- Java锁的逻辑(结合对象头和ObjectMonitor)
- 还在用饼状图?来瞧瞧这些炫酷的百分比可视化新图形(附代码实现)⛵
- 自动注册实体类到EntityFrameworkCore上下文,并适配ABP及ABPVNext
- 基于Sklearn机器学习代码实战
cri-dockerd是什么?
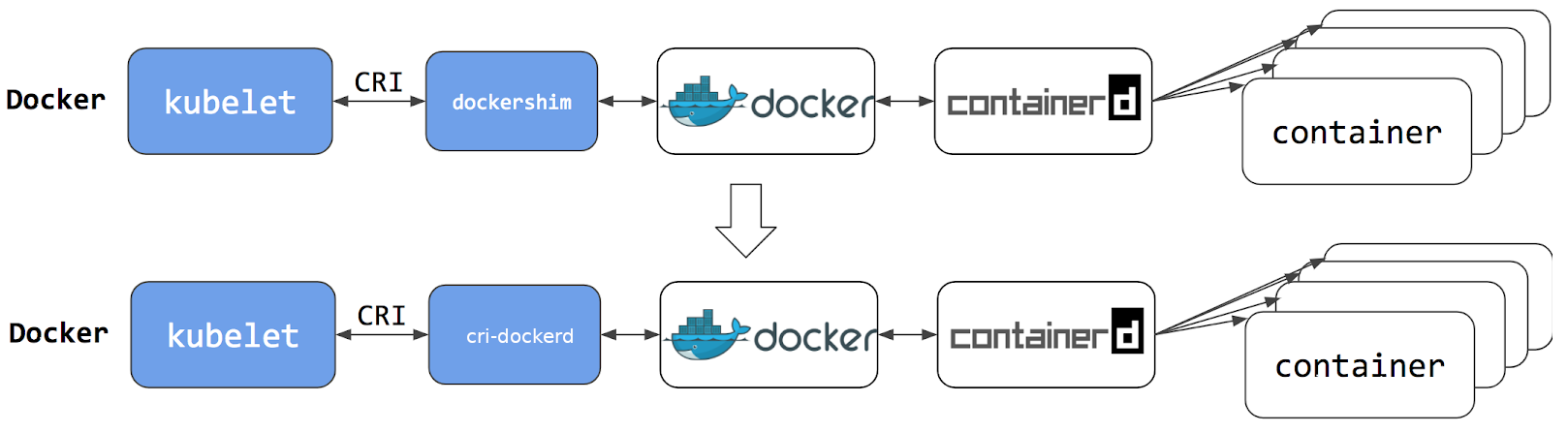
在 Kubernetes v1.24 及更早版本中,我们使用docker作为容器引擎在k8s上使用时,依赖一个dockershim的内置k8s组件;k8s v1.24发行版中将dockershim组件给移除了;取而代之的就是cri-dockerd(当然还有其它容器接口);简单讲CRI就是容器运行时接口(Container Runtime Interface,CRI),也就是说cri-dockerd就是以docker作为容器引擎而提供的容器运行时接口;即我们想要用docker作为k8s的容器运行引擎,我们需要先部署好cri-dockerd;用cri-dockerd来与kubelet交互,然后再由cri-dockerd和docker api交互,使我们在k8s能够正常使用docker作为容器引擎; 。
好了,接下来我们先来说一下部署环境 。
OS:Ubuntu 22.04.2 。
Container Runtime:Docker CE 23.0.1 。
CRI:cri-dockerd:0.3.0 。
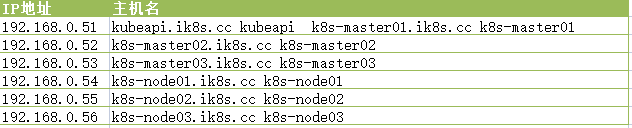
以下步骤需要在每个服务器上都要部署 。
部署时间服务chronyd 。
apt update && apt install chrony
配置阿里云时间服务器 。
pool ntp1.aliyun.com iburst maxsources 4
提示:在/etc/chrony/chrony.conf中加入上述配置,将其他pool开头的配置注释掉; 。
重启chrony,并验证 。
root@k8s-master01:~# systemctl restart chrony
root@k8s-master01:~# systemctl status chrony
● chrony.service - chrony, an NTP client/server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/chrony.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2023-04-01 20:22:44 CST; 6s ago
Docs: man:chronyd(8)
man:chronyc(1)
man:chrony.conf(5)
Process: 3052 ExecStart=/usr/lib/systemd/scripts/chronyd-starter.sh $DAEMON_OPTS (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 3061 (chronyd)
Tasks: 2 (limit: 4530)
Memory: 1.3M
CPU: 40ms
CGroup: /system.slice/chrony.service
├─3061 /usr/sbin/chronyd -F 1
└─3062 /usr/sbin/chronyd -F 1
Apr 01 20:22:44 k8s-master01.ik8s.cc systemd[1]: Starting chrony, an NTP client/server...
Apr 01 20:22:44 k8s-master01.ik8s.cc chronyd[3061]: chronyd version 4.2 starting (+CMDMON +NTP +REFCLOCK +RTC +PRIVDROP +SCFILTER +SIGND +>
Apr 01 20:22:44 k8s-master01.ik8s.cc chronyd[3061]: Frequency -3.785 +/- 18.293 ppm read from /var/lib/chrony/chrony.drift
Apr 01 20:22:44 k8s-master01.ik8s.cc chronyd[3061]: Using right/UTC timezone to obtain leap second data
Apr 01 20:22:44 k8s-master01.ik8s.cc chronyd[3061]: Loaded seccomp filter (level 1)
Apr 01 20:22:44 k8s-master01.ik8s.cc systemd[1]: Started chrony, an NTP client/server.
Apr 01 20:22:50 k8s-master01.ik8s.cc chronyd[3061]: Selected source 120.25.115.20 (ntp1.aliyun.com)
Apr 01 20:22:50 k8s-master01.ik8s.cc chronyd[3061]: System clock TAI offset set to 37 seconds
root@k8s-master01:~# chronyc sources
MS Name/IP address Stratum Poll Reach LastRx Last sample
===============================================================================
^* ntp1.aliyun.com 2 6 17 13 +950us[+3545us] +/- 23ms
root@k8s-master01:~#
提示:使用chronyc sources命令能够看到从那个服务器同步时间,能够看我们配置的服务器地址就表示chrony服务配置没有问题; 。
借用hosts文件做主机名解析 。
root@k8s-master01:~# cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost
127.0.1.1 k8s-server
# The following lines are desirable for IPv6 capable hosts
::1 ip6-localhost ip6-loopback
fe00::0 ip6-localnet
ff00::0 ip6-mcastprefix
ff02::1 ip6-allnodes
ff02::2 ip6-allrouters
192.168.0.51 kubeapi.ik8s.cc kubeapi
192.168.0.51 k8s-master01.ik8s.cc k8s-master01
192.168.0.52 k8s-master02.ik8s.cc k8s-master02
192.168.0.53 k8s-master03.ik8s.cc k8s-master03
192.168.0.54 k8s-node01.ik8s.cc k8s-node01
192.168.0.55 k8s-node02.ik8s.cc k8s-node02
192.168.0.56 k8s-node03.ik8s.cc k8s-node03
root@k8s-master01:~#
各节点禁用swap设备 。
root@k8s-master01:~# swapoff -a
root@k8s-master01:~# cat /etc/fstab
# /etc/fstab: static file system information.
#
# Use 'blkid' to print the universally unique identifier for a
# device; this may be used with UUID= as a more robust way to name devices
# that works even if disks are added and removed. See fstab(5).
#
# <file system> <mount point> <type> <options> <dump> <pass>
# / was on /dev/ubuntu-vg/ubuntu-lv during curtin installation
/dev/disk/by-id/dm-uuid-LVM-TjXApGigP3NsOAzv7UAMUgV9BdMSVlrxfAjm6qSYs1DxA8Nzmr2DKaODbQf48e2m / ext4 defaults 0 1
# /boot was on /dev/sda2 during curtin installation
/dev/disk/by-uuid/db6b3290-0968-4e77-bdd7-ddc849cdda26 /boot ext4 defaults 0 1
#/swap.img none swap sw 0 0
root@k8s-master01:~#
提示:将fstab文件中,又不安swap设备的配置注释掉即可; 。
各节点禁用默认配置防火墙 。
root@k8s-master01:~# ufw disable
Firewall stopped and disabled on system startup
root@k8s-master01:~# ufw status
Status: inactive
root@k8s-master01:~#
安装docker 。
~# apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common -y
~# curl -fsSL http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/ubuntu/gpg | apt-key add -
~# add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable"
~# apt update
~# apt install docker-ce
配置docker容器引擎使用systemd作为CGroup的驱动 。
~# cat /etc/docker/daemon.json
{
"registry-mirrors": [
],
"exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"],
"log-driver": "json-file",
"log-opts": {
"max-size": "200m"
},
"storage-driver": "overlay2"
}
提示:如果你没有代理,也可以使用registry-mirrors来指明使用的镜像加速服务; 。
启动docker服务 。
systemctl daemon-reload && systemctl start docker && systemctl enable docker
配置docker使用代理服务 。
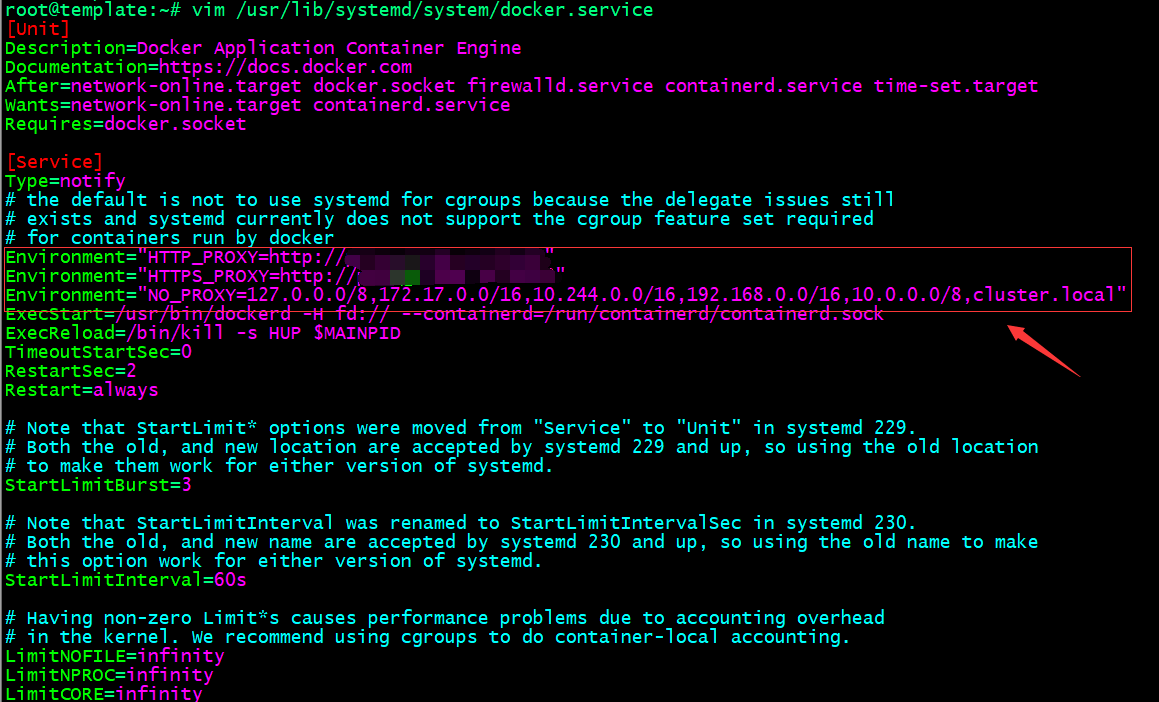
Environment="HTTP_PROXY=http://$PROXY_SERVER_IP:$PROXY_PORT"
Environment="HTTPS_PROXY=https://$PROXY_SERVER_IP:$PROXY_PORT"
Environment="NO_PROXY=127.0.0.0/8,172.17.0.0/16,10.244.0.0/16,192.168.0.0/16,10.0.0.0/8,cluster.local"
提示:在/usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service文件中加入以上配置,把自己的代理服务器地址更换上述$PROXY_SERVER_IP:$PROXY_PORT 。
即可; 。
重载和重启docker服务 。
~# systemctl daemon-reload
~# systemctl restart docker
安装cri-dockerd 。
~# curl -LO https://github.com/Mirantis/cri-dockerd/releases/download/v0.3.0/cri-dockerd_0.3.0.3-0.ubuntu-jammy_amd64.deb
~# apt install ./cri-dockerd_0.3.0.3-0.ubuntu-jammy_amd64.deb
提示:安装完cri-dockerd以后,对应服务会自动启动; 。
在各主机上生成kubelet和kubeadm等相关程序包的仓库 。
~# apt update && apt install -y apt-transport-https curl
~# curl -fsSL https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | apt-key add -
~# cat <<EOF >/etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/apt/ kubernetes-xenial main
EOF
~# apt update
安装kubelet、kubeadm和kubectl 。
~# apt install -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl
~# systemctl enable kubelet
确认版本 。
root@k8s-master01:~# kubeadm version
kubeadm version: &version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"26", GitVersion:"v1.26.3", GitCommit:"9e644106593f3f4aa98f8a84b23db5fa378900bd", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2023-03-15T13:38:47Z", GoVersion:"go1.19.7", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}
root@k8s-master01:~#
整合kubelet和cri-dockerd 。
配置cri-dockerd 。
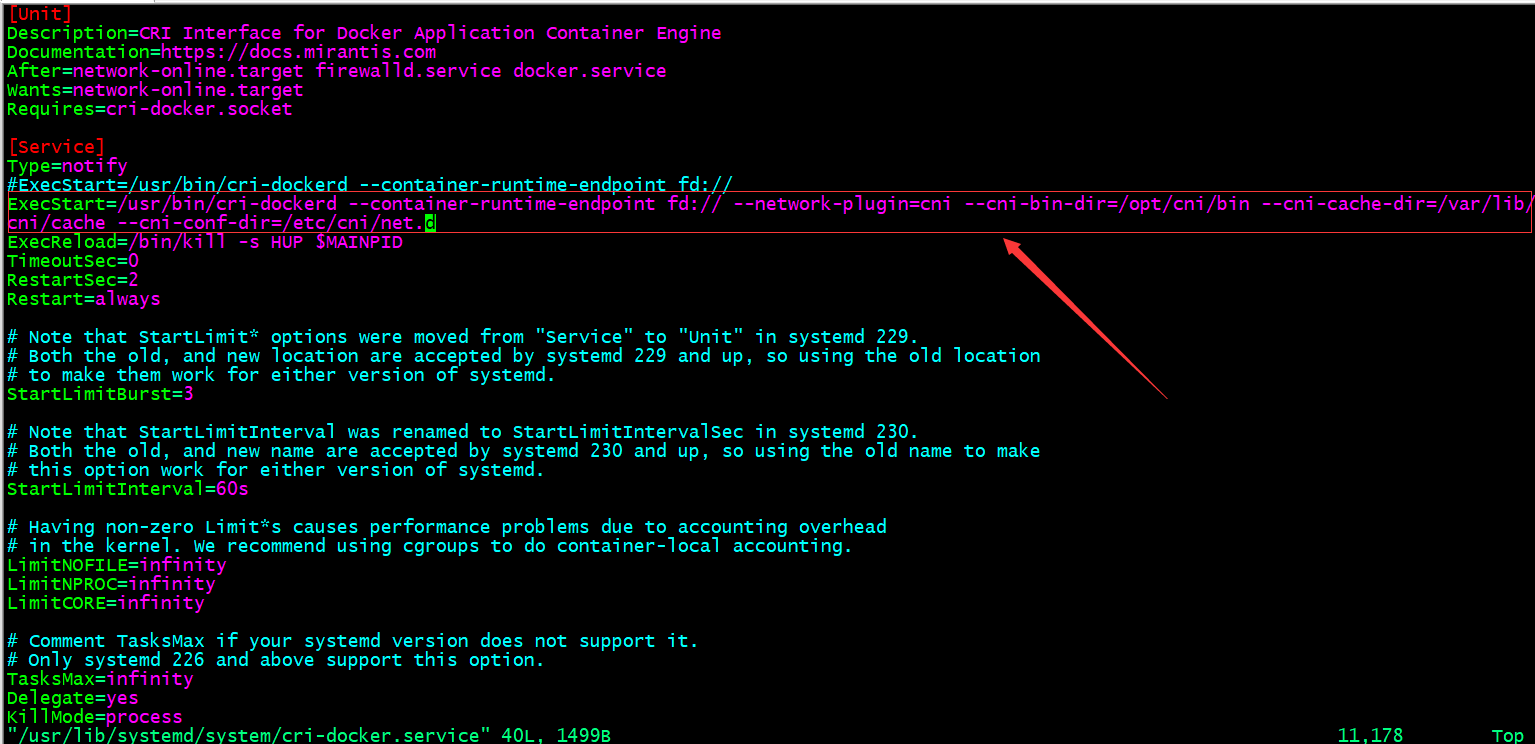
ExecStart=/usr/bin/cri-dockerd --container-runtime-endpoint fd:// --network-plugin=cni --cni-bin-dir=/opt/cni/bin --cni-cache-dir=/var/lib/
cni/cache --cni-conf-dir=/etc/cni/net.d
提示:在/usr/lib/systemd/system/cri-docker.service文件中添加上如上配置;--network-plugin:指定网络插件规范的类型,这里要使用CNI;--cni-bin-dir:指定CNI插件二进制程序文件的搜索目录;--cni-cache-dir:CNI插件使用的缓存目录;--cni-conf-dir:CNI插件加载配置文件的目录; 。
重启cri-dockerd服务 。
~# systemctl daemon-reload && systemctl restart cri-docker
配置kubelet 。
root@k8s-master01:~# cat /etc/sysconfig/kubelet
KUBELET_KUBEADM_ARGS="--container-runtime=remote --container-runtime-endpoint=/run/cri-dockerd.sock"
root@k8s-master01:~#
提示:如果没有sysconfig目录,请先创建,然后再创建kubelet文件;这一步就是告诉kubelet cri-dockerd的接口在哪里;该配置不是必须的,我们也可以在初始化集群时在kubeadm命令上使用“--cri-socket unix:///run/cri-dockerd.sock”选项来告诉kubelet cri-dockerd的socket文件路径; 。
初始化第一个master节点 。
列出镜像信息 。
root@k8s-master01:~# kubeadm config images list
registry.k8s.io/kube-apiserver:v1.26.3
registry.k8s.io/kube-controller-manager:v1.26.3
registry.k8s.io/kube-scheduler:v1.26.3
registry.k8s.io/kube-proxy:v1.26.3
registry.k8s.io/pause:3.9
registry.k8s.io/etcd:3.5.6-0
registry.k8s.io/coredns/coredns:v1.9.3
root@k8s-master01:~#
提示:k8s的镜像默认是谷歌仓库地址,需要代理才可以正常访问;如果你没有代理,请使用阿里云仓库也是可以的;用--image-repository="registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers"来指定使用阿里云镜像仓库中的镜像部署k8s集群; 。
下载镜像 。
root@k8s-master01:~# kubeadm config images pull
Found multiple CRI endpoints on the host. Please define which one do you wish to use by setting the 'criSocket' field in the kubeadm configuration file: unix:///var/run/containerd/containerd.sock, unix:///var/run/cri-dockerd.sock
To see the stack trace of this error execute with --v=5 or higher
root@k8s-master01:~#
提示:这里是让我们指定cri-dockerd的socket文件路径; 。
root@k8s-master01:~# kubeadm config images pull --cri-socket unix:///var/run/cri-dockerd.sock
[config/images] Pulled registry.k8s.io/kube-apiserver:v1.26.3
[config/images] Pulled registry.k8s.io/kube-controller-manager:v1.26.3
[config/images] Pulled registry.k8s.io/kube-scheduler:v1.26.3
[config/images] Pulled registry.k8s.io/kube-proxy:v1.26.3
[config/images] Pulled registry.k8s.io/pause:3.9
[config/images] Pulled registry.k8s.io/etcd:3.5.6-0
[config/images] Pulled registry.k8s.io/coredns/coredns:v1.9.3
root@k8s-master01:~# docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
registry.k8s.io/kube-apiserver v1.26.3 1d9b3cbae03c 2 weeks ago 134MB
registry.k8s.io/kube-controller-manager v1.26.3 ce8c2293ef09 2 weeks ago 123MB
registry.k8s.io/kube-scheduler v1.26.3 5a7904736932 2 weeks ago 56.4MB
registry.k8s.io/kube-proxy v1.26.3 92ed2bec97a6 2 weeks ago 65.6MB
registry.k8s.io/etcd 3.5.6-0 fce326961ae2 4 months ago 299MB
registry.k8s.io/pause 3.9 e6f181688397 5 months ago 744kB
registry.k8s.io/coredns/coredns v1.9.3 5185b96f0bec 10 months ago 48.8MB
root@k8s-master01:~#
提示:用上述命令就可以把初始化k8s集群所需镜像pull到本地; 。
初始化第一个master节点 。
kubeadm init \
--control-plane-endpoint="kubeapi.ik8s.cc" \
--kubernetes-version=v1.26.3 \
--pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16 \
--service-cidr=10.96.0.0/12 \
--token-ttl=0 \
--cri-socket unix:///run/cri-dockerd.sock \
--upload-certs
提示:如果要指定仓库地址,请使用--image-repository选项来指定对应仓库; 。
root@k8s-master01:~# kubeadm init \
> --control-plane-endpoint="kubeapi.ik8s.cc" \
> --kubernetes-version=v1.26.3 \
> --pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16 \
> --service-cidr=10.96.0.0/12 \
> --token-ttl=0 \
> --cri-socket unix:///run/cri-dockerd.sock \
> --upload-certs
[init] Using Kubernetes version: v1.26.3
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[preflight] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster
[preflight] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection
[preflight] You can also perform this action in beforehand using 'kubeadm config images pull'
[certs] Using certificateDir folder "/etc/kubernetes/pki"
[certs] Generating "ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver" certificate and key
[certs] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [k8s-master01.ik8s.cc kubeapi.ik8s.cc kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local] and IPs [10.96.0.1 192.168.0.51]
[certs] Generating "apiserver-kubelet-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/server" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/server serving cert is signed for DNS names [k8s-master01.ik8s.cc localhost] and IPs [192.168.0.51 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/peer" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/peer serving cert is signed for DNS names [k8s-master01.ik8s.cc localhost] and IPs [192.168.0.51 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/healthcheck-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver-etcd-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "sa" key and public key
[kubeconfig] Using kubeconfig folder "/etc/kubernetes"
[kubeconfig] Writing "admin.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "kubelet.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "controller-manager.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "scheduler.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet
[control-plane] Using manifest folder "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-apiserver"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-controller-manager"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-scheduler"
[etcd] Creating static Pod manifest for local etcd in "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[wait-control-plane] Waiting for the kubelet to boot up the control plane as static Pods from directory "/etc/kubernetes/manifests". This can take up to 4m0s
[kubelet-check] Initial timeout of 40s passed.
[apiclient] All control plane components are healthy after 59.502221 seconds
[upload-config] Storing the configuration used in ConfigMap "kubeadm-config" in the "kube-system" Namespace
[kubelet] Creating a ConfigMap "kubelet-config" in namespace kube-system with the configuration for the kubelets in the cluster
[upload-certs] Storing the certificates in Secret "kubeadm-certs" in the "kube-system" Namespace
[upload-certs] Using certificate key:
7f2c3f04e7549e3efd4f80549cb2d8e25e2bf0ba37a385e058bc1dfe50524fb8
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node k8s-master01.ik8s.cc as control-plane by adding the labels: [node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane node.kubernetes.io/exclude-from-external-load-balancers]
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node k8s-master01.ik8s.cc as control-plane by adding the taints [node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane:NoSchedule]
[bootstrap-token] Using token: 28ziy4.vc71wxv7n9qx38nw
[bootstrap-token] Configuring bootstrap tokens, cluster-info ConfigMap, RBAC Roles
[bootstrap-token] Configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to get nodes
[bootstrap-token] Configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to post CSRs in order for nodes to get long term certificate credentials
[bootstrap-token] Configured RBAC rules to allow the csrapprover controller automatically approve CSRs from a Node Bootstrap Token
[bootstrap-token] Configured RBAC rules to allow certificate rotation for all node client certificates in the cluster
[bootstrap-token] Creating the "cluster-info" ConfigMap in the "kube-public" namespace
[kubelet-finalize] Updating "/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf" to point to a rotatable kubelet client certificate and key
[addons] Applied essential addon: CoreDNS
[addons] Applied essential addon: kube-proxy
Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully!
To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Alternatively, if you are the root user, you can run:
export KUBECONFIG=/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster.
Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/
You can now join any number of the control-plane node running the following command on each as root:
kubeadm join kubeapi.ik8s.cc:6443 --token 28ziy4.vc71wxv7n9qx38nw \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:df4d6948bbd1a778135dd22f571527703ddacc5a871b372de1537c37f0e54cde \
--control-plane --certificate-key 7f2c3f04e7549e3efd4f80549cb2d8e25e2bf0ba37a385e058bc1dfe50524fb8
Please note that the certificate-key gives access to cluster sensitive data, keep it secret!
As a safeguard, uploaded-certs will be deleted in two hours; If necessary, you can use
"kubeadm init phase upload-certs --upload-certs" to reload certs afterward.
Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root:
kubeadm join kubeapi.ik8s.cc:6443 --token 28ziy4.vc71wxv7n9qx38nw \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:df4d6948bbd1a778135dd22f571527703ddacc5a871b372de1537c37f0e54cde
root@k8s-master01:~#
提示:能够看到上诉信息,说明第一个k8s主节点就初始化成功;按照上述提示,完成后续步骤即可; 。
验证kubectl是否可用,是否能够获取到节点信息?
root@k8s-master01:~# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
k8s-master01.ik8s.cc NotReady control-plane 4m30s v1.26.3
root@k8s-master01:~#
提示:到此第一个master节点就准备就绪; 。
加入node节点 。
root@k8s-node01:~# kubeadm join kubeapi.ik8s.cc:6443 --token 28ziy4.vc71wxv7n9qx38nw \
> --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:df4d6948bbd1a778135dd22f571527703ddacc5a871b372de1537c37f0e54cde \
> --control-plane --certificate-key 7f2c3f04e7549e3efd4f80549cb2d8e25e2bf0ba37a385e058bc1dfe50524fb8 --cri-socket unix:///run/cri-dockerd.sock
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[preflight] Reading configuration from the cluster...
[preflight] FYI: You can look at this config file with 'kubectl -n kube-system get cm kubeadm-config -o yaml'
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks before initializing the new control plane instance
[preflight] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster
[preflight] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection
[preflight] You can also perform this action in beforehand using 'kubeadm config images pull'
[download-certs] Downloading the certificates in Secret "kubeadm-certs" in the "kube-system" Namespace
[download-certs] Saving the certificates to the folder: "/etc/kubernetes/pki"
[certs] Using certificateDir folder "/etc/kubernetes/pki"
[certs] Generating "apiserver" certificate and key
[certs] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [k8s-node01.ik8s.cc kubeapi.ik8s.cc kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local] and IPs [10.96.0.1 192.168.0.54]
[certs] Generating "apiserver-kubelet-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/server" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/server serving cert is signed for DNS names [k8s-node01.ik8s.cc localhost] and IPs [192.168.0.54 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/peer" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/peer serving cert is signed for DNS names [k8s-node01.ik8s.cc localhost] and IPs [192.168.0.54 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/healthcheck-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver-etcd-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-client" certificate and key
[certs] Valid certificates and keys now exist in "/etc/kubernetes/pki"
[certs] Using the existing "sa" key
[kubeconfig] Generating kubeconfig files
[kubeconfig] Using kubeconfig folder "/etc/kubernetes"
[kubeconfig] Writing "admin.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "controller-manager.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "scheduler.conf" kubeconfig file
[control-plane] Using manifest folder "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-apiserver"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-controller-manager"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-scheduler"
[check-etcd] Checking that the etcd cluster is healthy
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet
[kubelet-start] Waiting for the kubelet to perform the TLS Bootstrap...
[etcd] Announced new etcd member joining to the existing etcd cluster
[etcd] Creating static Pod manifest for "etcd"
[etcd] Waiting for the new etcd member to join the cluster. This can take up to 40s
The 'update-status' phase is deprecated and will be removed in a future release. Currently it performs no operation
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node k8s-node01.ik8s.cc as control-plane by adding the labels: [node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane node.kubernetes.io/exclude-from-external-load-balancers]
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node k8s-node01.ik8s.cc as control-plane by adding the taints [node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane:NoSchedule]
This node has joined the cluster and a new control plane instance was created:
* Certificate signing request was sent to apiserver and approval was received.
* The Kubelet was informed of the new secure connection details.
* Control plane label and taint were applied to the new node.
* The Kubernetes control plane instances scaled up.
* A new etcd member was added to the local/stacked etcd cluster.
To start administering your cluster from this node, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Run 'kubectl get nodes' to see this node join the cluster.
root@k8s-node01:~#
提示:能够看到上述信息表示node节点加入成功;这里需要注意的是,加入node节点,需要指定cri-dockerd的socket文件位置; 。
验证:查看三个节点是否都以正常加入集群?
root@k8s-master01:~# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
k8s-master01.ik8s.cc NotReady control-plane 16m v1.26.3
k8s-node01.ik8s.cc NotReady control-plane 2m36s v1.26.3
k8s-node02.ik8s.cc NotReady control-plane 39s v1.26.3
k8s-node03.ik8s.cc NotReady control-plane 46s v1.26.3
root@k8s-master01:~#
提示:可以看到现在有3个node节点,但是都未准备就绪,这是因为我们在部署k8s集群时,还没有部署网络插件,所以对应节点都是处于未就绪状态; 。
部署网络插件 。
下载网络插件calico的部署清单 。
root@k8s-master01:~# wget https://docs.projectcalico.org/v3.25/manifests/calico.yaml --no-check-certificate
--2023-04-01 22:16:11-- https://docs.projectcalico.org/v3.25/manifests/calico.yaml
Resolving docs.projectcalico.org (docs.projectcalico.org)... 34.143.223.220, 18.139.194.139, 2406:da18:880:3802::c8, ...
Connecting to docs.projectcalico.org (docs.projectcalico.org)|34.143.223.220|:443... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 301 Moved Permanently
Location: https://docs.tigera.io/archive/v3.25/manifests/calico.yaml [following]
--2023-04-01 22:16:13-- https://docs.tigera.io/archive/v3.25/manifests/calico.yaml
Resolving docs.tigera.io (docs.tigera.io)... 34.142.149.67, 34.142.199.10, 2406:da18:880:3801::c8, ...
Connecting to docs.tigera.io (docs.tigera.io)|34.142.149.67|:443... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 238089 (233K) [text/yaml]
Saving to: ‘calico.yaml’
calico.yaml 100%[=======================================================================================>] 232.51K 22.4KB/s in 10s
2023-04-01 22:16:25 (22.4 KB/s) - ‘calico.yaml’ saved [238089/238089]
root@k8s-master01:~#
在k8s集群上应用清单 。
root@k8s-master01:~# kubectl apply -f ./calico.yaml
poddisruptionbudget.policy/calico-kube-controllers created
serviceaccount/calico-kube-controllers created
serviceaccount/calico-node created
configmap/calico-config created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/bgpconfigurations.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/bgppeers.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/blockaffinities.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/caliconodestatuses.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/clusterinformations.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/felixconfigurations.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/globalnetworkpolicies.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/globalnetworksets.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/hostendpoints.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ipamblocks.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ipamconfigs.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ipamhandles.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ippools.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ipreservations.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/kubecontrollersconfigurations.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/networkpolicies.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/networksets.crd.projectcalico.org created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/calico-kube-controllers created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/calico-node created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/calico-kube-controllers created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/calico-node created
daemonset.apps/calico-node created
deployment.apps/calico-kube-controllers created
root@k8s-master01:~#
验证:查看节点是否准备就绪?kube-system名称空间下的pods是否都running?
root@k8s-master01:~# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
k8s-master01.ik8s.cc Ready control-plane 36m v1.26.3
k8s-node01.ik8s.cc Ready control-plane 23m v1.26.3
k8s-node02.ik8s.cc Ready control-plane 21m v1.26.3
k8s-node03.ik8s.cc Ready control-plane 21m v1.26.3
root@k8s-master01:~# kubectl get pods -n kube-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
calico-kube-controllers-57b57c56f-qcr2v 1/1 Running 0 15m
calico-node-mg65h 1/1 Running 0 104s
calico-node-pxmt6 1/1 Running 0 92s
calico-node-ssft4 1/1 Running 0 77s
calico-node-w97sq 1/1 Running 0 84s
coredns-787d4945fb-8xkn2 1/1 Running 0 36m
coredns-787d4945fb-sbcfq 1/1 Running 0 36m
etcd-k8s-master01.ik8s.cc 1/1 Running 0 36m
etcd-k8s-node01.ik8s.cc 1/1 Running 0 23m
etcd-k8s-node02.ik8s.cc 1/1 Running 0 21m
etcd-k8s-node03.ik8s.cc 1/1 Running 0 21m
kube-apiserver-k8s-master01.ik8s.cc 1/1 Running 0 36m
kube-apiserver-k8s-node01.ik8s.cc 1/1 Running 0 23m
kube-apiserver-k8s-node02.ik8s.cc 1/1 Running 0 21m
kube-apiserver-k8s-node03.ik8s.cc 1/1 Running 0 21m
kube-controller-manager-k8s-master01.ik8s.cc 1/1 Running 1 (23m ago) 36m
kube-controller-manager-k8s-node01.ik8s.cc 1/1 Running 0 23m
kube-controller-manager-k8s-node02.ik8s.cc 1/1 Running 0 19m
kube-controller-manager-k8s-node03.ik8s.cc 1/1 Running 0 21m
kube-proxy-d9vd8 1/1 Running 0 36m
kube-proxy-f96j6 1/1 Running 0 21m
kube-proxy-hnqq2 1/1 Running 0 23m
kube-proxy-mt57g 1/1 Running 0 21m
kube-scheduler-k8s-master01.ik8s.cc 1/1 Running 1 (23m ago) 36m
kube-scheduler-k8s-node01.ik8s.cc 1/1 Running 0 23m
kube-scheduler-k8s-node02.ik8s.cc 1/1 Running 0 19m
kube-scheduler-k8s-node03.ik8s.cc 1/1 Running 0 21m
root@k8s-master01:~#
提示:可以看到kube-system名称空间下的pod都running且都是处于就绪状态,节点信息也都是处于就绪状态;至此基于cri-dockerd和docker的单master节点的k8s集群就搭建好了; 。
最后此篇关于基于docker和cri-dockerd部署k8sv1.26.3的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于基于docker和cri-dockerd部署k8sv1.26.3的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
很难说出这里问的是什么。这个问题是含糊的、模糊的、不完整的、过于宽泛的或修辞性的,无法以目前的形式得到合理的回答。如需帮助澄清此问题以便重新打开它,visit the help center 。 已关
我们可以说 O(K + (N-K)logK)相当于O(K + N logK)对于 1 < = K <= N ? 最佳答案 简短的回答是它们不等价,这取决于k 的值。如果k等于N,那么第一个复杂度是O(
我有以下解决方案,但我从其他评论者那里听说它是 O(N * K * K),而不是 O(N * K)其中 N 是 K 列表的(最大)长度,K 是列表的数量。例如,给定列表 [1, 2, 3] 和 [4,
我试图理解这些语法结构之间的语义差异。 if ((i% k) == (l % k) == 0) 和 if ((i % k) == 0 && (l % k) == 0) 最佳答案 您的特定表达式((i
我有时会使用一维数组: A = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4]) 或 2D 阵列(使用 scipy.io.wavfile 读取单声道或立体声信号): A = np.array([[1, 2
在文档聚类过程中,作为数据预处理步骤,我首先应用奇异向量分解得到U、S和Vt 然后通过选择适当数量的特征值,我截断了 Vt,这让我从阅读的内容中得到了很好的文档-文档相关性 here .现在我正在对矩
我问的是关于 Top K 算法的问题。我认为 O(n + k log n) 应该更快,因为……例如,如果您尝试插入 k = 300 和 n = 100000000,我们可以看到 O(n + k log
这个问题与另一个问题R:sample()密切相关。 。我想在 R 中找到一种方法来列出 k 个数字的所有排列,总和为 k,其中每个数字都是从 0:k 中选择的。如果k=7,我可以从0,1,...,7中
我目前正在评估基于隐式反馈的推荐系统。我对排名任务的评估指标有点困惑。具体来说,我希望通过精确度和召回率来进行评估。 Precision@k has the advantage of not requ
我在 Python 中工作,需要找到一种算法来生成所有可能的 n 维 k,k,...,k 数组,每个数组都沿轴有一行 1。因此,该函数接受两个数字 - n 和 k,并且应该返回一个数组列表,其中包含沿
我们有 N 对。每对包含两个数字。我们必须找到最大数 K,这样如果我们从给定的 N 对中取 J (1 2,如果我们选择三对 (1,2),我们只有两个不同的数字,即 1 和 2。 从一个开始检查每个可能
鉴于以下问题,我不能完全确定我当前的解决方案: 问题: 给定一个包含 n 元素的最大堆,它存储在数组 A 中,是否可以打印所有最大的 K 元素在 O(K*log(K)) 中? 我的回答: 是的,是的,
我明白了: val vector: RDD[(String, Array[String])] = [("a", {v1,v2,..}),("b", {u1,u2,..})] 想转换成: RDD[(St
我有 X 个正数,索引为 x_i。每个 x_i 需要进入 K 组之一(其中 K 是预先确定的)。令 S_j 为 K_j 中所有 x_i 的总和。我需要分配所有 x_i 以使所有 S_j 的方差最小化。
关闭。这个问题是not reproducible or was caused by typos .它目前不接受答案。 这个问题是由于错别字或无法再重现的问题引起的。虽然类似的问题可能是on-topi
我正在研究寻找原始数的算法,看到下面的语句,我不明白为什么。 while (k*k <= n) 优于 while (k <= Math.sqrt(n)) 是因为函数调用吗?该调用函数使用更多资源。 更
我想找到一种尽可能快的方法来将两个小 bool 矩阵相乘,其中小意味着 8x8、9x9 ... 16x16。这个例程会被大量使用,所以需要非常高效,所以请不要建议直截了当的解决方案应该足够快。 对于
有没有一种惯用的方法来获取 Set和 Function ,并获得 Map实时取景? (即 Map 由 Set 和 Function 组合支持,例如,如果将元素添加到 Set ,则相应的条目也存在于 M
这个问题在这里已经有了答案: Can a local variable's memory be accessed outside its scope? (20 个答案) returning addr
给定一个矩阵:- k = [1 2 3 ; 4 5 6 ; 7 8 NaN]; 如果我想用 0 替换一个数字,比如 2,我可以使用这个:k(k==2) =

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!