- Java锁的逻辑(结合对象头和ObjectMonitor)
- 还在用饼状图?来瞧瞧这些炫酷的百分比可视化新图形(附代码实现)⛵
- 自动注册实体类到EntityFrameworkCore上下文,并适配ABP及ABPVNext
- 基于Sklearn机器学习代码实战
这几天又在玩树莓派,先是搞了个物联网,又在尝试在树莓派上搞一些简单的神经网络,这次搞得是卷积识别mnist手写数字识别 。
训练代码在电脑上,cpu就能训练,很快的:
import
torch
import
torch.nn as nn
import
torch.optim as optim
from
torchvision
import
datasets, transforms
import
numpy as np
#
设置随机种子
torch.manual_seed(42
)
#
定义数据预处理
transform =
transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
#
transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))
])
#
加载训练数据集
train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(
'
data
'
, train=True, download=True, transform=
transform)
train_loader
= torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=64, shuffle=
True)
#
构建卷积神经网络模型
class
Net(nn.Module):
def
__init__
(self):
super(Net, self).
__init__
()
self.conv1
= nn.Conv2d(1, 10, kernel_size=5
)
self.pool
= nn.MaxPool2d(2
)
self.fc
= nn.Linear(10 * 12 * 12, 10
)
def
forward(self, x):
x
=
self.pool(torch.relu(self.conv1(x)))
x
= x.view(-1, 10 * 12 * 12
)
x
=
self.fc(x)
return
x
model
=
Net()
#
定义损失函数和优化器
criterion =
nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer
= optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01, momentum=0.5
)
#
训练模型
def
train(model, device, train_loader, optimizer, criterion, epochs):
model.train()
for
epoch
in
range(epochs):
for
batch_idx, (data, target)
in
enumerate(train_loader):
data, target
=
data.to(device), target.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
output
=
model(data)
loss
=
criterion(output, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if
batch_idx % 100 ==
0:
print
(f
'
Train Epoch: {epoch+1} [{batch_idx * len(data)}/{len(train_loader.dataset)}
'
f
'
({100. * batch_idx / len(train_loader):.0f}%)]\tLoss: {loss.item():.6f}
'
)
#
在GPU上训练(如果可用),否则使用CPU
device = torch.device(
"
cuda
"
if
torch.cuda.is_available()
else
"
cpu
"
)
model.to(device)
#
训练模型
train(model, device, train_loader, optimizer, criterion, epochs=5
)
#
保存模型为NumPy数据
model_state =
model.state_dict()
numpy_model_state
= {key: value.cpu().numpy()
for
key, value
in
model_state.items()}
np.savez(
'
model.npz
'
, **
numpy_model_state)
print
(
"
Model saved as model.npz
"
)
然后需要自己在dataset里导出一些图片:我保存在了mnist_pi文件夹下,“_”后面的是标签,主要是在pc端导出保存到树莓派下 。
树莓派推理端的代码,需要numpy手动重新搭建网络,并且需要手动实现conv2d卷积神经网络和maxpool2d最大池化,然后加载那些保存的矩阵参数,做矩阵乘法和加法 。
import
numpy as np
import
os
from
PIL
import
Image
def
conv2d(input, weight, bias, stride=1, padding=
0):
batch_size, in_channels, in_height, in_width
=
input.shape
out_channels, in_channels, kernel_size, _
=
weight.shape
#
计算输出特征图的大小
out_height = (in_height + 2 * padding - kernel_size) // stride + 1
out_width
= (in_width + 2 * padding - kernel_size) // stride + 1
#
添加padding
padded_input = np.pad(input, ((0, 0), (0, 0), (padding, padding), (padding, padding)), mode=
'
constant
'
)
#
初始化输出特征图
output =
np.zeros((batch_size, out_channels, out_height, out_width))
#
执行卷积操作
for
b
in
range(batch_size):
for
c_out
in
range(out_channels):
for
h_out
in
range(out_height):
for
w_out
in
range(out_width):
h_start
= h_out *
stride
h_end
= h_start +
kernel_size
w_start
= w_out *
stride
w_end
= w_start +
kernel_size
#
提取对应位置的输入图像区域
input_region =
padded_input[b, :, h_start:h_end, w_start:w_end]
#
计算卷积结果
x = input_region *
weight[c_out]
bia
=
bias[c_out]
conv_result
= np.sum(x, axis=(0,1, 2)) +
bia
#
将卷积结果存储到输出特征图中
output[b, c_out, h_out, w_out] =
conv_result
return
output
def
max_pool2d(input, kernel_size, stride=None, padding=
0):
batch_size, channels, in_height, in_width
=
input.shape
if
stride
is
None:
stride
=
kernel_size
out_height
= (in_height - kernel_size + 2 * padding) // stride + 1
out_width
= (in_width - kernel_size + 2 * padding) // stride + 1
padded_input
= np.pad(input, ((0, 0), (0, 0), (padding, padding), (padding, padding)), mode=
'
constant
'
)
output
=
np.zeros((batch_size, channels, out_height, out_width))
for
b
in
range(batch_size):
for
c
in
range(channels):
for
h_out
in
range(out_height):
for
w_out
in
range(out_width):
h_start
= h_out *
stride
h_end
= h_start +
kernel_size
w_start
= w_out *
stride
w_end
= w_start +
kernel_size
input_region
=
padded_input[b, c, h_start:h_end, w_start:w_end]
output[b, c, h_out, w_out]
=
np.max(input_region)
return
output
#
加载保存的模型数据
model_data = np.load(
'
model.npz
'
)
#
提取模型参数
conv_weight = model_data[
'
conv1.weight
'
]
conv_bias
= model_data[
'
conv1.bias
'
]
fc_weight
= model_data[
'
fc.weight
'
]
fc_bias
= model_data[
'
fc.bias
'
]
#
进行推理
def
inference(images):
#
执行卷积操作
conv_output = conv2d(images, conv_weight, conv_bias, stride=1, padding=
0)
conv_output
= np.maximum(conv_output, 0)
#
ReLU激活函数
#
maxpool2d
pool = max_pool2d(conv_output,2
)
#
执行全连接操作
flattened = pool.reshape(pool.shape[0], -1
)
fc_output
= np.dot(flattened, fc_weight.T) +
fc_bias
fc_output
= np.maximum(fc_output, 0)
#
ReLU激活函数
#
获取预测结果
predictions = np.argmax(fc_output, axis=1
)
return
predictions
folder_path
=
'
./mnist_pi
'
#
替换为图片所在的文件夹路径
def
infer_images_in_folder(folder_path):
for
file_name
in
os.listdir(folder_path):
file_path
=
os.path.join(folder_path, file_name)
if
os.path.isfile(file_path)
and
file_name.endswith((
'
.jpg
'
,
'
.jpeg
'
,
'
.png
'
)):
image
=
Image.open(file_path)
label
= file_name.split(
"
.
"
)[0].split(
"
_
"
)[1
]
image
= np.array(image)/255.0
image
= np.expand_dims(image,axis=
0)
image
= np.expand_dims(image,axis=
0)
print
(
"
file_path:
"
,file_path,
"
img size:
"
,image.shape,
"
label:
"
,label)
predicted_class
=
inference(image)
print
(
'
Predicted class:
'
, predicted_class)
infer_images_in_folder(folder_path)
。
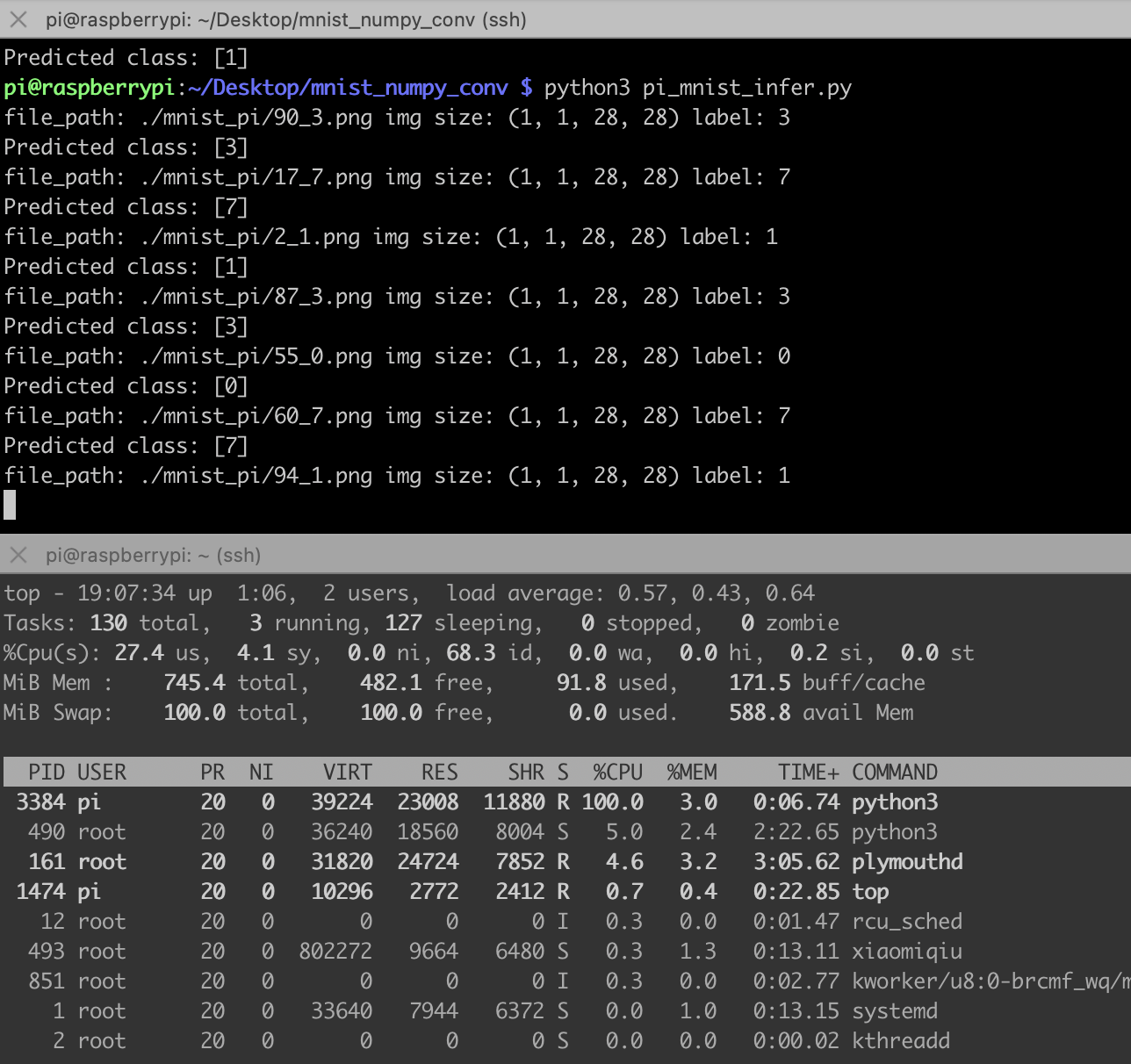
这代码完全就是numpy推理,不需要安装pytorch,树莓派也装不动pytorch,太重了,下面是推理结果,比之前的MLP网络慢很多,主要是手动实现的卷积网络全靠循环实现.
那我们给它加加速吧,下面是一个多线程加速程序:
import
numpy as np
import
os
from
PIL
import
Image
from
multiprocessing
import
Pool
def
conv2d(input, weight, bias, stride=1, padding=
0):
batch_size, in_channels, in_height, in_width
=
input.shape
out_channels, in_channels, kernel_size, _
=
weight.shape
#
计算输出特征图的大小
out_height = (in_height + 2 * padding - kernel_size) // stride + 1
out_width
= (in_width + 2 * padding - kernel_size) // stride + 1
#
添加padding
padded_input = np.pad(input, ((0, 0), (0, 0), (padding, padding), (padding, padding)), mode=
'
constant
'
)
#
初始化输出特征图
output =
np.zeros((batch_size, out_channels, out_height, out_width))
#
执行卷积操作
for
b
in
range(batch_size):
for
c_out
in
range(out_channels):
for
h_out
in
range(out_height):
for
w_out
in
range(out_width):
h_start
= h_out *
stride
h_end
= h_start +
kernel_size
w_start
= w_out *
stride
w_end
= w_start +
kernel_size
#
提取对应位置的输入图像区域
input_region =
padded_input[b, :, h_start:h_end, w_start:w_end]
#
计算卷积结果
x = input_region *
weight[c_out]
bia
=
bias[c_out]
conv_result
= np.sum(x, axis=(0,1, 2)) +
bia
#
将卷积结果存储到输出特征图中
output[b, c_out, h_out, w_out] =
conv_result
return
output
def
max_pool2d(input, kernel_size, stride=None, padding=
0):
batch_size, channels, in_height, in_width
=
input.shape
if
stride
is
None:
stride
=
kernel_size
out_height
= (in_height - kernel_size + 2 * padding) // stride + 1
out_width
= (in_width - kernel_size + 2 * padding) // stride + 1
padded_input
= np.pad(input, ((0, 0), (0, 0), (padding, padding), (padding, padding)), mode=
'
constant
'
)
output
=
np.zeros((batch_size, channels, out_height, out_width))
for
b
in
range(batch_size):
for
c
in
range(channels):
for
h_out
in
range(out_height):
for
w_out
in
range(out_width):
h_start
= h_out *
stride
h_end
= h_start +
kernel_size
w_start
= w_out *
stride
w_end
= w_start +
kernel_size
input_region
=
padded_input[b, c, h_start:h_end, w_start:w_end]
output[b, c, h_out, w_out]
=
np.max(input_region)
return
output
#
加载保存的模型数据
model_data = np.load(
'
model.npz
'
)
#
提取模型参数
conv_weight = model_data[
'
conv1.weight
'
]
conv_bias
= model_data[
'
conv1.bias
'
]
fc_weight
= model_data[
'
fc.weight
'
]
fc_bias
= model_data[
'
fc.bias
'
]
#
进行推理
def
inference(images):
#
执行卷积操作
conv_output = conv2d(images, conv_weight, conv_bias, stride=1, padding=
0)
conv_output
= np.maximum(conv_output, 0)
#
ReLU激活函数
#
maxpool2d
pool = max_pool2d(conv_output, 2
)
#
执行全连接操作
flattened = pool.reshape(pool.shape[0], -1
)
fc_output
= np.dot(flattened, fc_weight.T) +
fc_bias
fc_output
= np.maximum(fc_output, 0)
#
ReLU激活函数
#
获取预测结果
predictions = np.argmax(fc_output, axis=1
)
return
predictions
labels
=
[]
preds
=
[]
def
infer_image(file_path):
image
=
Image.open(file_path)
label
= file_path.split(
"
/
"
)[-1].split(
"
.
"
)[0].split(
"
_
"
)[1
]
image
= np.array(image) / 255.0
image
= np.expand_dims(image, axis=
0)
image
= np.expand_dims(image, axis=
0)
print
(
"
file_path:
"
, file_path,
"
img size:
"
, image.shape,
"
label:
"
, label)
predicted_class
=
inference(image)
print
(
'
Predicted class:
'
, predicted_class)
folder_path
=
'
./mnist_pi
'
#
替换为图片所在的文件夹路径
pool = Pool(processes=4)
#
设置进程数为2,可以根据需要进行调整
def
infer_images_in_folder(folder_path):
for
file_name
in
os.listdir(folder_path):
file_path
=
os.path.join(folder_path, file_name)
if
os.path.isfile(file_path)
and
file_name.endswith((
'
.jpg
'
,
'
.jpeg
'
,
'
.png
'
)):
pool.apply_async(infer_image, args
=
(file_path,))
pool.close()
pool.join()
infer_images_in_folder(folder_path)
。
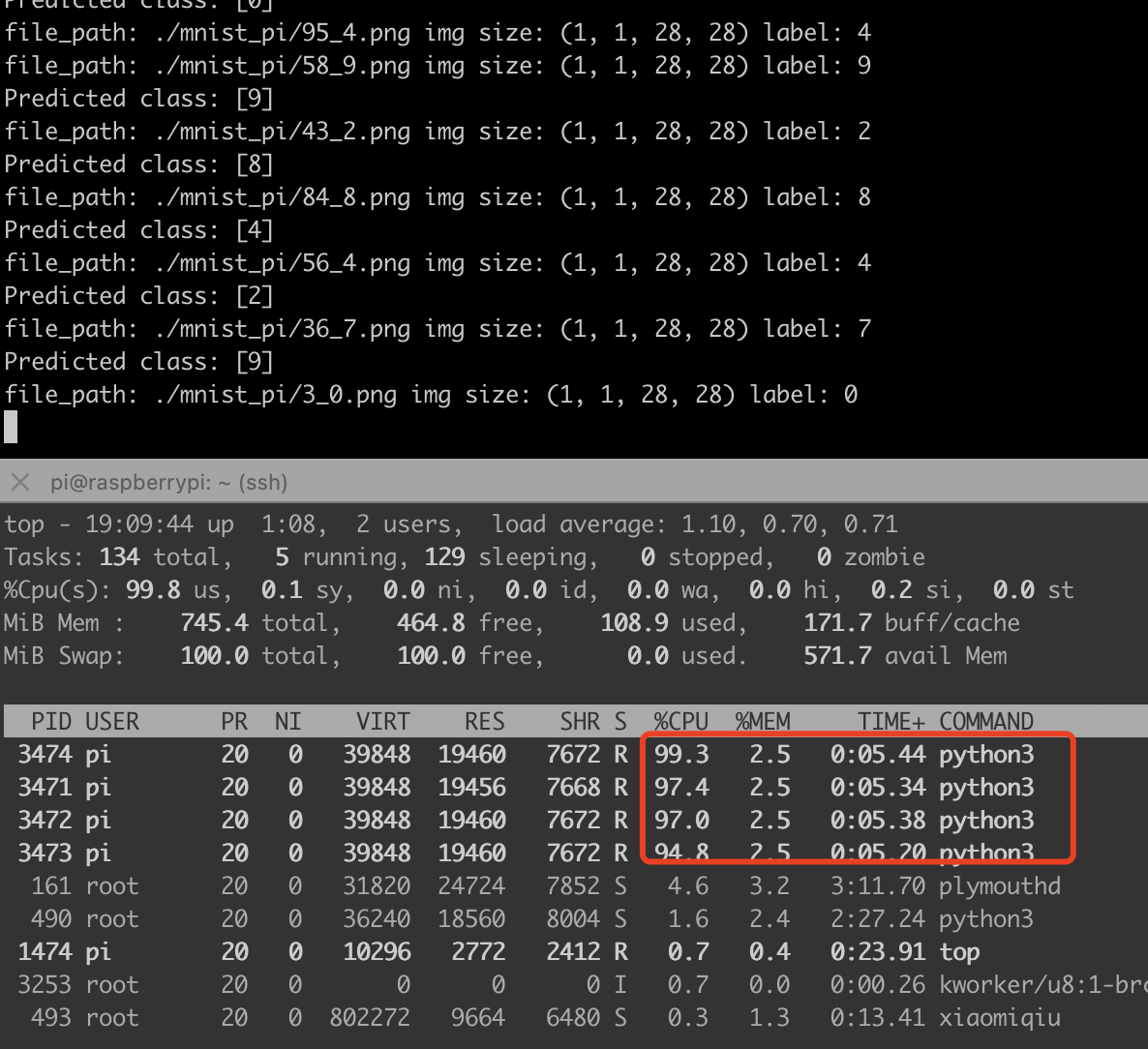
下图可以看出来,我的树莓派3b+,cpu直接拉满,速度提升4倍:
。
最后此篇关于在树莓派上实现numpy的conv2d卷积神经网络做图像分类,加载pytorch的模型参数,推理mnist手写数字识别,并使用多进程加速的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于在树莓派上实现numpy的conv2d卷积神经网络做图像分类,加载pytorch的模型参数,推理mnist手写数字识别,并使用多进程加速的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我正在尝试构建不同(但每个同质)类型的可遍历项的多个交叉产品。所需的返回类型是元组的可遍历对象,其类型与输入可遍历对象中的类型相匹配。例如: List(1, 2, 3) cross Seq("a",
import java.util.Scanner; public class BooleanProduct { public static void main(String[] args) {
任务 - 数字的最大 K 积 时间限制:1 内存限制:64 M 给定一个整数序列 N(1 ≤ N ≤ 10 月,| A i | ≤ 2.10 9)和数量 K(1 ≤ K ≤ N)。找出乘积最大的 K
考虑一个大小为 48x16 的 float 矩阵 A 和一个大小为 1x48 的 float vector b。 请建议一种在常见桌面处理器 (i5/i7) 上尽可能快地计算 b×A 的方法。 背景。
假设我有一个 class Rectangle(object): def __init__(self, len
设 A 为 3x3 阶矩阵。判断矩阵A的 boolean 积可以组成多少个不同的矩阵。 这是我想出的: #include int main() { int matri
背景 生成随机权重列表后: sizes = [784,30,10] weights = [np.random.randn(y, x) for x, y in zip(sizes[:-1],sizes[
我正在开发一个 python 项目并使用 numpy。我经常需要通过单位矩阵计算矩阵的克罗内克积。这些是我代码中的一个相当大的瓶颈,所以我想优化它们。我必须服用两种产品。第一个是: np.kron(n
有人可以提供一个例子说明如何使用 uBLAS 产品来乘法吗?或者,如果有更好的 C++ 矩阵库,您可以推荐我也欢迎。这正在变成一个令人头疼的问题。 这是我的代码: vector myVec(scala
我正在尝试开发一个Javascript程序,它会提示用户输入两个整数,然后显示这两个整数的和、乘积、差和商。现在它只显示总和。我实际上不知道乘法、减法和除法命令是否正在执行。这是 jsfiddle 的
如何使用 la4j 计算 vector (叉)积? vector 乘积为 接受两个 vector 并返回 vector 。 但是他们有scalar product , product of all e
在 C++ 中使用 Lapack 让我有点头疼。我发现为 fortran 定义的函数有点古怪,所以我尝试在 C++ 上创建一些函数,以便我更容易阅读正在发生的事情。 无论如何,我没有让矩阵 vecto
是否可以使用 Apple 的 Metal Performance Shaders 执行 Hadamard 产品?我看到可以使用 this 执行普通矩阵乘法,但我特别在寻找逐元素乘法,或者一种构造乘法的
我正在尝试使用 open mp 加速稀疏矩阵 vector 乘积,代码如下: void zAx(double * z, double * data, long * colind, long * row
有没有一种方法可以使用 cv::Mat OpenCV 中的数据结构? 我检查过 the documentation并且没有内置功能。但是我在尝试将标准矩阵乘法表达式 (*) 与 cv::Mat 类型的

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!