- ubuntu12.04环境下使用kvm ioctl接口实现最简单的虚拟机
- Ubuntu 通过无线网络安装Ubuntu Server启动系统后连接无线网络的方法
- 在Ubuntu上搭建网桥的方法
- ubuntu 虚拟机上网方式及相关配置详解
CFSDN坚持开源创造价值,我们致力于搭建一个资源共享平台,让每一个IT人在这里找到属于你的精彩世界.
这篇CFSDN的博客文章神经网络(BP)算法Python实现及应用由作者收集整理,如果你对这篇文章有兴趣,记得点赞哟.
本文实例为大家分享了python实现神经网络算法及应用的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下 。
首先用python实现简单地神经网络算法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
|
import
numpy as np
# 定义tanh函数
def
tanh(x):
return
np.tanh(x)
# tanh函数的导数
def
tan_deriv(x):
return
1.0
-
np.tanh(x)
*
np.tan(x)
# sigmoid函数
def
logistic(x):
return
1
/
(
1
+
np.exp(
-
x))
# sigmoid函数的导数
def
logistic_derivative(x):
return
logistic(x)
*
(
1
-
logistic(x))
class
neuralnetwork:
def
__init__(
self
, layers, activation
=
'tanh'
):
"""
神经网络算法构造函数
:param layers: 神经元层数
:param activation: 使用的函数(默认tanh函数)
:return:none
"""
if
activation
=
=
'logistic'
:
self
.activation
=
logistic
self
.activation_deriv
=
logistic_derivative
elif
activation
=
=
'tanh'
:
self
.activation
=
tanh
self
.activation_deriv
=
tan_deriv
# 权重列表
self
.weights
=
[]
# 初始化权重(随机)
for
i
in
range
(
1
,
len
(layers)
-
1
):
self
.weights.append((
2
*
np.random.random((layers[i
-
1
]
+
1
, layers[i]
+
1
))
-
1
)
*
0.25
)
self
.weights.append((
2
*
np.random.random((layers[i]
+
1
, layers[i
+
1
]))
-
1
)
*
0.25
)
def
fit(
self
, x, y, learning_rate
=
0.2
, epochs
=
10000
):
"""
训练神经网络
:param x: 数据集(通常是二维)
:param y: 分类标记
:param learning_rate: 学习率(默认0.2)
:param epochs: 训练次数(最大循环次数,默认10000)
:return: none
"""
# 确保数据集是二维的
x
=
np.atleast_2d(x)
temp
=
np.ones([x.shape[
0
], x.shape[
1
]
+
1
])
temp[:,
0
:
-
1
]
=
x
x
=
temp
y
=
np.array(y)
for
k
in
range
(epochs):
# 随机抽取x的一行
i
=
np.random.randint(x.shape[
0
])
# 用随机抽取的这一组数据对神经网络更新
a
=
[x[i]]
# 正向更新
for
l
in
range
(
len
(
self
.weights)):
a.append(
self
.activation(np.dot(a[l],
self
.weights[l])))
error
=
y[i]
-
a[
-
1
]
deltas
=
[error
*
self
.activation_deriv(a[
-
1
])]
# 反向更新
for
l
in
range
(
len
(a)
-
2
,
0
,
-
1
):
deltas.append(deltas[
-
1
].dot(
self
.weights[l].t)
*
self
.activation_deriv(a[l]))
deltas.reverse()
for
i
in
range
(
len
(
self
.weights)):
layer
=
np.atleast_2d(a[i])
delta
=
np.atleast_2d(deltas[i])
self
.weights[i]
+
=
learning_rate
*
layer.t.dot(delta)
def
predict(
self
, x):
x
=
np.array(x)
temp
=
np.ones(x.shape[
0
]
+
1
)
temp[
0
:
-
1
]
=
x
a
=
temp
for
l
in
range
(
0
,
len
(
self
.weights)):
a
=
self
.activation(np.dot(a,
self
.weights[l]))
return
a
|
使用自己定义的神经网络算法实现一些简单的功能:
小案例:
x: y 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
from
nn.neuralnetwork
import
neuralnetwork
import
numpy as np
nn
=
neuralnetwork([
2
,
2
,
1
],
'tanh'
)
temp
=
[[
0
,
0
], [
0
,
1
], [
1
,
0
], [
1
,
1
]]
x
=
np.array(temp)
y
=
np.array([
0
,
1
,
1
,
0
])
nn.fit(x, y)
for
i
in
temp:
print
(i, nn.predict(i))
|
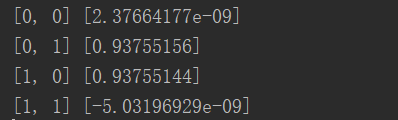
发现结果基本机制,无限接近0或者无限接近1 。
第二个例子:识别图片中的数字 。
导入数据:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
from
sklearn.datasets
import
load_digits
import
pylab as pl
digits
=
load_digits()
print
(digits.data.shape)
pl.gray()
pl.matshow(digits.images[
0
])
pl.show()
|
观察下:大小:(1797, 64) 。
数字0 。
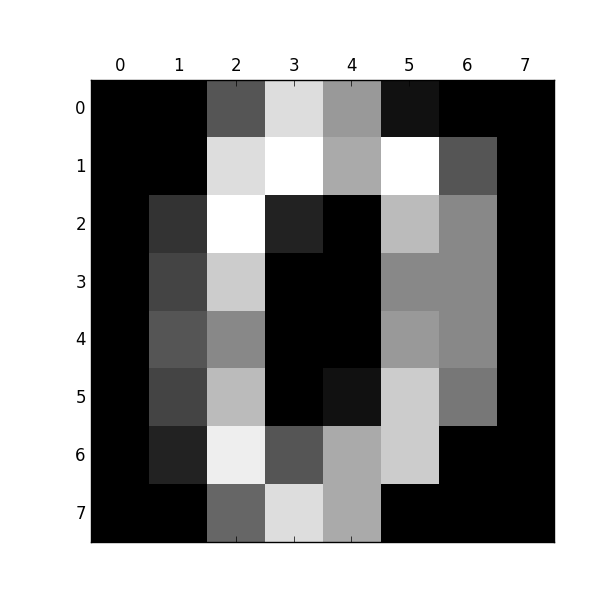
接下来的代码是识别它们:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
import
numpy as np
from
sklearn.datasets
import
load_digits
from
sklearn.metrics
import
confusion_matrix, classification_report
from
sklearn.preprocessing
import
labelbinarizer
from
nn.neuralnetwork
import
neuralnetwork
from
sklearn.cross_validation
import
train_test_split
# 加载数据集
digits
=
load_digits()
x
=
digits.data
y
=
digits.target
# 处理数据,使得数据处于0,1之间,满足神经网络算法的要求
x
-
=
x.
min
()
x
/
=
x.
max
()
# 层数:
# 输出层10个数字
# 输入层64因为图片是8*8的,64像素
# 隐藏层假设100
nn
=
neuralnetwork([
64
,
100
,
10
],
'logistic'
)
# 分隔训练集和测试集
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test
=
train_test_split(x, y)
# 转化成sklearn需要的二维数据类型
labels_train
=
labelbinarizer().fit_transform(y_train)
labels_test
=
labelbinarizer().fit_transform(y_test)
print
(
"start fitting"
)
# 训练3000次
nn.fit(x_train, labels_train, epochs
=
3000
)
predictions
=
[]
for
i
in
range
(x_test.shape[
0
]):
o
=
nn.predict(x_test[i])
# np.argmax:第几个数对应最大概率值
predictions.append(np.argmax(o))
# 打印预测相关信息
print
(confusion_matrix(y_test, predictions))
print
(classification_report(y_test, predictions))
|
结果:
矩阵对角线代表预测正确的数量,发现正确率很多 。
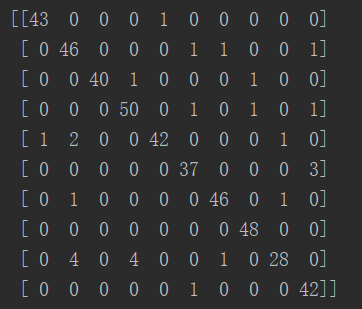
。
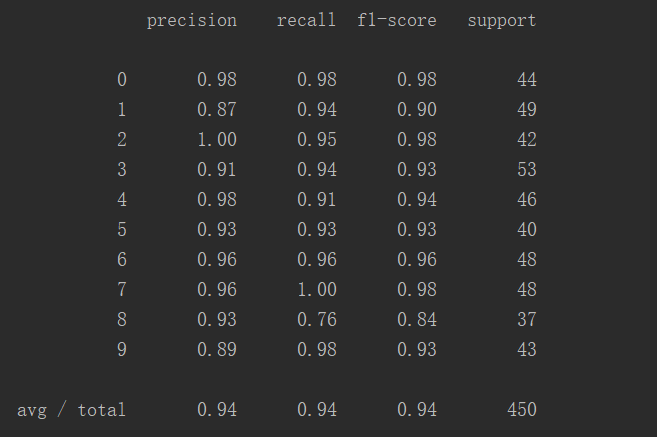
这张表更直观地显示出预测正确率:
共450个案例,成功率94% 。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我.
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/xuyiqing/p/8797048.html 。
最后此篇关于神经网络(BP)算法Python实现及应用的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于神经网络(BP)算法Python实现及应用的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
滑动窗口限流 滑动窗口限流是一种常用的限流算法,通过维护一个固定大小的窗口,在单位时间内允许通过的请求次数不超过设定的阈值。具体来说,滑动窗口限流算法通常包括以下几个步骤: 初始化:设置窗口
表达式求值:一个只有+,-,*,/的表达式,没有括号 一种神奇的做法:使用数组存储数字和运算符,先把优先级别高的乘法和除法计算出来,再计算加法和减法 int GetVal(string s){
【算法】前缀和 题目 先来看一道题目:(前缀和模板题) 已知一个数组A[],现在想要求出其中一些数字的和。 输入格式: 先是整数N,M,表示一共有N个数字,有M组询问 接下来有N个数,表示A[1]..
1.前序遍历 根-左-右的顺序遍历,可以使用递归 void preOrder(Node *u){ if(u==NULL)return; printf("%d ",u->val);
先看题目 物品不能分隔,必须全部取走或者留下,因此称为01背包 (只有不取和取两种状态) 看第一个样例 我们需要把4个物品装入一个容量为10的背包 我们可以简化问题,从小到大入手分析 weightva
我最近在一次采访中遇到了这个问题: 给出以下矩阵: [[ R R R R R R], [ R B B B R R], [ B R R R B B], [ R B R R R R]] 找出是否有任
我正在尝试通过 C++ 算法从我的 outlook 帐户发送一封电子邮件,该帐户已经打开并记录,但真的不知道从哪里开始(对于 outlook-c++ 集成),谷歌也没有帮我这么多。任何提示将不胜感激。
我发现自己像这样编写了一个手工制作的 while 循环: std::list foo; // In my case, map, but list is simpler auto currentPoin
我有用于检测正方形的 opencv 代码。现在我想在检测正方形后,代码运行另一个命令。 代码如下: #include "cv.h" #include "cxcore.h" #include "high
我正在尝试模拟一个 matlab 函数“imfill”来填充二进制图像(1 和 0 的二维矩阵)。 我想在矩阵中指定一个起点,并像 imfill 的 4 连接版本那样进行洪水填充。 这是否已经存在于
我正在阅读 Robert Sedgewick 的《C++ 算法》。 Basic recurrences section it was mentioned as 这种循环出现在循环输入以消除一个项目的递
我正在思考如何在我的日历中生成代表任务的数据结构(仅供我个人使用)。我有来自 DBMS 的按日期排序的任务记录,如下所示: 买牛奶(18.1.2013) 任务日期 (2013-01-15) 任务标签(
输入一个未排序的整数数组A[1..n]只有 O(d) :(d int) 计算每个元素在单次迭代中出现在列表中的次数。 map 是balanced Binary Search Tree基于确保 O(nl
我遇到了一个问题,但我仍然不知道如何解决。我想出了如何用蛮力的方式来做到这一点,但是当有成千上万的元素时它就不起作用了。 Problem: Say you are given the followin
我有一个列表列表。 L1= [[...][...][.......].......]如果我在展平列表后获取所有元素并从中提取唯一值,那么我会得到一个列表 L2。我有另一个列表 L3,它是 L2 的某个
我们得到二维矩阵数组(假设长度为 i 和宽度为 j)和整数 k我们必须找到包含这个或更大总和的最小矩形的大小F.e k=7 4 1 1 1 1 1 4 4 Anwser是2,因为4+4=8 >= 7,
我实行 3 类倒制,每周换类。顺序为早类 (m)、晚类 (n) 和下午类 (a)。我固定的订单,即它永远不会改变,即使那个星期不工作也是如此。 我创建了一个函数来获取 ISO 周数。当我给它一个日期时
假设我们有一个输入,它是一个元素列表: {a, b, c, d, e, f} 还有不同的集合,可能包含这些元素的任意组合,也可能包含不在输入列表中的其他元素: A:{e,f} B:{d,f,a} C:
我有一个子集算法,可以找到给定集合的所有子集。原始集合的问题在于它是一个不断增长的集合,如果向其中添加元素,我需要再次重新计算它的子集。 有没有一种方法可以优化子集算法,该算法可以从最后一个计算点重新
我有一个包含 100 万个符号及其预期频率的表格。 我想通过为每个符号分配一个唯一(且前缀唯一)的可变长度位串来压缩这些符号的序列,然后将它们连接在一起以表示序列。 我想分配这些位串,以使编码序列的预

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!