (
60
*
1000
)) - day *
24
*
60
- hour *
60
);
long
s = (timeMillis /
1000
- day *
24
*
60
*
60
- hour *
60
*
60
- min *
60
);
long
sss = (timeMillis - day *
24
*
60
*
60
*
1000
- hour *
60
*
60
*
1000
- min *
60
*
1000
- s *
1000
);
return
(day >
0
? day +
","
:
""
) + hour +
":"
+ min +
":"
+ s +
"."
+ sss;
}
/**
* 获取两个日期之间的天数
*
* @param before
* @param after
* @return
*/
public
static
double
getDistanceOfTwoDate(Date before, Date after) {
long
beforeTime = before.getTime();
long
afterTime = after.getTime();
return
(afterTime - beforeTime) / (
1000
*
60
*
60
*
24
);
}
public
static
String getFirstDayOfMonth() {
SimpleDateFormat format =
new
SimpleDateFormat(
"yyyy-MM-dd"
);
//获取当前月第一天:
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
c.add(Calendar.MONTH,
0
);
c.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH,
1
);
//设置为1号,当前日期既为本月第一天
String first = format.format(c.getTime());
return
first;
}
/**
* @param args
* @throws ParseException
*/
public
static
void
main(String[] args)
throws
ParseException {
// System.out.println(formatDate(parseDate("2010/3/6")));
// System.out.println(getDate("yyyy年MM月dd日 E"));
// long time = new Date().getTime()-parseDate("2012-11-19").getTime();
// System.out.println(time/(24*60*60*1000));
String sizeDate = formatDate(
new
Date(),
"yyyyMMdd"
);
System.out.println(sizeDate);
}
}
|
到此就结束了,具体的要实现什么排序,根据示例自己脑补扩展就好了,例子中备注也已经标注.
在使用排序注意两个坑 。
1.要排序的字段为空的异常处理 。
2.要排序的字段相等的异常处理 。
补充知识:Java中的自然排序和比较器排序 。
写在前面的话:刚开始学习着两者排序时我也是一头雾水,虽然能写出来但是稀里糊涂,几时该用哪个排序一点想法都没有,后来经过研究这两者的作用点不同,自然排序作用在实体类上,而比较器排序作用在装实体类的集合上.
1、自然排序:java.lang.Comparable 。
Comparable 接口中只提供了一个方法: compareTo(Object obj) ,该方法的返回值是 int 。如果返回值为正数,则表示当前对象(调用该方法的对象)比 obj 对象“大”;反之“小”;如果为零的话,则表示两对象相等.
总结为一句话:实现Comparable,重写 compareTo方法 。
案列:以TreeMap为例,默认的升序,可以重写自然排序的方法改变原有排序 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
public
static
void
testComparable(){
TreeMap<Car,Object> tmp =
new
TreeMap<Car,Object>();
tmp.put(
new
Car(
4
),
"肆"
);
tmp.put(
new
Car(
1
),
"壹"
);
tmp.put(
new
Car(
5
),
"伍"
);
tmp.put(
new
Car(
3
),
"三"
);
tmp.put(
new
Car(
2
),
"贰"
);
System.out.println(tmp);
//结果://{Car [price=5.0]=伍, Car [price=4.0]=肆, Car [price=3.0]=三, Car [price=2.0]=贰, Car [price=1.0]=壹}
}
//自定义TreeMap排序方法 自然排序
class
Car
implements
Comparable<Car>{
private
double
price;
public
double
getPrice() {
return
price;
}
public
void
setPrice(
double
price) {
this
.price = price;
}
public
Car(
int
price) {
super
();
this
.price = price;
}
@Override
public
int
compareTo(Car o) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if
(
this
.price>o.getPrice()){
return
-
1
;
//大的往前排
}
else
if
(
this
.price<o.getPrice()){
return
1
;
//小的往后排
}
else
{
return
0
;
}
}
@Override
public
String toString() {
return
"Car [price="
+ price +
"]"
;
}
|
2、比较器排序:java.util.Comparator 。
总结为一句话:实现Comparator 接口,重写compare方法 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
public
static
void
testComparator(){
//HashMap<Integer,Object> hm = new HashMap<Integer,Object>();
TreeMap<Integer,Object> tmp =
new
TreeMap<Integer,Object>(
new
MyComparatorBigtoSmall());
tmp.put(
4
,
"肆"
);
tmp.put(
1
,
"壹"
);
tmp.put(
5
,
"伍"
);
tmp.put(
3
,
"三"
);
tmp.put(
2
,
"贰"
);
//System.out.println(tmp);//默认排序结果:{1=壹, 2=贰, 3=三, 4=肆, 5=伍}
System.out.println(tmp);
//修改为比较器排序(升序){5=伍, 4=肆, 3=三, 2=贰, 1=壹}
}
//自定义TreeMap排序方法 比较器排序
class
MyComparatorBigtoSmall
implements
Comparator<Integer>{
@Override
public
int
compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return
o2-o1;
}
}
|
以上这篇java 实现Comparable接口排序,升序、降序、倒叙就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我.
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/C1041067258/article/details/86578188 。
最后此篇关于java 实现Comparable接口排序,升序、降序、倒叙的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于java 实现Comparable接口排序,升序、降序、倒叙的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我正在尝试对每个条目有多个值的关联数组进行排序。 例如 [0] => stdClass Object ( [type] => node [sid] => 158 [score] => 0.059600
我在 mysql 中有“日期”列以这种格式保存日期 2014 年 9 月 17 日(日-月-年) 我需要对它们进行升序排序,所以我使用了这个命令: SELECT * FROM table ORDER
我目前正在将 MySQL 存储过程重写为 MS SQL 存储过程,但遇到了问题。 在 MySQL 存储过程中,有一个游标,它根据最近的日期 (effdate) 选择一个值并将其放入变量 (thestt
我想要 gwt r.QuestionId- 排序。但是我得到未排序的 QuestionId 尽管我提到了 QuestionId ASC 的顺序。 SELECT r.QuestionId,
我有一个关于在 scandir 函数中排序的基本问题。到目前为止,我阅读了 POSIX readdir 的手册页,但没有找到有关订购保证的具体信息。 但是当我遍历大目录(无法更改,只读)时,我在多个系
基本上我必须从 SQL 数据库中构建项目列表,但是用户可以选择对 7 个过滤器的任意组合进行过滤,也可以选择要排序的列以及按方向排序。 正如您可以想象的那样,这会以大量不同的组合进行编码,并且数据集非
我有两张 table 。想象第一个是一个目录,包含很多文件(第二个表)。 第二个表(文件)包含修改日期。 现在,我想选择所有目录并按修改日期 ASC 对它们进行排序(因此,最新的修改最上面)。我不想显
我想先根据用户的状态然后根据用户名来排序我的 sql 请求。该状态由 user_type 列设置: 1=活跃,2=不活跃,3=创始人。 我会使用此请求来执行此操作,但它不起作用,因为我想在“活跃”成员
在 C++ 中,我必须实现一个“类似 Excel/Access”(引用)的查询生成器,以允许对数据集进行自定义排序。如果您在 Excel 中使用查询构建器或 SQL 中的“ORDER BY a, b,
我面临这样的挑战: 检索按字段 A 排序的文档 如果字段 B 存在/不为空 . 否则 按字段排序 C. 在 SQL 世界中,我会做两个查询并创建一个 UNION SELECT,但我不知道如何从 Mon
我想对源列表执行以下操作: map 列表 排序 折叠 排序 展开 列表 其中一些方法(例如map和toList)是可链接的,因为它们返回非空对象。但是,sort 方法返回 void,因为它对 List
我制作了一个用于分析 Windows 日志消息编号的脚本。 uniq -c 数字的输出很难预测,因为根据数字的大小会有不同的空白。此时,我手动删除了空白。 这是对消息进行排序和计数的命令: cat n
我有以下词典: mydict1 = {1: 11, 2: 4, 5: 1, 6: 1} mydict2 = {1: 1, 5: 1} 对于它们中的每一个,我想首先按值(降序)排序,然后按键(升序)排序
我刚刚开始使用泛型,目前在对多个字段进行排序时遇到问题。 案例: 我有一个 PeopleList 作为 TObjectList我希望能够通过一次选择一个排序字段,但尽可能保留以前的排序来制作类似 Ex
有没有办法在 sql 中组合 ORDER BY 和 IS NULL 以便我可以在列不为空时按列排序,但如果它为null,按另一列排序? 最佳答案 类似于: ORDER BY CASE WHEN
我有一个包含 2 列“id”和“name”的表。 id 是常规的自动增量索引,name 只是 varchar。 id name 1 john 2 mary 3 pop 4 mary 5 j
场景 网站页面有一个带有分页、过滤、排序功能的表格 View 。 表中的数据是从REST API服务器获取的,数据包含数百万条记录。 数据库 REST API 服务器 Web 服务器 浏览器 问
假设我有一本字典,其中的键(单词)和值(分数)如下: GOD 8 DONG 16 DOG 8 XI 21 我想创建一个字典键(单词)的 NSArray,首先按分数排序,然后按字
如何在 sphinx 上通过 sql 命令选择前 20 行按标题 WEIGHT 排序,接下来 20 行按标题 ASC 排序(总共 40 个结果),但不要给出重复的标题输出。 我尝试了这个 sql 命令
我有一个奇怪的问题,当从 SQLite 数据库中选择信息并根据日期排序时,返回的结果无效。 我的SQL语句是这样的: Select pk from usersDates order by dateti

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!