- Java锁的逻辑(结合对象头和ObjectMonitor)
- 还在用饼状图?来瞧瞧这些炫酷的百分比可视化新图形(附代码实现)⛵
- 自动注册实体类到EntityFrameworkCore上下文,并适配ABP及ABPVNext
- 基于Sklearn机器学习代码实战
begin 2023年04月15日16:49:35 。
本科软件工程专业有这么一门课叫《编译原理》,课程内容已经忘了七七八八,但尤为清楚的是上机大作业是拷贝的,课程分数92.
Given a language, define a representation for its grammar along with an interpreter that uses the representation to interpret sentences in the language. 。
给定一个语言,定义其语法的表示以及一个用该表示来解释该语言中的句子的解释器。——《设计模式:可复用面向对象软件的基础》 。
解释器模式是一种行为型设计模式.
Use the Interpreter pattern when there is a language to interpret, and you can represent statements in the language as abstract syntax trees.The Interpreter pattern works best when 。
the grammar is simple. For complex grammars, the class hierarchy for the grammar becomes large and unmanageable. Tools such as parser generators are a better alternative in such cases. They can interpret expressions without building abstract syntax trees, which can saves pace and possibly time. 。
efficiency is not a critical concern. The most efficient interpreters are usually not implemented by interpreting parse trees directly but by first translating them into another form. For example, regular expressions are often transformed into state machines. But even then,the translator can be implemented by the Interpreter pattern, so the pattern is still applicable. 。
当有语言要解释时,请使用解释器模式,您可以将语言中的语句表示为抽象语法树。解释器模式在以下情况下效果最佳:
解释器模式结构图
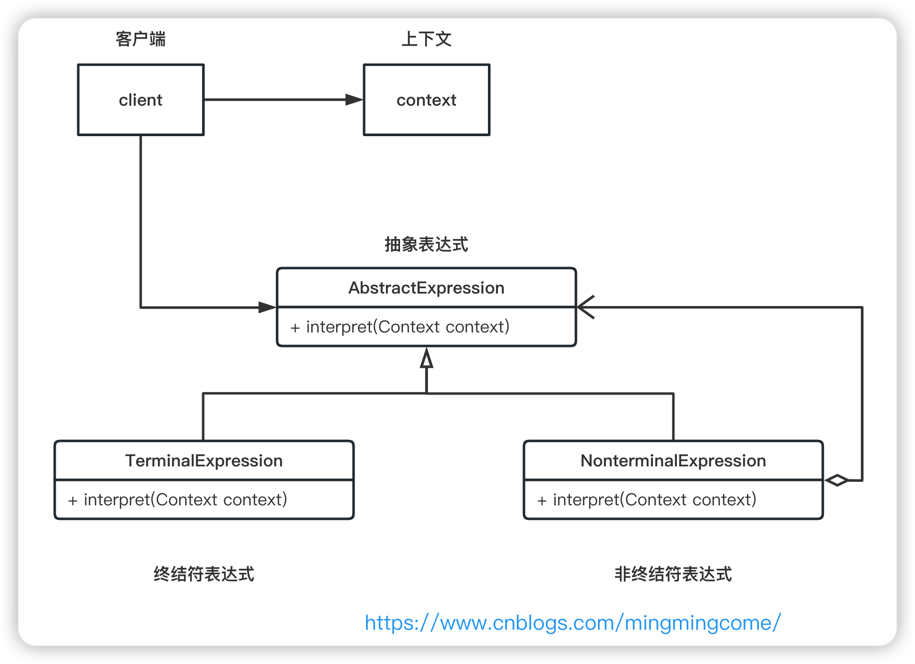
抽象表达式(AbstractExpression):
终结符表达式(TerminalExpression):
非终结符表达式(NonterminalExpression):
上下文(Context):
客户端(Client):
实现一个简单函数绘图语言解释器,解释下面代码:
rot is 0;
origin is (0, 0);
scale is (2,20);
for T from 1 to 300 step 1 draw (t,-ln(t));
scale is (20,0.1);
for T from 0 to 8 step 0.1 draw (t,exp(t));
scale is (2,1);
for T from 0 to 300 step 1 draw (t,0);
for T from 0 to 300 step 1 draw (0,t);
for T from 0 to 120 step 1 draw (t,t);
scale is (2,0.1);
for T from 0 to 55 step 1 draw (t,-(t*t));
scale is (10,5);
for T from 0 to 60 step 1 draw (t,sqrt(t));
当然,我们的解释器还需要具备识别注释、出错处理等基本功能,下面是我实现过程中遵循的一些小的原则:
解释器模式常用于对简单语言的编译或分析实例中,为了掌握好它的结构与实现,必须先了解编译原理中的“文法、句子、语法树”等相关概念.
文法是用于描述语言的语法结构的形式规则。如: rot is 0;origin is (0, 0);scale is (2,20); 用文法表示:
<句子> -> <主语><谓语><表语>
<主语> -> <代词> | <名词>
<谓语> -> <动词>
<表语> -> <名词> | <形容词>
<名词> -> rot|origin|scale
<动词> -> is
<形容词> -> 0|(0,0)|(2,20)
注:这里的符号"->"表示“定义为”的意思,用"<"和">"括住的是非终结符,没有括住的是终结符。
句子是语言的基本单位,是语言集中的一个元素,它由终结符构成,能由“文法”推导出.
如,上面的文法可以推导出 rot is 0;origin is (0, 0);scale is (2,20); ,所以这些都是句子.
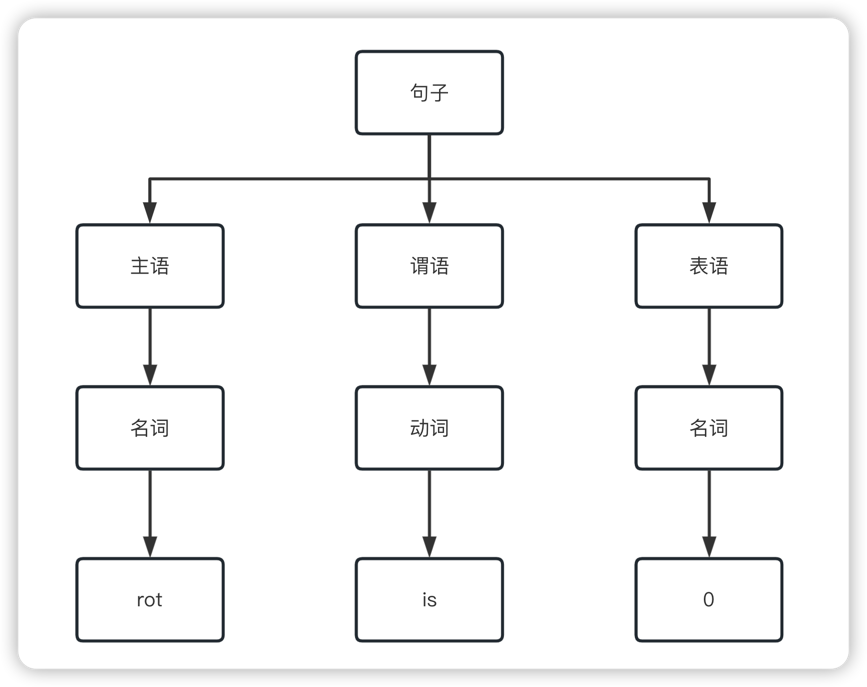
语法树是句子结构的一种树型表示,它代表了句子的推导结果,它有利于理解句子语法结构的层次.
rot is 0; 的语法树如下:
本代码示例代码相对于本文来说过于冗长,下面带有有所省略,有兴趣请参考我的github: interpreter .
代码示例主要流程:
抽象表达式:
// 语法
public interface Grammar {
void interpret(Parser parser);
}
终结符表达式:
// 终结符类型
public enum TokenType {
ROT, IS, ORIGIN, SCALE, FOR, FROM, TO, STEP, DRAW, // 保留字
T, // 参数
SEMICOLON, COMMA, LEFT_BRACKET, RIGHT_BRACKET, // 分隔符
EOF, // 文件结束符
PLUS, MINUS, MUL, DIV, // 运算符
LN, EXP, SQRT, SIN, COS, POWER, // 函数
NUMBER // 数字
}
// 具体终结符
public class Token implements Grammar {
public static final Map<String, Token> TOKEN_MAP;
static {
Map<String, Token> tokenMap = new HashMap<>();
tokenMap.put("ROT", new Token(TokenType.ROT, "ROT"));
tokenMap.put("IS", new Token(TokenType.IS, "IS"));
tokenMap.put("ORIGIN", new Token(TokenType.ORIGIN, "ORIGIN"));
tokenMap.put("SCALE", new Token(TokenType.SCALE, "SCALE"));
tokenMap.put("FOR", new Token(TokenType.FOR, "FOR"));
tokenMap.put("FROM", new Token(TokenType.FROM, "FROM"));
tokenMap.put("TO", new Token(TokenType.TO, "TO"));
tokenMap.put("STEP", new Token(TokenType.STEP, "STEP"));
tokenMap.put("DRAW", new Token(TokenType.DRAW, "DRAW"));
tokenMap.put(";", new Token(TokenType.SEMICOLON, ";"));
tokenMap.put("(", new Token(TokenType.LEFT_BRACKET, "("));
tokenMap.put(")", new Token(TokenType.RIGHT_BRACKET, ")"));
tokenMap.put(",", new Token(TokenType.COMMA, ","));
tokenMap.put("NUMBER", new Token(TokenType.NUMBER, null));
tokenMap.put("EOF", new Token(TokenType.EOF, null));
tokenMap.put("T", new Token(TokenType.T, "T"));
tokenMap.put("+", new Token(TokenType.PLUS, "+"));
tokenMap.put("-", new Token(TokenType.MINUS, "-"));
tokenMap.put("*", new Token(TokenType.MUL, "*"));
tokenMap.put("/", new Token(TokenType.DIV, "/"));
tokenMap.put("LN", new Token(TokenType.LN, null));
tokenMap.put("EXP", new Token(TokenType.EXP, null));
tokenMap.put("SQRT", new Token(TokenType.SQRT, null));
tokenMap.put("SIN", new Token(TokenType.SIN, null));
tokenMap.put("COS", new Token(TokenType.COS, null));
tokenMap.put("^", new Token(TokenType.POWER, null));
TOKEN_MAP = tokenMap;
}
private TokenType type;
private Object value;
public Token(TokenType type, Object value) {
this.type = type;
this.value = value;
}
public TokenType getType() {
return type;
}
public Object getValue() {
return value;
}
public Token setValue(Object value) {
this.value = value;
return this;
}
@Override
public void interpret(Parser parser) {
// do nothing
}
}
非终结符表达式(部分代码省略):
// 非终结符
// 旋转语句
public class RotateStatement implements Grammar {
@Override
public void interpret(Parser parser) {
/**
* 解释ROT IS NUMBER,即旋转角度,将角度存入上下文中,供后续语句使用。
* 语法分析:先识别ROT,然后再识别IS,最后识别NUMBER。
**/
parser.matchToken(TokenType.ROT);
parser.matchToken(TokenType.IS);
parser.setRot((Double) parser.getCurrentToken().getValue());
parser.matchToken(TokenType.NUMBER);
parser.matchToken(TokenType.SEMICOLON);
}
}
上下文(部分代码已省略):
// 解释器
public class Parser {
// 语法规则
private Lexer lexer;
// 当前token
private Token currentToken;
// 输出
private String output;
// 旋转角度
private double rot;
// 原点坐标
private double originX;
private double originY;
// 缩放比例
private double scaleX;
private double scaleY;
private double from;
private double to;
private double step;
private ExprNode xNode;
private ExprNode yNode;
// 语句解释映射
private Map<TokenType, Grammar> statementMap;
public Parser(Lexer lexer) {
this.lexer = lexer;
this.output = "";
this.rot = 0;
this.originX = 0;
this.originY = 0;
this.scaleX = 1;
this.scaleY = 1;
statementMap = new HashMap<>();
statementMap.put(TokenType.ROT, new RotateStatement());
statementMap.put(TokenType.ORIGIN, new OriginStatement());
statementMap.put(TokenType.SCALE, new ScaleStatement());
statementMap.put(TokenType.FOR, new ForStatement());
}
}
//
客户端:
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Semantic semantic = new Semantic();
semantic.analyze();
}
}
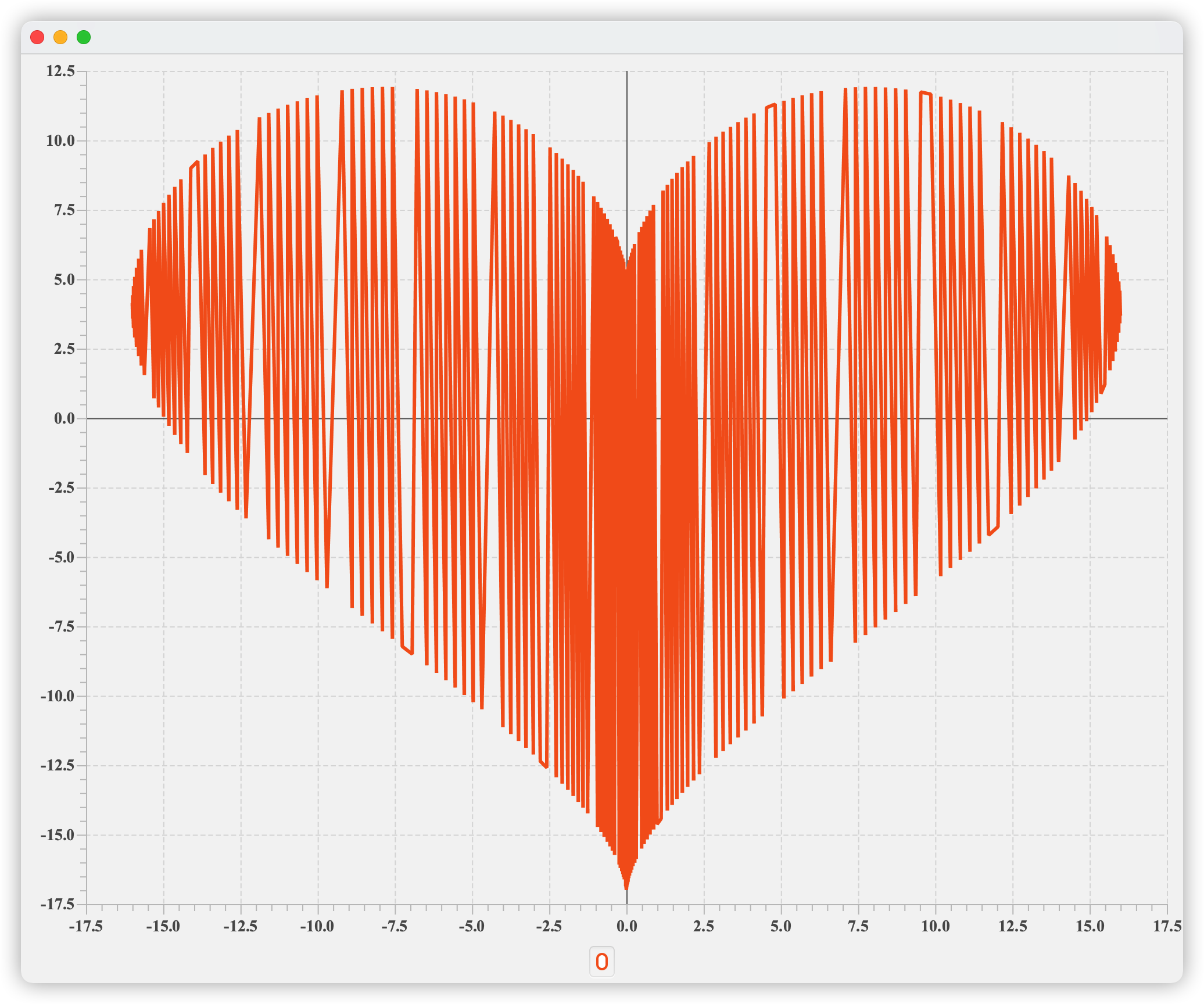
解释器执行结果:
因为写画图代码的时间正值520,所以随手查找了心形坐标函数,执行结果如下,祝天下所有有情人终成眷属.
当你需要解释某种语言,无论这种语句是否通用,也许只有你自己能解释,并且该语言能表示为语法树,有不会太复杂,可以使用解释器模式.
函数绘图语言解释器 。
解释器模式 。
2023年05月21日17:32:23 。
最后此篇关于解释器模式的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于解释器模式的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
对此感到疯狂,真的缺少一些东西。 我有webpack 4.6.0,webpack-cli ^ 2.1.2,所以是最新的。 在文档(https://webpack.js.org/concepts/mod
object Host "os.google.com" { import "windows" address = "linux.google.com" groups = ["linux"] } obj
每当我安装我的应用程序时,我都可以将数据库从 Assets 文件夹复制到 /data/data/packagename/databases/ .到此为止,应用程序工作得很好。 但 10 或 15 秒后
我在 cc 模式缓冲区中使用 hideshow.el 来折叠我不查看的文件部分。 如果能够在 XML 文档中做到这一点就好了。我使用 emacs 22.2.1 和内置的 sgml-mode 进行 xm
已结束。此问题不符合 Stack Overflow guidelines .它目前不接受答案。 我们不允许提出有关书籍、工具、软件库等方面的建议的问题。您可以编辑问题,以便用事实和引用来回答它。 关闭
根据java: public Scanner useDelimiter(String pattern) Sets this scanner's delimiting pattern to a patt
我读过一些关于 PRG 模式以及它如何防止用户重新提交表单的文章。比如this post有一张不错的图: 我能理解为什么在收到 2xx 后用户刷新页面时不会发生表单提交。但我仍然想知道: (1) 如果
看看下面的图片,您可能会清楚地看到这一点。 那么如何在带有其他一些 View 的简单屏幕中实现没有任何弹出/对话框/模式的微调器日期选择器? 我在整个网络上进行了谷歌搜索,但没有找到与之相关的任何合适
我不知道该怎么做,我一直遇到问题。 以下是代码: rows = int(input()) for i in range(1,rows): for j in range(1,i+1):
我想为重写创建一个正则表达式。 将所有请求重写为 index.php(不需要匹配),它不是以/api 开头,或者不是以('.html',或'.js'或'.css'或'.png'结束) 我的例子还是这样
MVC模式代表 Model-View-Controller(模型-视图-控制器) 模式 MVC模式用于应用程序的分层开发 Model(模型) - 模型代表一个存取数据的对象或 JAVA PO
我想为组织模式创建一个 RDF 模式世界。您可能知道,组织模式文档基于层次结构大纲,其中标题是主要的分组实体。 * March auxiliary :PROPERTIES: :HLEVEL: 1 :E
我正在编写一个可以从文件中读取 JSON 数据的软件。该文件包含“person”——一个值为对象数组的对象。我打算使用 JSON 模式验证库来验证内容,而不是自己编写代码。符合代表以下数据的 JSON
假设我有 4 张 table 人 公司 团体 和 账单 现在bills/persons和bills/companys和bills/groups之间是多对多的关系。 我看到了 4 种可能的 sql 模式
假设您有这样的文档: doc1: id:1 text: ... references: Journal1, 2013, pag 123 references: Journal2, 2014,
我有这个架构。它检查评论,目前工作正常。 var schema = { id: '', type: 'object', additionalProperties: false, pro
这可能很简单,但有人可以解释为什么以下模式匹配不明智吗?它说其他规则,例如1, 0, _ 永远不会匹配。 let matchTest(n : int) = let ran = new Rand
我有以下选择序列作为 XML 模式的一部分。理想情况下,我想要一个序列: 来自 my:namespace 的元素必须严格解析。 来自任何其他命名空间的元素,不包括 ##targetNamespace和
我希望编写一个 json 模式来涵盖这个(简化的)示例 { "errorMessage": "", "nbRunningQueries": 0, "isError": Fals
首先,我是 f# 的新手,所以也许答案很明显,但我没有看到。所以我有一些带有 id 和值的元组。我知道我正在寻找的 id,我想从我传入的三个元组中选择正确的元组。我打算用两个 match 语句来做到这

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!