- Java锁的逻辑(结合对象头和ObjectMonitor)
- 还在用饼状图?来瞧瞧这些炫酷的百分比可视化新图形(附代码实现)⛵
- 自动注册实体类到EntityFrameworkCore上下文,并适配ABP及ABPVNext
- 基于Sklearn机器学习代码实战
AC 自动机是 以 Trie 的结构为基础 ,结合 KMP 的思想 建立的自动机,用于解决多模式匹配等任务.
这里需要仔细解释一下 Trie 的结点的含义,Trie 中的结点表示的是某个模式串的前缀。我们在后文也将其称作状态。一个结点表示一个状态,Trie 的边就是状态的转移.
形式化地说,对于若干个模式串 \(s_1, s_2 \dots s_n\) ,将它们构建一棵字典树后的所有状态的集合记作 Q.
个人感觉这里是最难理解的.
AC 自动机利用一个 fail 指针来辅助多模式串的匹配.
状态 \(u\) 的 fail 指针指向另一个状态 \(v\) ,其中 \(v \in Q\) ,且 \(v\) 是 \(u\) 的最长后缀(即在若干个后缀状态中取最长的一个作为 fail 指针).
只需要知道,AC 自动机的失配指针指向当前状态的最长后缀状态即可.
构建 fail 指针,可以参考 KMP 中构造 Next 指针的思想.
考虑字典树中当前的结点 \(u\) , \(u\) 的父结点是 \(p\) , \(p\) 通过字符 \(c\) 的边指向 \(u\) ,即 \(trie[p,\mathtt{c}]=u\) 。假设深度小于 \(u\) 的所有结点的 fail 指针都已求得.
如果 \(\text{trie}[\text{fail}[p],\mathtt{c}]\) 存在:则让 \(u\) 的 fail 指针指向 \(\text{trie}[\text{fail}[p],\mathtt{c}]\) 。相当于在 \(p\) 和 \(\text{fail}[p]\) 后面加一个字符 \(c\) ,分别对应 \(u\) 和 fail[u].
如果 \(\text{trie}[\text{fail}[p],\mathtt{c}]\) 不存在:那么我们继续找到 \(\text{trie}[\text{fail}[\text{fail}[p]],\mathtt{c}]\) 。重复 \(1\) 的判断过程,一直跳 fail 指针直到根结点.
如果真的没有,就让 fail 指针指向根结点。 如此即完成了 \(\text{fail}[u]\) 的构建.
如此即完成了 \(\text{fail}[u]\) 的构建.
struct node {
int fail;
int tr[26];
int End;
} ac[N];
fail 是失配指针, tr 是字典树, End 是当前状态是否为一个字符串的结束.
这里就是最基本的字典树插入操作.
void Insert(char* s) {
int l = strlen(s), u = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < l; ++ i) {
if (ac[u].tr[s[i] - 'a'] == 0) {
ac[u].tr[s[i] - 'a'] = ++ tot;
}
u = ac[u].tr[s[i] - 'a'];
}
++ ac[u].End;
}
我们用队列广搜的方式来构建失败指针,按照上面的步骤:
如果 \(\text{trie}[\text{fail}[p],\mathtt{c}]\) 存在:则让 \(u\) 的 fail 指针指向 \(\text{trie}[\text{fail}[p],\mathtt{c}]\) 。相当于在 \(p\) 和 \(\text{fail}[p]\) 后面加一个字符 \(c\) ,分别对应 \(u\) 和 fail[u].
如果 \(\text{trie}[\text{fail}[p],\mathtt{c}]\) 不存在:那么我们继续找到 \(\text{trie}[\text{fail}[\text{fail}[p]],\mathtt{c}]\) 。重复 \(1\) 的判断过程,一直跳 fail 指针直到根结点.
如果真的没有,就让 fail 指针指向根结点。 如此即完成了 \(\text{fail}[u]\) 的构建.
void get_fail() {
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++ i) {
if (ac[0].tr[i] != 0) {
ac[ac[0].tr[i]].fail = 0;
q.emplace(ac[0].tr[i]);
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++ i) {
if (ac[u].tr[i]) {
ac[ac[u].tr[i]].fail = ac[ac[u].fail].tr[i];
q.emplace(ac[u].tr[i]);
} else {
ac[u].tr[i] = ac[ac[u].fail].tr[i];
}
}
}
}
这里我们用模板题来说明.
P3808 【模板】AC 自动机(简单版) - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn) 。
int ask(char* s) {
int l = strlen(s);
int u = 0, ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < l; ++ i) {
u = ac[u].tr[s[i] - 'a'];
for (int cur = u; cur && (~ac[cur].End); cur = ac[cur].fail) {
ans += ac[cur].End;
ac[cur].End = -1;
}
}
return ans;
}
这里给 End 打上标记,是为了防止重复搜到这一个模式串,然后重复加入了答案.
完整代码:
/*
The code was written by yifan, and yifan is neutral!!!
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
template<typename T>
inline T read() {
T x = 0;
bool fg = 0;
char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
fg |= (ch == '-');
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
return fg ? ~x + 1 : x;
}
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
int n, tot;
char s[N];
struct node {
int fail;
int tr[26];
int End;
} ac[N];
void Insert(char* s) {
int l = strlen(s), u = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < l; ++ i) {
if (ac[u].tr[s[i] - 'a'] == 0) {
ac[u].tr[s[i] - 'a'] = ++ tot;
}
u = ac[u].tr[s[i] - 'a'];
}
++ ac[u].End;
}
void get_fail() {
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++ i) {
if (ac[0].tr[i] != 0) {
ac[ac[0].tr[i]].fail = 0;
q.emplace(ac[0].tr[i]);
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++ i) {
if (ac[u].tr[i]) {
ac[ac[u].tr[i]].fail = ac[ac[u].fail].tr[i];
q.emplace(ac[u].tr[i]);
} else {
ac[u].tr[i] = ac[ac[u].fail].tr[i];
}
}
}
}
int ask(char* s) {
int l = strlen(s);
int u = 0, ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < l; ++ i) {
u = ac[u].tr[s[i] - 'a'];
for (int cur = u; cur && (~ac[cur].End); cur = ac[cur].fail) {
ans += ac[cur].End;
ac[cur].End = -1;
}
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
n = read<int>();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) {
scanf("%s", s + 1);
Insert(s + 1);
}
ac[0].fail = 0;
get_fail();
scanf("%s", s + 1);
cout << ask(s + 1) << '\n';
return 0;
}
P3796 【模板】AC 自动机(加强版) - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn) 。
这里 End 存储的不再是简单的 \(1\) 了,而是当前这个状态对应的模式串的编号,目的是最后输出字符串.
void Insert(string s, int num) {
int u = 0, l = s.size();
for (int i = 0; i < l; ++ i) {
if (!ac[u].tr[s[i] - 'a']) {
ac[u].tr[s[i] - 'a'] = ++ cnt;
clr(cnt);
}
u = ac[u].tr[s[i] - 'a'];
}
ac[u].End = num;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) {
cin >> st[i];
Insert(st[i], i);
Ans[i].first = 0;
Ans[i].second = i;
}
除了查询和主函数,其他代码都是一样的.
查询代码:
void ask(char* s) {
int l = strlen(s);
int u = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < l; ++ i) {
u = ac[u].tr[s[i] - 'a'];
for (int cur = u; cur; cur = ac[cur].fail) {
++ Ans[ac[cur].End].first;
}
}
}
这里的 Ans 是定义的答案数组, first 是记录出现的次数, second 是该状态的编号.
完整代码:
/*
The code was written by yifan, and yifan is neutral!!!
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
template<typename T>
inline T read() {
T x = 0;
bool fg = 0;
char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
fg |= (ch == '-');
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
return fg ? ~x + 1 : x;
}
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
int n, cnt;
char s[N];
string st[200];
struct node {
int fail, End;
int tr[26];
} ac[N];
pair<int, int> Ans[N];
void clr(int u) {
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++ i) {
ac[u].tr[i] = 0;
}
ac[u].fail = ac[u].End = 0;
}
void Insert(string s, int num) {
int u = 0, l = s.size();
for (int i = 0; i < l; ++ i) {
if (!ac[u].tr[s[i] - 'a']) {
ac[u].tr[s[i] - 'a'] = ++ cnt;
clr(cnt);
}
u = ac[u].tr[s[i] - 'a'];
}
ac[u].End = num;
}
void get_fail() {
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++ i) {
if (ac[0].tr[i] != 0) {
ac[ac[0].tr[i]].fail = 0;
q.emplace(ac[0].tr[i]);
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++ i) {
if (ac[u].tr[i]) {
ac[ac[u].tr[i]].fail = ac[ac[u].fail].tr[i];
q.emplace(ac[u].tr[i]);
} else {
ac[u].tr[i] = ac[ac[u].fail].tr[i];
}
}
}
}
void ask(char* s) {
int l = strlen(s);
int u = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < l; ++ i) {
u = ac[u].tr[s[i] - 'a'];
for (int cur = u; cur; cur = ac[cur].fail) {
++ Ans[ac[cur].End].first;
}
}
}
void work() {
cnt = 0;
clr(0);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) {
cin >> st[i];
Insert(st[i], i);
Ans[i].first = 0;
Ans[i].second = i;
}
get_fail();
scanf("%s", s + 1);
ask(s + 1);
sort(Ans + 1, Ans + n + 1, [](pii x, pii y) {
return x.first == y.first ? x.second < y.second : x.first > y.first;
});
int l = 1;
printf("%d\n", Ans[1].first);
while (Ans[l].first == Ans[1].first) {
cout << st[Ans[l].second] << '\n';
++ l;
}
}
int main() {
n = read<int>();
while (n) {
work();
n = read<int>();
}
return 0;
}
先拿这道题来引入。 P5357 【模板】AC 自动机(二次加强版) - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn) 。
你会发现它与 P3796 【模板】AC 自动机(加强版) - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn) 十分的相似,似乎只要将最后的找出现次数最大的模式串改为输出所有模式串的出现次数就行了 反正当时我是这样想的 ,然后略微修改代码后交上发现.
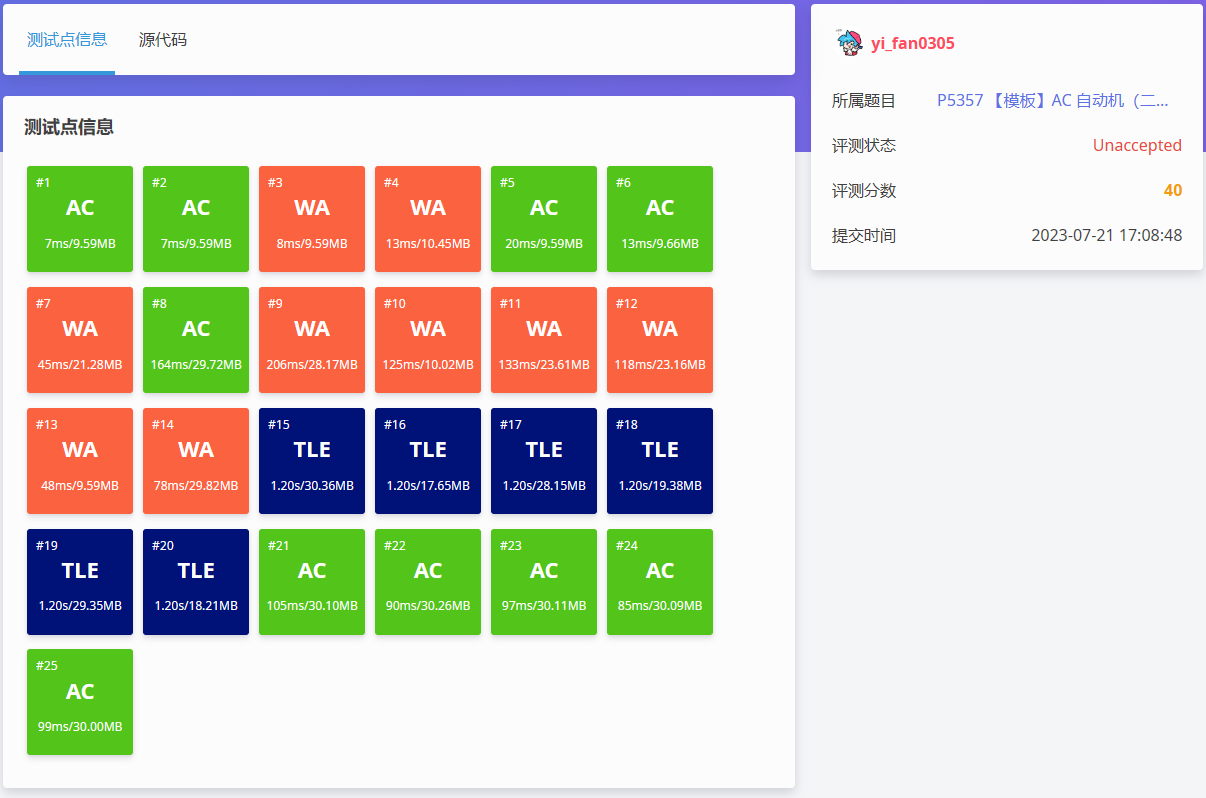
果然,二次加强版就是不一样…… 。
重新读题,意外发现最后一句话: 数据不保证任意两个模式串不相同 .
???不保证,读错题了!(不要犯这样的低级错误),这里还是比较简单的,只需要判一下重就好了,直接上代码,相信看到这里的聪明的你一定可以看懂它!修改的主要位置加上注释了.
/*
The code was written by yifan, and yifan is neutral!!!
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
template<typename T>
inline T read() {
T x = 0;
bool fg = 0;
char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
fg |= (ch == '-');
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
return fg ? ~x + 1 : x;
}
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
const int M = 2e6 + 5;
int n, tot;
int ans[N], mp[N];
string st[N];
char s[M];
queue<int> q;
struct node {
int End, fail;
int tr[26];
} ac[N];
void Insert(string s, int num) {
int l = s.length(), u = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < l; ++ i) {
if (!ac[u].tr[s[i] - 'a']) {
ac[u].tr[s[i] - 'a'] = ++ tot;
}
u = ac[u].tr[s[i] - 'a'];
}
if (!ac[u].End) {// 修改点 1
ac[u].End = num;
}
mp[num] = ac[u].End;
}
void get_fail() {
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++ i) {
if (ac[0].tr[i]) {
ac[ac[0].tr[i]].fail = 0;
q.emplace(ac[0].tr[i]);
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++ i) {
if (ac[u].tr[i]) {
ac[ac[u].tr[i]].fail = ac[ac[u].fail].tr[i];
q.emplace(ac[u].tr[i]);
} else {
ac[u].tr[i] = ac[ac[u].fail].tr[i];
}
}
}
}
void ask(char* s) {
int l = strlen(s), u = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < l; ++ i) {
u = ac[u].tr[s[i] - 'a'];
for (int cur = u; cur; cur = ac[cur].fail) {
++ ans[ac[cur].End];
}
}
}
int main() {
n = read<int>();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) {
cin >> st[i];
Insert(st[i], i);
}
get_fail();
scanf("%s", s + 1);
ask(s + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) {
printf("%d\n", ans[mp[i]]); // 修改点 2
}
return 0;
}
再次提交,得到了这样的结果.
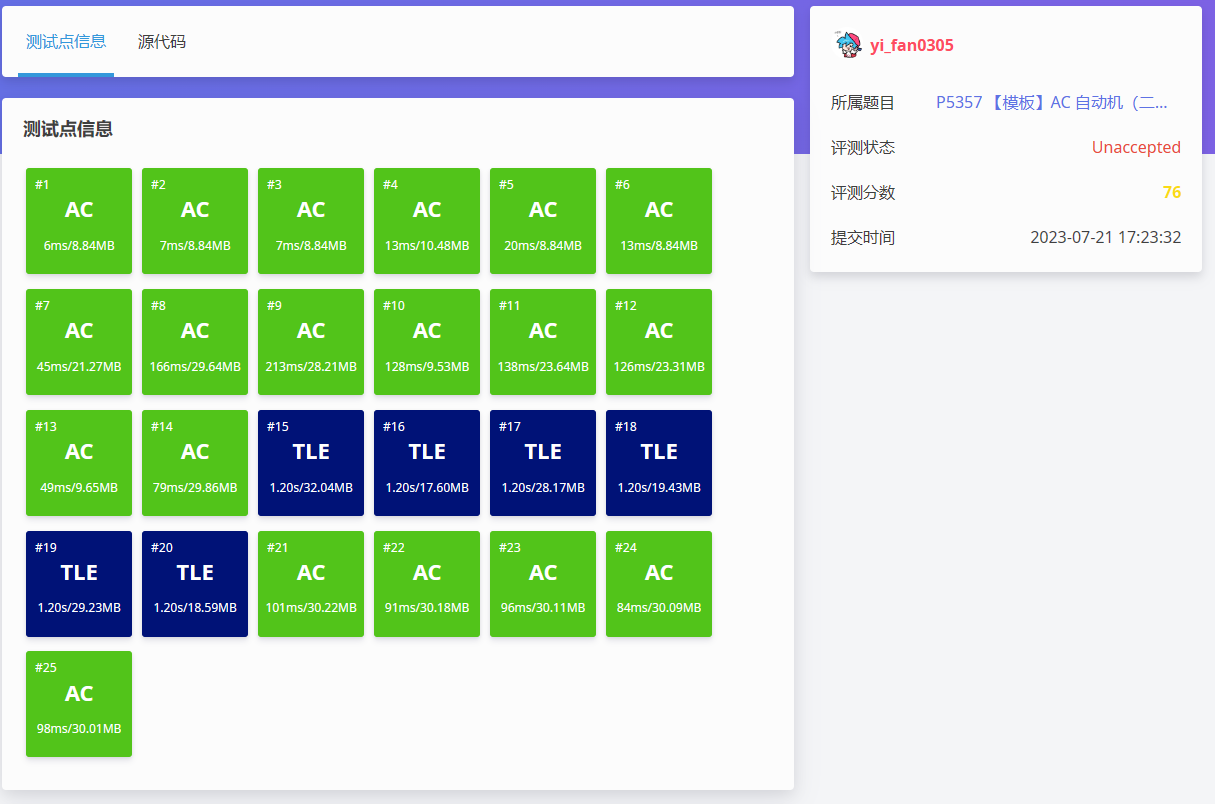
没办法,去 \(\texttt{OI-Wiki}\) 上看了看,发现原来有优化,优化的方式使用 拓扑排序 ! 。
不会拓扑排序的朋友先去学习一下拓扑排序吧。 拓扑排序 - OI Wiki (oi-wiki.org) 。
我们为什么会 T 呢?
看这段代码 。
void ask(char* s) {
int l = strlen(s), u = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < l; ++ i) {
u = ac[u].tr[s[i] - 'a'];
for (int cur = u; cur; cur = ac[cur].fail) {
++ ans[ac[cur].End];
}
}
}
我们沿着 fail 指针一步一步地跳,对于下面的图.
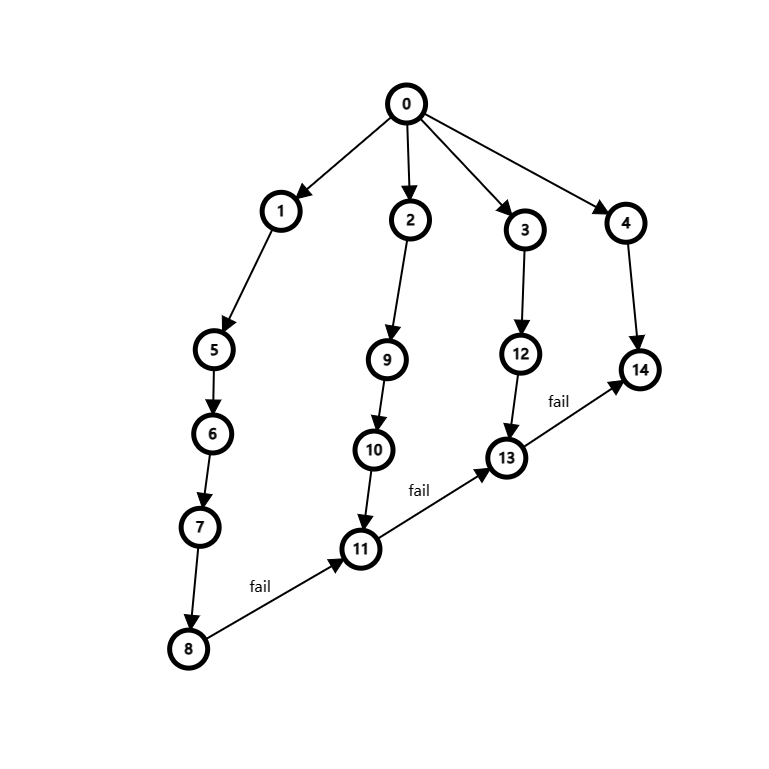
我们假设:
先搜到 \(14\) 号节点,答案更新;然后搜到了 \(13\) 号节点,答案更新,再找到 \(14\) 号节点,答案更新;之后搜到了 \(11\) 号节点,顺着 fail 答案更新;再之后搜到了 \(8\) 号节点,顺着 fail 答案更新.
你会发现,效率慢的很!然后就被这道题卡了.
如何提高效率的,我们可以在 \(8、11、13、14\) 号节点上各打上标记,然后从 \(8\) 号开始,标记顺着 fail 传递过去,最后统计的答案为: \(8\) 号统计了 \(1\) 次, \(11\) 号统计了 \(2\) 次, \(13\) 号统计了 \(3\) 次, \(14\) 号统计了 \(4\) 次,这样统计的答案与一次又一次地更新是一样的,但是这种方法效率高了很多.
具体怎么实现呢,就用拓扑排序,把 fail 指针作为边,最后 fail 指针一定不会成环,所以可以跑拓扑排序,修改一下代码就可以了.
/*
The code was written by yifan, and yifan is neutral!!!
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
template<typename T>
inline T read() {
T x = 0;
bool fg = 0;
char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
fg |= (ch == '-');
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
return fg ? ~x + 1 : x;
}
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
const int M = 2e6 + 5;
int n, tot;
int ans[N], mp[N], in[N];
string st[N];
char s[M];
queue<int> q;
struct node {
int End, fail, tag;
int tr[26];
} ac[N];
void Insert(string s, int num) {
int l = s.length(), u = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < l; ++ i) {
if (!ac[u].tr[s[i] - 'a']) {
ac[u].tr[s[i] - 'a'] = ++ tot;
}
u = ac[u].tr[s[i] - 'a'];
}
if (!ac[u].End) {
ac[u].End = num;
}
mp[num] = ac[u].End;
}
void get_fail() {
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++ i) {
if (ac[0].tr[i]) {
ac[ac[0].tr[i]].fail = 0;
q.emplace(ac[0].tr[i]);
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++ i) {
if (ac[u].tr[i]) {
ac[ac[u].tr[i]].fail = ac[ac[u].fail].tr[i];
q.emplace(ac[u].tr[i]);
++ in[ac[ac[u].fail].tr[i]];
} else {
ac[u].tr[i] = ac[ac[u].fail].tr[i];
}
}
}
}
void ask(char* s) {
int l = strlen(s), u = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < l; ++ i) {
u = ac[u].tr[s[i] - 'a'];
++ ac[u].tag; // 修改部分 1
}
}
void topsort() { // 修改部分 2
for (int i = 1; i <= tot; ++ i) {
if (!in[i]) {
q.emplace(i);
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
int fr = q.front();
q.pop();
ans[ac[fr].End] = ac[fr].tag;
int u = ac[fr].fail;
ac[u].tag += ac[fr].tag;
if (! (-- in[u])) {
q.emplace(u);
}
}
}
int main() {
n = read<int>();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) {
cin >> st[i];
Insert(st[i], i);
}
get_fail();
scanf("%s", s + 1);
ask(s + 1);
topsort();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) {
printf("%d\n", ans[mp[i]]);
}
return 0;
}
然后,我们就得到了想要的 AC! 。
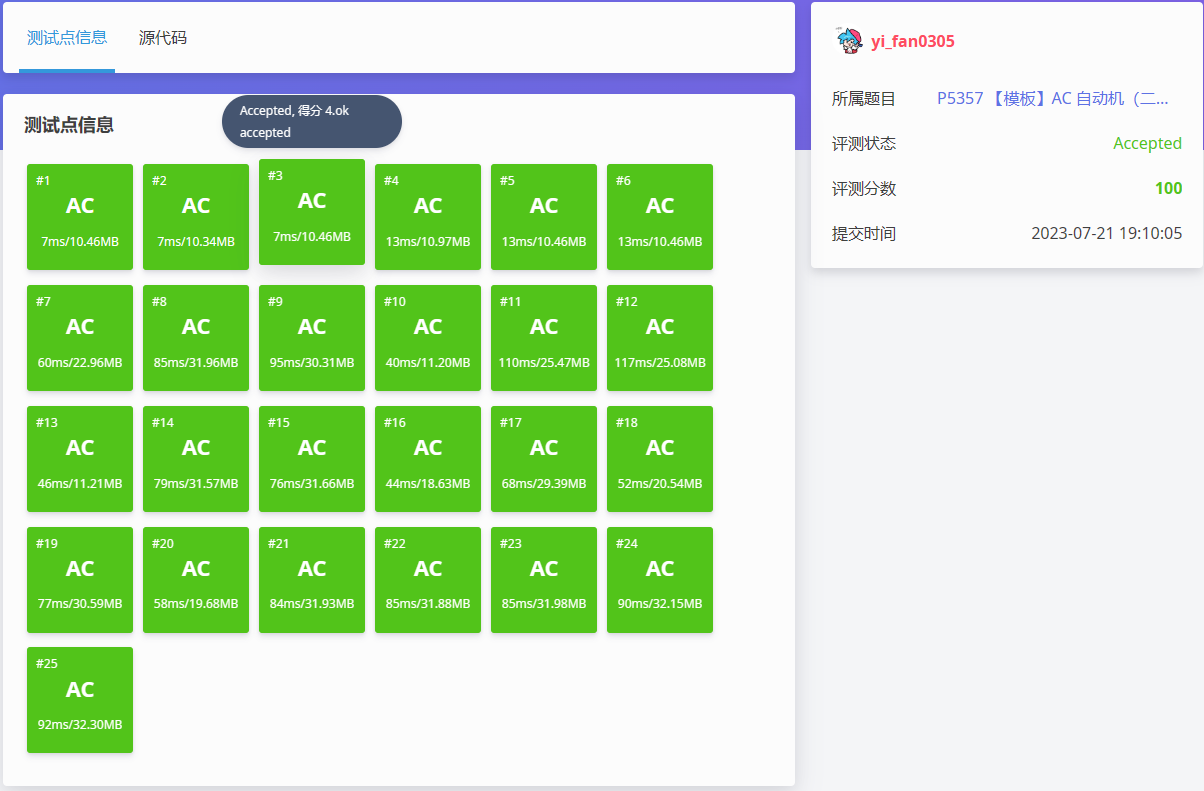
完结! 。
最后此篇关于「学习笔记」AC自动机的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于「学习笔记」AC自动机的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
OkHttp的作用 OkHttp is an HTTP client。 如果是HTTP的方式想得到数据,就需要我们在页面上输入网址,如果网址没有问题,就有可能返回对应的String字符串,如果这个地址
Record 一个重要的字符串算法,这是第三次复习。 通过总结我认为之所以某个算法总是忘记,是因为大脑始终没有认可这种算法的逻辑(也就是脑回路)。 本篇主要讲解从KMP的应用场景,
SQL 注入基础 【若本文有问题请指正】 有回显 回显正常 基本步骤 1. 判断注入类型 数字型 or 字符型 数字型【示例】:
标签: #Prompt #LLM 创建时间:2023-04-28 17:05:45 链接: 课程(含JupyterNotebook) , 中文版 讲师: An
Swift是供iOS和OS X应用编程的新编程语言,基于C和Objective-C,而却没有C的一些兼容约束。Swift采用了安全的编程模式和添加现代的功能来是的编程更加简单、灵活和有趣。界面则基于
VulnStack-红日靶机七 概述 在 VulnStack7 是由 5 台目标机器组成的三层网络环境,分别为 DMZ 区、第二层网络、第三层网络。涉及到的知识点也是有很多,redis未授权的利用
红日靶机(一)笔记 概述 域渗透靶机,可以练习对域渗透的一些知识,主要还是要熟悉 powershell 语法,powershell 往往比 cmd 的命令行更加强大,而很多渗透开源的脚本都是 po
八大绩效域详细解析 18.1 干系人绩效域 跟干系人所有相关的活动. 一、预期目标 ①与干系人建立高效的工作关系 ②干系人认同项目目标 ③支持项目的干系人提高
18.3 开发方法和生命周期绩效域 跟开发方法,项目交付节奏和生命周期相关的活动和职能. 一、预期目标: ①开发方法与项目可交付物相符合; ②将项目交付与干系人价值紧密
18.7 度量绩效域 度量绩效域涉及评估项目绩效和采取应对措施相关的活动和职能度量是评估项目绩效,并采取适当的应对措施,以保持最佳项目绩效的过程。 一、 预期目标: ①对项目状况
pygraphviz 安装,windows系统: 正确的安装姿势: Prebuilt-Binaries/PyGraphviz at master · CristiFati/Prebuilt-Binar
今天给大家介绍IDEA开发工具如何配置devtools热加载工具。 1、devtools原理介绍 spring-boot-devtools是spring为开发者提供的热加载
一 什么是正则表达式 // 正则表达式(regular expression)是一个描述字符模式的对象; // JS定义RegExp类表示正则表达式; // String和RegExp都定义了使用
目前是2022-04-25 23:48:03,此篇博文分享到互联网上估计是1-2个月后的事了,此时的OpenCV3最新版是3.4.16 这里前提是gcc,g++,cmake都需要安装好。 没安装好的,
一、概述 1、Flink 是什么 Apache Flink is a framework and distributed processing engine for stateful comput
一、window 概述 Flink 通常处理流式、无限数据集的计算引擎,窗口是一种把无限流式数据集切割成有限的数据集进行计算。window窗口在Flink中极其重要。 二、window 类型 w
一、触发器(Trigger) 1.1、案例一 利用global window + trigger 计算单词出现三次统计一次(有点像CountWindow) 某台虚拟机或者mac 终端输入:nc -
一、时间语义 在Flink 中涉及到三个重要时间概念:EventTime、IngestionTime、ProcessingTime。 1.1、EventTime EventTime 表示日志事
一、概述 以wordcount为例,为什么每次输入数据,flink都能统计每个单词的总数呢?我们都没有显示保存每个单词的状态值,但是每来一条数据,都能计算单词的总数。事实上,flink在底层维护了每
一、概述 checkpoint机制是Flink可靠性的基石,可以保证Flink集群在某个算子因为某些原因(如 异常退出)出现故障时,能够将整个应用流图的状态恢复到故障之前的某一状态,保 证应用流图状

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!