- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章使用Spring的AbstractRoutingDataSource实现多数据源切换示例由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
最近因为项目需要在做两个项目间数据同步的需求,具体是项目1的数据通过消息队列同步到项目2中,因为这个更新操作还涉及到更新多个库的数据,所以就需要多数据源切换的操作。下面就讲讲在Spring中如何进行数据源切换。这里是使用AbstractRoutingDataSource类来完成具体的操作,AbstractRoutingDataSource是Spring2.0后增加的.
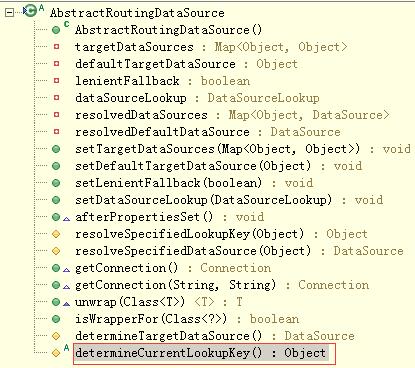
实现数据源切换的功能就是自定义一个类扩展AbstractRoutingDataSource抽象类,其实该相当于数据源DataSourcer的路由中介,可以实现在项目运行时根据相应key值切换到对应的数据源DataSource上。先看看AbstractRoutingDataSource的源码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
public
abstract
class
AbstractRoutingDataSource
extends
AbstractDataSource
implements
InitializingBean {
/* 只列出部分代码 */
private
Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources;
private
Object defaultTargetDataSource;
private
boolean
lenientFallback =
true
;
private
DataSourceLookup dataSourceLookup =
new
JndiDataSourceLookup();
private
Map<Object, DataSource> resolvedDataSources;
private
DataSource resolvedDefaultDataSource;
@Override
public
Connection getConnection()
throws
SQLException {
return
determineTargetDataSource().getConnection();
}
@Override
public
Connection getConnection(String username, String password)
throws
SQLException {
return
determineTargetDataSource().getConnection(username, password);
}
protected
DataSource determineTargetDataSource() {
Assert.notNull(
this
.resolvedDataSources,
"DataSource router not initialized"
);
Object lookupKey = determineCurrentLookupKey();
DataSource dataSource =
this
.resolvedDataSources.get(lookupKey);
if
(dataSource ==
null
&& (
this
.lenientFallback || lookupKey ==
null
)) {
dataSource =
this
.resolvedDefaultDataSource;
}
if
(dataSource ==
null
) {
throw
new
IllegalStateException(
"Cannot determine target DataSource for lookup key ["
+ lookupKey +
"]"
);
}
return
dataSource;
}
protected
abstract
Object determineCurrentLookupKey();
}
|
从源码可以看出AbstractRoutingDataSource继承了AbstractDataSource并实现了InitializingBean,AbstractRoutingDataSource的getConnection()方法调用了determineTargetDataSource()的该方法,这里重点看determineTargetDataSource()方法代码,方法里使用到了determineCurrentLookupKey()方法,它是AbstractRoutingDataSource类的抽象方法,也是实现数据源切换要扩展的方法,该方法的返回值就是项目中所要用的DataSource的key值,拿到该key后就可以在resolvedDataSource中取出对应的DataSource,如果key找不到对应的DataSource就使用默认的数据源.
自定义类扩展AbstractRoutingDataSource类时就是要重写determineCurrentLookupKey()方法来实现数据源切换功能。下面是自定义的扩展AbstractRoutingDataSource类的实现:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
/**
* 获得数据源
*/
public
class
MultipleDataSource
extends
AbstractRoutingDataSource{
@Override
protected
Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return
DynamicDataSourceHolder.getRouteKey();
}
}
|
DynamicDataSourceHolder类如下,实现对数据源的操作功能:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
/**
* 数据源操作类
*/
public
class
DynamicDataSourceHolder {
private
static
ThreadLocal<String> routeKey =
new
ThreadLocal<String>();
/**
* 获取当前线程的数据源路由的key
*/
public
static
String getRouteKey()
{
String key = routeKey.get();
return
key;
}
/**
* 绑定当前线程数据源路由的key
* 使用完成后必须调用removeRouteKey()方法删除
*/
public
static
void
setRouteKey(String key)
{
routeKey.set(key);
}
/**
* 删除与当前线程绑定的数据源路由的key
*/
public
static
void
removeRouteKey()
{
routeKey.remove();
}
}
|
下面在xml文件中配置多个数据源:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
<!-- 数据源 -->
<
bean
id
=
"dataSource1"
class
=
"org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"
>
<
property
name
=
"driverClassName"
value
=
"net.sourceforge.jtds.jdbc.Driver"
>
</
property
>
<
property
name
=
"url"
value
=
"jdbc:jtds:sqlserver://127.0.0.1;databaseName=test"
>
</
property
>
<
property
name
=
"username"
value
=
"***"
></
property
>
<
property
name
=
"password"
value
=
"***"
></
property
>
</
bean
>
<
bean
id
=
"dataSource2"
class
=
"org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"
>
<
property
name
=
"driverClassName"
value
=
"net.sourceforge.jtds.jdbc.Driver"
>
</
property
>
<
property
name
=
"url"
value
=
"jdbc:jtds:sqlserver://127.0.0.2:1433;databaseName=test"
>
</
property
>
<
property
name
=
"username"
value
=
"***"
></
property
>
<
property
name
=
"password"
value
=
"***"
></
property
>
</
bean
>
<!-- 配置多数据源映射 -->
<
bean
id
=
"multipleDataSource"
class
=
"MultipleDataSource"
>
<
property
name
=
"targetDataSources"
>
<
map
key-type
=
"java.lang.String"
>
<
entry
value-ref
=
"dataSource1"
key
=
"dataSource1"
></
entry
>
<
entry
value-ref
=
"dataSource2"
key
=
"dataSource2"
></
entry
>
</
map
>
</
property
>
<!-- 默认数据源 -->
<
property
name
=
"defaultTargetDataSource"
ref
=
"dataSource1"
>
</
property
>
</
bean
>
|
到这里基本的配置就完成了,下面只要在需要切换数据源的地方调用方法就行了,一般是在dao层操作数据库前进行切换的,只需在数据库操作前加上如下代码即可:
|
1
|
DynamicDataSourceHolder.setRouteKey(
"dataSource2"
);
|
上面介绍的是在dao层当需要切换数据源时手动加上切换数据源的代码,也可以使用AOP的方式,把配置的数据源类型都设置成注解标签,在dao层中需要切换数据源操作的方法或类上写上注解标签,这样实现起来可操作性也更强.
|
1
2
3
4
|
@DataSourceKey
(
"dataSource1"
)
public
interface
TestEntityMapper
extends
MSSQLMapper<TestEntity> {
public
void
insertTest(TestEntity testEntity);
}
|
DataSourceKey注解代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
@Target
({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention
(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public
@interface
DataSourceKey {
String value()
default
""
;
}
|
注解配置完后就要写一个实现数据源切换的类,如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
public
class
MultipleDataSourceExchange {
/**
* 拦截目标方法,获取由@DataSource指定的数据源标识,设置到线程存储中以便切换数据源
*/
public
void
beforeDaoMethod(JoinPoint point)
throws
Exception {
Class<?> target = point.getTarget().getClass();
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) point.getSignature();
// 默认使用目标类型的注解,如果没有则使用其实现接口的注解类
for
(Class<?> cls : target.getInterfaces()) {
resetDataSource(cls, signature.getMethod());
}
resetDataSource(target, signature.getMethod());
}
/**
* 提取目标对象方法注解和类注解中的数据源标识
*/
private
void
resetDataSource(Class<?> cls, Method method) {
try
{
Class<?>[] types = method.getParameterTypes();
// 默认使用类注解
if
(cls.isAnnotationPresent(DataSourceKey.
class
)) {
DataSourceKey source = cls.getAnnotation(DataSourceKey.
class
);
DynamicDataSourceHolder.setRouteKey(source.value());
}
// 方法注解可以覆盖类注解
Method m = cls.getMethod(method.getName(), types);
if
(m !=
null
&& m.isAnnotationPresent(DataSourceKey.
class
)) {
DataSourceKey source = m.getAnnotation(DataSourceKey.
class
);
DynamicDataSourceHolder.setRouteKey(source.value());
}
}
catch
(Exception e) {
System.out.println(cls +
":"
+ e.getMessage());
}
}
}
|
代码写完后就要在xml配置文件上添加配置了(只列出部分配置):
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
<
bean
id
=
"multipleDataSourceExchange"
class
=
"MultipleDataSourceExchange "
/>
<
bean
id
=
"txManager"
class
=
"org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"
>
<
property
name
=
"dataSource"
ref
=
"multipleDataSource"
/>
</
bean
>
<
tx:advice
id
=
"txAdvice"
transaction-manager
=
"txManager"
>
<
tx:attributes
>
<
tx:method
name
=
"insert*"
propagation
=
"NESTED"
rollback-for
=
"Exception"
/>
<
tx:method
name
=
"add*"
propagation
=
"NESTED"
rollback-for
=
"Exception"
/>
...
</
tx:attributes
>
</
tx:advice
>
<
aop:config
>
<
aop:pointcut
id
=
"service"
expression
=
"execution(* com.datasource..*.service.*.*(..))"
/>
<!-- 注意切换数据源操作要比持久层代码先执行 -->
<
aop:advisor
advice-ref
=
"multipleDataSourceExchange"
pointcut-ref
=
"service"
order
=
"1"
/>
<
aop:advisor
advice-ref
=
"txAdvice"
pointcut-ref
=
"service"
order
=
"2"
/>
</
aop:config
>
|
到此就完成使用AOP的方式实现多数据源的动态切换了.
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/weknow619/p/6415900.html 。
最后此篇关于使用Spring的AbstractRoutingDataSource实现多数据源切换示例的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于使用Spring的AbstractRoutingDataSource实现多数据源切换示例的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我尝试阅读有关 Spring BOM、Spring Boot 和 Spring IO 的文档。 但是没有说明,我们应该如何一起使用它们? 在我的项目中,我们已经有了自己的 Parent POM ,所以
我正在开发的很酷的企业应用程序正在转向 Spring。这对所有团队来说都是非常酷和令人兴奋的练习,但也是一个巨大的压力源。我们所做的是逐渐将遗留组件移至 Spring 上下文。现在我们有一个 huuu
我正在尝试使用 @Scheduled 运行 Spring 批处理作业注释如下: @Scheduled(cron = "* * * * * ?") public void launchMessageDi
我对这两个概念有点困惑。阅读 Spring 文档,我发现,例如。 bean 工厂是 Spring 容器。我还读到“ApplicationContext 是 BeanFactory 的完整超集”。但两者
我们有一个使用 Spring BlazeDS 集成的应用程序。到目前为止,我们一直在使用 Spring 和 Flex,它运行良好。我们现在还需要添加一些 Spring MVC Controller 。
假设我有一个类(class) Person带属性name和 age ,它可以像这样用 Spring 配置: 我想要一个自定义的 Spring 模式元素,这很容易做到,允许我在我的 Sp
如何在 Java 中以编程方式使用 Spring Data 创建 MongoDB 复合索引? 使用 MongoTemplate 我可以创建一个这样的索引:mongoTemplate.indexOps(
我想使用 spring-complex-task 执行我的应用程序,并且我已经构建了复杂的 spring-batch Flow Jobs,它执行得非常好。 你能解释一下spring批处理流作业与spr
我实现了 spring-boot 应用程序,现在我想将它用作非 spring 应用程序的库。 如何初始化 lib 类,以便 Autowiring 的依赖项按预期工作?显然,如果我使用“new”创建类实
我刚开始学习 spring cloud security,我有一个基本问题。它与 Spring Security 有何不同?我们是否需要在 spring boot 上构建我们的应用程序才能使用 spr
有很多人建议我使用 Spring Boot 而不是 Spring 来开发 REST Web 服务。我想知道这两者到底有什么区别? 最佳答案 总之 Spring Boot 减少了编写大量配置和样板代码的
您能向我解释一下如何使用 Spring 正确构建 Web 应用程序吗?我知道 Spring 框架的最新版本是 4.0.0.RELEASE,但是 Spring Security 的最新版本是 3.2.0
我如何才能知道作为 Spring Boot 应用程序的一部分加载的所有 bean 的名称?我想在 main 方法中有一些代码来打印服务器启动后加载的 bean 的详细信息。 最佳答案 如spring-
我有一个使用 Spring 3.1 构建的 RESTful API,也使用 Spring Security。我有一个 Web 应用程序,也是一个 Spring 3.1 MVC 应用程序。我计划让移动客
升级到 Spring 5 后,我在 Spring Rabbit 和 Spring AMQP 中遇到错误。 两者现在都设置为 1.5.6.RELEASE 有谁知道哪些版本应该与 Spring 5 兼容?
我现在已经使用 Spring Framework 3.0.5 和 Spring Security 3.0.5 多次了。我知道Spring框架使用DI和AOP。我还知道 Spring Security
我收到错误 Unable to Location NamespaceHandler when using context:annotation-config running (java -jar) 由
在 Spring 应用程序中嵌入唯一版本号的策略是什么? 我有一个使用 Spring Boot 和 Spring Web 的应用程序。 它已经足够成熟,我想对其进行版本控制并在运行时看到它显示在屏幕上
我正在使用 spring data jpa 进行持久化。如果存在多个具有相同名称的实体,是否有一种方法可以将一个实体标记为默认值。类似@Primary注解的东西用来解决多个bean的依赖问题 @Ent
我阅读了 Spring 框架的 DAOSupport 类。但是我无法理解这些 DAOSuport 类的优点。在 DAOSupport 类中,我们调用 getXXXTemplate() 方法来获取特定的

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!