- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章Spring MVC Annotation验证的方法由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
简介说明 。
使用spring mvc的annotation验证可以直接对view model的简单数据验证,注意,这里是简单的,如果model的数据验证需要有一些比较复杂的业务逻辑性在里头,只是使用annotation做验证是比较难的.
以下是使用spring mvc自带的annotation验证,加上自定义的一个@tel的annotation验证例子,此例子具有:
1、支持多语言(国际化) 。
2、对默认数据先进行转化,比如int、date类型如果传入空值时,会抛异常,默认给定值 。
先看配置:
1、web.xml 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
<?xml version=
"1.0"
encoding=
"utf-8"
?>
<web-app version=
"3.0"
xmlns=
"http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi=
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xmlschema-instance"
xsi:schemalocation="http:
//java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http:
//java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd">
<display-name>test spring mvc -
1
</display-name>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextconfiglocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-
class
>org.springframework.web.servlet.dispatcherservlet</servlet-
class
>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextconfiglocation</param-name>
<param-value></param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>
1
</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<listener>
<listener-
class
>org.springframework.web.context.contextloaderlistener</listener-
class
>
</listener>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
</web-app>
|
这里没什么好说的,只是把spring.xml配置加入到contextconfiglocation中 。
2、spring.xml 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
|
<?xml version=
"1.0"
encoding=
"utf-8"
?>
<beans
xmlns=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi=
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xmlschema-instance"
xmlns:tx=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:context=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemalocation="http:
//www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http:
//www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http:
//www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http:
//www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd
http:
//www.springframework.org/schema/context
http:
//www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd
http:
//www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http:
//www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.0.xsd">
<!--注解说明 -->
<context:annotation-config />
<!-- 默认的注解映射的支持 -->
<mvc:annotation-driven validator=
"validator"
conversion-service=
"conversionservice"
/>
<!-- 把标记了
@controller
注解的类转换为bean -->
<context:component-scan base-
package
=
"com.my"
/>
<!-- 视图解释类 -->
<bean
class
=
"org.springframework.web.servlet.view.internalresourceviewresolver"
>
<property name=
"prefix"
value=
"/web-inf/views/"
/>
<property name=
"suffix"
value=
".jsp"
/><!--可为空,方便实现自已的依据扩展名来选择视图解释类的逻辑 -->
<property name=
"viewclass"
value=
"org.springframework.web.servlet.view.jstlview"
/>
</bean>
<!-- 资源文件:messages.properties -->
<bean id=
"messagesource"
class
=
"org.springframework.context.support.resourcebundlemessagesource"
>
<property name=
"basenames"
>
<list>
<value>messages</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 验证器 -->
<bean id=
"validator"
class
=
"org.springframework.validation.beanvalidation.localvalidatorfactorybean"
>
<property name=
"validationmessagesource"
ref=
"messagesource"
/>
</bean>
<!-- 自定义数据类型转换器 -->
<bean id=
"conversionservice"
class
=
"org.springframework.format.support.formattingconversionservicefactorybean"
>
<property name=
"converters"
>
<list>
<bean
class
=
"com.my.controller.converter.intconverter"
/>
<bean
class
=
"com.my.controller.converter.dateconverter"
/>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
|
在<mvc:annotation-driven/>中加入conversion-service,然后在conversion-service中加入系统默认的转换器,如上有intconverter和dateconverter,当然,也可以是自定的别的类型,这是全局的.
在validator验证器中加入了支持多语言的properties,当然,spring的多语言是基于http header的accept-language.
3、controller 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
package
com.my.controller;
import
java.util.list;
import
javax.validation.valid;
import
org.springframework.stereotype.controller;
import
org.springframework.validation.bindingresult;
import
org.springframework.validation.fielderror;
import
org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.modelattribute;
import
org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.requestmapping;
import
org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.requestmethod;
import
org.springframework.web.servlet.modelandview;
import
com.my.controller.bean.user4;
@controller
@requestmapping
(value=
"av"
)
public
class
testannotationvalidcontroller {
@requestmapping
public
modelandview index() {
modelandview view =
new
modelandview(
"/testannotationvalid/index"
,
"user4"
,
new
user4());
return
view;
}
@requestmapping
(value=
"/add"
, method=requestmethod.post)
public
modelandview add(
@modelattribute
@valid
user4 user, bindingresult result) {
modelandview view =
new
modelandview(
"/testannotationvalid/index"
);
view.addobject(
"user4"
, user);
if
(result.haserrors()) {
list<fielderror> errors = result.getfielderrors();
for
(fielderror err : errors) {
system.out.println(
"objectname:"
+ err.getobjectname() +
"\tfieldname:"
+ err.getfield()
+
"\tfieldvalue:"
+ err.getrejectedvalue() +
"\tmessage:"
+ err.getdefaultmessage() +
"\tcode:"
);
}
}
return
view;
}
}
|
这是一个简单的controller,在add中,有一个@valid的annotation,这是必需的,不加这个,annotation验证将不起作用 。
4、user4.java model实体类 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
|
package
com.my.controller.bean;
import
java.util.date;
import
javax.validation.constraints.max;
import
javax.validation.constraints.min;
import
javax.validation.constraints.notnull;
import
javax.validation.constraints.past;
import
javax.validation.constraints.pattern;
import
javax.validation.constraints.size;
import
org.hibernate.validator.constraints.email;
import
org.hibernate.validator.constraints.length;
import
org.hibernate.validator.constraints.notblank;
public
class
user4 {
private
long
id;
@notblank
(message=
"{valid.name}"
)
private
string name;
@length
(min=
4
, max=
20
, message=
"{valid.password}"
)
private
string password;
@notblank
(message=
"{valid.required}"
)
@email
(message=
"{valid.email}"
)
private
string email;
@notnull
(message=
"{valid.required}"
)
private
boolean
married;
@min
(value=
18
, message=
"{valid.agemin}"
)
@max
(value=
100
, message=
"{valid.agemax}"
)
private
int
age;
@notnull
(message=
"{valid.required}"
)
@past
(message=
"{valid.birthday}"
)
private
date birthday;
@pattern
(regexp=
"^[a-za-z]{2,}$"
, message=
"{valid.address}"
)
private
string address;
@size
(min=
1
, message=
"{valid.likesmin}"
)
private
string[] likes;
@com
.my.controller.validator.tel(message=
"{valid.tel}"
, min=
3
)
private
string tel;
public
long
getid() {
return
id;
}
public
void
setid(
long
id) {
this
.id = id;
}
public
string getname() {
return
name;
}
public
void
setname(string name) {
this
.name = name;
}
public
string getpassword() {
return
password;
}
public
void
setpassword(string password) {
this
.password = password;
}
public
string getemail() {
return
email;
}
public
void
setemail(string email) {
this
.email = email;
}
public
boolean
ismarried() {
return
married;
}
public
void
setmarried(
boolean
married) {
this
.married = married;
}
public
int
getage() {
return
age;
}
public
void
setage(
int
age) {
this
.age = age;
}
public
date getbirthday() {
return
birthday;
}
public
void
setbirthday(date birthday) {
this
.birthday = birthday;
}
public
string getaddress() {
return
address;
}
public
void
setaddress(string address) {
this
.address = address;
}
public
string[] getlikes() {
return
likes;
}
public
void
setlikes(string[] likes) {
this
.likes = likes;
}
public
string gettel() {
return
tel;
}
public
void
settel(string tel) {
this
.tel = tel;
}
}
|
除了@tel之外,其它都是spring自带的annotation,当然还有别的,自行搜索下 。
5、message.properties 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
valid.required=字段值不能为空
valid.name=用户名不能为空
valid.password=密码最小
4
位
valid.agemin=年龄不能小于{
1
}岁
valid.agemax=年龄不能大于{
1
}岁
valid.email=邮箱格式不正确
valid.address=联系地址不正确
valid.birthday=生日不能大于今天
valid.likesmin=喜好最小不能小于
1
个
valid.tel=手机号码不能小于{min}位
|
对应的是user4 model的annotation的message值。如果需要国际化的多语言,只需要加入多一个messages_en_us.properties这样名字的文件即可.
6、@tel 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
package
com.my.controller.validator;
import
java.lang.annotation.elementtype;
import
java.lang.annotation.retention;
import
java.lang.annotation.retentionpolicy;
import
java.lang.annotation.target;
import
javax.validation.constraint;
import
javax.validation.payload;
@target
({elementtype.field, elementtype.method})
@retention
(retentionpolicy.runtime)
@constraint
(validatedby=telvalidator.
class
)
public
@interface
tel {
int
min()
default
0
;
string message();
class
<?>[] groups()
default
{};
class
<?
extends
payload>[] payload()
default
{};
}
|
新建一个interface,注意,annotation的interface java是这样写的:@interface 。
telvalidator
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
package
com.my.controller.validator;
import
javax.annotation.resource;
import
javax.validation.constraintvalidator;
import
javax.validation.constraintvalidatorcontext;
import
org.springframework.context.support.resourcebundlemessagesource;
public
class
telvalidator
implements
constraintvalidator<tel, string> {
@resource
private
resourcebundlemessagesource messagesource;
private
tel tel;
@override
public
void
initialize(tel tel) {
this
.tel = tel;
}
@override
public
boolean
isvalid(string value, constraintvalidatorcontext constraintcontext) {
boolean
isvalid;
if
(value !=
null
&& value.length() >= tel.min()) {
isvalid =
true
;
}
else
{
isvalid =
false
;
}
if
(!isvalid) {
constraintcontext.disabledefaultconstraintviolation();
constraintcontext.buildconstraintviolationwithtemplate(tel.message()).addconstraintviolation();
}
return
isvalid;
}
}
|
这是@tel的验证实现方法.
7、converter 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
package
com.my.controller.converter;
import
org.springframework.core.convert.converter.converter;
public
class
intconverter
implements
converter<string, integer> {
@override
public
integer convert(string text) {
if
(text ==
null
||
""
.equals(text)) {
return
0
;
}
else
{
try
{
integer value = integer.parseint(text);
return
value;
}
catch
(exception e) {
return
0
;
}
}
}
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
package
com.my.controller.converter;
import
java.text.parseexception;
import
java.text.simpledateformat;
import
java.util.date;
import
org.springframework.core.convert.converter.converter;
public
class
dateconverter
implements
converter<string, date> {
@override
public
date convert(string text) {
simpledateformat dateformat =
new
simpledateformat(
"yyyy-mm-dd"
);
dateformat.setlenient(
false
);
try
{
return
dateformat.parse(text);
}
catch
(parseexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
return
null
;
}
}
|
这两个是全局的类型默认转换器.
8、测试jsp 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
<%@ page language=
"java"
contenttype=
"text/html; charset=utf-8"
pageencoding=
"utf-8"
%>
<%@ taglib uri=
"http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"
prefix=
"c"
%>
<%@ taglib uri=
"http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt"
prefix=
"fmt"
%>
<%@ taglib uri=
"http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/functions"
prefix=
"fn"
%>
<%@ taglib prefix=
"st"
uri=
"http://www.springframework.org/tags"
%>
<%@ taglib prefix=
"sf"
uri=
"http://www.springframework.org/tags/form"
%>
<!doctype html
public
"-//w3c//dtd html 4.01 transitional//en"
"http://www.w3.org/tr/html4/loose.dtd"
>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv=
"content-type"
content=
"text/html; charset=utf-8"
>
<title>index</title>
</head>
<body>
<sf:form action=
"${pagecontext.request.contextpath}/av/add"
method=
"post"
modelattribute=
"user4"
>
user name:<sf:input path=
"name"
/><sf:errors path=
"name"
/><br/>
password:<sf:input path=
"password"
/><sf:errors path=
"password"
/><br/>
e-mail:<sf:input path=
"email"
/><sf:errors path=
"email"
/><br/>
age:<sf:input path=
"age"
/><sf:errors path=
"age"
/><br/>
birthday:<sf:input path=
"birthday"
/><sf:errors path=
"birthday"
/><br/>
address:<sf:input path=
"address"
/><sf:errors path=
"address"
/><br/>
married:
<sf:radiobutton path=
"married"
label=
"yes"
value=
"true"
/>
<sf:radiobutton path=
"married"
label=
"no"
value=
"false"
/>
<sf:errors path=
"married"
/><br/>
likes:
<sf:checkbox path=
"likes"
label=
"football"
value=
"football"
/>
<sf:checkbox path=
"likes"
label=
"badminton"
value=
"badminton"
/>
<sf:checkbox path=
"likes"
label=
"pingpong"
value=
"pingpong"
/>
<sf:errors path=
"likes"
/><br/>
tel:<sf:input path=
"tel"
/><sf:errors path=
"tel"
/><br/>
<input type=
"submit"
value=
"add"
/>
<hr/>
errors:<br/><sf:errors path=
"*"
></sf:errors>
<hr/>
likes:<c:foreach items=
"${user4.likes}"
var=
"item"
>${item},</c:foreach>
</sf:form>
</body>
</html>
|
注意,在form中的modelattribute属性值,它对应的是user4类名,小写开头,否则会出错 。
9、页面ui结果:
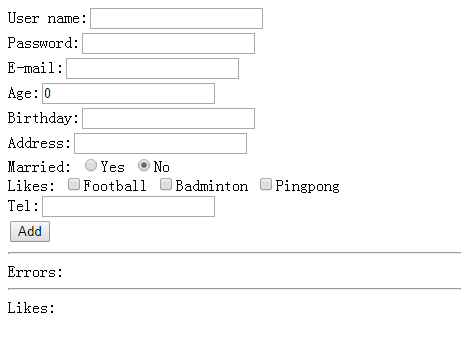
点击add button后:
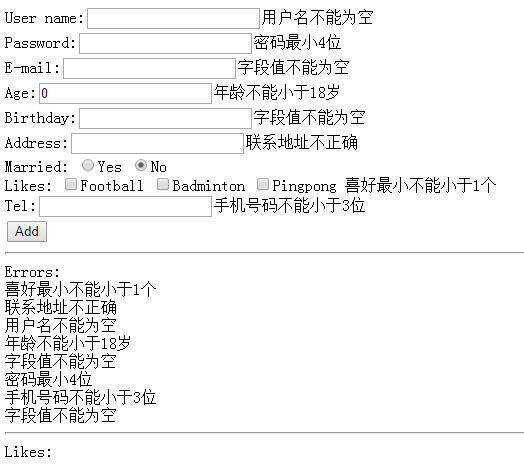
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我.
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/HD/p/4123146.html 。
最后此篇关于Spring MVC Annotation验证的方法的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于Spring MVC Annotation验证的方法的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我有一个我想暂时存储的对象。该对象现在在 Controller 中, Controller 将生成一个 View 。 AJAX 请求从 View 发送到下一个 Controller 。那一刻我需要先前
从MVC 2开始,我们可以轻松创建区域。现在,我的问题与嵌套区域(区域内部的区域)有关。 选择我的“father”区域文件夹,右键单击> Add> NO选项以获取new Area。 是否有可能以其他方
关闭。这个问题不满足Stack Overflow guidelines .它目前不接受答案。 想改善这个问题吗?更新问题,使其成为 on-topic对于堆栈溢出。 7年前关闭。 Improve thi
我已经尝试了一些谷歌搜索和堆栈流搜索,但事实证明这比我想象的要难找到。我需要为我们的商店迁移到 ASP.NET MVC 2 的管理提供理由。最大的帮助将是任何企业级站点或使用 ASP.NET MVC
关闭。这个问题是opinion-based 。目前不接受答案。 想要改进这个问题吗?更新问题,以便 editing this post 可以用事实和引文来回答它。 . 已关闭 6 年前。 Improv
我有一些常见的网页,它们将出现在多个 MVC 应用程序中。对于这些页面,我想在不同的 MVC 网站之间重用相同的源代码( Controller + View )。这样做的最佳方法是什么? ASP.NE
我正在使用 Spring MVC 来构建我的应用程序。 当用户在浏览器中运行应用程序时,我想显示一个默认的 jsp。我不想用 web.xml 中的标记。 我想我可以用 我已经创建了一个文件夹并添
我可能在这里分析过度了,但是根据我对 MVC 的阅读,似乎有很多关于如何做事情的观点。 是否有一个“最佳实践”网站或文档来定义 MVC 各个部分的职责? 请记住,我使用 EF/Repository&U
当杰里米和查德 posted about their FubuMvc project ,他们提到的差异化因素之一是他们的“雷霆穹顶校长”: The “Thunderdome Principle” –
我正在为 Spring MVC 应用程序实现缓存清除系统。 为了让这个系统正常工作,我必须从给定的 url 中删除“缓存破坏代码”。假设我生成的缓存破坏代码是“123”,我有一个 .css url:/
在调试 ASP.NET MVC 源时,我发现使用了“MVC-ControllerTypeCache.xml” 文件。但我无法理解这个文件的用途。我的意思是这个文件存储在哪里?asp.net MVc 如
我刚刚在我的本地机器上安装了 Visual Studio 11 和 MVC 4 beta。但是,每当我打开一个 MVC 3 项目(我想保留为 MVC 3)时,所有引用都已更新为版本 4 DLL。当然它
我有一个 MVC 3 应用程序,它具有一些核心功能(最重要的是自动化),但主要用作不同区域或模块的门户。我想将它组织到不同的模块中,只需稍作更改也可以部署为他们自己的网站。 该项目由论坛、博客引擎、用
我有自己的服务器,正在考虑将我的一个解决方案升级到 ASP.NET MVC 4,然后再升级其余的 (3+)。 作为其中的一部分,我下载了 the standalone installer对于 ASP.
构图 我有一个 MVC 项目,其中包含 C# 类,这些类最终通过 ajax 等进行序列化和使用。我使用 TypeLite 生成这些 C# 类的定义( here 讨论了 TypeLite 的替代方案),
我正在尝试了解现代 Web 应用程序架构。在 ASP.NET MVC 中,所有业务逻辑类都在 Model 中,Controller 接受并引导用户请求。如果我使用它,是否可以使用本身是 MVC 架构但
我有一个带有 OWIN 的 WebAPI 2 应用程序。现在我正在尝试向所有内容添加一个 MVC 5 Controller ,但没有找到我的 MVC 路由。我收到以下错误: No HTTP resou
在 MVC 3 中,他们添加了我一直在使用的依赖解析器。在回答某人对您发表评论的问题时,您应该使用 Ninject MVC 3 插件。 所以我的问题是为什么要使用它而不是内置的?如果这是要走的路,你如
我是 ASP.NET MVC 的新手,我正在寻找最不痛苦的方法来设置全局错误处理、日志记录和报告(通过电子邮件)。仅供引用,我的 ASP.NET MVC 应用程序在 Azure 中作为 Web 角色托
何时使用 MVC View 页面和 MVC View 内容页面?它们有什么区别? 最佳答案 **MVC View Page 用于创建页面,MVC VewP Content Page 用于创建页面并指定

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!