- Java锁的逻辑(结合对象头和ObjectMonitor)
- 还在用饼状图?来瞧瞧这些炫酷的百分比可视化新图形(附代码实现)⛵
- 自动注册实体类到EntityFrameworkCore上下文,并适配ABP及ABPVNext
- 基于Sklearn机器学习代码实战
ABP 框架中的缓存系统核心包是 Volo.Abp.Caching ,而对于分布式缓存的支持,abp 官方提供了基于 Redis 的方案,需要安装 Volo.Abp.Caching.StackExchangeRedis 集成包。默认的情况下,在我们使用 ABP CLI 创建 ABP 框架模板项目的时候已经集成了这个包,我们不需要手动进行安装.
ABP 框架中的缓存系统在 ASP.NET Core的分布式缓存系统 上进行扩展,从而为了使分布式缓存使用起来更加方便。理所当然的,ABP 框架的缓存系统兼容 ASP.NET Core 原生的分布式缓存使用方式,关于 ASP.NET Core 分布式缓存的使用,可以参考我之前的文章 ASP.NET Core - 缓存之分布式缓存 ,也可以看下官方文档 ASP.NET Core 中的分布式缓存 .
那么 ABP 框架中的缓存系统扩展了什么呢?ASP.NET Core 的分布式缓存又有哪些不便之处呢 ?ASP.NET Core 通过 IDistributedCache 抽象了分布式缓存的存取操作,但是有这个两个问题:
它对缓存值的存取是基于 byte 数组的,而不是对象.
这使得我们在使用分布式缓存的时候需要先将实例对象进行序列化/反序列化,之后再转码为 byte 数组。如果每个使用分布式缓存的地方都这么做将会有很多的重复冗余的代码,这是需要抽取封装的.
为了能实现多个应用公用缓存,达成分布式缓存的左右,它将所有的缓存项存放在同一个 Key 池之中.
这就可能会有问题,我们要特别注意缓存键的设置,如果开发人员不注意,很可能将一些缓存相互覆盖了,特别是共用缓存的应用比较多,或者多租户的情况下,这造成的问题可能很严重,而且很难排查.
ABP 框架的缓存系统扩展了通用的泛型接口 IDistributedCache<TCacheItem> ,泛型类型就是缓存值的类型,用于解决上面提到的问题:
该接口内部实现了对缓存对象 序列化/反序列化 的逻辑。 默认使用 JSON 序列化, 我们如果有需要可以替换 依赖注入 系统中 IDistributedCacheSerializer 服务的实现来覆盖默认的方式.
该接口会根据缓存中对象类型自动向缓存key添加 缓存名称 前缀。 默认缓存名是缓存对象的全类名(如果类名以CacheItem 结尾, 那么CacheItem 会被忽略,不应用到缓存名称上),开发人员也可以在缓存类上使用 CacheName 特性 设置缓存的名称. 。
如果是多租户应用的话,它会自动将当前的租户id添加到缓存键中, 以区分不同租户的缓存项 。 如果租户之间需要共享缓存对象, 我们可以在缓存类打上 IgnoreMultiTenancy 特性,声明当前缓存不区分组合.
允许为每个应用程序定义 全局缓存键前缀 , 不同的应用程序可以在共享的分布式缓存中拥有自己的隔离池. 。
它提供了 错误容忍 机制,对分布式缓存存取过程中的异常进行了处理,例如分布式缓存服务连接失败等,避免因缓存问题导致应用出错。 因为缓存本身就只是一种用于提升应用性能的策略,如果因为分布式缓存的问题导致应用出错,业务逻辑无法继续执行,那就得不偿失了。缓存系统应该是,就算将其从应用中摘除,也不影响应用业务逻辑正常执行的东西,只是性能可能差了点.
它额外提供了 GetManyAsync 和 SetManyAsync 等方法, 支持对缓存的批量操作,可以显著提高批处理的性能.
这里还是以控制台应用作为演示,Web 应用中使用比控制台更简单,因为 Web 应用中已经集成了缓存模块,不需要再自行引入。首先,通过以下命令生成一个 ABP 的控制台启动模板:
abp new AbpCacheSample -t console
之后,如果是使用基于内存的分布式缓存的话,只需要安装 Volo.Abp.Caching 包即可.
Install-package Volo.Abp.Caching
之后,在项目的模块文件中添加模块依赖
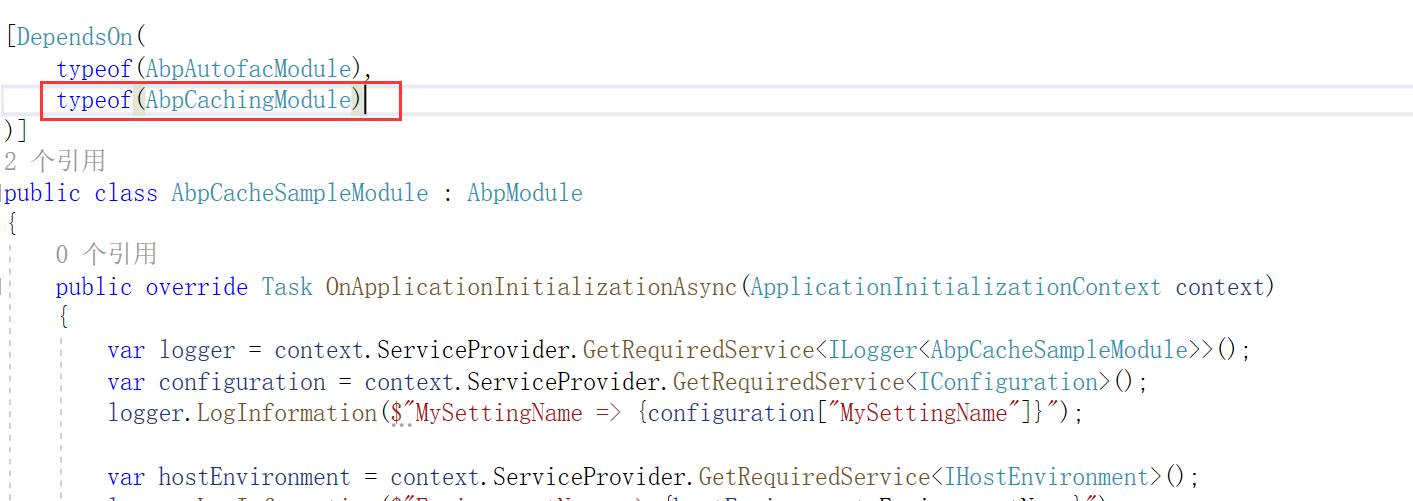
这里不需要再进行依赖关系的配置,因为在 AbpCacheModule模块的初始化之中已经配置好了相关的内容,通过源码可以看到:

当然,你也可以更高效地在项目所在的文件夹使用以下命令,省掉对模块依赖的配置.
abp add-package Volo.Abp.Caching
如果是使用 Redis 分布式缓存的话,需要安装 Volo.Abp.Caching.StackExchangeRedis 集成包,这个包对 Microsoft.Extensions.Caching.StackExchangeRedis 进行了扩展,它简化了 Redis 缓存的配置,也是前面提到的 GetManyAsync 和SetManyAsync 等更加性能的方法的实现所在.
install-package Volo.Abp.Caching.StackExchangeRedis
同时,模块依赖改成以下这样:
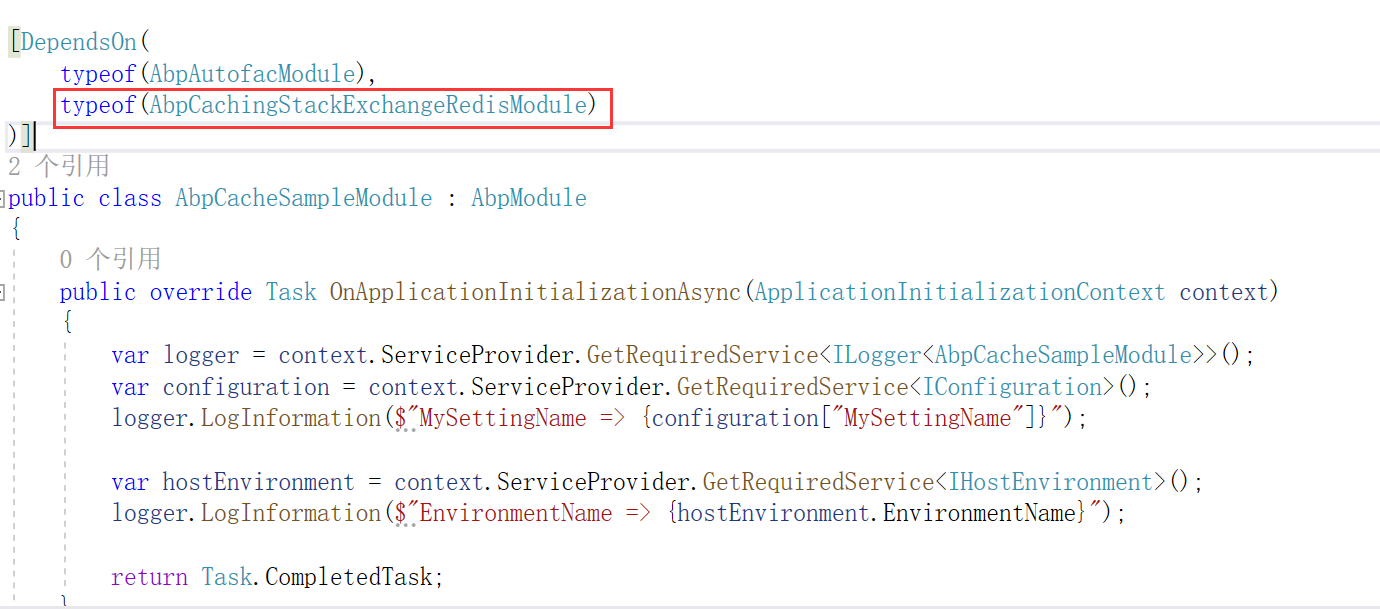
同样的,模块初始化的时候也已经配置好 Redis 缓存使用的内容:

通过源码我们也可以看到,Redis 相应的配置是从配置文件中的 "Redis" 节点读取的,我们可以在appsettings.json 中添加以下内容启用 Redis 缓存:
{
"Redis": {
"IsEnabed": true, // 控制 Redis 分布式缓存是否启用
"Configuration": "xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:6379,password=123456" // Redis 连接字符串
}
}
这里其实就是通过配置信息中的 "Redis:Configuration" 节点配置 RedisCacheOpions 选项,这个选项是微软标准的 Redi s缓存支持包中的,如果有需要,我们可以在代码中通过以下方式对该选项进行配置:
[DependsOn(
typeof(AbpAutofacModule),
typeof(AbpCachingStackExchangeRedisModule)
)]
public class AbpCacheSampleModule : AbpModule
{
public override void ConfigureServices(ServiceConfigurationContext context)
{
Configure<RedisCacheOptions>(option =>
{
// ...
});
}
}
首先我们定义缓存类:
/// <summary>
/// 缓存中,会以缓存类的全类名作为建,如果类名以 CacheItem 结尾,CacheItem 会被忽略
/// </summary>
// [CacheName("DateTime")] 也可以通过 CacheName 特性设置缓存键
public class DateTimeCacheItem
{
public DateTime Now { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
之后,只需要在要用到的服务中注入 IDistributedCache 泛型接口即可:
public class HelloWorldService : ITransientDependency
{
public const string CacheKey = nameof(HelloWorldService);
private readonly IDistributedCache<DateTimeCacheItem> _distributedCache;
public HelloWorldService(IDistributedCache<DateTimeCacheItem> distributedCache)
{
_distributedCache = distributedCache;
}
public async Task SayHelloAsync()
{
// 常规的 IDisctributedCache 的同名方法,不过 ABP 框架中进行了扩展
// 使其支持泛型,可以直接存取对象
//var cacheValue = await _distributedCache.GetAsync(CacheKey);
//if (cacheValue == null)
//{
// cacheValue = new DateTimeCacheItem
// {
// Name = CacheKey,
// Now = DateTime.Now,
// };
// await _distributedCache.SetAsync(
// CacheKey, // 缓存键,最终的键会是 缓存名称(缓存类全类名去除CacheItem,或CacheName特性设置的名称) + 这里的键
// cacheValue, // 直接存取对象,而不用自己序列化/反序列化 以及转码
// new DistributedCacheEntryOptions // 一样可以通过选项设置缓存策略
// {
// SlidingExpiration = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(1)
// });
//}
// ABP 框架新增的方法
var cacheValue = await _distributedCache.GetOrAddAsync(
CacheKey,
async () =>
{
return await Task.FromResult(new DateTimeCacheItem()
{
Name = CacheKey,
Now = DateTime.Now
});
},
() => new DistributedCacheEntryOptions
{
SlidingExpiration= TimeSpan.FromMinutes(1)
});
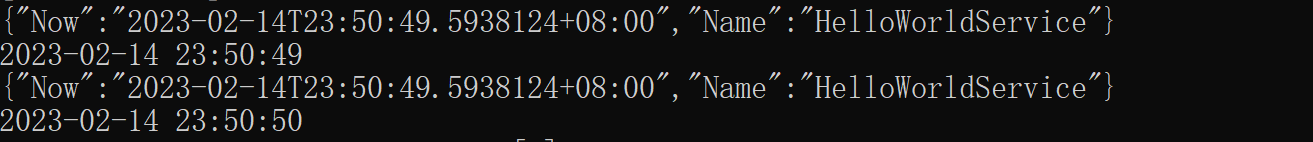
Console.WriteLine(JsonSerializer.Serialize(cacheValue));
Console.WriteLine(DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
}
}
除了可以使用 string 类型作为缓存键之外,我们还可以通过 IDistributedCache<CacheKey, CacheItem> 接口使用其他类型,甚至复杂类型作为缓存键,使用复杂类型作为缓存键的时候需要重写 ToString() 方法.
public class MyCacheKey
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public override string ToString()
{
return Id + Name;
}
}
public class HelloWorldService : ITransientDependency
{
private readonly IDistributedCache<DateTimeCacheItem, int> _distributedCacheKeyInt;
private readonly IDistributedCache<DateTimeCacheItem, MyCacheKey> _distiributedCacheKey;
public HelloWorldService(
IDistributedCache<DateTimeCacheItem, int> distributedCacheKeyInt,
IDistributedCache<DateTimeCacheItem, MyCacheKey> distiributedCacheKey)
{
_distributedCache = distributedCache;
}
public async Task SayHelloAsync()
{
_ = await _distributedCacheKeyInt.GetOrAddAsync(
1,
async () =>
{
return await Task.FromResult(new DateTimeCacheItem
{
Name = "1",
Now = DateTime.Now
});
},
() => new DistributedCacheEntryOptions { SlidingExpiration = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(10) }
);
_ = await _distiributedCacheKey.GetOrAddAsync(
new MyCacheKey { Id = 1, Name = "MyKey" },
async () =>
{
return await Task.FromResult(new DateTimeCacheItem
{
Name = "1",
Now = DateTime.Now
});
},
() => new DistributedCacheEntryOptions { SlidingExpiration = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(10) }
);
}
}
批量进行缓存存取操作的方式如下:
_ = await _distributedCache.GetOrAddManyAsync(new List<string> { "Key1", "Key2" }, async keys =>
{
return await Task.FromResult(
keys.Select(k => new KeyValuePair<string, DateTimeCacheItem>(k, new DateTimeCacheItem { Name = k, Now = DateTime.Now }))
.ToList()
);
},
() => new DistributedCacheEntryOptions { SlidingExpiration = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(10) });
ABP的分布式缓存接口定义了以下批量操作方法,当你需要在一个方法中调用多次缓存操作时,这些方法可以提高性能 。
这些不是标准的ASP.NET Core缓存方法, 所以其他的分布式缓存方案可能不支持。而 ABP 通过 Volo.Abp.Caching.StackExchangeRedis 实现了 Redis 分布式缓存下的批量操作。如果采用了其他方案实现分布式缓存,而提供程序不支持的情况下,会回退到循环调用 SetAsync 和 GetAsync 方法.
以上就是 ABP 框架中缓存系统的基本使用。除此之外,ABP 框架提供了 AbpDistributedCacheOptions 选项用于配置一些缓存策略,可用属性:
另外,还有ABP 框架下的缓存系统还有以下一些功能:
错误处理 。
当为你的对象设计缓存时, 通常会首先尝试从缓存中获取值. 如果在缓存中找不到该值, 则从来源查询对象. 它可能在数据库中, 或者可能需要通过HTTP调用远程服务器. 。
在大多数情况下, 你希望容忍缓存错误; 如果缓存服务器出现错误, 也不希望取消该操作. 相反, 你可以默默地隐藏(并记录)错误并从来源查询. 这就是ABP框架默认的功能. 。
ABP的分布式缓存异常处理, 默认记录并隐藏错误,有一个全局修改该功能的选项.所有的IDistributedCache (和 IDistributedCache<TCacheItem, TCacheKey>)方法都有一个可选的参数hideErrors, 默认值为null. 如果此参数设置为null, 则全局生效, 否则你可以选择单个方法调用时隐藏或者抛出异常. 。
工作单元级别的缓存 。
分布式缓存服务提供了一个有趣的功能. 假设你已经更新了数据库中某本书的价格, 然后将新价格设置到缓存中, 以便以后使用缓存的值. 如果设置缓存后出现异常, 并且更新图书价格的事务被回滚了, 该怎么办?在这种情况下, 缓存值是错误的. 。
IDistributedCache<..>方法提供一个可选参数, considerUow, 默认为false. 如果将其设置为true, 则你对缓存所做的更改不会应用于真正的缓存存储, 而是与当前的工作单元关联. 你将获得在同一工作单元中设置的缓存值, 但仅当前工作单元成功时更改才会生效. 。
可替换的键、值处理方式 。
IDistributedCacheSerializer 。
IDistributedCacheSerializer 服务用于序列化和反序列化缓存内容. 默认实现是 Utf8JsonDistributedCacheSerializer 类, 它使用 IJsonSerializer 服务将对象转换为 JSON, 反之亦然. 然后, 它使用 UTC8 编码将 JSON 字符串转换为分布式缓存接受的字节数组. 。
如果你想实现自己的序列化逻辑, 可以自己实现并替换此服务. 。
IDistributedCacheKeyNormalizer 。
默认情况下, IDistributedCacheKeyNormalizer是由DistributedCacheKeyNormalizer类实现的. 它将缓存名称、应用程序缓存前缀和当前租户id添加到缓存键中. 如果需要更高级的键规范化, 可以自己实现并替换此服务. 。
参考文章: ABP 官方文档 - 缓存 。
ABP 系列总结: 目录: ABP 系列总结 上一篇: ABP - 依赖注入(2) 。
最后此篇关于ABP-缓存模块(1)的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于ABP-缓存模块(1)的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我阅读了有关 JSR 107 缓存 (JCache) 的内容。 我很困惑:据我所知,每个 CPU 都管理其缓存内存(无需操作系统的任何帮助)。 那么,为什么我们需要 Java 缓存处理程序? (如果C
好吧,我是 jQuery 的新手。我一直在这里和那里搞乱一点点并习惯它。我终于明白了(它并不像某些人想象的那么难)。因此,鉴于此链接:http://jqueryui.com/sortable/#dis
我正在使用 Struts 2 和 Hibernate。我有一个简单的表,其中包含一个日期字段,用于存储有关何时发生特定操作的信息。这个日期值显示在我的 jsp 中。 我遇到的问题是hibernate更
我有点不确定这里发生了什么,但是我试图解释正在发生的事情,也许一旦我弄清楚我到底在问什么,就可能写一个更好的问题。 我刚刚安装了Varnish,对于我的请求时间来说似乎很棒。这是一个Magneto 2
解决 Project Euler 的问题后,我在论坛中发现了以下 Haskell 代码: fillRow115 minLength = cache where cache = ((map fill
我正试图找到一种方法来为我网络上的每台计算机缓存或存储某些 python 包。我看过以下解决方案: pypicache但它不再被积极开发,作者推荐 devpi,请参见此处:https://bitbuc
我想到的一个问题是可以从一开始就缓存网络套接字吗?在我的拓扑中,我在通过双 ISP 连接连接到互联网的 HAProxy 服务器后面有 2 个 Apache 服务器(带有 Google PageSpee
我很难说出不同缓存区域 (OS) 之间的区别。我想简要解释一下磁盘\缓冲区\交换\页面缓存。他们住在哪里?它们之间的主要区别是什么? 据我了解,页面缓存是主内存的一部分,用于存储从 I/O 设备获取的
1.题目 请你为最不经常使用(LFU)缓存算法设计并实现数据结构。 实现 LFUCache 类: LFUCache(int capacity) - 用数据结构的容量 capacity 初始化对象 in
1.题目 请你设计并实现一个满足 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存 约束的数据结构。 实现 LRUCache 类: ① LRUCache(int capacity) 以正整数作为容量 capacity
我想在访问该 View 时关闭某些页面的缓存。它适用于简单查询模型对象的页面。 好像什么时候 'django.middleware.cache.FetchFromCacheMiddleware', 启
documents为 ExePackage element state Cache属性的目的是 Whether to cache the package. The default is "yes".
我知道 docker 用图层存储每个图像。如果我在一台开发服务器上有多个用户,并且每个人都在运行相同的 Dockerfile,但将镜像存储为 user1_myapp . user2 将其存储为 use
在 Codeigniter 中没有出现缓存问题几年后,我发现了一个问题。我在其他地方看到过该问题,但没有适合我的解决方案。 例如,如果我在 View 中更改一些纯 html 文本并上传新文件并按 F5
我在 Janusgraph 文档中阅读了有关 Janusgraph Cache 的内容。关于事务缓存,我几乎没有怀疑。我在我的应用程序中使用嵌入式 janusgrah 服务器。 如果我只对例如进行读取
我想知道是否有来自终端的任何命令可以用来匹配 Android Studio 中执行文件>使缓存无效/重新启动的使用。 谢谢! 最佳答案 According to a JetBrains employe
我想制作一个 python 装饰器来内存函数。例如,如果 @memoization_decorator def add(a, b, negative=False): print "Com
我经常在 jQuery 事件处理程序中使用 $(this) 并且从不缓存它。如果我愿意的话 var $this = $(this); 并且将使用变量而不是构造函数,我的代码会获得任何显着的额外性能吗?
是的,我要说实话,我不知道varnish vcl,我可以解决一些基本问题,但是我不太清楚,这就是为什么我遇到问题了。 我正在尝试通过http请求设置缓存禁止,但是该请求不能通过DNS而是通过 Varn
在 WP 站点上加载约 4000 个并发用户时遇到此问题。 这是我的配置: F5 负载均衡器 ---> Varnish 4,8 核,32 Gb RAM ---> 9 个后端,4 个核,每个 16 RA

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!