- Java锁的逻辑(结合对象头和ObjectMonitor)
- 还在用饼状图?来瞧瞧这些炫酷的百分比可视化新图形(附代码实现)⛵
- 自动注册实体类到EntityFrameworkCore上下文,并适配ABP及ABPVNext
- 基于Sklearn机器学习代码实战
本文首发公众号:小码A梦 。
回溯算法是一种常见的算法,常见用于解决排列组合、排列问题、搜索问题等算法,在一个搜索空间中寻找所有的可能的解。通过向分支不断尝试获取所有的解,然后找到合适的解,找完一个分支后再往回搜索。 回溯算法通常使用递归的方式 实现.
回溯本质是一种 暴力搜索法 ,列出所有可能的解,然后找到合适的解。以 a、b、c的排列组合为例,画出全排列组合.
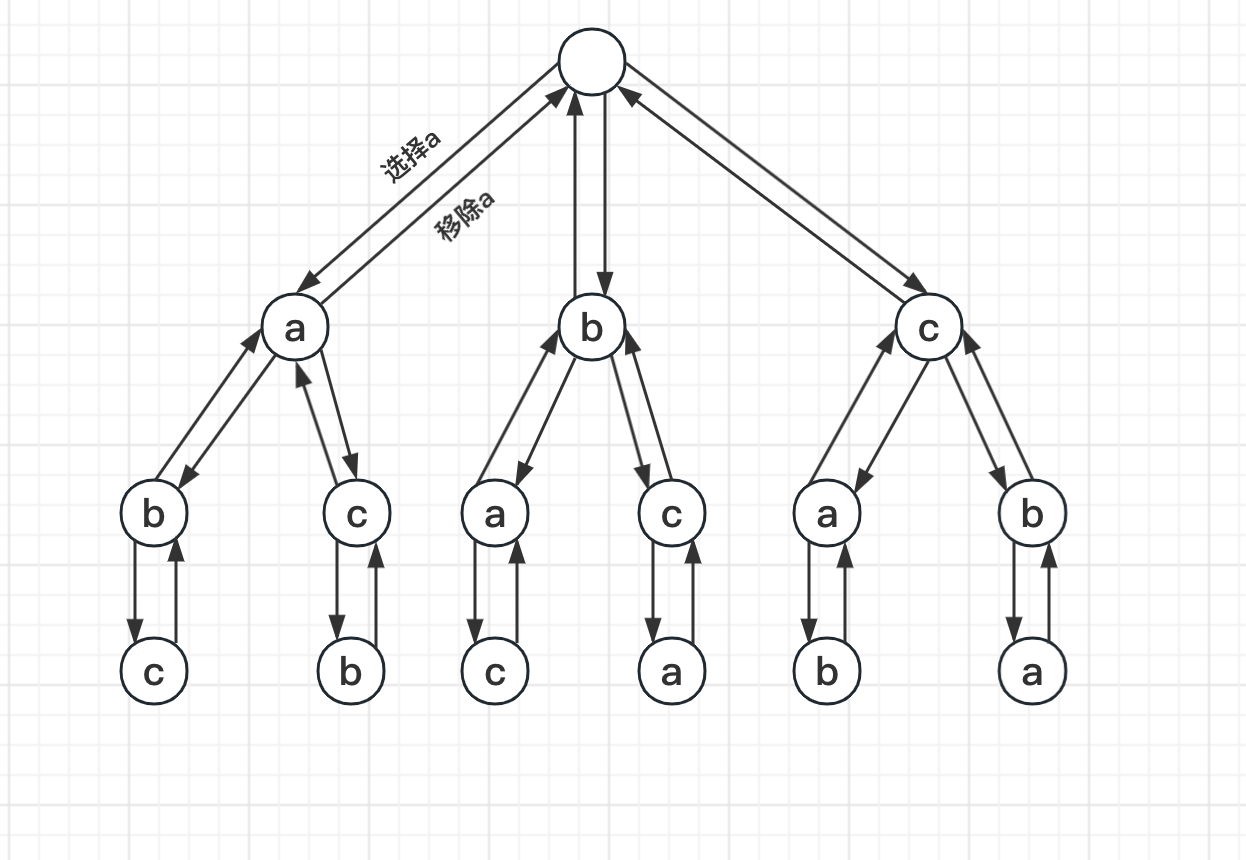
以上排列组合回溯步骤:
根据以上的步骤得出一个简单的回溯算法的模板:
public Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result;
LinkedList<Integer> path;
//记录那些元素被遍历过
boolean[] used;
private List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
result = new ArrayList<>();
path = new LinkedList<>();
used = new boolean[nums.length];
permuteHelper(nums);
return result;
}
private void permuteHelper(int[] nums) {
if (递归终止条件) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
//遍历各个元素
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
used[i] = true;
//选择元素
path.add(nums[i]);
permuteHelper(nums);
//移除元素
path.removeLast();
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
以上代码使用递归,递归一般要设置一个终止条件,然后遍历整个元素,通过链表选择元素和移除元素.
上面所说的,回溯主要解决一些排列组合、排列问题、搜索问题等问题,LeetCode 有很多类似的问题,这里选取了几个比较常见的题目.

这是一个比较典型的排列组合问题,本题采用的是求总和,使用总和减去遍历的数据,最后得到结果为零,就是符合的组合.
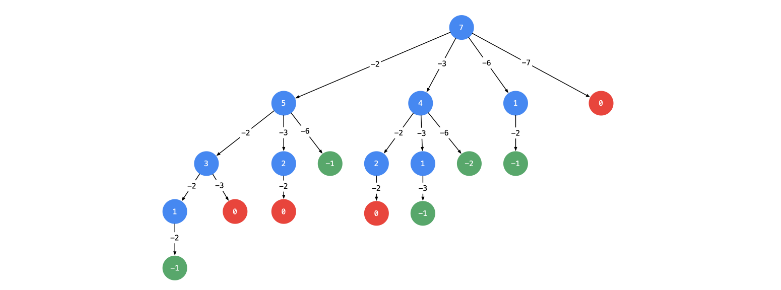
最终代码:
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
int[] candidate;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
candidate = candidates;
recall(0,target,new LinkedList<>());
return list;
}
private void recall(int start, int target, LinkedList<Integer> path) {
if (target == 0) {
list.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i <candidate.length ; i++) {
int sub = target - candidate[i];
if (sub < 0) {
break;
}
path.add(candidate[i]);
recall(i,sub,path);
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
recall 使用递归方法遍历分支,而使用链表的特性,记录遍历的节点,如果不符合要求就上一个分支回撤,同时链表移除最后一个结点.

这题的解题思路和上面的组合总和是差不多的,唯一不同的是元素 不能被重复遍历 ,使用一个变量记录遍历的起始值,遍历过的数据,下次往后一位开始遍历.
代码如下:
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
int[] candidate;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
candidate = candidates;
recall(0,target,new LinkedList<>());
return list;
}
private void recall(int start, int target, LinkedList<Integer> path) {
if (target == 0) {
list.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i <candidate.length ; i++) {
//这里解决集合重复问题
if (i > start && candidate[i] == candidate[i-1]) {
continue;
}
int sub = target - candidate[i];
if (sub < 0) {
break;
}
path.add(candidate[i]);
recall(i + 1,sub,path);
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
start 记录遍历的起始值,其他解题方法和上面的组合求和是类似的。题目还有一个要求是不能出现重复的组合,就需要判断 candidate[i] == candidate[i-1] 就忽略该数据,往后继续遍历.
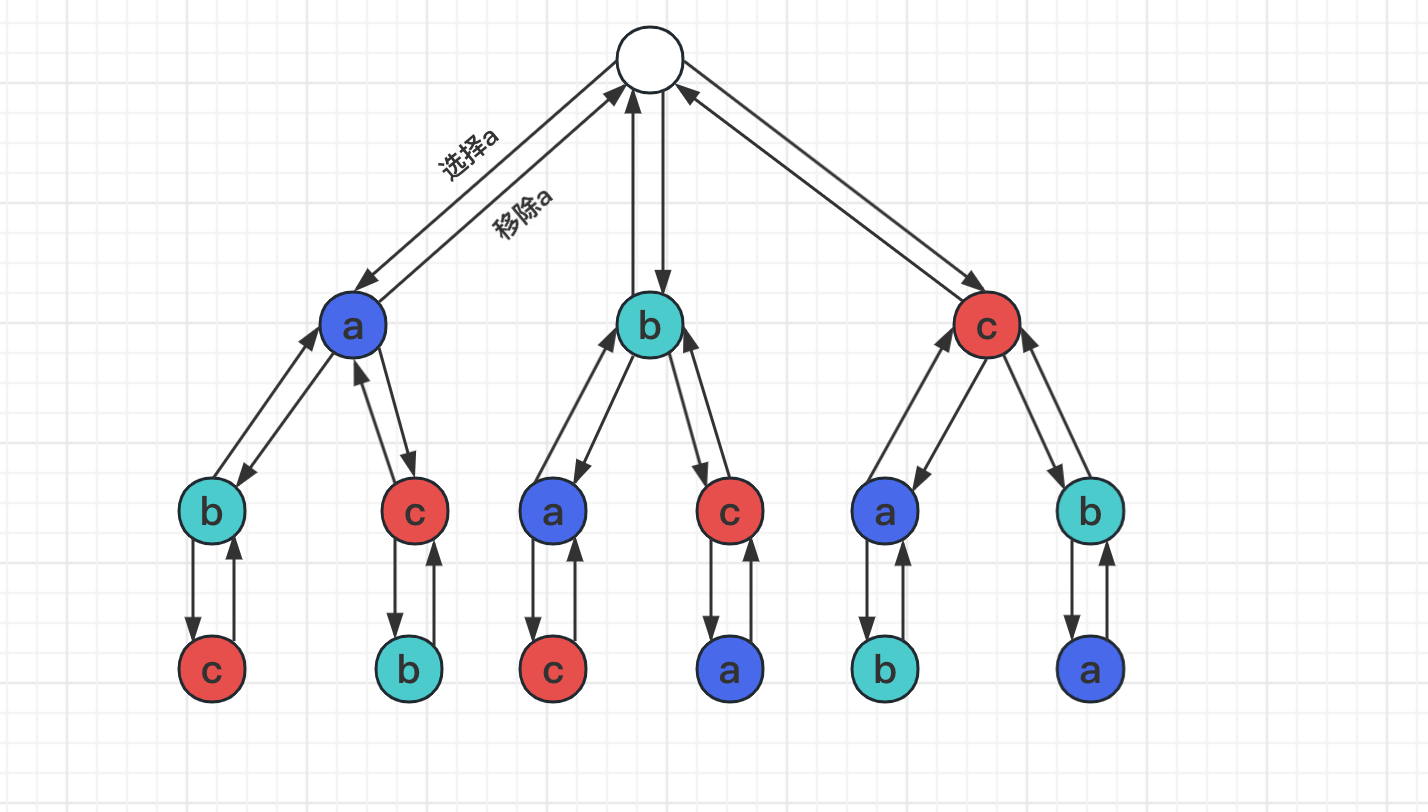
代码整理如下:
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] used;
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0) {
return result;
}
used = new boolean[nums.length];
permuteHelper(nums);
return result;
}
private void permuteHelper(int[] nums) {
if (path.size() == nums.length) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (used[i]) {
continue;
}
used[i] = true;
path.add(nums[i]);
permuteHelper(nums);
path.removeLast();
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
使用 used 记录哪些数据遍历过,遍历过的数据不会遍历,其他也是使用递归搜索.
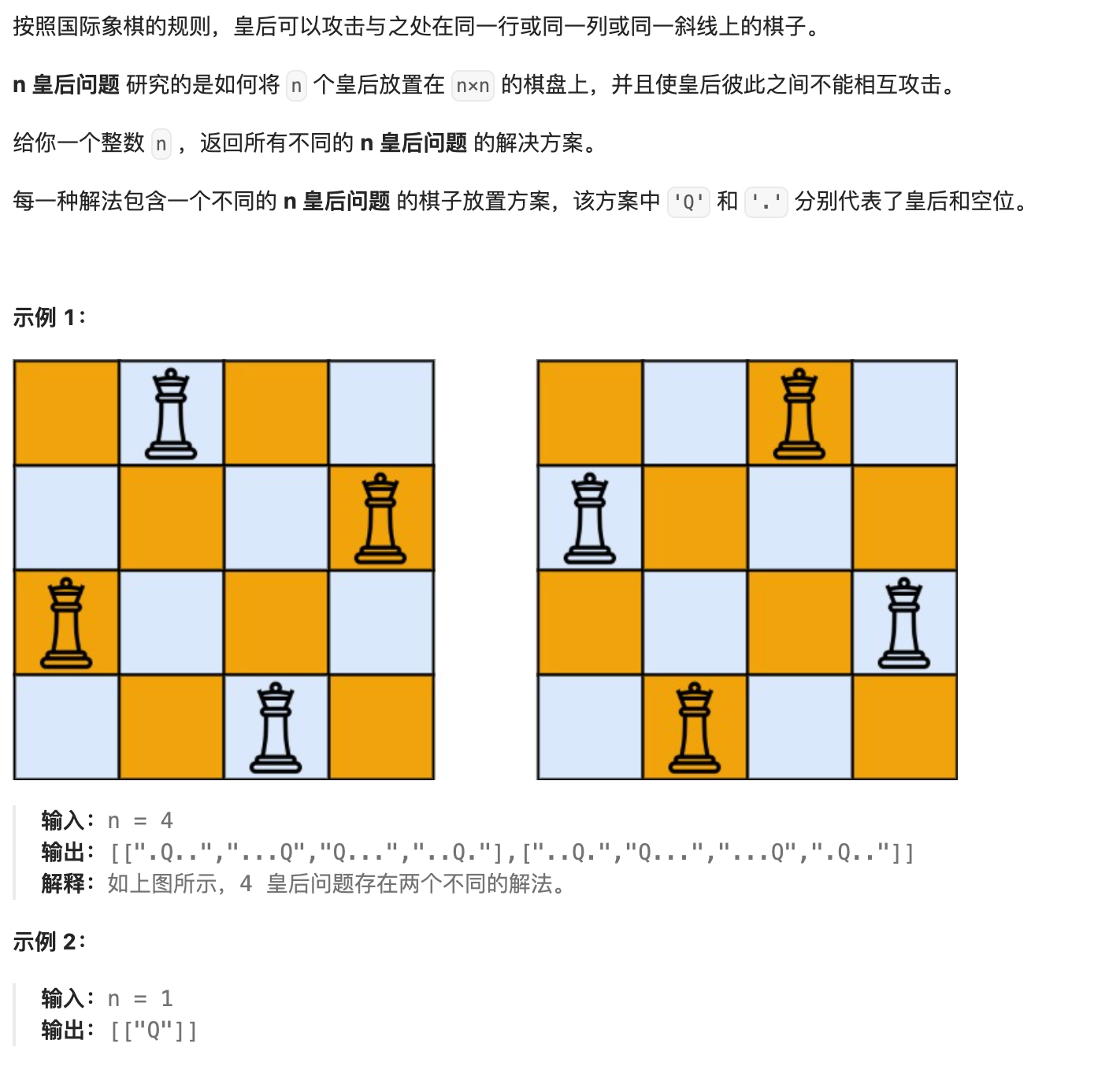
N 皇后问题是一个经典的回溯算法问题,是面试比较常见的问题。在一个 n * n 的棋盘上,每个格子放入的元素后,查看是够有同行、同列、左上方以及右上方是否冲突,冲突就回溯,不冲突就继续往下遍历.
class Solution {
List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
// 初始化棋盘 "." 表示空,"Q"表示皇后,
char[][] board = new char[n][n];
for (char[] c : board) {
Arrays.fill(c, '.');
}
backtrack(board, 0);
return res;
}
private void backtrack(char[][] board, int row) {
//终止条件
if (row == board.length) {
res.add(charToList(board));
return;
}
//每一行列数(也就是长度)
int n = board[row].length;
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
//排除相互攻击的格子
if (!isValid(board,row,col)) {
continue;
}
//放入Q
board[row][col] = 'Q';
//进入下一行放皇后
backtrack(board,row + 1);
//撤销Q
board[row][col] = '.';
}
}
private boolean isValid(char[][] board, int row, int col) {
int n = board.length;
//检查列是否有皇后冲突
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (board[i][col] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
//检查右上方是否有皇后冲突
for (int i = row - 1,j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < n; i--,j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
//检查左上方是否有皇后冲突
for (int i = row - 1,j = col - 1; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--,j--) {
if (board[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public List<String> charToList(char[][] board) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
list.add(String.copyValueOf(board[i]));
}
return list;
}
}
回溯算法尝试在问题的解空间中搜索可能的解,并在搜索过程中进行选择、撤销选择和终止搜索,直到找到解或确定无解为止.
最后此篇关于图解LeetCode算法汇总——回溯的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于图解LeetCode算法汇总——回溯的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
在我的类里面,我学习了 Prolog 回溯算法和 Rete forprop 算法,但我也被告知 Rete 可用于进行反向传播。 这是如何运作的?它在哪些方面与 Prolog 回溯相似/不同? 例如,这
两个 friend P1 和 P2 向共同的 friend P3 发送相同的消息 M。 然而由于一些网络损坏,P3 一次只能接收一个字符不知道接收到的字符是属于 P1 还是 P2。 此外,P3 可能会
我最近发了几个理解递归和回溯的问题,我觉得我现在得到了一些东西,并尝试编写一个测试,我确实解决了数独问题,但是当我以另一种格式编写代码时,代码卡了一会儿,返回False,说明这个问题无解。 grid
有人可以指导我或解释如何在 LISP 中执行回溯吗?任何示例或链接将不胜感激。我确实尝试过谷歌,但是他们都没有足够简单的例子让我理解。 谢谢 最佳答案 典型的方法是将不可变状态向下传递到调用堆栈,辅助
我正在使用 apache 2.2.14 运行 Backtrack 5 R2 (ubuntu) 的完全库存安装。我尝试运行一个简单的 index.html 文件,其中包含一些 javascript 代码
如何在 Javascript 中获取回溯? 理想的特征: 入口函数名称,或匿名函数的一些有意义的标识符, 每个级别的参数列表, 行号。 这可以用标准的 ECMAScript 完成吗? 如果没有,是否可
本文首发公众号:小码A梦 回溯算法是一种常见的算法,常见用于解决排列组合、排列问题、搜索问题等算法,在一个搜索空间中寻找所有的可能的解。通过向分支不断尝试获取所有的解,然后找到合适的
Python 是否支持为每个异常/引发/断言显示相同的自定义错误消息(无论代码在哪里中断)? 我目前对它的破解使用了一个装饰器。我有一个函数main它显示回溯很好,但我希望它也打印my_var (在函
输入: 3,4,8,7,3 5,S,7,2,3, 8,5,5,8,10 9,3,3,8,7 6,10,3,G,1 目标是找到从起点(S)到目标(G)的最佳路径。 我们可以向上、向下、向左、向右移动。
我想匹配一个包含“json”(出现超过 2 次)且两个“json”之间没有字符串“from”的字符串。 For example(what I want the string match or not)
我正在尝试使用回溯方法找到熄灯游戏的解决方案。我无法理解此过程的算法。我的方法是枚举从 0 到 2n2 - 1 的所有整数,并将每个整数转换为具有 n*n 位的二进制数。然后,将其分成n2个二进制数字
所以我正在阅读这本书《服从测试山羊》,在学习 Python 时我在第六章中遇到了一个问题。它说我应该能够运行我们在本章和前一章中设置的功能测试,没有错误;但是,我不断收到我不知道如何修复的回溯。 Tr
我需要一些关于 Android 日志文件反混淆的帮助。 问题是如果我有这样的异常: ... 10-16 10:03:10.488: E/AndroidRuntime(25723): Cau
我有一个看起来像这样的表: here | there | -------+-------+ {1,1} | {1,1} | {1,1} | {2,1} | {1,1} | {1,2} |
我写了一小段代码,它应该接受一个字符数组并让它看起来像计算机正在输入文本。很简单,对吧?但是当我运行它时,Terminal 告诉我: *** stack smashing detected ***:
Python 中的堆栈跟踪显示文件路径。有什么方法可以让它们显示完全限定的函数名称吗? 例子: class Foo(object): def bar(self): raise
我决定深入学习回溯的概念,我有以下任务: 给定N个投资者,M个城市,N×M个投资者偏好矩阵P(P[i,j]=1,当第i个投资者希望在第j个城市建矿池;P[i, j] = 0 那么他是中立的,当 P[i
设 E - 图 G 中所有边的集合问题是从G中找到顶点的最小子集S,它满足条件:S = E 中每个顶点的所有出边的总和 换句话说:边是街道,我们可以在顶点上放置路灯。如果我们在一个顶点上放置一盏路灯—
我正在尝试做这个我在查找面试问题时遇到的问题。我们被问及将 r 个硬币放置在 n*m 网格上的方法数量,使得每行和每列至少包含一个硬币。 我想到了一个回溯解决方案,按行主要顺序处理网格中的每个单元格,
我使用 DexGuard混淆。我有来自崩溃日志和映射文件的堆栈跟踪。当我运行 retrace.bat 并为其提供堆栈跟踪和映射文件时,输出仍然是混淆格式。 最佳答案 您是否在使用 ProGuard 的

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!