这期看标题已经能猜到了,主要讲的是成绩排行功能,还有对应的文件读写。那么废话不多说,让我们有请今天的主角...的设计稿:
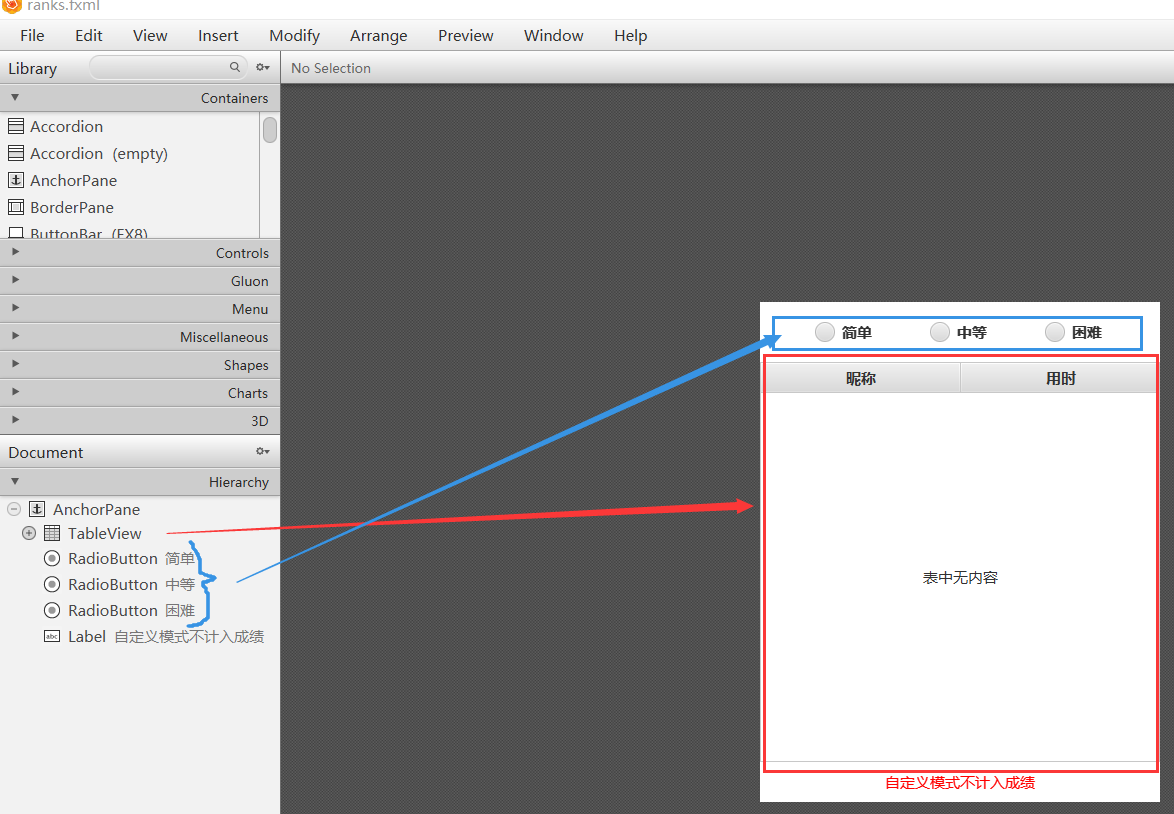
那么主角是何方神圣呢?当然是图中的大框框——TableView。关于这个控件的选取没有太多讲究,你也可以用文本域,手动换行来显示。我只是觉得使用表格显示看起来更规范些。接下来考虑数据来源,最直接的来源是每局游戏结束后的用时。不过这还不够,想要有排行一条记录可不行,也就是我们还要保存以往的记录,一般来讲10条即可。至于采用何种方式存取,那就具体情况具体分析了。像这个只是我本人制作分享,采用文件存取能够演示功能就行。有些朋友可能是为了课程设计来学习,需要配合数据库使用也可以, 下面来看看文件存取的代码实现.
首先就是文件和目录的创建问题,都开始写代码了就尽量把这些工作交给程序来完成:
static {
// 每次调用此类都先判断目录和文件是否存在
try {
File directory = new File(PREFIX + "/src/ranks");
if (!directory.exists() || !directory.isDirectory()) {
// 目录不存在, 自动创建
directory.mkdirs();
}
for (String path : RECORD_PATHS) {
path = PREFIX + path;
File file = new File(path);
if (!file.exists()) {
// 文件不存在, 自动创建
if (file.createNewFile()) {
// 创建成功, 写入内置数据
BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(path));
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
writer.write("未命名 999\n");
}
writer.flush();
writer.close();
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Error on [Class:FileIO, Method:static segment]=>");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
需要注意的是使用文件存取的容易引起的问题就是文件相对路径可能并不完全适用,如果你遇到问题还请分析是否由路径错误导致。我对文件路径处理方式如下( 路径拼接为绝对路径 ):
// 完整路径前缀
public static String PREFIX = System.getProperty("user.dir");
// 排行榜文件相对路径
public static final String[] RECORD_PATHS = {
"\\src\\ranks\\easy.txt",
"\\src\\ranks\\medium.txt",
"\\src\\ranks\\hard.txt"
};
然后就是文件读写,做法如下:
/**
* 读取文件
*
* @param filePath 文件路径
* @return 排行数据集合
*/
public static ObservableList<String[]> readFromFile(String filePath) {
ObservableList<String[]> list = FXCollections.observableArrayList();
try {
// 拼接路径, 创建读取对象
filePath = PREFIX + filePath;
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath));
// 读取数据
String line = null;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
list.add(line.split(" "));
}
reader.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Error on [Class:FileIO, Method:readFromFile]=>");
e.printStackTrace();
}
return list;
}
/**
* 向文件内写入数据
*
* @param filePath 文件路径
* @param record 待更新数据项
*/
public static void writeToFile(String filePath, String[] record) {
try {
// 获取已有数据
ObservableList<String[]> list = readFromFile(filePath);
// 将记录插入到合适位置
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
if (record[1].compareTo(list.get(i)[1]) <= 1) {
list.add(i, record);
break;
}
}
// 移除多余记录
list.remove(10);
// 重新写入数据
BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(PREFIX + filePath));
for (String[] item : list) {
writer.write(item[0] + " " + item[1] + "\n");
}
writer.flush();
writer.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Error on [Class:FileIO, Method:writeToFile]=>");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
这里大家可能对Observation这个接口不太熟悉,使用它是因为TableView指定了它为数据源的类型。关于它的说明,官方文档介绍如下:
A list that allows listeners to track changes when they occur. Implementations can be created using methods in FXCollections such as observableArrayList, or with a SimpleListProperty. 。
允许侦听器在发生更改时跟踪更改的列表。实现可以使用FXCollections中的方法来创建,比如observableArrayList,或者使用SimpleListProperty.
数据处理工作准备完毕后就是展示环节。从本文最开始的设计图可以看出表格由两列内容,一个是玩家昵称,另一个是用时。在代码中对应写法如下:
@FXML // 排行展示表
private TableView<String[]> table;
@FXML // 表格列
private TableColumn<String[], String> name, time;
// 用于存放数据的列表
private ObservableList<String[]> data;
// 设置数据源
table.setItems(data);
// 设置单元格大小
table.setFixedCellSize(36.0);
// 设置每个 TableColumn 的 cellValueFactory
name.setCellValueFactory(cellData -> new SimpleStringProperty(cellData.getValue()[0]));
time.setCellValueFactory(cellData -> new SimpleStringProperty(cellData.getValue()[1]));
那么有关难度的单选按钮是干嘛用的呢?很明显是区分不同难度下的成绩,下面是相关实现:
@FXML // 单选按钮, 难度
private RadioButton easy, medium, hard;
// 单选按钮组
private ToggleGroup degree;
// 单选按钮分组
degree = new ToggleGroup();
easy.setToggleGroup(degree);
medium.setToggleGroup(degree);
hard.setToggleGroup(degree);
// 默认选中简单, 并加载数据
easy.setSelected(true);
data = FileIO.readFromFile(RECORD_PATHS[0]);
table.setItems(data);
// 难度按钮选中事件
degree.selectedToggleProperty().addListener(((observable, oldValue, newValue) -> {
String id = ((RadioButton) newValue).getId();
// 根据不同按钮设置不同文件路径
if (id.equals("easy")) {
data = FileIO.readFromFile(RECORD_PATHS[0]);
} else if (id.equals("medium")) {
data = FileIO.readFromFile(RECORD_PATHS[1]);
} else {
data = FileIO.readFromFile(RECORD_PATHS[2]);
}
table.setItems(data);
}));
然后让我们回到整个流程开始,获取游戏用时,即游戏胜利时的处理。上期我们讲计时事件中有这样一段代码( 使用runLater是因为在动画或布局处理期间不允许使用showAndWait,也就是无法使用提示框 ):
// 自定义模式不计入成绩
if (GAME != GameEnum.CUSTOM) {
Platform.runLater(() -> showDialog());
}
这个 showDialog 方法就是关键,它的完整内容如下:
/**
* 用时少于排行版某一项, 输入玩家名称
*/
private void showDialog() {
// 创建带输入的对话框
TextInputDialog dialog = new TextInputDialog();
dialog.setTitle("新纪录!");
dialog.setHeaderText("请输入您的昵称:");
dialog.getDialogPane().setGraphic(null);
dialog.setOnCloseRequest(event -> {
// 处理取消或关闭事件时输入为空的情况
String userInput = dialog.getEditor().getText();
if (userInput == null || userInput.trim().equals("")) {
event.consume(); // 阻止关闭操作
Alert alert = new Alert(Alert.AlertType.ERROR);
alert.setContentText("您必须输入些什么");
alert.showAndWait();
}
});
// 输入事件
Optional<String> result = dialog.showAndWait();
result.ifPresent(name -> {
// 获取输入, 保存到文件
String filePath = null;
if (name == null || name.equals("")) {
name = "player";
}
String[] record = new String[]{name, TIMER + ""};
switch (GAME) {
case HARD:
filePath = RECORD_PATHS[2];
break;
case MEDIUM:
filePath = RECORD_PATHS[1];
break;
case EASY:
filePath = RECORD_PATHS[0];
default:
break;
}
FileIO.writeToFile(filePath, record);
});
}
看上去似乎充分避免了玩家在游戏结束不输入的情况,事实上并非如此。在带输入的提示框弹出后点击右上角 ❎ 关闭,虽然仍会弹出警告框提醒玩家未输入,但最终还是会在没有输入的情况下关闭。这里我觉得可以使用死循环来改善,即额外定义一个变量初始值为false,只有当获取到输入内容后初始值变为true,才允许结束循环。感兴趣的朋友们可以尝试下,本期内容到此结束,感谢观看.
——————————————我———是———分———割———线————————————— 。
天气好热啊🥵,除了呆在空调屋刷手机什么都不想干啦!可是还有好多事要办,必须出门,热死我算了😭 。







我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!