- Java锁的逻辑(结合对象头和ObjectMonitor)
- 还在用饼状图?来瞧瞧这些炫酷的百分比可视化新图形(附代码实现)⛵
- 自动注册实体类到EntityFrameworkCore上下文,并适配ABP及ABPVNext
- 基于Sklearn机器学习代码实战
开发过程中我们会遇到很多使用线程池的场景,例如异步短信通知,异步发邮件,异步记录操作日志,异步处理批量Excel解析。这些异步处理的场景我们都可以把它放在线程池中去完成,当然还有很多场景也都可以使用线程池,掌握线程池后开发中自己灵活应用.
例如在生成订单的时候给用户发送短信,生成订单的结果不应该被发送短信的成功与否所左右,也就是说生成订单这个主操作是不依赖于发送短信这个操作,我们就可以把发送短信这个操作置为异步操作。当然也有的小伙伴会说我使用多线程不就行了,为啥还要使用线程池,那我就先聊一下线程和线程池的优缺点.
使用线程的缺点:
1:每次new Thread对象的时候,新建对象这样性能很差.
2:线程缺乏管理,有可能无限创建线程,这样可能造成系统资源的浪费或者OOM(内存溢出).
使用线程池的优点:
1:重用存在的线程,减少线程的创建,性能良好.
2:可以有效的控制最大的线程并发数,提高系统资源的利用率.
说完上面就知道使用线程池有多好了吧,那知道了线程池的好处,我们怎样使用线程池呢?好了重点对象出现了【PS 对象出现了汪汪汪🐶】.
这个时候可能会有小伙伴疑问为什么要先聊线程池呢?Spring的异步处理写的很好直接用不就完事了,因为线程池和Spring的异步处理有着千丝万缕的关系,仔细看就知道了.
Java中使用线程池,那就要深刻理解大名鼎鼎的ThreadPoolExecutor对象。那怎么创建这个对象的,请看给的源码So Easy (学会了创建对象,同事再不担心你的学习能力了,广告词) 。
/**
* Creates a new {
@code
ThreadPoolExecutor}
*
@param
corePoolSize the number of threads to keep in the pool, even
* if they are idle, unless {
@code
allowCoreThreadTimeOut} is set
*
@param
maximumPoolSize the maximum number of threads to allow in the
* pool
*
@param
keepAliveTime when the number of threads is greater than
* the core, this is the maximum time that excess idle threads
* will wait for new tasks before terminating.
*
@param
unit the time unit for the {
@code
keepAliveTime} argument
*
@param
workQueue the queue to use for holding tasks before they are
* executed. This queue will hold only the {
@code
Runnable}
* tasks submitted by the {
@code
execute} method.
*/
public
ThreadPoolExecutor(
int
corePoolSize,
int
maximumPoolSize,
long
keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue
<Runnable>
workQueue) {
this
(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), defaultHandler);
}
很多人一看就是运用几个参数创建对象,确实不难。但是这几个参数的表达的意思懂吗,看英文确实有点不懂,好了那我就仔细聊聊这几个参数,继续学英语【这是真正学英语,不是电视剧中的学英语】 。
1:corePoolSize,线程池中的核心线程,当提交一个新的任务时候,线程池会创建一个新的线程执行任务,直到当前的线程数等于corePoolSize;如果当前线程数为corePoolSize,继续提交新的任务到阻塞队列中,等待被执行.
2:maximumPoolSize,线程池中允许的最大的线程数,如果阻塞队列满了,继续提交新的任务,则创建新的线程执行任务。前提是当前线程数小于maximumPoolSize.
3:keepAliveTime,线程池维护线程所允许的时间,当线程池中的数量大于corePoolSize时候,如果没有任务提交,核心线程外的线程不会被立即销毁,而是等待时间超过了keepAliveTime.
4:unit,keepAliveTime的时间单位.
5:workQueue:用来保存等待被执行任务的阻塞队列,且任务必须实现Runable接口.
6:threadFactory,他是threadFactory类型的变量,用来创建线程,默认使用Executors.defaultThreadFactory()来创建线程.
7:handler:线程池的饱和策略,当阻塞队列满了,且没有空闲的工作线程,如果继续提交任务,必须采取一种策略处理该任务,线程池提供了4种策略: 7.1、AbortPolicy:直接抛出异常,默认策略; 7.2、CallerRunsPolicy:用调用者所在的线程来执行任务; 73、DiscardOldestPolicy:丢弃阻塞队列中靠最前的任务,并执行当前任务; 7.4、DiscardPolicy:直接丢弃任务; 上面的4种策略都是ThreadPoolExecutor的内部类。 当然也可以根据应用场景实现RejectedExecutionHandler接口,自定义饱和策略.
好了看到上面的解释应该比较懂了吧,如果不懂那我再画一张图,帮你更好的理解线程池的工作原理,如下图:
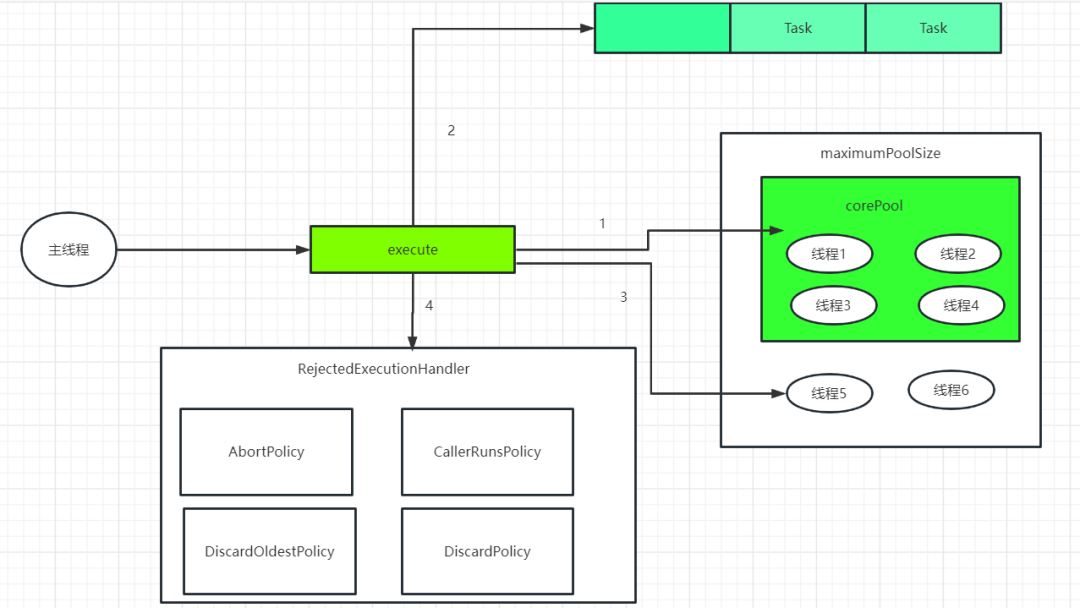
看了上图如果还不懂,那我就给你上个代码,保证你看懂了【PS因为我刚开始就给你说了So Easy,不骗你】(呸呸呸,咋有点渣).
public
class
ThreadPoolTest {
public
static
void
main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutor pools
=
createPool();
int
activeCount = -1
;
int
queueSize = -1
;
while
(
true
) {
if
(activeCount != pools.getActiveCount() || queueSize !=
pools.getQueue().size()) {
System.out.println(
"活跃的线程的个数:" +
pools.getActiveCount());
System.out.println(
"队列中线程的个数:" +
pools.getQueue().size());
System.out.println(
"最大的线程的个数" +
pools.getMaximumPoolSize());
activeCount
=
pools.getActiveCount();
queueSize
=
pools.getQueue().size();
System.out.println(
"========================================="
);
}
}
}
//
创建线程池,通过更改线程池的参数方便你更好的理解线程池
//
其中第六个参数你也可以改成ThreadPoolExecutor默认的:Executors.defaultThreadFactory()
private
static
ThreadPoolExecutor createPool() {
ThreadPoolExecutor pools
=
new
ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 2, 30
,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new
ArrayBlockingQueue<>(1
),
r
->
{
Thread t
=
new
Thread(r);
return
t;
},
new
ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
System.out.println(
"The PoolExecutor is create done"
);
pools.execute(()
->
{
sleep(
100
);
});
//
这个里面就可以写自己的业务
pools.execute(() ->
{
sleep(
10
);
});
pools.execute(()
->
{
sleep(
10
);
});
return
pools;
}
private
static
void
sleep(
int
seconds) {
try
{
System.out.println(
" " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " "
);
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(seconds);
}
catch
(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
好了理解了线程池,那就引入本文的重点Spring的异步处理。如果是使用Spring Boot项目那只需要2个注解就能搞定了。如下:
第一步加@EnableAsync注解,如下图:
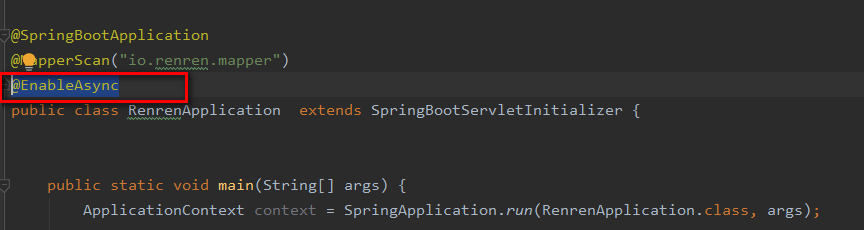
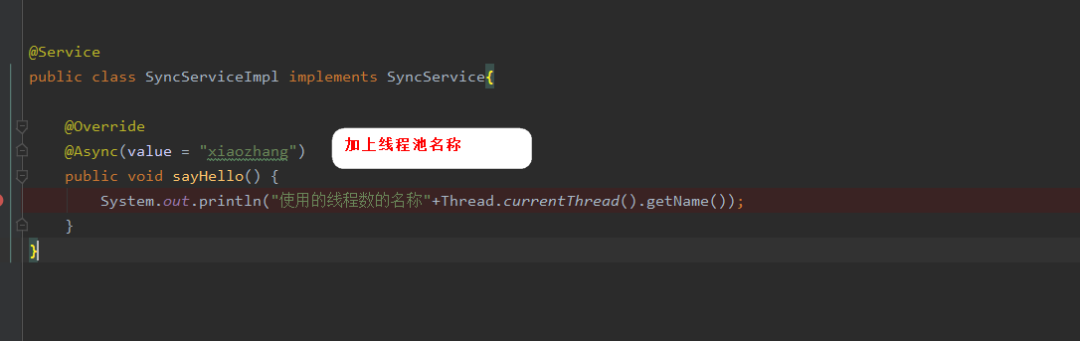
第二步在要使用的方法上加@Async注解,如下:

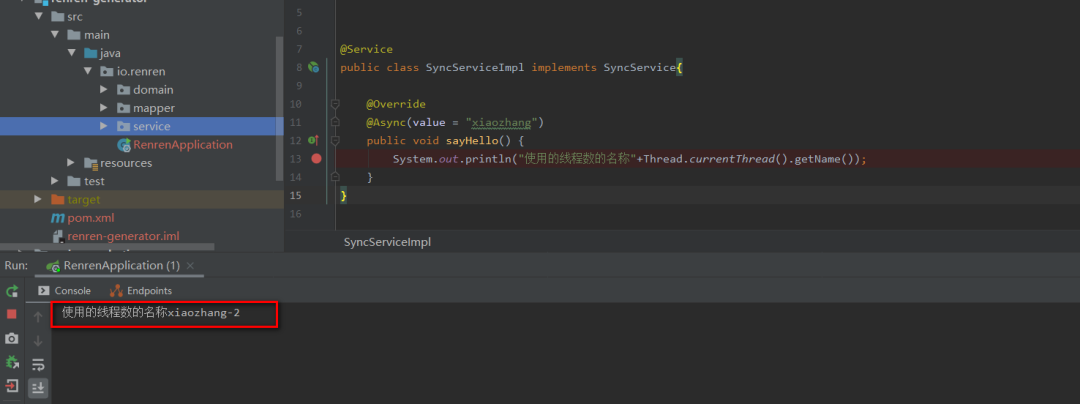
然后就可以直接使用了,如下是运行结果,加了Async注解和没加注解出来的名字不一样,有兴趣的小伙伴可以试一下没加注解打印出来的是什么名字:
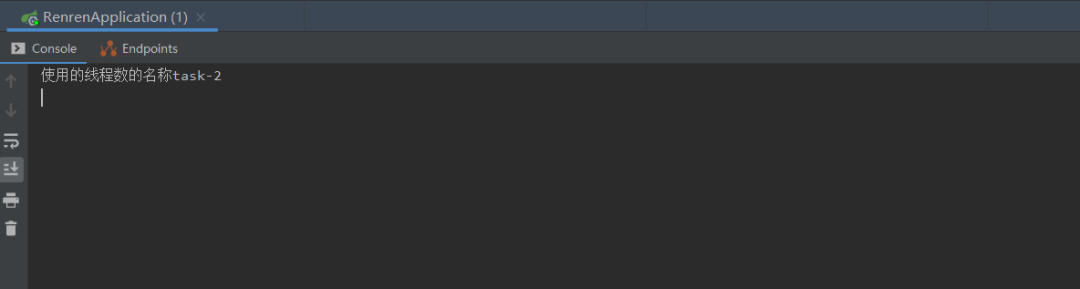
当然可能使用Spring Boot版本不同,打印出来的线程名称可能会有点不同。这个时候可能会有小伙伴说这使用也太简单了,讲上面的线程池没有啊.
继续看,容我仔细说。我们先看下面2个注解 。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(AsyncConfigurationSelector.
class
)
public
@
interface
EnableAsync {
/**
* Indicate the 'async' annotation type to be detected at either class
* or method level.
* 默认情况下,要开启异步操作,要在相应的方法或者类上加上@Async注解
*/
Class
<?
extends
Annotation> annotation()
default
Annotation.
class
;
/**
* Indicate whether subclass-based (CGLIB) proxies are to be created as opposed
* to standard Java interface-based proxies.
* true表示启用CGLIB代理
*/
boolean
proxyTargetClass()
default
false
;
/**
* Indicate the order in which the {
@link
AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor}
* should be applied.
* 直接定义:它的执行顺序(因为可能有多个@EnableXXX)
*/
int
order()
default
Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
}
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public
@
interface
Async {
/**
* A qualifier value for the specified asynchronous operation(s).
* 这个value值是用来指定执行器的
*/
String value()
default
""
;
}
最重要的还是上面的@Import注解导入的类:AsyncConfigurationSelector。这种方式我以前的文章说过很多次了,如果看过我以前写的文章的,对这种导入应该很熟悉,所以我直接说这个类的作用了。这个类帮我们导入了ProxyAsyncConfiguration这个类,然后又帮我们注入了AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor这个类。它就是和@Async比较相关的一个类了。从上的源码可议看出,支持@Asycn注解异步处理我们写的业务处理方法,交给了AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor。具体的实现功能交给了它的继承类AsyncExecutionInterceptor。由于主要功能处理都在AsyncExecutionInterceptor这个类中所以我主要聊这个类了.
首先是这个方法:
@Override
@Nullable
//
见名知意就知道这个是获取线程池的方法,
//
这个厉害了。如果父类返回的defaultExecutor 为null,
//
那就new一个SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor作为默认的执行器,所以我们上文中
//
如果没有指定线程池,那么就默认给我们一个默认的:SimpleAsyncTaskExecuto
protected
Executor getDefaultExecutor(@Nullable BeanFactory beanFactory) {
Executor defaultExecutor
=
super
.getDefaultExecutor(beanFactory);
return
(defaultExecutor !=
null
? defaultExecutor :
new
SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor());
}
先简单说一下这个默认的线程池,看完这个默认的线程池解释就知道我最开始为什么要先说一下线程池了.
SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor:异步执行用户任务的SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor。每次执行用户提交给它的任务时,它会启动新的线程,并允许开发者控制并发线程的上限(concurrencyLimit),从而起到一定的资源节流作用。默认时,concurrencyLimit取值为-1,即不启用资源节流,所以它不是真的线程池,这个类不重用线程,每次调用都会创建一个新的线程(因此建议我们在使用@Aysnc的时候,自己配置一个线程池,节约资源) 。
然后看获取默认线程池的方法,这个方法很牛,先看代码后面解释为什么牛🐂【PS里面中文都是添加的,老外们不会中文】.
protected
Executor getDefaultExecutor(@Nullable BeanFactory beanFactory) {
if
(beanFactory !=
null
) {
//
这个处理很有意思,它是用用的try catch的技巧去处理的
try
{
//
如果容器内存在唯一的TaskExecutor(子类),就直接返回了
return
beanFactory.getBean(TaskExecutor.
class
);
}
catch
(NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException ex) {
//
这是出现了多个TaskExecutor类型的话,那就按照名字去拿 `taskExecutor`且是Executor类型
try
{
return
beanFactory.getBean(DEFAULT_TASK_EXECUTOR_BEAN_NAME, Executor.
class
);
}
//
如果再没有找到,也不要报错,而是接下来创建一个默认的处理器
//
这里输出一个info信息
catch
(NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex2) {
}
}
catch
(NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
try
{
return
beanFactory.getBean(DEFAULT_TASK_EXECUTOR_BEAN_NAME, Executor.
class
);
}
catch
(NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex2) {
}
//
这里还没有获取到,就放弃。用本地默认的executor吧~~~
//
子类可以去复写此方法,发现为null的话可议给一个默认值~~~~比如`AsyncExecutionInterceptor`默认给的就是`SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor`作为执行器的
//
Giving up -> either using local default executor or none at all...
}
}
return
null
;
}
好了看了获取默认线程池的方法了,对我们后面配置程序中自己的线程池就有了很大的帮助了,慢慢知道我一开始为啥要先聊线程池了吗,放心不会骗你的【PS呸呸呸 这句话说的是不是有点渣) 。
然后我们再聊线程异步执行的方法如下:

这个三个步骤就是执行异步的核心我会一个一个说:
determineAsyncExecutor方法 。
/**
* Determine the specific executor to use when executing the given method.
* Should preferably return an {
@link
AsyncListenableTaskExecutor} implementation.
*
@return
the executor to use (or {
@code
null}, but just if no default executor is available)
*/
@Nullable
protected
AsyncTaskExecutor determineAsyncExecutor(Method method) {
//
如果缓存中能够找到该方法对应的执行器,就立马返回了
AsyncTaskExecutor executor =
this
.executors.get(method);
if
(executor ==
null
) {
Executor targetExecutor;
//
抽象方法:AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor有实现。
//
就是@Async注解的value值
String qualifier =
getExecutorQualifier(method);
//
现在知道@Async直接的value值的作用了吧。就是制定执行此方法的执行器的(容器内执行器的Bean的名称)
//
当然有可能为null。注意此处是支持@Qualified注解标注在类上来区分Bean的
//
注意:此处targetExecutor仍然可能为null
//
使用自定义线程池d额时候Async注解的value值最好加上线程池的名称
if
(StringUtils.hasLength(qualifier)) {
targetExecutor
= findQualifiedExecutor(
this
.beanFactory, qualifier);
}
else
{
targetExecutor
=
this
.defaultExecutor.get();
}
if
(targetExecutor ==
null
) {
return
null
;
}
executor
= (targetExecutor
instanceof
AsyncListenableTaskExecutor ?
(AsyncListenableTaskExecutor) targetExecutor :
new
TaskExecutorAdapter(targetExecutor));
this
.executors.put(method, executor);
}
return
executor;
}
好了上面的代码中提到AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor这个类的getExecutorQualifier方法了,这个方法也是极其重要的点,所以我直接拉出来,如下:
/**
* Return the qualifier or bean name of the executor to be used when executing the
* given method, specified via {
@link
Async#value} at the method or declaring
* class level. If {
@code
@Async} is specified at both the method and class level, the
* method's {
@code
#value} takes precedence (even if empty string, indicating that
* the default executor should be used preferentially).
*/
@Override
@Nullable
protected
String getExecutorQualifier(Method method) {
//
Maintainer's note: changes made here should also be made in
//
AnnotationAsyncExecutionAspect#getExecutorQualifier
//
可以见它就是去方法拿到@Async的value值。
//
这下知道配置这个注解的作用了吧。
Async async = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(method, Async.
class
);
if
(async ==
null
) {
async
= AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(method.getDeclaringClass(), Async.
class
);
}
return
(async !=
null
? async.value() :
null
);
}
根据这个@Async的配置,会得到具体的Executor,也就是线程池如下:

好了那获取到异步执行的线程池,那就开始执行具体的方法了,这个不聊了也就是我们写的业务方法。执行完方法后干嘛呢?当然就是第三步骤处理返回值啊,如下:
/**
* Delegate for actually executing the given task with the chosen executor.
* 用选定的执行者实际执行给定任务
*/
@Nullable
protected
Object doSubmit(Callable<Object> task, AsyncTaskExecutor executor, Class<?>
returnType) {
//
根据不同的返回值类型,来采用不同的方案去异步执行,但是执行器都是executor
if
(CompletableFuture.
class
.isAssignableFrom(returnType)) {
return
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->
{
try
{
return
task.call();
}
catch
(Throwable ex) {
throw
new
CompletionException(ex);
}
}, executor);
}
//
//
ListenableFuture接口继承自Future 是Spring自己扩展的一个接口。
else
if
(ListenableFuture.
class
.isAssignableFrom(returnType)) {
return
((AsyncListenableTaskExecutor) executor).submitListenable(task);
}
//
普通的submit
else
if
(Future.
class
.isAssignableFrom(returnType)) {
return
executor.submit(task);
}
else
{
//
没有返回值的情况下 也用sumitt提交,按时返回null
executor.submit(task);
return
null
;
}
一共四个分支,前面三个都是判断是否是 Future 类型的。而我们的程序走到了最后的一个 else,含义就是如果返回值不是 Future 类型的。直接把任务 submit 到线程池之后,就返回了一个 null。这可不得爆出空指针异常吗?但是源码为什么只支持 void 和 Future 的返回类型?
因为底层的线程池只支持这两种类型的返回。只是Spring的做法稍微有点坑,直接把其他的返回类型的返回值都处理为 null 了.
好了Spring处理异步的过程都说了,我们也看到Spring的异步处理器不是太好,需要我们自己配置默认的线程池,还有如果程序中有返回结果一定要记得把返回结果用Futrue封装一下,要不然写出来的程序可能出现空指针的情况【PS你已经是一个成熟的开发了,要记得自己避免空指针。嘿嘿又一句广告词】.
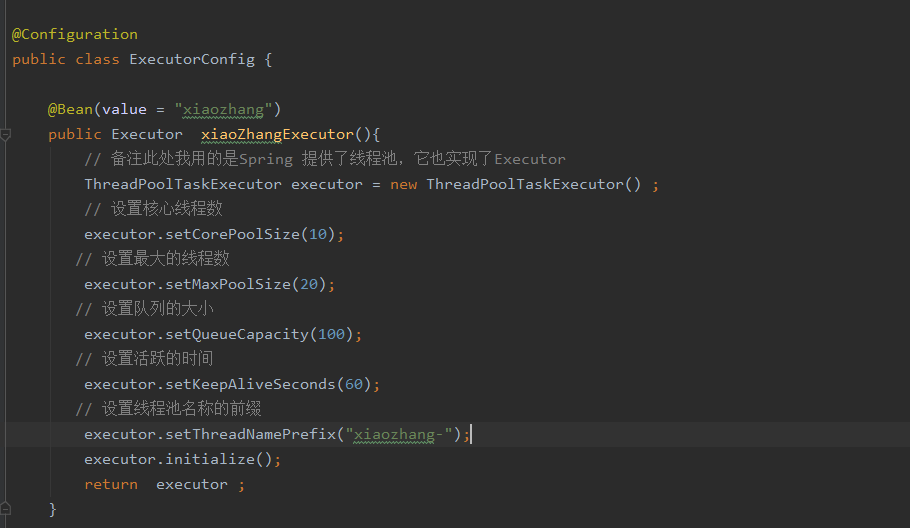
那我就把Spring异步处理程序优化一点,自定义自己的异步的线程池如下图,不贴代码了,这个很重要要不要复制粘了自己多敲点代码吧:
结果:
PS :使用自定义线程池的时候@Async注解的value记得加上线程池的名称,但是线程池不能滥用,但是一个项目里面是可以有多个自定义线程池的。根据你的业务场景来划分。比如举个简单的例子,业务主流程上可以用一个线程池,但是当主流程中的某个环节出问题了,假设需要发送预警短信。发送预警短信的这个操作,就可以用另外一个线程池来做.
线程池的那些参数具体配置多少,需要自己根据服务器的配置,访问的用户量等等其他的一些信息来进行配置,我只是让大家理解线程池参数表达的意义,让大家自己配置线程池参数更加方便.
最后此篇关于Java线程池和Spring异步处理高级篇的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于Java线程池和Spring异步处理高级篇的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我将 Bootstrap 与 css 和 java 脚本结合使用。在不影响前端代码的情况下,我真的很难在css中绘制这个背景。在许多问题中,人们将宽度和高度设置为 0%。但是由于我的导航栏,我不能使用
我正在用 c 编写一个程序来读取文件的内容。代码如下: #include void main() { char line[90]; while(scanf("%79[^\
我想使用 javascript 获取矩阵数组的所有对 Angular 线。假设输入输出如下: input = [ [1,2,3], [4,5,6], [7,8,9], ] output =
可以用pdfmake绘制lines,circles和other shapes吗?如果是,是否有documentation或样本?我想用jsPDF替换pdfmake。 最佳答案 是的,有可能。 pdfm
我有一个小svg小部件,其目的是显示角度列表(参见图片)。 现在,角度是线元素,仅具有笔触,没有填充。但是现在我想使用一种“内部填充”颜色和一种“笔触/边框”颜色。我猜想line元素不能解决这个问题,
我正在为带有三角对象的 3D 场景编写一个非常基本的光线转换器,一切都工作正常,直到我决定尝试从场景原点 (0/0/0) 以外的点转换光线。 但是,当我将光线原点更改为 (0/1/0) 时,相交测试突
这个问题已经有答案了: Why do people write "#!/usr/bin/env python" on the first line of a Python script? (22 个回
如何使用大约 50 个星号 * 并使用 for 循环绘制一条水平线?当我尝试这样做时,结果是垂直(而不是水平)列出 50 个星号。 public void drawAstline() { f
这是一个让球以对角线方式下降的 UI,但球保持静止;线程似乎无法正常工作。你能告诉我如何让球移动吗? 请下载一个球并更改目录,以便程序可以找到您的球的分配位置。没有必要下载足球场,但如果您愿意,也可以
我在我的一个项目中使用 Jmeter 和 Ant,当我们生成报告时,它会在报告中显示 URL、#Samples、失败、成功率、平均时间、最短时间、最长时间。 我也想在报告中包含 90% 的时间线。 现
我有一个不寻常的问题,希望有人能帮助我。我想用 Canvas (android) 画一条 Swing 或波浪线,但我不知道该怎么做。它将成为蝌蚪的尾部,所以理想情况下我希望它的形状更像三角形,一端更大
这个问题已经有答案了: Checking Collision of Shapes with JavaFX (1 个回答) 已关闭 8 年前。 我正在使用 JavaFx 8 库。 我的任务很简单:我想检
如何按编号的百分比拆分文件。行数? 假设我想将我的文件分成 3 个部分(60%/20%/20% 部分),我可以手动执行此操作,-_-: $ wc -l brown.txt 57339 brown.tx
我正在努力实现这样的目标: 但这就是我设法做到的。 你能帮我实现预期的结果吗? 更新: 如果我删除 bootstrap.css 依赖项,问题就会消失。我怎样才能让它与 Bootstrap 一起工作?
我目前正在构建一个网站,但遇到了 transform: scale 的问题。我有一个按钮,当用户将鼠标悬停在它上面时,会发生两件事: 背景以对 Angular 线“扫过” 按钮标签颜色改变 按钮稍微变
我需要使用直线和仿射变换绘制大量数据点的图形(缩放图形以适合 View )。 目前,我正在使用 NSBezierPath,但我认为它效率很低(因为点在绘制之前被复制到贝塞尔路径)。通过将我的数据切割成
我正在使用基于 SVM 分类的 HOG 特征检测器。我可以成功提取车牌,但提取的车牌除了车牌号外还有一些不必要的像素/线。我的图像处理流程如下: 在灰度图像上应用 HOG 检测器 裁剪检测到的区域 调
我有以下图片: 我想填充它的轮廓(即我想在这张图片中填充线条)。 我尝试了形态学闭合,但使用大小为 3x3 的矩形内核和 10 迭代并没有填满整个边界。我还尝试了一个 21x21 内核和 1 迭代,但
我必须找到一种算法,可以找到两组数组之间的交集总数,而其中一个数组已排序。 举个例子,我们有这两个数组,我们向相应的数字画直线。 这两个数组为我们提供了总共 7 个交集。 有什么样的算法可以帮助我解决
简单地说 - 我想使用透视投影从近裁剪平面绘制一条射线/线到远裁剪平面。我有我认为是使用各种 OpenGL/图形编程指南中描述的方法通过单击鼠标生成的正确标准化的世界坐标。 我遇到的问题是我的光线似乎

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!