- Java锁的逻辑(结合对象头和ObjectMonitor)
- 还在用饼状图?来瞧瞧这些炫酷的百分比可视化新图形(附代码实现)⛵
- 自动注册实体类到EntityFrameworkCore上下文,并适配ABP及ABPVNext
- 基于Sklearn机器学习代码实战
在 第一篇 中我们大致分析了从: 创建舞台 -> 添加显示对象-> 更新显示对象 的源码实现 。
这一篇将主要分析几个常用显示对象自各 draw 方法的实现 。
让我们看向例子 examples/Text_simple.html 。
这个例子中使用了三个显示对象类 Bitmap 、Text 、 Shape 。
以下例子中添加了一个 image 。
var image = new createjs.Bitmap("imagePath.png");
stage.addChild(image);
当调用 stage.update 后,会调用显示对象的 draw 方法,如果是 Container 类,则继续递归调用其 draw 方法 。
这样所有 stage 舞台上的显示对象的 draw 方法都会被调用到,注意 canvas 的上下文对象 ctx 参数都会被传入 。
分两步:
如果 DisplayObject 类内有缓存,则绘制缓存 。
如果没有缓存则循环显示列表调用每个 child 的 draw 方法 child 都为 DisplayObject 实例,还判断了 DisplayObject 实例的 isVisible 如果不可见则不绘制 。
// Container 类 源码 160 - 176 行
p.draw = function(ctx, ignoreCache) {
if (this.DisplayObject_draw(ctx, ignoreCache)) { return true; }
// 用 slice 的原因是防止绘制过程中 children 发生变更导致出错
var list = this.children.slice();
for (var i=0,l=list.length; i<l; i++) {
var child = list[i];
if (!child.isVisible()) { continue; }
// draw the child:
ctx.save();
child.updateContext(ctx);
child.draw(ctx);
ctx.restore();
}
return true;
};
child 就为一个 Bitmap 对象 。
直接看 Bitmap 类实现的 draw 方法如下:
// Bitmap 类 源码 142-159
p.draw = function(ctx, ignoreCache) {
if (this.DisplayObject_draw(ctx, ignoreCache)) { return true; }
var img = this.image, rect = this.sourceRect;
if (img.getImage) { img = img.getImage(); }
if (!img) { return true; }
if (rect) {
// some browsers choke on out of bound values, so we'll fix them:
var x1 = rect.x, y1 = rect.y, x2 = x1 + rect.width, y2 = y1 + rect.height, x = 0, y = 0, w = img.width, h = img.height;
if (x1 < 0) { x -= x1; x1 = 0; }
if (x2 > w) { x2 = w; }
if (y1 < 0) { y -= y1; y1 = 0; }
if (y2 > h) { y2 = h; }
ctx.drawImage(img, x1, y1, x2-x1, y2-y1, x, y, x2-x1, y2-y1);
} else {
ctx.drawImage(img, 0, 0);
}
return true;
};
就三步:
有缓存则绘制缓存 。
如果有 rect 限制,有目标尺寸 rect 限制,则绘制成 rect 尺寸,调用 canvas 的 drawImage 原生方法并传入目标尺寸 。
如果没有 rect 限制,则直接调用 canvas 的 drawImage 原生方法 。
先不管 ctx.drawImage(img, x1, y1, x2-x1, y2-y1, x, y, x2-x1, y2-y1); 这一句, 。
具体语法可以查询 https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/CanvasRenderingContext2D/drawImage 。
注意: ctx.drawImage(img, 0, 0); 后两个参数值是图象的 x, y 坐标, 。
都传了 0 好家伙直接 "hardcode" 了,绘制时不用考虑图像的位置吗?
都画在了 0, 0 位置画在左上角?
这不科学,如果用户指定了图像位置比如 x = 100, y = 80 那怎么办?
如果我来实现,直觉上就会想要把此处改为 ctx.drawImage(img, 0 + x, 0 + y),
但 EaselJS 并没有,但却又能正常工作?,先搁置,继续往下看就会明白 。
绘制文本 。
创建一个文本 txt 。
txt = new createjs.Text("text on the canvas... 0!", "36px Arial", "#FFF");
直接看向 Text 的 draw 实例方法:
// Text 类 源码 208 - 217 行
p.draw = function(ctx, ignoreCache) {
if (this.DisplayObject_draw(ctx, ignoreCache)) { return true; }
var col = this.color || "#000";
if (this.outline) { ctx.strokeStyle = col; ctx.lineWidth = this.outline*1; }
else { ctx.fillStyle = col; }
this._drawText(this._prepContext(ctx));
return true;
};
依然先判断缓存 。
文本默认为黑色 。
如果有 outline 则 lineWidth 被设置限制宽度,用显示文本周边的框 。
调用 this._drawText(this._prepContext(ctx)),
_prepContext 存着的上下文中预设的默认样式 。
Text 的 _drawText 方法是真正执行绘制文本的的逻辑(支持换行) 。
// Text 类 源码 339 - 390 行
p._drawText = function(ctx, o, lines) {
var paint = !!ctx;
if (!paint) {
ctx = Text._workingContext;
ctx.save();
this._prepContext(ctx);
}
var lineHeight = this.lineHeight||this.getMeasuredLineHeight();
var maxW = 0, count = 0;
var hardLines = String(this.text).split(/(?:\r\n|\r|\n)/);
for (var i=0, l=hardLines.length; i<l; i++) {
var str = hardLines[i];
var w = null;
if (this.lineWidth != null && (w = ctx.measureText(str).width) > this.lineWidth) {
// text wrapping:
var words = str.split(/(\s)/);
str = words[0];
w = ctx.measureText(str).width;
for (var j=1, jl=words.length; j<jl; j+=2) {
// Line needs to wrap:
var wordW = ctx.measureText(words[j] + words[j+1]).width;
if (w + wordW > this.lineWidth) {
if (paint) { this._drawTextLine(ctx, str, count*lineHeight); }
if (lines) { lines.push(str); }
if (w > maxW) { maxW = w; }
str = words[j+1];
w = ctx.measureText(str).width;
count++;
} else {
str += words[j] + words[j+1];
w += wordW;
}
}
}
if (paint) { this._drawTextLine(ctx, str, count*lineHeight); }
if (lines) { lines.push(str); }
if (o && w == null) { w = ctx.measureText(str).width; }
if (w > maxW) { maxW = w; }
count++;
}
if (o) {
o.width = maxW;
o.height = count*lineHeight;
}
if (!paint) { ctx.restore(); }
return o;
};
步骤:
paint 为 false 即没有传 ctx 时 仅用于测量文本的尺寸,并不实际绘制到舞台上 。
通过 String(this.text).split(/(?:\r\n|\r|\n)/); 这一句将通过回车与换行符得到多行文本 。
循环分解出的文本数组,ctx.measureText 测量文本宽度后判断是否大于 lineWidth 如果加上后面一断文本大于,则需新启一行 。
调用 _drawTextLine() 方法绘制文本 。
调用 canvas 真实 api ctx.fillText 绘制文本 。
// Text 类 源码 399 - 403 行
p._drawTextLine = function(ctx, text, y) {
// Chrome 17 will fail to draw the text if the last param is included but null, so we feed it a large value instead:
if (this.outline) { ctx.strokeText(text, 0, y, this.maxWidth||0xFFFF); }
else { ctx.fillText(text, 0, y, this.maxWidth||0xFFFF); }
};
发现没有 ctx.fillText 处传的 x 还是 hardcode 硬编码 0 而坐标 y 还是相对坐标,都绘制到 canvas 上了还不是绝对坐标能行吗?
不科学啊 。
是时候探究了! 。
draw 方法内使用的坐标都是硬编码或相对坐标,但又可以如期绘制正确的绝对坐标位置 。
是时候看一下之前遗留的 updateContext 方法了 。
还记得第一篇中 stage.update 内 draw 方法前的一句 this.updateContext(ctx); 吗 。
实际上最终调用的是 DisplayObject 类的 updateContext 实例方法如下:
// DisplayObject.js 源码 787-810 行
p.updateContext = function(ctx) {
var o=this, mask=o.mask, mtx= o._props.matrix;
if (mask && mask.graphics && !mask.graphics.isEmpty()) {
mask.getMatrix(mtx);
ctx.transform(mtx.a, mtx.b, mtx.c, mtx.d, mtx.tx, mtx.ty);
mask.graphics.drawAsPath(ctx);
ctx.clip();
mtx.invert();
ctx.transform(mtx.a, mtx.b, mtx.c, mtx.d, mtx.tx, mtx.ty);
}
this.getMatrix(mtx);
var tx = mtx.tx, ty = mtx.ty;
if (DisplayObject._snapToPixelEnabled && o.snapToPixel) {
tx = tx + (tx < 0 ? -0.5 : 0.5) | 0;
ty = ty + (ty < 0 ? -0.5 : 0.5) | 0;
}
ctx.transform(mtx.a, mtx.b, mtx.c, mtx.d, tx, ty);
ctx.globalAlpha *= o.alpha;
if (o.compositeOperation) { ctx.globalCompositeOperation = o.compositeOperation; }
if (o.shadow) { this._applyShadow(ctx, o.shadow); }
};
o._props 是 src/easeljs/geom/DisplayProps.js DisplayProps 类的实例 。
DisplayProps 主要负责了显示对象的以下属性操作 。
visible、alpha、shadow、compositeOperation、matrix 。
mtx= o._props.matrix 在 DisplayObject 实例属性 _props 对象中得到 matrix 。
updateContext 就是在上下文中应用不同的 matrix 实现上下文中的“变幻” 。
首先就是对 mask 遮罩的处理,遮罩是通过绘制 Graphics 后对上下文进行 ctx.clip 实现的 。
如果存在 mask 当前显示对象有遮罩,通过 mask.getMatrix 把遮罩的 matrix 。
ctx.transform 将上下文变化至遮罩所在的“状态” 。
绘制遮罩 mask.graphics.drawAsPath(ctx) 。
还原矩阵 mtx.invert(); 回到当前显示对象的“状态” 。
至此 mask 部分处理完毕 。
回到当前显示对象的 getMatrix 获取矩阵后应用矩阵变化 。
getMatrix 做了两件事 。
// DisplayObject.js 源码 1020-1024 行
p.getMatrix = function(matrix) {
var o = this, mtx = matrix || new createjs.Matrix2D();
return o.transformMatrix ? mtx.copy(o.transformMatrix) :
(mtx.identity() && mtx.appendTransform(o.x, o.y, o.scaleX, o.scaleY, o.rotation, o.skewX, o.skewY, o.regX, o.regY));
};
注意这一句 mtx.appendTransform(o.x, o.y, o.scaleX, o.scaleY, o.rotation, o.skewX, o.skewY, o.regX, o.regY)) 。
就是将当前显示对象的变幻属性合到矩阵中 。
得到新的 matrix 后调用 ctx.transform(mtx.a, mtx.b, mtx.c, mtx.d, tx, ty); 实现一系列变化 。
至于 src/easeljs/geom/Matrix2D.js 矩阵类 。
平时在 css 中的使用的变化 scale, rotate, translateX, translateY 最后都是矩阵变幻实现的 。
矩阵变幻的好处一次可以实现多种变化,只是不那么直观 。
至于矩阵为什么可以实现变幻,我这小学数学水平可讲不清楚,推荐 3blue1brown 的视频看完肯定会醍醐灌顶 。
我的总结是矩阵实现的是对坐标轴的线性变幻,直接将坐标轴原点变幻到绘制点!! 。
所以在具体 draw 绘制时 x,y 坐标可以硬编码或使用相对坐标,因为 draw 之前已经使用矩阵把整体坐标轴变幻到位了 。
绘制完后又会重置回来开始新的对象的变幻 。
Shape 类代码非常少,实现绘制的是 Graphics 类 。
Shape 只是作为 Graphics 实例的载体 。
使用 shape.graphics 属性即可访问 。
Shape.js 源码 106-110 行
p.draw = function(ctx, ignoreCache) {
if (this.DisplayObject_draw(ctx, ignoreCache)) { return true; }
this.graphics.draw(ctx, this);
return true;
};
矢量图形类 Graphics 在 src/easeljs/display/Graphics.js 。
通常 Graphics 用于绘制矢量图形 。
可单独使用,也可以在 Shape 实例内调用 。
var g = new createjs.Graphics();
g.setStrokeStyle(1);
g.beginStroke("#000000");
g.beginFill("red");
g.drawCircle(0,0,30);
要实现 Grapihcs 绘制,就得组合一系列绘图命令 。
一系列绘制命令被存储在了 _instructions 数组属性内 。
这些命令被称为 Command Objects 命令对象 。
源码 1653 行 - 2459 行都是命令对象 。
命令对象分别都暴露了一个 exec 方法 。
比如 MoveTo 命令 。
// Graphics.js 源码 1700 - 1702 行
(G.MoveTo = function(x, y) {
this.x = x; this.y = y;
}).prototype.exec = function(ctx) { ctx.moveTo(this.x, this.y); };
比如圆形绘制命令 。
// Graphics.js 源码 2292 - 2295 行
(G.Circle = function(x, y, radius) {
this.x = x; this.y = y;
this.radius = radius;
}).prototype.exec = function(ctx) { ctx.arc(this.x, this.y, this.radius, 0, Math.PI*2); };
下面是圆角矩形的也是在 Graphics 静态方法 。
(G.RoundRect = function(x, y, w, h, radiusTL, radiusTR, radiusBR, radiusBL) {
this.x = x; this.y = y;
this.w = w; this.h = h;
this.radiusTL = radiusTL; this.radiusTR = radiusTR;
this.radiusBR = radiusBR; this.radiusBL = radiusBL;
}).prototype.exec = function(ctx) {
var max = (this.w<this.h?this.w:this.h)/2;
var mTL=0, mTR=0, mBR=0, mBL=0;
var x = this.x, y = this.y, w = this.w, h = this.h;
var rTL = this.radiusTL, rTR = this.radiusTR, rBR = this.radiusBR, rBL = this.radiusBL;
if (rTL < 0) { rTL *= (mTL=-1); }
if (rTL > max) { rTL = max; }
if (rTR < 0) { rTR *= (mTR=-1); }
if (rTR > max) { rTR = max; }
if (rBR < 0) { rBR *= (mBR=-1); }
if (rBR > max) { rBR = max; }
if (rBL < 0) { rBL *= (mBL=-1); }
if (rBL > max) { rBL = max; }
ctx.moveTo(x+w-rTR, y);
ctx.arcTo(x+w+rTR*mTR, y-rTR*mTR, x+w, y+rTR, rTR);
ctx.lineTo(x+w, y+h-rBR);
ctx.arcTo(x+w+rBR*mBR, y+h+rBR*mBR, x+w-rBR, y+h, rBR);
ctx.lineTo(x+rBL, y+h);
ctx.arcTo(x-rBL*mBL, y+h+rBL*mBL, x, y+h-rBL, rBL);
ctx.lineTo(x, y+rTL);
ctx.arcTo(x-rTL*mTL, y-rTL*mTL, x+rTL, y, rTL);
ctx.closePath();
};
exec 方法才是真正调用 canvas context 绘制的地方 。
G 就是 Graphics 的简写,在 250 行 var G = Graphics,
这些单独的绘图命令其实就是 G 的一些静态方法,只是这些静态方法又拥有各自不同的 exec 实例方法实现具体的绘图 。
而 Graphics 的实例方法又会将绘图命令 append 一个 “静态方法的实例” 存储数组内 。
比如 lineTo , 注意是 new G.MoveTo(x,y) 一个命令 。
// Graphics.js 源码 469 - 471 行
p.moveTo = function(x, y) {
return this.append(new G.MoveTo(x,y), true);
};
下面是 append 源码,命令都存在 _activeInstructions 数组内 。
// Graphics.js 源码 1024 - 1029 行
p.append = function(command, clean) {
this._activeInstructions.push(command);
this.command = command;
if (!clean) { this._dirty = true; }
return this;
};
再看通用的 draw 方法 。
// Graphics.js 源码 434-440 行
p.draw = function(ctx, data) {
this._updateInstructions();
var instr = this._instructions;
for (var i=this._storeIndex, l=instr.length; i<l; i++) {
instr[i].exec(ctx, data);
}
};
draw 内的主要逻辑就是用循环调用 _instructions 存储的“命令对象”执行命令对象的 exec 方法 。
_instructions 的命令是通过 _updateInstructions 方法从 _activeInstructions 数组内复制的 。
// Graphics.js 源码 1593-1627 行
p._updateInstructions = function(commit) {
var instr = this._instructions, active = this._activeInstructions, commitIndex = this._commitIndex;
debugger
if (this._dirty && active.length) {
instr.length = commitIndex; // remove old, uncommitted commands
instr.push(Graphics.beginCmd);
var l = active.length, ll = instr.length;
instr.length = ll+l;
for (var i=0; i<l; i++) { instr[i+ll] = active[i]; }
if (this._fill) { instr.push(this._fill); }
if (this._stroke) {
// doesn't need to be re-applied if it hasn't changed.
if (this._strokeDash !== this._oldStrokeDash) {
instr.push(this._strokeDash);
}
if (this._strokeStyle !== this._oldStrokeStyle) {
instr.push(this._strokeStyle);
}
if (commit) {
this._oldStrokeStyle = this._strokeStyle;
this._oldStrokeDash = this._strokeDash;
}
instr.push(this._stroke);
}
this._dirty = false;
}
// 如果 commit 了,把 _activeInstructions 当前命令集合清空,且游标指向 this._instructions 的最后位置
if (commit) {
active.length = 0;
this._commitIndex = instr.length;
}
};
还有一些方法(如:beginStroke beginFill) 内调用了 _updateInstructions(true) 注意传的是 true 。
比如:
p.beginStroke = function(color) {
return this._setStroke(color ? new G.Stroke(color) : null);
};
p._setStroke = function(stroke) {
this._updateInstructions(true);
if (this.command = this._stroke = stroke) {
stroke.ignoreScale = this._strokeIgnoreScale;
}
return this;
};
注意: 这里收集的命令暂时不会被放到 this._instructions 数组内 。
直到有 append 方法执行过 dirty 为 true 了 才会把 stroke 命令添加到 this._instructions 数组 。
因为没有 append 任何实质的内容(圆,线,矩形等),则不需要执行 stroke ,beginFill 等命令,因为无意义 。
p._updateInstructions 到底干了啥?
主要是在 draw 之前不断收集命令, 在多处都有调用 _updateInstructions 。
这些操作 commit 均为 true 表明后面的绘制是新的开始,将之前的一系列绘制命令归为一个路径绘制,下一个得新启一个路径绘制 。
使用 this._commitIndex 游标重新指示命令数组内的位置 。
debugger 调试一下看看 。
在 easeljs-NEXT.js 的 5226 行加上 debugger 。
浏览器中打开 examples/Graphics_simple.html 文件,并打开浏览器调试工具 。
Graphics_simple.html 文件的 javascript 代码内有一个 drawSmiley 方法 。
function drawSmiley() {
var s = new createjs.Shape();
var g = s.graphics;
//Head
g.setStrokeStyle(10, 'round', 'round');
g.beginStroke("#000");
g.beginFill("#FC0");
g.drawCircle(0, 0, 100); //55,53
//Mouth
g.beginFill(); // no fill
g.arc(0, 0, 60, 0, Math.PI);
//Right eye
g.beginStroke(); // no stroke
g.beginFill("#000");
g.drawCircle(-30, -30, 15);
//Left eye
g.drawCircle(30, -30, 15);
return s;
}
很明显通过 debugger 先调用了 setStrokeStyle 。

当调用 setStrokeStyle、beginStroke、beginFill 等都会执行 _updateInstructions 命令 。
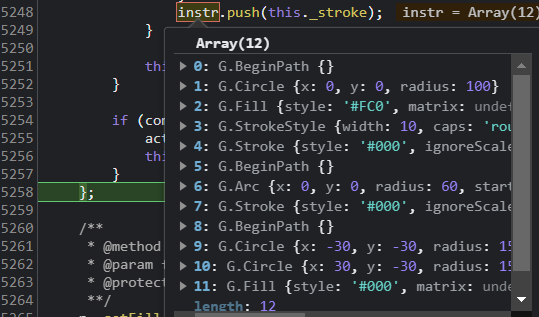
当执行到 g.drawCircle(0, 0, 100); 此时命令才会被一起收集顺序如下 。
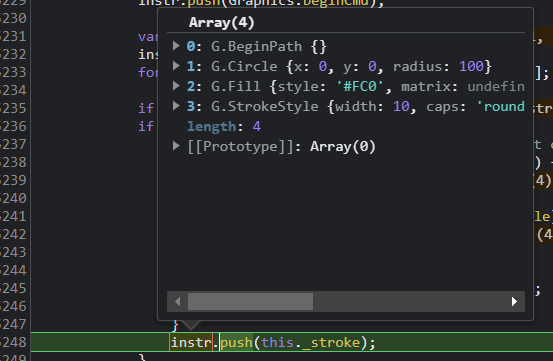
发现没有,与我们在调用顺序不一样 。
g.setStrokeStyle(10, 'round', 'round');
g.beginStroke("#000");
g.beginFill("#FC0");
g.drawCircle(0, 0, 100); //55,53
BeginPath -> Circle -> Fill -> StrokeStyle 。
这是 Canvas 真正正常执行的顺序 。
BeginPath 也在每次 dirty (append 方法导至 dirty 为 true) 时添加,beginPath 当然是另启一个新的路径绘制了 。
这一篇分析的是,最常用的三个显示对象 。
下一篇分析另三个稍显高级的显示对象 。
博客园: http://cnblogs.com/willian/ github: https://github.com/willian12345/ 。
最后此篇关于EaselJS源码分析系列--第二篇的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于EaselJS源码分析系列--第二篇的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我刚刚继承了一个旧的 PostgreSQL 安装,需要进行一些诊断以找出该数据库运行缓慢的原因。在 MS SQL 上,您可以使用 Profiler 等工具来查看正在运行的查询,然后查看它们的执行计划。
将目标从Analytics(分析)导入到AdWords中,然后在Analytics(分析)中更改目标条件时,是否可以通过更改将目标“重新导入”到AdWords,还是可以自动选择? 最佳答案 更改目标值
我正在使用google analytics api来获取数据。我正在获取数据,但我想验证两个参数,它们在特定日期范围内始终为0。我正在获取['ga:transactions']和['ga:goalCo
我使用Google API从Google Analytics(分析)获取数据,但指标与Google Analytics(分析)的网络界面不同。 即:我在2015年3月1日获得数据-它返回综合浏览量79
我在我的Web应用程序中使用sammy.js进行剔除。我正在尝试向其中添加Google Analytics(分析)。我很快找到了following plugin来实现页面跟踪。 我按照步骤操作,页面如
当使用 Xcode 分析 (product>analyze) 时,有没有办法忽略给定文件中的任何错误? 例如编译指示之类的? 我们只想忽略第三方代码的任何警告,这样当我们的代码出现问题时,它对我们
目录 EFK 1. 日志系统 2. 部署ElasticSearch 2.1 创建handless服务 2.2 创建s
关闭。这个问题不满足Stack Overflow guidelines .它目前不接受答案。 想改善这个问题吗?更新问题,使其成为 on-topic对于堆栈溢出。 7年前关闭。 Improve thi
GCC/G++ 是否有可用于输出分析的选项? 能够比较以前的代码与新代码之间的差异(大小、类/结构的大小)将很有用。然后可以将它们与之前的输出进行比较以进行比较,这对于许多目的都是有用的。 如果没有此
我正在浏览 LYAH,并一直在研究处理列表时列表理解与映射/过滤器的使用。我已经分析了以下两个函数,并包含了教授的输出。如果我正确地阅读了教授的内容,我会说 FiltB 的运行速度比 FiltA 慢很
在 MySQL 中可以使用 SET profiling = 1; 设置分析 查询 SHOW PROFILES; 显示每个查询所用的时间。我想知道这个时间是只包括服务器的执行时间还是还包括将结果发送到前
我用 Python 编写了几个用于生成阶乘的模块,我想测试运行时间。我找到了一个分析示例 here我使用该模板来分析我的模块: import profile #fact def main():
前几天读了下mysqld_safe脚本,个人感觉还是收获蛮大的,其中细致的交代了MySQL数据库的启动流程,包括查找MySQL相关目录,解析配置文件以及最后如何调用mysqld程序来启动实例等,有着
上一篇:《人工智能大语言模型起源篇,低秩微调(LoRA)》 (14)Rae 和同事(包括78位合著者!)于2022年发表的《Scaling Language Models: Methods, A
1 内网基础 内网/局域网(Local Area Network,LAN),是指在某一区域内有多台计算机互联而成的计算机组,组网范围通常在数千米以内。在局域网中,可以实现文件管理、应用软件共享、打印机
1 内网基础 内网/局域网(Local Area Network,LAN),是指在某一区域内有多台计算机互联而成的计算机组,组网范围通常在数千米以内。在局域网中,可以实现文件管理、应用软件共享、打印机
我有四列形式的数据。前三列代表时间,value1,value 2。第四列是二进制,全为 0 或 1。当第四列中对应的二进制值为0时,有没有办法告诉excel删除时间、值1和值2?我知道这在 C++ 或
我正在运行一个进行长时间计算的 Haskell 程序。经过一些分析和跟踪后,我注意到以下内容: $ /usr/bin/time -v ./hl test.hl 9000045000050000 Com
我有一个缓慢的 asp.net 程序正在运行。我想分析生产服务器以查看发生了什么,但我不想显着降低生产服务器的速度。 一般而言,配置生产盒或仅本地开发盒是标准做法吗?另外,您建议使用哪些程序来实现这一
我目前正在尝试分析 Haskell 服务器。服务器永远运行,所以我只想要一个固定时间的分析报告。我尝试只运行该程序 3 分钟,然后礼貌地要求它终止,但不知何故,haskell 分析器不遵守术语信号,并

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!